Abstract
Due to their controlled size, sensitivity to external stimuli, and ease-of-use, microgel colloids are unique building blocks for soft materials made by crosslinking polymers on the micrometer scale. Despite the plethora of work published, many questions about their internal structure, interactions, and phase behavior are still open. The reasons for this lack of understanding are the challenges arising from the small size of the microgel particles, complex pairwise interactions, and their solvent permeability. Here we describe pathways toward a complete understanding of microgel colloids based on recent experimental advances in nanoscale characterization, such as super-resolution microscopy, scattering methods, and modeling.
Subject terms: Polymers, Colloids, Gels and hydrogels, Super-resolution microscopy
Despite their widespread use, many fundamental questions about the internal structure of microgels are still open. Here the authors describe several pathways toward a complete understanding of microgel colloids based on recent experimental advances in nanoscale characterization.
Introduction
The term “microgel” usually refers to a cross-linked polymer network of colloidal size that is swollen in a good solvent and has a diameter between ~100 nm and several micrometers1–3 (Fig. 1). Colloidal hydrogels are a common subtype where the continuous phase is water. Often, but not always, these networks exhibit conformational changes in response to changes in their environment, such as the solvent composition or temperature1,4,5. The sensitivity to external stimuli, such as temperature, pH, or solvent conditions, is an essential feature of many microgels, in particular for the most widely studied type of microgels, based on pNIPAM (poly-N-isopropylacrylamide) and its derivatives1,6 (Fig. 1b). Here, we consider homogeneous suspensions of these particles at different densities from the dilute to the highly packed regime, as well as microgels adsorbed at surfaces. It is also possible to synthesize larger, millimeter-sized, gel particles7, or to study two-dimensional assemblies at an interface8,9. Additional functions, for example, for chemical transformation or sensing applications10,11, can be added using core–shell particles or by decorating the microgels with inorganic nanoparticles12,13. Microgels are already used in several applications as viscosity modifiers and lubricants14, for CO2 capturing15 or 3D bioprinting16, as biocompatible additives and delivery vehicles17, sensors, or stimuli-responsive color-changing systems18,19.
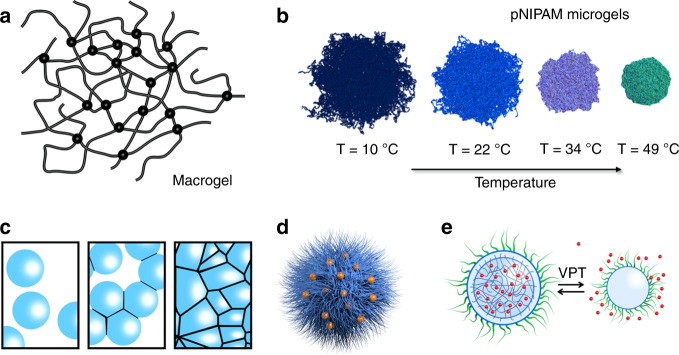
Fig. 1. Polymer microgel morphology, swelling, packing, and functionality.
a Sketch of a macroscopic polymer gel with a statistically homogeneous distribution of permanent or reversible cross-links. In a good solvent, the gel is swollen, and the degree of swelling is controlled by a balance between the mixing entropy, favoring swelling, and the elastic penalty when stretching the polymer chains between cross-links21,36. b Volume-phase transition (VPT) of stimuli-responsive microgel particles. Microgels are colloidal-sized polymer gels, typically with a radius of 1 μm or less, where the crosslinker density is usually decaying from the center to the periphery1,27. The polymers in the network can be neutral (nonionic) or carrying charged groups. The images shown are adapted with permission from ref. 75 (Copyright American Chemical Society, 2017) and depict the results from atomistic computer simulations of neutral microgels with a cross-link gradient and modeled at different temperatures. The polymer represents pNIPAM, poly-N-isopropylacrylamide, which has a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) in water of TLCST ≃ 32 °C81. In agreement with experiments, the simulations show that below TLCST, the microgel colloid is highly swollen while above it collapses. c Swollen microgels are soft and compressible spheres, in osmotic equilibrium with the solvent phase and other microgels. At higher concentrations, particles pack densely and form a crystal or amorphous phase. With increasing total polymer concentration, the microgel particles become compressed, facet, and shrink4, details of which have a profound impact on the effective pairwise interactions91 and the macroscopic flow properties25. d By attaching metallic nanoparticles, such as gold, or by encapsulating pharmaceutically active substances, functional microgels can be obtained12,13. The mean distance between plasmonic nanoparticles can be probed optically, and microgels with the appropriate polymer chemistry can act as sensors10,11. e Triggering the VPT by temperature, pH, or optically can be used to expel molecules in a biological environment in a controlled way and at a targeted site. The graphic, adapted with permission from ref. 24 (Copyright 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.), shows a sketch of a microgel particle filled with small active molecules (red dots) and decorated with polyethylene glycol (green hairs) to improve biocompatibility.
Despite their popularity and widespread application, the internal structure of microgels is not well-understood. During the microgel synthesis, the degrees of freedom for the polymer strands are intentionally reduced by forming covalent cross-links between polymer chains. The chemical cross-linking itself is a nonequilibrium process, and it does not necessarily progress uniformly, which may lead to spatial fluctuations, gradients, and heterogeneities in the microgel particle architecture20. For a complete understanding of a microgel colloid as a material building block or a carrier, it is imperative to know the spatial distribution of polymer and cross-link densities on the nanoscale.
Initially, many studies assumed that microgels could be described simply as spherical, homogeneous gel particles, as discussed in ref. 1. Based on this assumption, the Flory–Rehner theory of polymer gels can be applied to make predictions about the elastic properties, and the swelling in a good solvent21,22. However, already more than 20 years ago, it was noticed that this scenario is highly unlikely, and that density gradients in the microgel conformation cannot be ignored1,23. Currently, the dominating picture is that standard microgel particles consist of a polymer gel core with a radially decaying cross-link density, and polymer dangling ends sticking out into the solvent. The dangling ends and the polymer strands in-between cross-links will thermally fluctuate, on nanometer-length scales, while the average spatial distribution of cross-links remains unchanged.
The inhomogeneous internal structure of microgels has profound consequences on the properties of microgel assemblies and their interactions. The cross-link density, and its spatial distribution, determines the elasticity and the swelling behavior, as well as the porosity of the gel network. The latter is vital for the uptake and release of small molecules24. The spatial distribution of cross-links and the properties of the interface control the onset of repulsive pairwise interactions between microgels, which is crucial for the jamming transition of densely packed microgels and also for their viscous losses25. In addition, the cross-links guarantee that microgels retain their structural integrity under shear, packing, and most other perturbations. The microscopic size and the hierarchical structure, from the atomic to mesoscopic-length scales, are at the core of microgel properties and their technological and fundamental relevance26. Progress toward a complete characterization of microgel colloids is, therefore, of great importance. In this perspective article, we will summarize the critical results obtained using conventional techniques, and discuss a set of innovative methods and emerging data.
Microgel characterization with nanoscale resolution
In the following sections, we will discuss the essential techniques that are applied to characterize microgels and concentrated suspensions of microgels, summarized in Fig. 2. We will emphasize new and emerging superresolution microscopy approaches that have already shed light on many critical open questions. We will highlight pathways and challenges toward a complete characterization of microgel colloids.
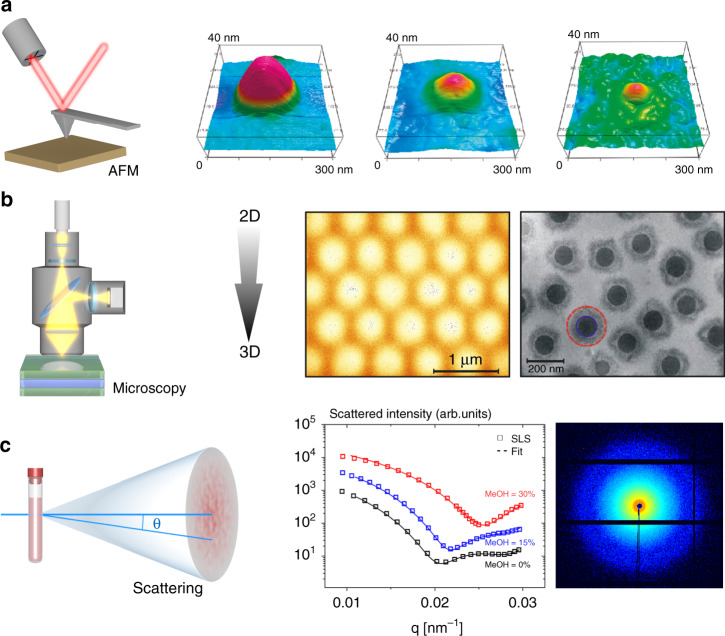
Fig. 2. Conventional experimental techniques employed to characterize microgels and microgel assemblies.
a Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is used to measure the shape and swelling of microgels adsorbed at a surface or interface66,68,69. Upon drying, the microgels flatten and acquire a lens-like shape. The AFM images on the right, adapted with permission from ref. 67 (Copyright American Chemical Society, 2010), show the erosion of a biodegradable microgel attached to a hydrophilic glass substrate after 0, 24, and 434 h under ambient, dry conditions. b Microscopy: microgels have been studied using various microscopy techniques. Conventional light microscopy can probe microgels and their position, but not their morphology due to the lack of resolution. Using confocal laser-scanning microscopy (CLSM), the center position of microgels in dense assemblies can be tracked in situ in three dimensions. The bulk structure and phase transitions of microgel assemblies can be studied26. The first image shows an CLSM section of a fluorescein-dyed crystal assembled from 690-nm-diameter pNIPAM microgels, adapted with permission from ref. 18 (Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH, D-69469 Weinheim, 2002). Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) has the nanoscale-resolving power, but the sample preparation is difficult; rapid cooling may perturb the polymer conformation, and moreover the contrast is extremely low for the highly swollen networks. These difficulties have prevented widespread usage of cryo-TEM for the study of microgels. The second image shows a cryo-TEM micrograph of a 0.2 wt.% aqueous suspension of polystyrene core/pNIPAM shell particles, kept at room temperature, adapted with permission from ref. 65 (Copyright Springer Nature, 2008). The dashed circle indicates the hydrodynamic radius, as determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS). c Most of the experimental data on microgels stem from scattering, using light, neutrons, or X-rays. Scattering techniques provide information about the polymer density–density correlations in situ, and this information can be used to test models about the density profile, packing, interpenetration, and deswelling on a length scale from the nanometer to the micron range. The first image shows static light-scattering (SLS) curves obtained for submicron-sized pNIPAM microgels suspended at low concentration in a water/methanol mixture for different methanol contents, reprinted from ref. 58 (Fig. 1a), with permission from Elsevier, Copyright (2016). The second image shows a small-angle X-ray scattering pattern obtained from a jammed suspension of hybrid microgels (pNIPAMs) with an embedded ellipsoidal hematite core, adapted from ref. 127 by permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Scattering techniques
When swollen, microgels are composed of a densely cross-linked core and a fuzzy corona. Already in 1994, Wu et al. postulated a core–shell-like structure based on the reaction kinetics23. It took until 2004 when Stieger et al. measured the particle form factor and derived a model for the radial polymer-density profile ρ(r)27,28. Neutrons, X-rays, or light can be used to measure the particle- form factor, depending on the size of the microgels, all suggesting qualitatively similar results for ρ(r)29,30. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is routinely employed on dilute systems to derive the microgel hydrodynamic radius RH from their random Brownian motion29. Small-angle neutron scattering has been used to assess the nanoscale correlation length ξ of the local polymer concentration fluctuations22. Scattering techniques can also be applied to hollow microgels as shown recently by Dubbert et al.31.
Scattering methods using X-ray, neutrons, and light do have the required nanoscale-resolving power and have thus been employed frequently27,30,32,33. However, they only provide information about radially averaged properties of an ensemble of particles, and therefore, information on a single-particle level is not accessible. Moreover, scattering methods work best if the constituents are composed of one material dispersed in a medium and are isotropic, i.e., they have a spherical shape, like a solid spherical particle or polymers in a good solvent, where only isotropic means can be measured. Scattering methods are less suited for anisotropic, deforming, densely packed, or interdigitated objects. In contrast to fluorescence microscopy, they lack specificity and perform poorly for hybrid, multicomponent particles, and microgels composed of chemically distinct entities. Nonetheless, refined scattering methods can overcome some of these shortcomings. Isotope labeling can be used to suppress structure factor contributions stemming from interparticle correlations, and reveal the single-particle-form factor, even at very high densities28. Using zero-average contrast (ZAC)–SANS, Mohanty et al. recently reported data on particle–particle interpenetration at elevated microgel densities34.
Two other methods that provide nanoscale, polymer-level, information on microgels, averaged over a large volume, are neutron spin–echo (NSE) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The methods can provide valuable information about the local dynamics and fluctuations that can then be linked to the heterogeneity of the gel network35,36.
Light microscopy and nanoscopy
Compared with scattering techniques, optical microscopy offers essential advantages, such as access to single-particle information and chemical specificity using dye labels in fluorescent microscopy. Modern 3D-confocal laser-scanning microscopy (CLSM) became popular in the field of soft condensed matter in the 1990s37, and it has been applied to microgels soon after. In Fig. 2b, we show the results from a study by Debord et al. from the year 2002 on microgel photonic crystals18. The image reveals the strength and weaknesses of conventional optical imaging methods. It is easily possible to identify individual microgel particles with a diffraction-limited resolution of several hundreds of nanometers; however, all details on a particle or subparticle level are washed out. CLSM has been used repeatedly and successfully to study the center position of particles in dense assemblies8,38,39. Information on shorter length scales, until recently, could only be obtained from scattering techniques or electron microscopy, within the limitations of these methods.
The advent of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy (SRFM) techniques40 has opened up a whole new dimension for the characterization of soft polymeric materials41,42. Microgels and microgel assemblies have been one of the first systems that have benefited from these new developments. In contrast to solid particles, such as PMMA or polystyrene colloids43, for microgels, there has been an urgent need for improved resolution on sub-particle-length scales. Moreover, an active community has been working with dye-labeled microgels for two decades.
A broad range of far-field SRFM techniques has been developed in recent years. Some of these techniques, for example, linear structured illumination and 4Pi microscopy, do not attempt to beat the Abbe diffraction limit in microscopy and thus, by design, the resolution is limited. Still, these methods can deliver twofold improvements in lateral, and even more in axial, resolution, compared with optimized conventional microscopy using oil-immersion, high-numerical aperture objectives44. Another class of methods covers the so-called “true SRFM,” which can in fact overcome the diffraction limit. Examples include stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy45, photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM)46, stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM)47, and some more recent advanced implementations based on similar principles, such as (d)irect-STORM48, PAINT (point accumulation for imaging in nanoscale topography), and others41,49. Here, we will focus on these nanoscopy techniques50,51. All nanoscopy techniques employ a nonlinear optical principle on a fluorescence-labeled specimen, since a linear optical system cannot overcome the Abbe diffraction limit.
In STED, the fluorescent dyes are quenched using a so-called doughnut beam, and subsequently the excitation only remains in the center. The hole of the doughnut can in theory be made arbitrarily small, decreasing the optical resolution to the nanoscale. Already more than 10 years ago, Hell et al. reported an optical resolution of 5.8 nm (width of the point-spread function)52. More commonly, a resolution of 20–30 nm can be obtained, limited by the bleaching of the dye and its brightness. A disadvantage of conventional STED is that only the lateral resolution is improved, while the axial resolution along the z direction remains diffraction-limited.
PALM and STORM are single-molecule fluorescence techniques. At least initially, when both techniques were introduced, the fundamental difference between the two methods was that PALM uses photoswitchable fluorescent proteins (endogenously expressed), while STORM uses synthetic dye labeling51. For soft materials and polymers, only the latter is of concern, and in this paper, we will focus our attention on STORM. STED microscopy uses a deterministic method, meaning that an image is acquired in “one-scan,” while STORM and PALM are “stochastic” methods. For the last-mentioned, individual fluorophores are excited sequentially in time, which leads to dye “blinking”. Consequently, the single-molecule fluorescent signal is recorded without overlap of the diffraction-limited images (Fig. 3). From the accumulation of a larger number of positions of dye-labeled molecules, a superresolved image can be reconstructed, which does imply long acquisition times, on the order of tens of seconds or minutes, and thus in most cases, only static samples can be measured. It has been shown early on that three-dimensional information can be optically encoded, and optical imaging with a 20–30-nm lateral and 50– 60-nm axial resolution was reported on cellular structures more than 10 years ago53.
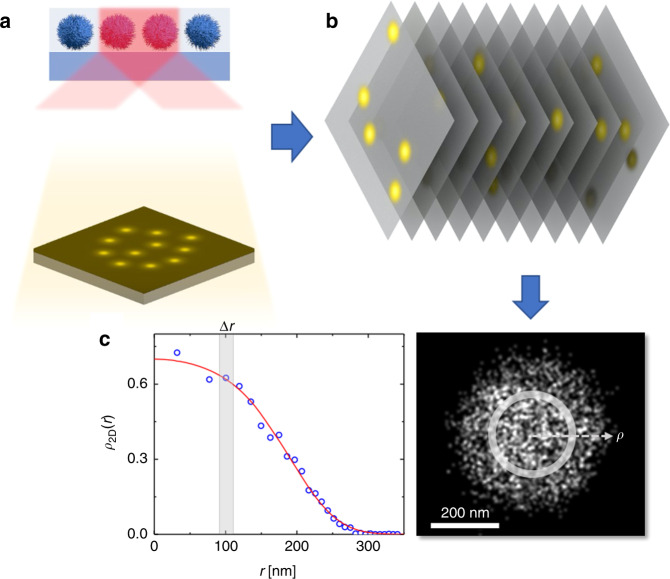
Fig. 3. Superresolution fluorescent microscopy (SRFM).
The most widely used method for soft-material imaging is single-molecule localization microscopy via direct STochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (dSTORM)48,57,58. In dSTORM, a microgel can be labeled using conventional synthetic cyanine dyes such as Cy5 or dyes from the Alexa family. These dyes are then used as molecular photoswitches. a Highly inclined illumination of a microgel suspension with a laser beam (red shaded) to illuminate the dye-labeled particles within a few-μm depth, next to a glass coverslip, in blue. The inclined or evanescent field illumination reduces nonspecific fluorescence originating from the bulk of the sample. The illumination is provided by a powerful laser to achieve sparse fluorophore blinking, as shown in the image below. In contrast, another laser wavelength is used to tune the density of blinking molecules58. b For every dSTORM image, thousands of frames are acquired whereby each frame consists of thousands of fluorophore localizations, with typically thousands of photons detected per localization. The image acquisition takes up to several minutes, and therefore the microgels have to be immobilized on a glass substrate or trapped in a solid jammed or crystalline phase as in refs. 25,110. c Experimental result for a swollen microgel particle attached to a glass substrate and reconstructed by dSTORM in 2D with a 30-nm lateral resolution. From individual or ensemble-averaged images of this type, the density profile ρ2D(r) can be obtained by summing up the dye localizations in concentric rings around the center of mass. For spherical particles, ρ2D(r) can be converted into the three-dimensional (3D) density profile ρ(r) as explained in refs. 58,86. Alternatively, the can be obtained directly in 3D as shown in Fig. 4. The dSTORM image and the single-microgel ρ2D(r) data have been adapted from ref. 58 (Fig. 2b; Supplementary Fig. S2), with permission from Elsevier, Copyright (2016). The solid red line shows the fit with Eq. (1) and Rc = 227 nm and σ = 40.5 nm.
Another recent development is correlative microscopy, where two or more microscopy techniques are applied in tandem on the same sample to leverage the strengths of each method while offsetting their weaknesses54. 4Pi single-molecule switching nanoscopy (4PiSMSN)55 combines iPALM (interferometric PALM) and dual-objective 4Pi microscopy, and can achieve 10–20-nm isotropic resolution. Recently, Hell et al. combined the two SRFM principles of STED and single-molecule localization in a technique called MINFLUX, and they reported an ~1-nm precision56. MINFLUX is a relatively new technique that has not yet been applied widely to soft materials. Still, its advent is showcasing that an improved resolution down to the molecular scale is within reach. The combination of electron microscopy and SRFM is a powerful approach already used for imaging microgels decorated with inorganic nanoparticles, exploiting the differences in contrast in such hybrid systems57.
In biology, superresolution techniques have become very popular since the mid-2000s, and to this end, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2014 was awarded to Hell, Moerner, and Betzig. Nonetheless, it took several more years until superresolution techniques could get a strong foothold in soft materials science, and the application to microgels proved to be instrumental for this, as we will highlight in the next section57,58. A major advantage of STORM is the use of synthetic dyes that can be applied directly to polymeric materials or colloids, provided the dye labeling is done correctly, and the solvent conditions are suitable. Yet, the solvent puts some constraints on the material properties since the dyes require certain additives and an oxygen-scavenging buffer system59. Using solvent additives needed for best imaging results means that low ionic-strength conditions, e.g., for studies of ionic microgels60, cannot be easily accessed. We note in passing that some covalently bound switchable labels do neither require a particular buffer61 nor does the more recent PAINT approach (point accumulation for imaging in nanoscale topography)41,49. In practice, nanoscopy of individual solid particles has been performed early on as proof-of-principle for the method and to determine the optical resolution45, but the efforts usually ended there. Other soft-matter systems are either mobile, such as polymers or surfactants in solution, or difficult to dye-label appropriately, for example, polymer melts. Microgels offer an ideal platform in this respect since they are porous and spongy and can be dye-labeled throughout, while at the same time remain in contact with the solvent40.
SRFM can only provide accurate image information if the thermal density fluctuations are suppressed to length scales smaller than the desired resolution. This limit imposes sample-specific constraints, and for microgels, these are given by the correlation length ξ between cross-links in the range of several nanometers and the thickness of the fuzzy corona in the swollen state22,32,62,63. Nonetheless, even if the individual polymer molecule position cannot be measured, nanoscopy can still provide high-resolution images of the mean density in real space, similar to what scattering techniques of soft materials provide in reciprocal space. Moreover, the advantages of single-particle imaging and specific dye labeling can still be leveraged.
Electron microscopy
Until recently, electron microscopy was virtually the only imaging method that could provide nanoscale resolution. To this end, conventional scanning electron microscopy is commonly applied to collapsed microgels in the vacuum1. Flattening of the soft microgels upon drying can lead to overestimates of the size. However, the shape change can also be exploited technologically since compressed microgels can be employed as microlenses64. Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) is applied occasionally to image microgels in the hydrated and swollen state. Still, due to the low contrast, the image quality tends to be rather poor. Crassous, Ballauff, and coworkers have shown that the size of microgel-coated polystyrene particles can be extracted from cryo-TEM images65 (Fig. 2b). However, cryo-TEM has not yet revealed any quantitative information about the polymer density and its distribution inside the microgel.
Atomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) can probe the swelling and deswelling of microgels adsorbed to a surface66–69. However, the interaction of the AFM tip with the microgel and polymer indentation can complicate quantitative data analysis66. AFM does provide access to individual particle properties, and it can be applied to surface-adsorbed microgels, so it brings added value under these conditions70. It does, however, not provide direct, nanoscale-resolved images, and it certainly does not allow us to look inside the microgels or to study dense assemblies.
Numerical modeling
A complete characterization of nanoscale objects is always a challenging task, and getting optimal results usually requires a combination of techniques. Numerical simulations also play an essential role since they can test specific effects explicitly, and can help to establish minimal models. Hard-sphere colloids, as well as different polymeric and soft-matter systems, have been modeled extensively and successfully71. Modeling and simulations of microgels, however, have lagged. Recently, first studies on mesoscale modeling of microgels have been reported72,73. The reasons for the limited results on microgel numerical modeling can be attributed to the complexity of the microgel network architecture, the still relatively poorly understood particle–particle interactions, as well as challenges in the understanding of the molecular origins of swelling and deswelling74. Despite these difficulties, significant efforts toward atomistic modeling are now underway. Pioneered by Zaccarelli and coworkers, atomistic models of the entire microgel were generated and successfully compared with experiments75,76 (Fig. 1b). While the models are atomistic, the force laws between the atoms still need to be adjusted ad hoc to reproduce experimental data. It remains an open question how predictive these models can be, and whether they can help to understand more complex architectures and dense assemblies.
Characterization of microgels with superresolution microscopy
The properties of the polymer, the solvent, as well as the microgel architecture define how microgels act. On a more coarse-grained level, this can be translated into the elasticity of the individual microgels, microgel–microgel interaction potentials, as well the osmotic pressure balance between the microgel and the solvent phase. The latter depends on the solvent composition and ions released into the solvent by the microgels themselves. A thorough understanding of the individual microgel network characteristics, and in particular the polymer density throughout the particle, will help us predict microgel behavior.
This perspective addresses in depth the properties of swollen microgels in solution. However, we will first briefly touch upon microgels at T > TLCST. Collapsed microgels are dense and homogeneous30; they behave very much like regular solid colloidal particles77. They feature, to a varying degree and depending on the synthesis parameters, charged groups at the surface, leading to double-layer repulsion and van der Waals (vdW) attraction, a situation that is often described by the DLVO interaction potential78. Depending on the degree of charging, the solvent ionic strength, and the vdW attractions, the collapsed microgel particles form a stable colloidal suspension; they flocculate or form a colloidal gel. In this paper, we will not address the aggregated particle assemblies and note that a rapid temperature quench of thermosensitive pNIPAM provides a way to prepare colloidal particle gels79,80. Temperature-induced aggregation of microgels is always reversible since in the swollen state, vdW attractions are weak.
Microgel architecture and properties of isolated microgels
The vast majority of work is investigating microgels based on the monomer N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) or its close derivatives26. The NIPAM molecule is widely used because the homopolymer displays a coil-to-globule transition at a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) TLCST ≃ 32 °C, studied by Wu and Wang in 199881. Free radical precipitation polymerization of the monomer is conducted in the presence of a cross-linker, typically N,N -methylenebisacrylamide (BIS), and initiated by potassium peroxodisulfate (KPS). Sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) can be added as a stabilizer. During the synthesis, the cross-linker is consumed faster than the monomers, and therefore the core of the microgel particles is more densely cross-linked compared with the corona. Many variations of these synthesis protocols have been reported, with the aim, for example, to modify the response to stimuli, to create other architectures like multi-responsive-layer microgels82 or hollow microgels31. Microgels are usually dispersed in water and highly swollen under good solvent conditions at T < TLCST. The solvent quality can be changed such that the microgels deswell and eventually collapse, which is also known as the volume-phase transition (VPT). The latter can also be achieved by changing the pH83, solvent composition (adding, e.g., methanol)58, and by applying a high external osmotic pressure84.
Common neutral microgels feature a core–shell structure, and scattering data suggest a radial polymer-density profile ρ(r) of the type
| 1 |
with a core radius Rc and a shell thickness controlled by the “fuzziness” parameter σ27,58. It was shown that RH ≈ Rc + 2σ provides a good estimate for the hydrodynamic radius27,58. More homogeneous microgels can be obtained by slowly adding the BIS cross-linker to the monomer solution, as described in ref. 85. Microgels synthesized, according to this recipe, have not yet been used widely. Bergman et al.86 speculated that homogeneous microgels might not be advantageous in practice, since the core–shell architecture is responsible for many of the unique and useful properties of microgels, for example, the soft onset of pairwise interactions. Here we will focus our attention on the standard type.
The characterization of microgels with scattering techniques is limited in two ways. First, the scattering of particles in solution records the Fourier transform of the pair-distance distribution function of the scattering density, which is a radially averaged signal in reciprocal space87. Possible particle anisotropies are very difficult to extract from a static scattering signal29. Second, scattering takes an ensemble average over a large number of particles. Polydispersity in terms of size, network morphology, but possibly also shape, is impossible to disentangle from scattering data. Therefore, attempts to obtain more detailed information about the microgel network morphology are futile.
Testing the applicability of the fuzzy-sphere model, when more details of the network morphology can be resolved, has been the point of departure for the first STORM-superresolution study on microgels58,86. Conley et al. showed that pNIPAM microgels, attached to a hydrophilic substrate, possess a nearly ideal spherical shape (Fig. 4a), and that the core and shell polydispersity is highly correlated58. They reported density profiles of micron-sized, individual microgels synthesized with ≃ 5% BIS, with a localization-density profile well described by the fuzzy-sphere model (Fig. 3c). More recently, Bergmann et al. showed that microgels obtained using higher cross-linker concentrations display unexpected deviations from the fuzzy-sphere model. They developed an interesting new method to resolve the network morphology. Utilizing the interaction of the freely diffusing fluorescent dye rhodamine 6G with the polymer network, they achieve indirect labeling, without altering the microgel chemical composition. Interestingly, they find that the polymer density in the core decays linearly before falling off exponentially in the corona (Fig. 4c). This additional weaker decay is only observed for BIS concentrations above 5%, and therefore had remained undetected in the first STORM study on microgels, see ref. 58.
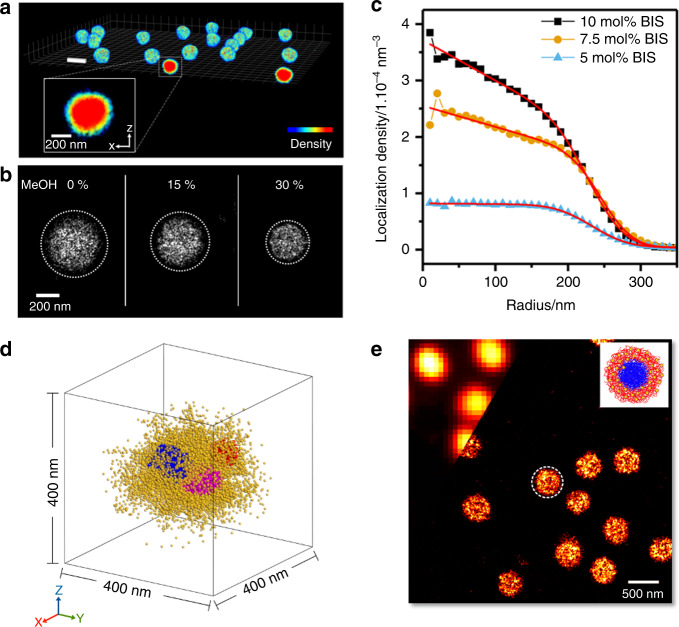
Fig. 4. SRFM characterization of individual microgels.
a 3D-dSTORM rendering of individual swollen neutral pNIPAM microgels (BIS 5%) in pure water, weakly adsorbed to a glass substrate (T = 22 °C). The glass coverslips were treated with piranha solution (a 4:1 solution of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide), which results in a highly hydrophilic surface (water contact angle 0° as reported in ref. 128). Inset: enlarged color-coded view of the internal density distribution. b Two-dimensional dSTORM of the same microgel particle and deswelling upon addition of methanol (MeOH). The dashed circles indicate the hydrodynamic diameter. Both panels adapted from ref. 58 (Fig. 2), with permission from Elsevier, Copyright (2016). c Density profile of dye localizations for similar neutral pNIPAM microgels suspended in pure water. The panel shows the results from a dSTORM study of microgels synthesized with different amounts of cross-linker (BIS = 5– 10%). For BIS concentrations above 5%, the data suggest a linearly increasing density toward the particle center. Reproduced from ref. 86 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry. d Single-molecule localization microscopy of near-spherical swollen microgel particles at 20 °C adsorbed to a polylysine-coated glass coverslip. The fluorescence localizations are determined for a small fraction of microgel cross-linker that has been dye-labeled. The (red, blue, and magenta)-color-labeled patches indicate clusters of increased cross-link density, while the localizations in the surrounding matrix are depicted in yellow, image reproduced with permission from ref. 88 (Copyright Royal Society of Chemistry, 2018). e dSTORM imaging of swollen pNIPAM-core–pNIPMAM-shell microgels in water deposited on a polylysine-coated glass coverslip. Inset: sketch of the particles. In the left upper corner, a part of the diffraction-limited image is shown. The dashed circle indicates the hydrodynamic diameter measured by DLS. The graphic was reproduced with permission from ref. 57 (Copyright American Chemical Society, 2016).
Another recent SRFM study has focused on the properties of the microgel core. Karanastasis et al. report in situ 3D imaging, using 4PiSMSN, with a ~20-nm isotropic resolution88. This is likely the highest optical resolution reported for microgel optical imaging to date. They exploit the specificity of fluorescent labeling and directly tag part of the cross-linker with a dye. To this end, they obtain 3D maps of localizations of cross-link sites. They find that the cross-link density in the core is not homogeneous but rather clustered, as shown in Fig. 4d, with cluster sizes of tens of nanometers, embedded in a lower cross-link density matrix. Their findings agree with earlier proposals that the polymer cross-linking is structurally heterogeneous35. This direct observation of cross-link clustering inside the microgel core may help to explain the results by Bergmann et al., shown in Fig. 4c. The study also demonstrates the rapid progress with respect to resolution and specificity, in 3D real-space imaging of microgels with potential applications to many other soft-matter systems42.
A shortcoming of the study of Karanastasis et al. is the fact that the subset of dye-labeled cross-links, shown in Fig. 4d, is confined to a smaller volume than expected88. They find that Eq. (1) can describe the density distribution, but Rc + 2σ = 171 nm is much smaller than RH = 330 nm88. The authors suggest that the dye-labeled cross-linker at 0.1% is consumed more rapidly compared with the BIS cross-linker at 2%. At least part of the difference in size could also be due to the lack of cross-linker in the corona, formed by the dangling polymer ends, and contributing to RH. In a parallel study, Siemes et al. also reported cross-linker density profiles using a novel diarylethene-based photoswitchable cross-linker with a highly fluorescent closed and a nonfluorescent open form. Interestingly, they report density profiles not in agreement with Eq. (1), a yet unexplained finding61. While the direct labeling of cross-linker molecules by these two groups is interesting and important, more work will be needed to unravel these contradicting results.
A better understanding of the network morphology and density distribution ρ(r) should, in principle, provide a basis to model the swelling behavior of microgels quantitatively. Despite the efforts made in the past73,89, this has not yet been achieved. More work is underway, using atomistic and mesoscale models to achieve this goal72,75,76,90. The challenge is to relate the measured density profile of the swollen microgel to the cross-linker gradient. Boon and Schurtenberger used a “nesting doll” model where each layer, with a specific cross-link density, is treated with the Flory–Rehner theory for swollen macrogels, and the energy functional of the entire microgel is minimized for a given cross-linker gradient89. However, for high cross-linker densities above 5% BIS, Bergmann et al. claim poor agreement between their experimental STORM data and this model. Recent experimental results by others, indicating cross-linker clusters inside the microgel core and heterogeneous domains within the network61,88, might provide clues for improvements of the nesting doll model. However, the treatment of the low-density brush-like outer corona might be challenging within the framework of the model62,63,91. The corona region can occupy up to 30–50% of the total volume of the swollen microgel62,63,91. Moreover, the outer shell dominates the onset of pairwise repulsive interactions when particles get into contact. The situation might be even direr for ionic microgels where Monte-Carlo simulations suggest that some of the dangling ends might stretch out to distances much larger than the core radius92. In a recent paper, Bergman et al. proposed that for ionic poly(NIPAM-co-acrylic acid) microgels, the corona and cross-linked core swelling can be considered as two separate entities93. Currently only DLS is able to reliably quantify the corona swelling, by measuring the hydrodynamic radius RH. Due to the extremely low density of the corona, both scattering and microscopy techniques have been unable to provide quantitative data. Selective dye labeling and improved contrast using better, brighter, and more stable dye markers hold promise to get a better grip on corona properties in future SRFM studies94.
The field of nanoscopy of microgels is still relatively new, and many microgel systems and questions around microgel properties have not yet been addressed. For example, it would be fascinating to image ionic microgels39,95, also under different solvent conditions and ionic strengths. Equally, ultralow cross-linked96 and very small microgels97 would benefit from a better characterization of their morphology. We expect that such studies will be conducted within the next few years, providing more high-quality data as an input for theoretical models and simulations.
Functional microgels and microgel–nanoparticle hybrids
Most of the recent advances in nanoscale characterization have been targeted toward simple, radially isotropic microgels. Here, we would like to point toward not only experimentally more challenging but also highly exciting applications of nanoscale imaging, such as functional microgels, for example, microgels with certain comonomers, polymer–nanoparticle hybrids, Janus particles, or microgel-based colloidal molecules98–101. A comprehensive discussion of functional microgels would be beyond the scope of this paper and can be found elsewhere12. However, the power of SRFM when applied to such functional systems has already been demonstrated by Gelissen et al. in one of the first STORM studies on microgels57. They successfully combined SRFM and electron microscopy (TEM) to unravel structural details of microgel core–shell particles (Fig. 4e), and microgels decorated with gold nanoparticles. Experiments of this type set the stage for the future development toward new levels of resolution and specificity, through multicolor dye labeling, based on SRFM54.
Adsorbed microgels on functionalized surfaces
Microgels are frequently studied at interfaces or deposited on a glass surface for analysis, both in the wet and the dry state. In the first SRFM study of microgels58, as well as subsequent work57,86,88, the microgels were attached to a glass substrate and immobilized. Based on 3D-dSTORM (Fig. 4a), Conley et al. reported microgels of spherical shape when attached to a hydrophilic glass substrate. The 3D images were, however, not analyzed quantitatively, and the calibration of the z axis in 3D-dSTORM is delicate102. The possibility of calibration errors thus leaves some ambiguity about the microgel sphericity in this study. This question was recently addressed by Alvarez et al., also using 3D-dSTORM. They studied the deformation and spreading of microgels on functionalized surfaces in an aqueous environment103. As shown in Fig. 5, they found that on hydrophobic surfaces, microgels spread and acquire a pancake-like shape, while on hydrophilic surfaces, microgels retain their spherical shape. The systematic data by Alvarez et al. thus confirm the original results of Conley et al., but they also show that one has to be careful with such studies.
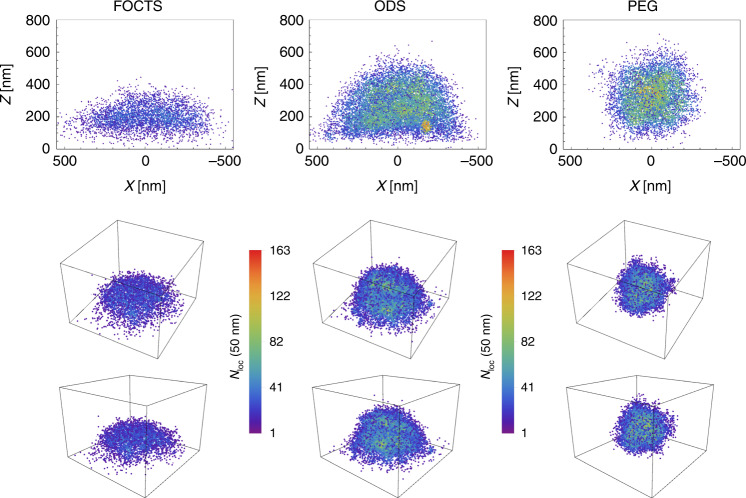
Fig. 5. Adsorbed pNIPAM microgels on surface-functionalized glass imaged with three-dimensional dSTORM103.
The upper graphs show a vertical section (y plane) of the localization-density distribution. The lower graphs show three-dimensional renderings at two different viewing angles. The functionalization with hydrophobic trichloro-(1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorooctyl)silane (FOCTS), or n-octadecyltrimethoxysilane (ODS), results in a flattened lens-like shape, while on surfaces functionalized with hydrophylic O-(2-aminoethy)polyethylene glycol (PEG), the microgel particles retain their spherical shape in agreement with the data reported previously in ref. 58 and shown in Figs. 3 and 4. The figure was reproduced with permission from ref. 103 (Copyright American Chemical Society, 2019).
Effective pairwise interactions between microgels
The local particle–particle interaction potential and the spatial distribution of microgel particles determine the properties of microgel-based materials at T < TLCST. For neutral particles, the compressibility of the microgel network and corona defines the pairwise particle interactions25,91. The contributions due to van der Waals attraction forces are usually weak ≪kBT due to the low polymer density in the swollen state. For ionic microgels, additional contributions due to the overlap of the ionic clouds come into play78. For simplicity, we restrict our discussion to neutral microgels where possible contributions of the DLVO type, both attractive and repulsive, are small or negligible. Therefore, we only need to consider repulsive forces that arise from elastic deformations of the microgel. The most common way to address this problem is to model repulsive interactions with a Hertz contact potential. This approach is equivalent to treating the soft microgel particles as homogeneous elastic spheres104. The model can be generalized to a multi-Hertzian potential, i.e., a multilayer structure of coupled Hertzian potentials, to take account for the fuzzy polymer-density profile91. Other models assume a homogeneous soft core covered by a polymer brush formed by dangling ends62,63. Such approaches can fit the experimental data well. They do, however, require several adjustable parameters that have not yet been linked quantitatively to the fundamental properties of the polymer network and its morphology. Based on the new and emerging knowledge from SRFM, we believe that it should soon be possible to improve this situation and attain a better quantitative understanding of microgel–microgel pairwise interactions. Efforts are also underway in our laboratory, for example, to directly measure pair-interaction potentials using optical tweezers, inspired by recent measurements on colloidal star polymers105.
Structure and morphology of densely packed microgel-based materials
The colloidal phase behavior of microgels, and charged and neutral soft spheres in general, has been the subject of many studies95,106–108. For a sufficiently monodisperse pNIPAM microgel suspension that is slowly cooled below TLCST, we expect crystallization at an effective volume fraction ζ ≳ 0.5. For a polydispersity greater than δRH/RH ~ 0.1 or for a rapid quench, crystallization is suppressed or slowed down, leading to an amorphous solid phase108. In an experiment, it is not always obvious which phase has been obtained. Typically, for smaller microgels, the crystal phase shows iridescence109, whereas, for larger, micron-sized, microgels, small-angle light scattering (SALS) can detect the presence or absence of sharp Bragg peaks110. In both cases, the particles eventually touch and, upon reaching higher values of ζ > 0.7, have to adapt their morphology. A number of things can happen. Microgels can deform like elastic spheres2,8,106, they can interpenetrate, or they can shrink28,111. Usually, all three processes may proceed at the same time, such that the total free energy reaches a local or global minimum.
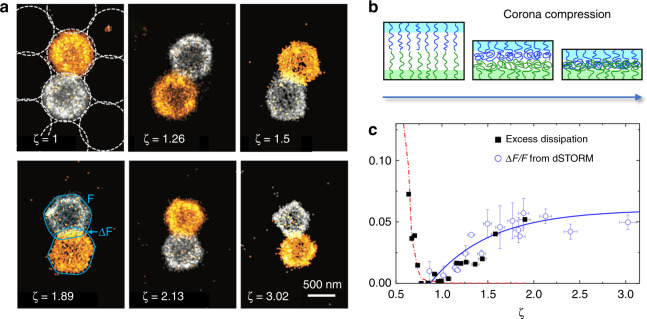
Recent SRFM experiments have been instrumental in identifying the various responses of microgels upon packing110. These experiments also highlighted the enormous potential of SRFM techniques applied to microgels and soft matter in general since they illustrated how qualitatively new information about bulk polymeric systems can be obtained. In the study reported in ref. 110, submicron-sized, highly swollen pNIPAM microgels were synthesized with ≈5% BIS cross-linker. Dense suspensions were prepared above TLCST and then quenched to 22 °C, well below the LCST. Effective volume fractions from ζ = 0.7 to ζ ≃ 3 were investigated. We may note in passing that overpacking (ζ > 1) cannot be reached using incompressible soft colloids, for example oil droplets in a dense emulsion112. The dSTORM experiments revealed that the packing progresses in different stages. In Fig. 6a, we reproduce typical two-color dSTORM images for several packing fractions. Initially, the fuzzy corona is compressed onto the core, resulting in rather homogeneous soft spheres at ζ = 1. Next, the particles deform, facet, and weakly interpenetrate, thereby reducing spatial density fluctuations. Eventually, no further interpenetration takes place, prevented by the network topology. Once this stage is reached, the spatial polymer distribution is nearly homogeneous on length scales larger than the network correlation length ξ, as confirmed by the vanishingly low light-scattering contrast110, and the microgels shrink when increasing the concentration further.
Fig. 6. Densely packed suspensions of neutral microgels: deformation, interpenetration, and compression.
a Two-color 2D dSTORM of dye-labeled microgels embedded in a matrix of unlabeled microgel particles, indicated by dashed circles in the left upper panel. ζ is the effective volume fraction. SRFM imaging of specifically labeled microgel pairs reveals partial interpenetration, faceting, and finally isotropic compression, leading to a decreasing global size. Contour lines are shown for ζ = 1.89 to illustrate the overlap area ΔF relative to the total area F of a particle for the image section shown. Image adapted from ref. 110. b Interpenetration mechanism at the particle–particle interface suggested in ref. 25 based on the dSTORM data. c Evidence that the dissipative behavior, expressed by the excess dissipation at ω ≃ 1 rad/s, scales with the overlap area 0.4 × ΔF/F. The solid blue line is a guide to the eye, and the red dash-dotted line denotes . These results suggest that information from nanoscale SRFM imaging can be directly used to model viscoelastic properties. Panels (b) and (c) were adapted from ref. 25.
The neutral microgels studied in refs. 25,110 are of the most common pNIPAM based type, with a radius of RH ≃ 500 nm and ≃5% BIS, and therefore the results are representative for many microgel studies carried out in the past. However, a plethora of other types of microgels have been discussed as well, and the characteristics can vary substantially. Differences can arise due to different polymer chemistry, size, cross-link density, and charges. We expect SRFM to play an essential role in disentangling the packing behavior of dense microgel suspensions for a number of microgel types and under different conditions. Potentially, SRFM can also be applied under out-of-equilibrium conditions, such as macroscopic shear deformation. Still, we need to keep in mind that it takes minutes25, rather than seconds, to record a single dSTORM image. Recently, progress in localization microscopy has been reported pointing toward second-scale image acquisition in biological applications, but the performance of these approaches has not yet been tested on soft materials113.
A fascinating open question, concerning dense microgel suspensions, is the spontaneous deswelling by counterion clouds114. Earlier work by Fernandez-Nieves et al. showed that microgels deswell when subject to a high external osmotic pressure, by adding dextran to the solution84. Scotti et al. suggested that the counterions released by the microgels themselves could lead to a reduction in particle size with increasing microgel concentration. From this, they conclude that in bimodal or polydisperse mixtures, larger particles selectively shrink. As a consequence, uniform shrinkage may suppress or delay the liquid-to-solid transition and facilitate crystallization115. If and under which conditions such deswelling may occur is not entirely clear and has been debated25,92,116. SRFM and scattering techniques will play a pivotal role in settling this question.
Rheology of microgel-based materials
Microgels possess remarkable properties, such as a very low mass density, porosity, softness, and responsiveness to external stimuli. The nano- and microscale properties of microgels are widely exploited in bulk formulations where microgels act as viscosity modifiers and lubricants2,14. Microgels have also become popular model systems in experimental studies of soft and adaptive colloids in highly concentrated and jammed suspensions3,106,117–121.
The rheology of microgels is especially interesting because it is susceptible to the particle morphology, swelling, and particle–particle interactions. Mattsson et al. reported that some microgel systems can be overpacked up to ninefold (ζ ≈ 9), and exhibit viscous flow properties over the entire range122, while other systems, like the one discussed in Fig. 6, jam at ζ ≈ 0.6 like elastic spheres and form fairly strong solids for ζ > 125,62,109,110 with elastic moduli exceeding 103 Pa. Clearly, the microscopic properties of the microgels must be responsible for this fundamentally different macroscopic behavior. Ikeda et al. discussed the interplay between the entropically driven glass transition and the buildup of deformation energy due to contact formation108. Quite generally, the size, the softness, and the architecture of microgels play an important role97. However, in many previous studies, the microgels under investigation have not been characterized in much detail. Modern SRFM techniques provide an opening here to make progress toward a complete characterization of individual microgels, dense microgel-based systems, and consequently reach a better understanding of their rheological properties. In the following section, we present an example of such an attempt to use the microscopic knowledge obtained from SRFM for the interpretation of rheological data.
Oscillatory shear experiments on neutral, submicron-sized pNIPAM microgels, some dating back to the 1990s109, have reported a sharp onset of the low-frequency (ω ~ 1 rad/s) elastic modulus at random close packing or “jamming,” followed by a more gradual linear increase for ζ > 125,107. Some experiments suggest a critical behavior at ζc ~ ζJ ~ 0.6, characteristic of a jamming transition62,104,107,109. To account for the increase in the elastic modulus , different elaborate models have been proposed62,63,91,104,107–108. A quantitative assessment of the microscopic packing behavior, a key ingredient for all modeling attempts, has been missing however. In particular, it was unknown to which extent microgel particles facet or interpenetrate, and if and when they may spontaneously shrink. We recently established such a relationship between the nanoscale structure and the rheological properties, using two-color dSTORM microscopy25. The packing evolution, shown in Fig. 6a, suggests that for ζ < 1, pairwise interactions are dominated by the compression of the microgel corona. For ζ > 1, we observe the faceting and subtle interpenetration of fairly homogeneous soft spheres followed by the shrinkage or isotropic compression of the individual microgels. In tandem, for ζ > 1, the low-frequency elastic shear modulus increases linearly with ζ. From this, we conclude that for ζ > 1, the elastic modulus is set by the jamming and compression of homogeneous microgel spheres. At lower concentrations, the corona compression dominates that of the pairwise interactions between microgels, and therefore rises much more rapidly once particles are touching, for ζ ≳ 0.6. Similar results for have been reported recently by Pellet and Cloitre107. We also looked at losses under oscillatory shear. For weak corona compression ζ < 1, the loss modulus G″(ω) matches the trend expected for other soft spheres with lubrified interfaces, such as emulsion droplets. At higher densities however, the contribution of viscous losses increases substantially. The latter can be quantified by the ratio of the loss modulus and the storage modulus at low frequencies, . Interestingly, we find that the degree of overlap between adjacent microgels measured by dSTORM, ΔF/F, is directly proportional to the excess dissipation, as shown in Fig. 6c.
Conclusions and outlook
There have been tremendous advances toward a complete characterization of microgel colloids over the last few years. The emerging superresolution microscopy techniques have primarily driven this progress since 2016. While the first experiment focused on validating the method, more recently, we have seen many fascinating examples of how SRFM microscopy can improve our understanding of microgels and microgel-based materials. More studies of this kind will follow, addressing different types of microgels and microgel-based materials, looking at encapsulation and release of pharmacological substances, flavor, or fragrances24,123.
At the same time, it remains essential to question each time the accuracy and meaningfulness of fluorescence microscopy data, notably when pushing the resolution limit toward the 10-nm scale. Recent work suggested cross-link clustering in the microgel core and deviations from the fuzzy- sphere model, as discussed in Fig. 4. Likely, these results point toward interesting and emerging new phenomena that will help us to better understand the structure, morphology, and swelling of microgels. Nevertheless, it will be important to corroborate the results by reproducing them in other labs, ideally with a different dye or labeling chemistry. Moreover, it will also be important to carefully consider the influence of polydispersity, and the way the data are analyzed in SRFM. Often, image sections are recorded, which are projections from an image slice onto a 2D plane, from which an ensemble average is calculated, and sometimes these results are transformed back to 3D58,86. In addition, the finite optical resolution and possible imaging artifacts have to be considered. Until now, most SRFM images have been recorded for adsorbed microgels or microgels located within a few-particle diameters next to a glass surface. As recently shown and discussed in Fig. 5, the presence of an interface can strongly influence the microgel shape, and thus, care has to be taken when interpreting such data.
In parallel to the rapid advances in microscopy, there has also been substantial progress with other characterization techniques. Modern scattering techniques can reveal important information, and can be applied to large bulk systems. Due to the possibility to perform contrast variation, neutron scattering is very powerful34. Many other techniques remain very useful, and there is certainly a tremendous potential for correlative approaches. The combination of SRFM, electron microscopy, scattering, and other methods seems to be ideal for addressing many of the open questions about microgels.
In this paper, we have focused our attention almost exclusively on the structural aspects of microgels. Most of the recent progress in superresolution microscopy has been made in this arena. While some SRFM techniques may also allow dynamic studies, there has been little research activity to date. Localization methods such as STORM are very slow, and it will be challenging to reach sub-second time resolution without compromising on image quality and resolution. Other SRFM techniques, such as STED, are faster, but to date, have not been applied to microgels. Time-resolved scattering techniques124, inelastic neutron scattering125 and neutron spin echo (NSE)126, diffusing wave spectroscopy62, oscillatory shear25,107, NMR35, dynamic AFM70, and other conventional techniques, however, can provide a plethora of information about the motion and internal relaxation of microgels, from the nanoscopic to the mesoscopic scales. In the future, we expect more studies that will combine modern high-resolution structural characterization methods with advanced dynamical measurements.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Maxime Bergman for help preparing the paper and for many useful remarks and comments. We acknowledge funding by the Swiss National Science Foundation through Project Nos. 188494 and 183651, and through the National Center of Competence in Research Bio-Inspired Materials. Financial support by the European Union through the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Innovative Training Networks (ITN) “SuperCol” under grant No. 860914 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author contributions
The paper was planned and written by F.S.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Saunders BR, Vincent B. Microgel particles as model colloids: theory, properties and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999;80:1–25. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fernandez-Nieves, A., Wyss, H., Mattsson, J. & Weitz, D. A., Microgel Suspensions: Fundamentals and Applications (John Wiley & Sons, 2011).
- 3.Brijitta J, Schurtenberger P. Responsive hydrogel colloids: Structure, interactions, phase behaviour, and equilibrium and non-equilibrium transitions of microgel dispersions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;40:87–103. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cloitre M, Borrega R, Monti F, Leibler L. Structure and flow of polyelectrolyte microgels: from suspensions to glasses. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2003;4:221–230. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schneider J, Wiemann M, Rabe A, Bartsch E. On tuning microgel character and softness of cross-linked polystyrene particles. Soft Matter. 2017;13:445–457. doi: 10.1039/c6sm02007k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pelton RH, Chibante P. Preparation of aqueous latices with n-isopropylacrylamide. Colloids Surf. 1986;20:247–256. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wyss HM, Franke T, Mele E, Weitz DA. Capillary micromechanics: measuring the elasticity of microscopic soft objects. Soft Matter. 2010;6:4550–4555. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang Z, et al. Thermal vestige of the zero-temperature jamming transition. Nature. 2009;459:230–233. doi: 10.1038/nature07998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fernández-Rodríguez MÁ, et al. Tunable 2d binary colloidal alloys for soft nanotemplating. Nanoscale. 2018;10:22189–22195. doi: 10.1039/c8nr07059h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li X, Gao Y, Serpe MJ. Stimuli-responsive assemblies for sensing applications. Gels. 2016;2:8. doi: 10.3390/gels2010008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Choe A, et al. Stretchable and wearable colorimetric patches based on thermoresponsive plasmonic microgels embedded in a hydrogel film. NPG Asia Mater. 2018;10:912–922. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Plamper FA, Richtering W. Functional microgels and microgel systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017;50:131–140. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sánchez-Iglesias A, et al. Synthesis of multifunctional composite microgels via in situ ni growth on pnipam-coated au nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2009;3:3184–3190. doi: 10.1021/nn9006169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Andablo-Reyes E, et al. Microgels as viscosity modifiers influence lubrication performance of continuum. Soft Matter. 2019;15:9614–9624. doi: 10.1039/c9sm01802f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yue M, Hoshino Y, Ohshiro Y, Imamura K, Miura Y. Temperature-responsive microgel films as reversible carbon dioxide absorbents in wet environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:2654–2657. doi: 10.1002/anie.201309758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Highley CB, Song KH, Daly AC, Burdick JA. Jammed microgel inks for 3d printing applications. Adv. Sci. 2019;6:1801076. doi: 10.1002/advs.201801076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Murthy N, et al. A macromolecular delivery vehicle for protein-based vaccines: acid-degradable protein-loaded microgels. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:4995–5000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0930644100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Debord JD, Eustis S, S ByulDebord, Lofye MT, Lyon LA. Color-tunable colloidal crystals from soft hydrogel nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2002;14:658–662. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Isapour G, Lattuada M. Bioinspired stimuli-responsive color-changing systems. Adv. Mater. 2018;30:1707069. doi: 10.1002/adma.201707069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hyatt JS, et al. Segregation of mass at the periphery of n-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic-acid microgels at high temperatures. Phys. Rev. E. 2015;92:030302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.92.030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rubinstein, M. et al. Polymer Physics, Vol. 23 (Oxford University Press, New York, 2003).
- 22.Fernandez-Barbero A, Fernandez-Nieves A, Grillo I, Lopez-Cabarcos E. Structural modifications in the swelling of inhomogeneous microgels by light and neutron scattering. Phys. Rev. E. 2002;66:051803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.66.051803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wu X, Pelton RH, Hamielec AE, Woods DR, McPhee W. The kinetics of poly (n-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex formation. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1994;272:467–477. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Smeets NMB, Hoare T. Designing responsive microgels for drug delivery applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2013;51:3027–3043. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Conley GM, Zhang C, Aebischer P, Harden JL, Scheffold F. Relationship between rheology and structure of interpenetrating, deforming and compressing microgels. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10181-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lyon LA, Fernandez-Nieves A. The polymer/colloid duality of microgel suspensions. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2012;63:25–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-032511-143735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stieger M, Richtering W, Pedersen JS, Lindner P. Small-angle neutron scattering study of structural changes in temperature sensitive microgel colloids. J. Chem. Phys. 2004;120:6197–6206. doi: 10.1063/1.1665752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gasser U, et al. Form factor of pnipam microgels in overpacked states. J. Chem. Phys. 2014;141:034901. doi: 10.1063/1.4885444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zemb, T. & Lindner, P. Neutrons, X-Rays and Light: Scattering Methods Applied to Soft Condensed Matter (Elsevier, North Holland, 2002).
- 30.Reufer M, Díaz-Leyva P, Lynch I, Scheffold F. Temperature-sensitive poly (n-isopropyl-acrylamide) microgel particles: a light scattering study. Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys. 2009;28:165–171. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2008-10387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dubbert J, et al. How hollow are thermoresponsive hollow nanogels? Macromolecules. 2014;47:8700–8708. [Google Scholar]
- 32.TG Mason, MY Lin. Density profiles of temperature-sensitive microgel particles. Phys. Rev. E. 2005;71:040801. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.71.040801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cors M, et al. Spatial distribution of core monomers in acrylamide-based core-shell microgels with linear swelling behaviour. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50164-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mohanty PS, et al. Interpenetration of polymeric microgels at ultrahigh densities. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1487. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01471-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Di Lorenzo F, Seiffert S. Nanostructural heterogeneity in polymer networks and gels. Polym. Chem. 2015;6:5515–5528. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Witte J, et al. A comparison of the network structure and inner dynamics of homogeneously and heterogeneously crosslinked pnipam microgels with high crosslinker content. Soft Matter. 2019;15:1053–1064. doi: 10.1039/c8sm02141d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Van Blaaderen A, Imhof A, W Hage, A Vrij. Three-dimensional imaging of submicrometer colloidal particles in concentrated suspensions using confocal scanning laser microscopy. Langmuir. 1992;8:1514–1517. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Paloli D, Mohanty PS, Crassous JJ, Zaccarelli E, Schurtenberger P. Fluid–solid transitions in soft-repulsive colloids. Soft Matter. 2013;9:3000–3004. doi: 10.1063/1.4866644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nöjd S, Mohanty PS, Bagheri P, Yethiraj A, Schurtenberger P. Electric field driven self-assembly of ionic microgels. Soft Matter. 2013;9:9199–9207. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Patterson G, Davidson M, Manley S, Lippincott-Schwartz J. Superresolution imaging using single-molecule localization. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2010;61:345–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.012809.103444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wöll D, Flors C. Super-resolution fluorescence imaging for materials science. Small Methods. 2017;1:1700191. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aloi A, Voets IK. Soft matter nanoscopy. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;34:59–73. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kegel WK, van Blaaderen A. Direct observation of dynamical heterogeneities in colloidal hard-sphere suspensions. Science. 2000;287:290–293. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5451.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Leung BO, Chou KC. Review of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy for biology. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011;65:967–980. doi: 10.1366/11-06398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Klar TA, Jakobs S, Dyba M, Egner A, Hell SW. Fluorescence microscopy with diffraction resolution barrier broken by stimulated emission. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 2000;97:8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.15.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Betzig E, et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–1645. doi: 10.1126/science.1127344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rust MJ, Bates M, Zhuang X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (storm) Nat. Methods. 2006;3:793–796. doi: 10.1038/nmeth929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Heilemann M, et al. Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging with conventional fluorescent probes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:6172–6176. doi: 10.1002/anie.200802376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Purohit A, Centeno SP, Wypysek SK, Richtering W, Wöll D. Microgel paint–nanoscopic polarity imaging of adaptive microgels without covalent labelling. Chem. Sci. 2019;10:10336–10342. doi: 10.1039/c9sc03373d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hell SW. Far-field optical nanoscopy. Science. 2007;316:1153–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.1137395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tam J, Merino D. Stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (storm) in comparison with stimulated emission depletion (sted) and other imaging methods. J. Neurochem. 2015;135:643–658. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rittweger E, Han KY, Irvine SE, Eggeling C, Hell SW. Sted microscopy reveals crystal colour centres with nanometric resolution. Nat. Photonics. 2009;3:144. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Huang B, Wang W, Bates M, Zhuang X. Three-dimensional super-resolution imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. Science. 2008;319:810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1153529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hauser M, et al. Correlative super-resolution microscopy: new dimensions and new opportunities. Chem. Rev. 2017;117:7428–7456. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Huang F, et al. Ultra-high resolution 3d imaging of whole cells. Cell. 2016;166:1028–1040. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Balzarotti F, et al. Nanometer resolution imaging and tracking of fluorescent molecules with minimal photon fluxes. Science. 2017;355:606–612. doi: 10.1126/science.aak9913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gelissen APH, et al. 3d structures of responsive nanocompartmentalized microgels. Nano Lett. 2016;16:7295–7301. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Conley GM, Nöjd S, Braibanti M, Schurtenberger P, Scheffold F. Superresolution microscopy of the volume phase transition of pnipam microgels. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016;499:18–23. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dempsey GT, Vaughan JC, Chen KH, Bates M, Zhuang X. Evaluation of fluorophores for optimal performance in localization-based super-resolution imaging. Nat. Methods. 2011;8:1027. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Holmqvist P, Mohanty PS, Nägele G, Schurtenberger P, Heinen M. Structure and dynamics of loosely cross-linked ionic microgel dispersions in the fluid regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012;109:048302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.048302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Siemes E, et al. Nanoscopic visualization of cross-linking density in polymer networks with diarylethene photoswitches. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018;57:12280–12284. doi: 10.1002/anie.201807741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Scheffold F, et al. Brushlike interactions between thermoresponsive microgel particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010;104:128304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.128304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Romeo G, Ciamarra MP. Elasticity of compressed microgel suspensions. Soft Matter. 2013;9:5401–5406. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Serpe MJ, Kim J, Lyon LA. Colloidal hydrogel microlenses. Adv. Mater. 2004;16:184–187. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Crassous JJ, et al. Direct imaging of temperature-sensitive core-shell latexes by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2008;286:805–812. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Höfl S, Zitzler L, Hellweg T, Herminghaus S, Mugele F. Volume phase transition of smart microgels in bulk solution and adsorbed at an interface: A combined afm, dynamic light, and small angle neutron scattering study. Polymer. 2007;48:245–254. [Google Scholar]
- 67.South AB, Lyon LA. Direct observation of microgel erosion via in-liquid atomic force microscopy. Chem. Mater. 2010;22:3300–3306. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Schulte MF, Scotti A, Gelissen APH, Richtering W, Mourran A. Probing the internal heterogeneity of responsive microgels adsorbed to an interface by a sharp sfm tip: comparing core–shell and hollow microgels. Langmuir. 2018;34:4150–4158. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b03811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Matsui S, Nishizawa Y, Uchihashi T, Suzuki D. Monitoring thermoresponsive morphological changes in individual hydrogel microspheres. ACS Omega. 2018;3:10836–10842. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Aufderhorst-Roberts A, et al. Nanoscale mechanics of microgel particles. Nanoscale. 2018;10:16050–16061. doi: 10.1039/c8nr02911c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Peter C, Kremer K. Multiscale simulation of soft matter systems. Faraday Discuss. 2010;144:9–24. doi: 10.1039/b919800h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ghavami A, Kobayashi H, Winkler RG. Internal dynamics of microgels: a mesoscale hydrodynamic simulation study. J. Chem. Phys. 2016;145:244902. doi: 10.1063/1.4972893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Nikolov S, Fernandez-Nieves A, Alexeev A. Mesoscale modeling of microgel mechanics and kinetics through the swelling transition. Appl. Math. Mech. 2018;39:47–62. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pelton R. Poly (n-isopropylacrylamide)(pnipam) is never hydrophobic. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;348:673–674. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gnan, N., Rovigatti, L., Bergman, M. & Zaccarelli, E. In silico synthesis of microgel particles. Macromolecules50, 8777–8786 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b01600 (2017). further permissions related to the material excerpted should be directed to the American Chemical Society. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 76.Ninarello A, et al. Modeling microgels with a controlled structure across the volume phase transition. Macromolecules. 2019;52:7584–7592. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.9b01122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hunter, R. J. Foundations of Colloid Science (Oxford University Press, 2001).
- 78.Israelachvili, J. N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces (Academic Press, 2015).
- 79.Liao W, Zhang Y, Guan Y, Zhu XX. Gelation kinetics of thermosensitive pnipam microgel dispersions. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011;212:2052–2060. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Minami, S., Suzuki, D. & Urayama, K. Rheological aspects of colloidal gels in thermoresponsive microgel suspensions: Formation, structure, linear and nonlinear viscoelasticity. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci.43, 113–124 (2019).
- 81.Wu C, Wang X. Globule-to-coil transition of a single homopolymer chain in solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998;80:4092. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Brugnoni M, et al. Swelling of a responsive network within different constraints in multi-thermosensitive microgels. Macromolecules. 2018;51:2662–2671. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hoare T, Pelton R. Highly ph and temperature responsive microgels functionalized with vinylacetic acid. Macromolecules. 2004;37:2544–2550. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Fernández-Nieves A, Fernández-Barbero A, Vincent B, De las Nieves FJ. Osmotic de-swelling of ionic microgel particles. J. Chem. Phys. 2003;119:10383–10388. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Still T, Chen K, Alsayed AM, Aptowicz KB, Yodh AG. Synthesis of micrometer-size poly (n-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles with homogeneous crosslinker density and diameter control. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;405:96–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.05.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bergmann S, Wrede O, Huser T, Hellweg T. Super-resolution optical microscopy resolves network morphology of smart colloidal microgels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018;20:5074–5083. doi: 10.1039/c7cp07648g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Glatter, O. Scattering Methods and Their Application in Colloid and Interface Science (Elsevier, 2018).
- 88.Karanastasis AA, et al. 3d mapping of nanoscale crosslink heterogeneities in microgels. Mater. Horiz. 2018;5:1130–1136. doi: 10.1039/c8mh00644j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Boon N, Schurtenberger P. Swelling of micro-hydrogels with a crosslinker gradient. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017;19:23740–23746. doi: 10.1039/c7cp02434g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Moreno AJ, Verso FL. Computational investigation of microgels: synthesis and effect of the microstructure on the deswelling behavior. Soft Matter. 2018;14:7083–7096. doi: 10.1039/c8sm01407h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bergman MJ, et al. A new look at effective interactions between microgel particles. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:5039. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07332-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nöjd S, et al. Deswelling behaviour of ionic microgel particles from low to ultra-high densities. Soft Matter. 2018;14:4150–4159. doi: 10.1039/c8sm00390d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bergman MJ, Pedersen JS, Schurtenberger P, Boon N. Controlling the morphology of microgels by ionic stimuli. Soft Matter. 2020;16:2786–2794. doi: 10.1039/c9sm02170a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Grimm JB, et al. Bright photoactivatable fluorophores for single-molecule imaging. Nat. Methods. 2016;13:985–988. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gottwald D, Likos CN, Kahl G, Löwen H. Phase behavior of ionic microgels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004;92:068301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.068301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Scotti A, et al. Exploring the colloid-to-polymer transition for ultra-low crosslinked microgels from three to two dimensions. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1–8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09227-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Menut P, Seiffert S, Sprakel J, Weitz DA. Does size matter? elasticity of compressed suspensions of colloidal-and granular-scale microgels. Soft Matter. 2012;8:156–164. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Yuan Q, et al. Synthesis of a colloidal molecule from soft microgel spheres. ACS Macro Lett. 2016;5:565–568. doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.6b00187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wong JE, Gaharwar AK, Müller-Schulte D, Bahadur D, Richtering W. Dual-stimuli responsive pnipam microgel achieved via layer-by-layer assembly: magnetic and thermoresponsive. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008;324:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Witt MU, et al. Distribution of cofe2o4 nanoparticles inside pnipam-based microgels of different cross-linker distributions. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2019;123:2405–2413. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b09236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Xu W, et al. Synthesis of polyampholyte janus-like microgels by coacervation of reactive precursors in precipitation polymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020;59:1248–1255. doi: 10.1002/anie.201910450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Raab M, et al. Using dna origami nanorulers as traceable distance measurement standards and nanoscopic benchmark structures. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19905-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Alvarez LH, et al. Deformation of microgels at solid-liquid interfaces visualized in three-dimension. Nano Lett. 2019;19:8862–8867. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b03688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Bonnecaze, R. T. & Cloitre, M. Micromechanics of soft particle glasses. In (Ed. M. Cloitre) High Solid Dispersions 117–161 (Springer, 2010).
- 105.Huang F, et al. Pair potential of charged colloidal stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009;102:108302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.108302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Yunker PJ, et al. Physics in ordered and disordered colloidal matter composed of poly (n-isopropylacrylamide) microgel particles. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2014;77:056601. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/77/5/056601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Pellet C, Cloitre M. The glass and jamming transitions of soft polyelectrolyte microgel suspensions. Soft Matter. 2016;12:3710–3720. doi: 10.1039/c5sm03001c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Ikeda A, Berthier L, Sollich P. Disentangling glass and jamming physics in the rheology of soft materials. Soft Matter. 2013;9:7669–7683. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Senff H, Richtering W. Temperature sensitive microgel suspensions: colloidal phase behavior and rheology of soft spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 1999;111:1705–1711. [Google Scholar]
- 110.Conley GM, Aebischer P, Nöjd S, Schurtenberger P, Scheffold F. Jamming and overpacking fuzzy microgels: deformation, interpenetration, and compression. Sci. Adv. 2017;3:e1700969. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.De Aguiar IB, et al. Deswelling and deformation of microgels in concentrated packings. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:10223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10788-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Jorjadze I, Pontani L-L, Brujic J. Microscopic approach to the nonlinear elasticity of compressed emulsions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013;110:048302. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.048302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zhu L, Zhang W, Elnatan D, Huang B. Faster storm using compressed sensing. Nat. Methods. 2012;9:721. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Scotti A, et al. The role of ions in the self-healing behavior of soft particle suspensions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:5576–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516011113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Gasser U, Scotti A, Fernandez-Nieves A. Spontaneous deswelling of microgels controlled by counterion clouds. Phys. Rev. E. 2019;99:042602. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.99.042602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Scotti A, et al. Deswelling of microgels in crowded suspensions depends on cross-link density and architecture. Macromolecules. 2019;52:3995–4007. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mohanty PS, Paloli D, Crassous JJ, Zaccarelli E, Schurtenberger P. Effective interactions between soft-repulsive colloids: experiments, theory, and simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2014;140:094901. doi: 10.1063/1.4866644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Seth JR, Mohan L, Locatelli-Champagne C, Cloitre M, Bonnecaze RT. A micromechanical model to predict the flow of soft particle glasses. Nat. Mater. 2011;10:838–843. doi: 10.1038/nmat3119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Nakaishi A, et al. Elastic and flow properties of densely packed binary microgel mixtures with size and stiffness disparities. Macromolecules. 2018;51:9901–9914. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Thorne JB, Vine GJ, Snowden MJ. Microgel applications and commercial considerations. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011;289:625. [Google Scholar]
- 121.Vlassopoulos D, Cloitre M. Tunable rheology of dense soft deformable colloids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;19:561–574. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Mattsson J, et al. Soft colloids make strong glasses. Nature. 2009;462:83. doi: 10.1038/nature08457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Wang M, Doi T, McClements DJ. Encapsulation and controlled release of hydrophobic flavors using biopolymer-based microgel delivery systems: sustained release of garlic flavor during simulated cooking. Food Res. Int. 2019;119:6–14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Keidel R, et al. Time-resolved structural evolution during the collapse of responsive hydrogels: the microgel-to-particle transition. Sci. Adv. 2018;4:eaao7086. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aao7086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Sierra-Martin B, Retama JR, Laurenti M, Barbero AF, Cabarcos EL. Structure and polymer dynamics within pnipam-based microgel particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;205:113–123. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2013.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Scherzinger C, Holderer O, Richter D, Richtering W. Polymer dynamics in responsive microgels: influence of cononsolvency and microgel architecture. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012;14:2762–2768. doi: 10.1039/c2cp23328b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Dagallier C, Dietsch H, Schurtenberger P, Scheffold F. Thermoresponsive hybrid microgel particles with intrinsic optical and magnetic anisotropy. Soft Matter. 2010;6:2174–2177. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Wright, D. S., Flavel, B. S. & Quinton, J. S. Streaming zeta potential measurements of surface-bound organosilane molecular species. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 634–636 (IEEE, 2006).