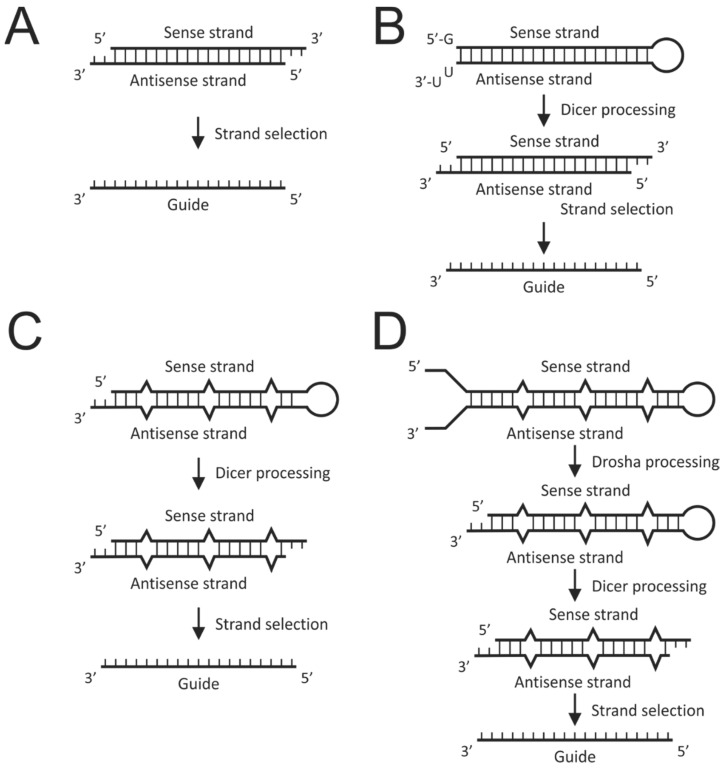
Figure 2.
Synthetic and expressed activators of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. (A). Small interfering RNA (siRNA), typically produced as synthetic sequences, are perfectly matched 19–21 nucleotide duplex RNAs with two nucleotide 3′ overhangs. Each strand contains terminal 5′ phosphate and 3′ hydroxyl groups. siRNAs mimic miRNA duplexes and enter the RNAi pathway when taken up by RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Strand selection occurs to remove the passenger strand and activated RISC silences cognate mRNA. (B) Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) are generally expressed from RNA polymerase III promoters as a single RNA sequence that folds into a stem loop. As mimics of pre-miRNA, shRNA are recognized and processed by Dicer to form siRNAs that then then enter RISC. (C) Artificial pre-miRNAs are imperfectly matched stem loop RNAs that resemble naturally occurring pre-miRNA. As such, they are processed by Dicer into miRNA duplexes and subsequently enter RISC. (D) The design of artificial pri-miRNAs (apri-miRNAs) is based on the architecture of naturally occurring pri-miRNA and are recognized and processed by the microprocessor complex, exported from the nucleus, processed by Dicer, and then taken up by RISC.