Figure 6.
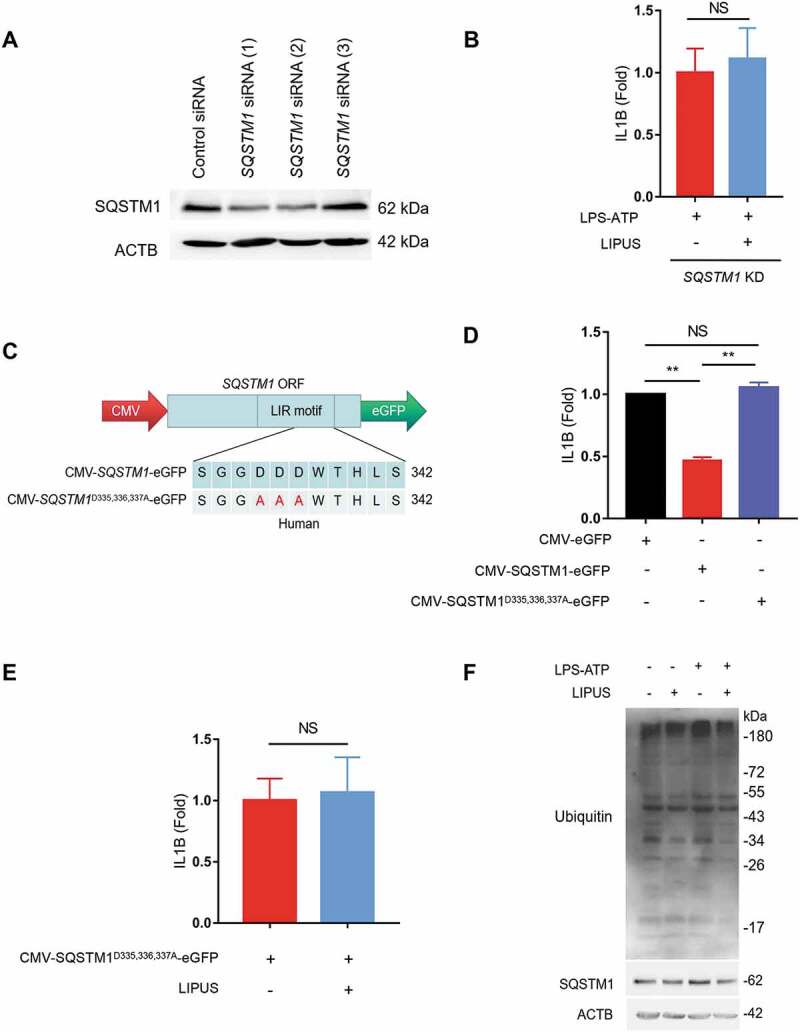
Autophagy-dependent degradation of SQSTM1 contributes to LIPUS-mediated inhibition of mature IL1B production. (A) Specific SQSTM1 siRNAs were used to knockdown SQSTM1 level. (B) After pretreatment with SQSTM1 siRNA (1) for 24 h, the THP-1 cells were treated with LPS (12 h) and ATP (30 min) and then treated with or without LIPUS (20 min). Sixty min later, the mature IL1B level was examined by ELISA. (C) Diagrams of the indicated plasmids for exogenous expression of SQSTM1 (CMV-SQSTM1-eGFP) and its mutant (CMV-SQSTM1D335,336,337A-eGFP). (D) THP-1 cells were transfected with CMV-SQSTM1-eGFP and CMV-SQSTM1D335,336,337A-eGFP plasmids for 24 h and then treated with LPS (12 h) plus ATP (30 min). One hour later, the levels of IL1B in supernatants were examined by ELISA. CMV-eGFP plasmid was used as the control. (E) CMV-SQSTM1D335,336,337A-eGFP plasmid was transfected into THP-1 cells for 24 h and the cells were then exposed to LPS-ATP with or without LIPUS treatment. The release of mature IL1B was tested by ELISA assay. (F) Using anti-ubiquitin and anti-SQSTM1 antibody, western blotting analyses for THP-1 cells that treated with LPS (12 h), ATP (30 min) with or without LIPUS (20 min). The above statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t test. NS, not significant, **p < 0.01.
