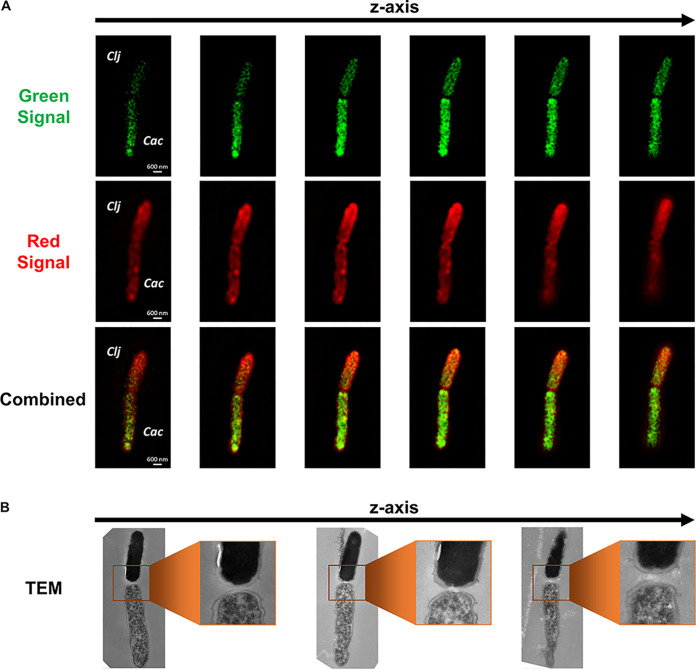
FIG 3.
Correlative confocal and electron microscopy of the C. acetobutylicum-C. ljungdahlii fusion event and the exchange of protein between the two organisms. (A) Fluorescence SR-SIM imaging of a cell fusion event between C. acetobutylicum-FAST (Cac) and Red-labeled C. ljungdahlii (Clj) shows the exchange of proteins between the organisms. The green protein from C. acetobutylicum-FAST (FAST bound to HMBR) is diffusing into the C. ljungdahlii’s cytoplasm. Red-stained proteins (CellTracker Deep Red) from C. ljungdahlii display a reverse gradient diffusing into C. acetobutylicum-FAST’s cytoplasm. The identity of each cell was based on the strength of the fluorescence signal. (B) Correlative TEM of the same fusion pair revealed the characteristic ultrastructure of each cell and confirmed the initial identification. The top cell was C. ljungdahlii with homogeneous cytoplasm, while the bottom cell was a differentiated C. acetobutylicum-FAST cell. The middle TEM section shows the interaction at the poles between the two strains consistent with the TEM images of Fig. 1 and Fig. S1.