Abstract
It was December 2019 that china reported series of patients with respiratory symptoms, a disease that later named COVID-19; and from there spread to other countries around the world; and in February 2020, the world health organization declared COVID-19 as a pandemic. From the beginning, it was assumed that COVID-19 occurrence in pediatric patients is less and has less severity but nowadays; there are a reports that shows severe cases with multiple organ involvement.
The most manifestation symptom is fever but convulsion is rare as the first manifestation symptom.
Here we describe a 3 years old; previously healthy boy that presented with repeated fever induced seizure and status epilepticus and positive RT-PCR for COVID-19 that in the first day; brain CT scan revealed brain edema and 5 days later, there was intracerebral hemorrhage in brain MRI.
Abbreviations: ER, emergency room; GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; MIS-C, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children with COVID-19; PICU, pediatric intensive care unit; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
Keywords: COVID-19, febrile seizure, Pediatric, Status epileticus
Introduction
It was December 2019 that in Wuhan, China series of patients presented with respiratory symptoms [1], a disease that its cause, the novel coronavirus (SARS-COV-2), was identified in samples of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from a patient in Wuhan and named COVID-19 and from China rapidly spread to other countries all around the world so that in February 2020 the world health organization declared it as a pandemic [[2], [3], [4]].
The rate of infection with covid-19 in children is low and the first pediatric case reported on January 20, 2020 was a 10 years old boy in Wuhan [4] and in the early phase of pandemic; those whom infected had relatively milder clinical symptoms compared with infected adults [5]; but as the time passed and the number of infected pediatric patients increased, there were several reports of multiple organ involvement in pediatric COVID-19 patients and according to the last reports [[6], [7], [8], [9]];WHO developed a new definition :” multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children with COVID-19 (MIS-C)” [10].
MIS-C definition criteria are: Children and adolescents 0–19 years of age with fever > 3 days, and two of the following:
-
a)
Rash or bilateral non-purulent conjunctivitis or muco-cutaneous inflammation signs (oral, hands or feet).
-
b)
Hypotension or shock.
-
c)
Features of myocardial dysfunction, pericarditis, valvulitis, or coronary abnormalities (including echocardiography findings or elevated Troponin/NT-proBNP)
-
d)
Evidence of coagulopathy (by PT, PTT, and elevated d-Dimers).
-
e)
Acute gastrointestinal problems (diarrhea, vomiting, or abdominal pain).
And; elevated markers of inflammation such as ESR, C-reactive protein, or procalcitonin.
And; No other obvious microbial cause of inflammation, including bacterial sepsis, staphylococcal or streptococcal shock syndromes.
And; evidence of COVID-19 (RT-PCR, antigen test or serology positive), or likely contact with patients with COVID-19 [10].
In this case report; we describe a 3 years old with MIS-C that his first presentation was: repeated seizures induced by fever (status epilepticus).
Case presentation
A 3 years old boy that was previously healthy, taken to emergency room (ER)of Namazi Hospital due to abnormal movement;(Namazi Hospital ;the largest hospital in south of Iran with 750 beds is located in Shiraz city that is the main tertiary referral center in south of Iran which has 18 bed general pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) and 9 bed surgery PICU).He was well up to 12 h prior to admission that presented with high grade fever (39.5 °C) so visited by a pediatrician that found no abnormal sign and just acetaminophen was prescribed for fever relief, but fever didn’t subside. He presented with oral foamy discharge and jerky movement of hands and feet about 30 min before admission in the hospital (he had history of contact in a ceremony, a day before, but no one that were there, had fever nor contact to suspected patients).
On arrival to ER, his initial vital signs were: Glasgow coma score(GCS) :10/15
Heart rate(HR):160, respiratory rate(RR):45, blood pressure:110/78. In ER; the patient had two episodes of tonic colonic convulsions that lasted one minute with about 5 min interval that stopped with parenteral midazolam and due to repeated convulsions so phenobarbital started and transferred to PICU.
In PICU, his GCS was 10/15 and had another tonic-clonic seizure so phenobarbital (5 mg/kg) in addition to levetiracetam 30 mg/kg was given; but convulsions didn’t stop so intubated and phenobarbital 1 mg/kg/hour and midazolam 1 mg/kg/hour intravenous infusion started and neuroprotection strategies were employed for him.
In his initial laboratory data (listed in Table 1), WBC:6800 with 70 % neutrophil and 23 % lymphocyte, CRP: 105 were detected. Meropenem, vancomycin and acyclovir started for him and also reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain-reaction (RT-PCR) assay for COVID-19 with nasopharyngeal swan taken.
Table 1.
Initial laboratory results.
| Test (reference value) normal range | Results |
|---|---|
| Ferritin (ng/ml) M*: 22.81–275 F*: 4.63–204 | 212 |
| COVID Real-time PCR | Positive |
| White blood cells (count/ml) | 3600 |
| Lymphocyte (count/ml) | 390 |
| Procalcitonin ≤0.3 | 4.3 |
| C- reactive protein (mg/L) <6 | 105 |
| Creatine phosphokinase (U/L) M: <171 F:<145 | 195 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) <480 | 900 |
| Troponin (ng/ml) <19 | 79 |
| D-Dimer (ng/ml) <500 | 3155 |
| Calcium (mg/dl) 8.5–10.5 | 9.3 |
| Magnesium (mg/dl) 1.6–2.6 | 1.6 |
| Aspartate transaminase (U/L) M: <37 F: <31 | 44 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) M: <41 F: <31 | 21 |
| Albumin (g/dl) 3.5–5 | 4.3 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dl) 8–20 | 10 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) M: 0.8–1.3 F: 0.6–1.2 | 0.4 |
| Prothrombin time/INR | 17.9/1.33 |
| Partial thromboplastin (sec.) | 28.7 |
| Blood culture | Negative |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (mm/hr) | 45 |
| Fibrinogen (200–400) | 366 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) 3.5–5.5 | 4.1 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) 135–145 | 143 |
| Typical Chest CT finding | Patchy infiltration |
*M: male, F: female.
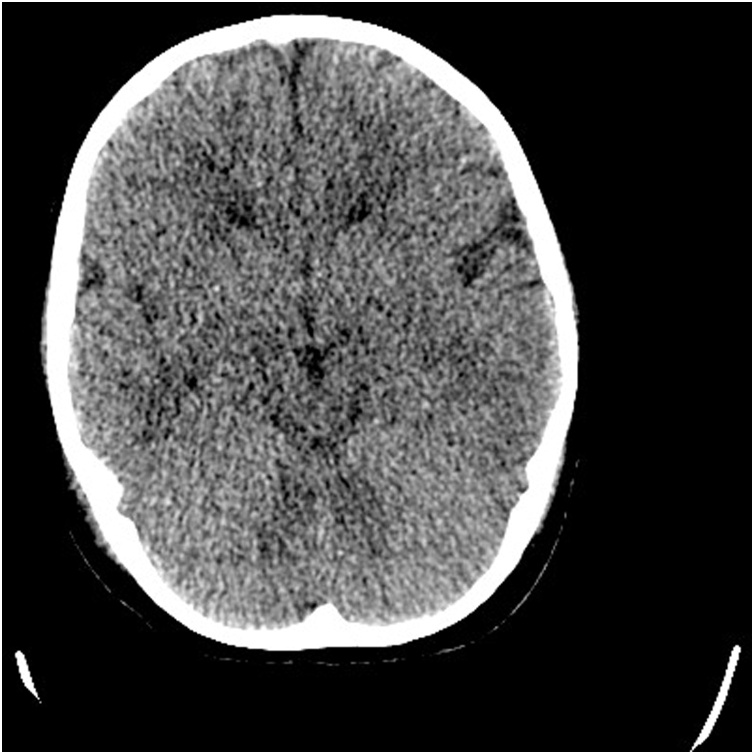
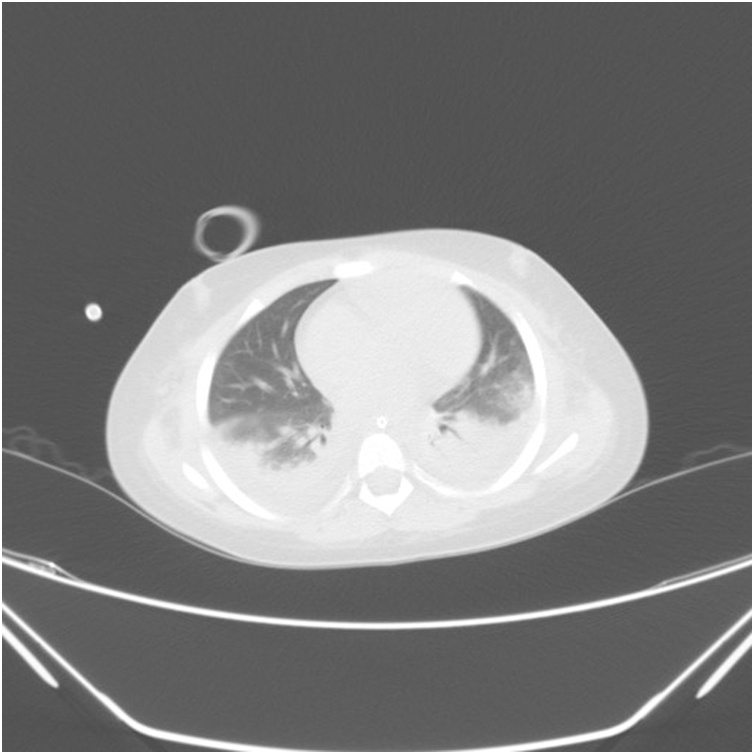
In a brain CT scan in day 1; it showed a severe brain edema (Fig. 1) and chest CT scan was suspicious to COVID-19 (Fig. 2). A 24 h later; lumbar puncture (LP) was done that revealed: no cell, protein: 14 and sugar was 125 and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure was 33 cm of water(cmH2O).
Fig. 1.
Brain CT on day of admission in PICU.
Fig. 2.
Chest CT on day of admission in PICU, in favor of COVID-19.
The patient also fulfilled the criteria of “multi-system inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19(his initial RT-PCR was negative but the other one that sent 3 days later was positive).
In day two, the patient became hypotensive so inotrope started but echocardiography was normal. In the following 2 days, inotrope increased to maintain normal mean arterial pressure and still the patient was febrile so intravenous globulin (IVIG) was given. (hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid and thiamine(HAT) had been started before)
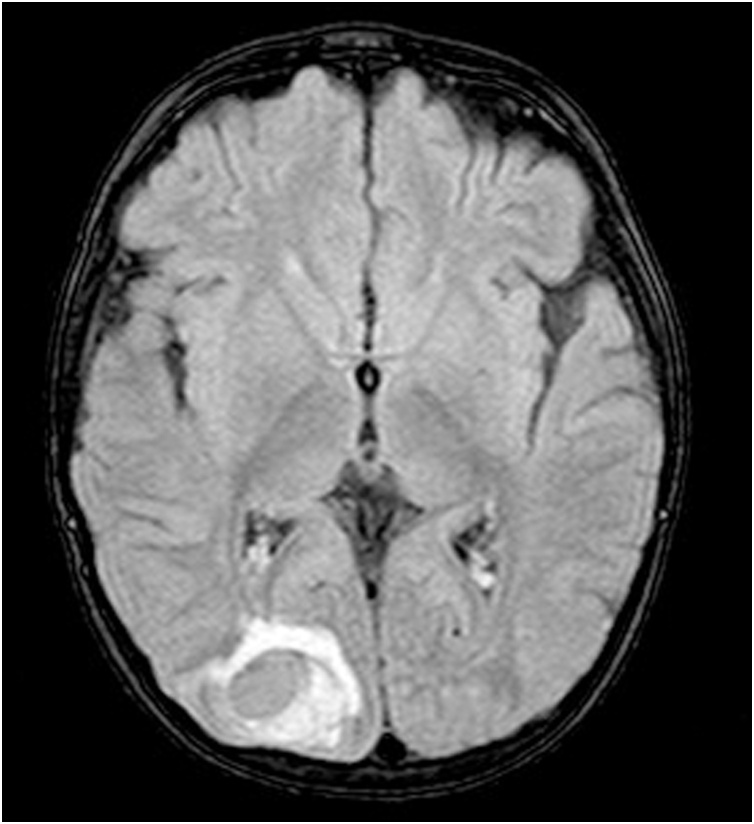
After IVIG infusion; we could decrease inotrope but still he had intermittent fever so brain MRI was done that revealed intracerebral hemorrhage in the right occipital lobe (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Brain MRI ;ICH in right occipital lobe.
In the 8th day, the patient extubated from ventilator and tolerated; his GCS was 15/15 with normal neurologic exam.
On the 14th day, the patient discharged home with good condition.
Discussion
In the beginning; the rate of infected pediatric patients were less so it was believed that they are less susceptible and the most common symptoms in severe pediatric patients were; tachypnea, fever, cough, nausea/vomiting and diarrhea, fatigue/myalgia and headache [11]; but as the disease spread to other countries, there were reports that the first presentation were liver failure [9] or with the presentation of Kawasaki like disease with cardiac involvement [[6], [7], [8]], so we expect to see organ involvement in patients with COVID-19 even without respiratory symptoms.
Before 2019, we had two outbreaks of coronaviruses: the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2002 and the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) in 2012; that in both of them neurological manifestations in patients with respiratory tract infections with neuroinvasion had been described before [12]. Neurological problems found in the patients with coronavirus infection were: febrile seizures, convulsions, change in mental status, encephalomyelitis and encephalitis [12].
In SARS, the first cases with neurological manifestations presented with seizure [13,14].
In MERS, the most neurological presentations were seizure and encephalopathy [15] but intracerebral hemorrhage also have been reported [16].
In a retrospective study that Mao L et al. did in China; it showed: Patients with more severe infection had neurologic manifestations, such as acute cerebrovascular diseases (5.7 %), impaired consciousness (14.8 %), and skeletal muscle injury (19.3 %) but in their study mean age was 52.7 years [17].
In a multicenter retrospective study in 49 hospitals in Hubei, China by Lu L. et al. neither acute symptomatic seizures nor status epilepticus was observed [18].
Vollono C. et al. describe a 78 years old woman infected with COVID-19 whose primary presentation was a focal status epilepticus [19].
A 32 years old woman with fever and dry cough that developed with generalized tonic-clonic seizure reported by Karimi N. et al. that was positive for COVID-19 and her brain MRI was normal and CSF tested was negative for COVID [20].
Moriguchi J. et al. reported a 24 years old man with SARS-CoV-2 meningitis and convulsion that the specific SARS-CoV-2 RNA was not detected in the nasopharyngeal swab but was detected in a CSF [21].
In Iran; Sharifi-Razavi et al. described a 79 years old man with history of 3 days fever and acute loss of consciousness that had a massive intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) in the right hemisphere, accompanied by intraventricular and subarachnoid hemorrhage and later, RT-PCR of oropharyngeal swab became positive [22].
Toscano G. et al. reported 5 adult patients developed Guillain–Barré syndrome 5–10 days after the onset of COVID-19 with an initial presentation of lower limb weakness, parasthesia and ataxia that their CSF’s RT-PCR were negative [23].
Shenker J. et al. reported a 12 years old boy with MIS-C presented with status epilepticus. Brain imaging, CSF cell count and PCR of CSF for COVID-19 were normal [24].
Coronaviruses has capability the neuroinvasion [12] and the presence of ACE2 receptors in the nervous system and in skeletal muscle are the suggesting a mechanism for SARS-CoV-2-related neuromuscular injury [25,26].
In kawasaki disease; altered mental status, seizures, and hemiplegia had been reported that was thought to be due to vasculitis [27].
Apart from ACE2, COVID-19-associated nervous system damage may also be caused by septic shock, hypoxic injury, fever (in children), metabolic derangements and immune responses.
In our patient; RT-PCR of CSF was negative so one possibility of the repeated convulsions was autoimmune reaction and another was fever although direct invasion of virus cannot be excluded even with negative PCR but ICH that had been reported before [22], that could be co-incidence and related to his old age, but in our patient might be due to direct invasion of CNS by COVID-19.
The above data indicate that SARS-CoV-2 may infect the nervous system and skeletal muscle as well as the respiratory tract especially in severe cases that have MIS-C; thus, clinicians should consider COVID-19 as a differential diagnosis for patients with neurological manifestations.
In pediatric cases, it is important to emphasize that COVID19 could be another risk factor for febrile seizures (taking into account that other types of coronaviruses could also be involved) although it is known that influenza virus and enterovirus are the most frequently associated to this condition [28,29].
And even in the absence or respiratory symptoms, occurrence of neurologic symptoms might be the first presentation of COVID-19 and MIS-C and should be assessed for, especially in the critically ill pediatric patients.
Funding/Support
The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Shiraz University of Medical sciences. Written informed consent was obtained from the parents and sent to the ethics committee.
Authors' contributions
Dr. Saeed planned the study and wrote the manuscript. Dr. Shorafa gathered patients' data and submitted the manuscript. Drs Saeed and Shorafa edited the manuscript. Both authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
The first presentation of COVID-19 in pediatric patient could be apart from respiratory complaint and pediatrician should be aware of nervous system complications of it.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
References
- 1.Lu H., Stratton C.W., Tang Y.W. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan China: the mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol. 2020;92:401–402. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W. China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019 [published January 24, 2020] N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Health Organization . 2020. Situation report 1 2020 (World Health Organization). Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), situation report-1. 21 January 2020 [Internet]. Geneva. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chan J.F., Yuan S., Kok K.H., To K.K., Chu H., Yang J. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jin Y.H., Cai L., Cheng Z.S., Cheng H., Deng T., Fan Y.P. A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version) Mil Med Res. 2020;7:4. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-0233-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Riphagen S., Gomez X., Gonzalez-Martinez C., Wilkinson N., Theocharis P. Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1. Epub 2020/05/11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.DeBiasi R.L., Song X., Delaney M., Bell M., Smith K., Pershad J. Severe COVID-19 in children and young adults in the Washington, DC metropolitan region. J Pediatr. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jones V.G., Mills M., Suarez D., Hogan C.A., Yeh D., Bradley Segal J. COVID-19 and Kawasaki disease: novel virus and novel case. Hosp Pediatr. 2020 doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-0123. Epub 2020/04/09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saeed A., Shorafa E., Shahramian I., Afshari M., Salahifard M., Parooie F. An 11-year-old boy infected with COVID-19 with presentation of acute liver failure. Hepatitis Monthly. 2020 doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.104415. Online ahead of Print; In Press (In Press) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2020. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents with COVID-19: scientific brief, 15 May 2020.https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/332095 License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sun D., Li H., Lu X., Xiao H., Ren J., Zhang F.R. Clinical features of severe pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan: a single center’s observational study. World J Pediatr. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s12519-020-00354-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bohmwald K., Gálvez N.M.S., Ríos M., Kalergis A.M. Neurologic alterations due to respiratory virus infections. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:386. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hung Ec, Chim Ss, Chan Pk, Tong Yk, Ng Ek, Chiu Rw. Detection of SARS coronavirus RNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin Chem. 2003;49:2108–2109. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2003.025437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lau K.K., Yu W.C., Chu C.M., Lau S.T., Sheng B., Yuen K.Y. Possible central nervous system infection by SARS coronavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:342–344. doi: 10.3201/eid1002.030638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Saad M., Omrani A.S., Baig K., Bahloul A., Elzein F., Matin M.A. Clinical aspects and outcomes of 70 patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a single-center experience in Saudi Arabia. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;29:301–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Algahtani H., Subahi A., Shirah B. Neurological complications of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus: a report of two cases and review of the literature. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2016;2016 doi: 10.1155/2016/3502683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mao L., Wang M., Chen S., He Q., Chang J., Hong C. Neurological manifestations of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective case series study. JAMA Neurol. 2020;10(April) doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lu L., Xiong W., Liu D., Liu J., Yang D., Li N. New onset acute symptomatic seizure and risk factors in coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective multicenter study [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 18] Epilepsia. 2020 doi: 10.1111/epi.16524. 10.1111/epi.16524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vollono C., Rollo E., Romozzi M., Frisullo G., Servidei S., Borghetti A. Focal status epilepticus as unique clinical feature of COVID-19: a case report. Seizure. 2020;78:109–112. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2020.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Karimi N., Shafiri Razavi A., Rouhani N. Frequent convulsive seizures in an adult patient with COVID-19: a case report. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2020;22(3) March. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Moriguchi J., Harii N., Goto J., Harada D., Sugawara H., Takamino J. A first case of Meningitis/Encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. Int J Infect Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.03.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sharifi-Razavi A., Karimi N., Rouhani N. COVID-19 and intracerebral haemorrhage: causative or coincidental? New Microbes New Infect. 2020;35 doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100669. Published 2020 Mar 27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Toscano G., Palmerini F., Ravaglia S., Ruiz L., Invernizzi P., Cuzzoni M.G. Guillain–Barré syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2. N Engl J Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2009191. Apr 17 [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shenker J., Trogen B., Schroeder L., Ratner A.J., Kahn P. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children associated with status epilepticus. J Pediatr. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.07.062. S0022-3476(20)30961-30966. 23 Jul. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhao Y., Zhao Z., Wang Y., Zhou Y., Ma Y., Zuo W. 2020. Single-cell RNA expression profiling of ACE2, the putative receptor of Wuhan 2019-nCov.bioRxiv 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wu Y., Xu X., Chen Z., Duan J., Hashimoto K., Yang L. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain Behav Immun. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.03.031. Mar 30 [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tabarki B., Mahdhaoui A., Selmi H., Yacoub M., Essoussi A.S. Kawasaki disease with predominant central nervous system involvement. Pediatr Neurol. 2001 doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(01)00290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim S.Y., Lee N.M., Yi D.Y., Yun S.W., Lim I.S., Chae S.A. Seasonal distribution of febrile seizure and the relationship with respiratory and enteric viruses in Korean children based on nationwide registry data. Seizure. 2019;73:9–13. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2019.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Carman K.B., Isikay S., Calik M., Karal Y., Kocak O., Ozcelik A. Viral etiological causes of febrile seizures for respiratory pathogens (EFES study) Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(2):496–502. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1526588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]