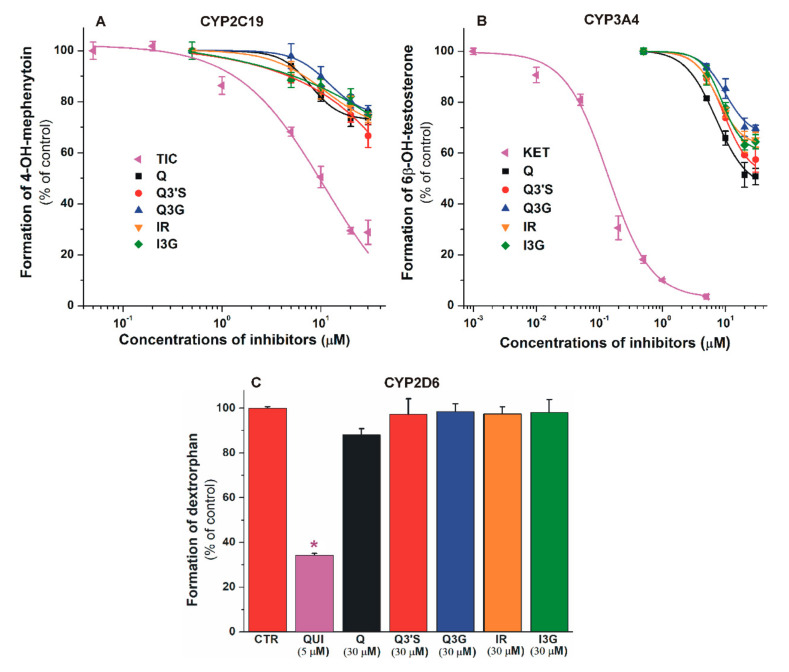
Figure 2.
Inhibitory effects of Q, Q3′S, Q3G, IR, I3G, and positive controls on cytochrome P450 (CYP)2C19 (A), 3A4 (B), and 2D6 ((C); * p < 0.01) enzymes. Inhibition of CYP2C19-catalyzed S-mephenytoin hydroxylation (positive control: ticlopidine, TIC; IC50 = 4.3 μM), CYP3A4-catalyzed testosterone hydroxylation (positive control: ketoconazole, KET; IC50 = 0.2 μM), and CYP2D6-catalyzed dextromethorphan O-demethylation (positive control: quinidine, QUI; IC50 = 0.2 μM) by flavonoids (substrate concentrations: 5 µM in each assay). CYP2C19: statistically significant (p < 0.01) decrease in metabolite formation was induced by 5 μM of TIC, 10 μM of Q, and 20 μM of Q3′S, Q3G, IR, and I3G. CYP3A4: statistically significant (p < 0.01) decrease in metabolite formation was induced by 0.05 μM of KET, 5 μM of Q, 20 μM of Q3G, and 10 μM of Q3′S, IR, and I3G (Q, quercetin; Q3′S, quercetin-3′-sulfate; Q3G, quercetin-3-glucuronide; IR, isorhamnetin; I3G, isorhamnetin-3-glucuronide).