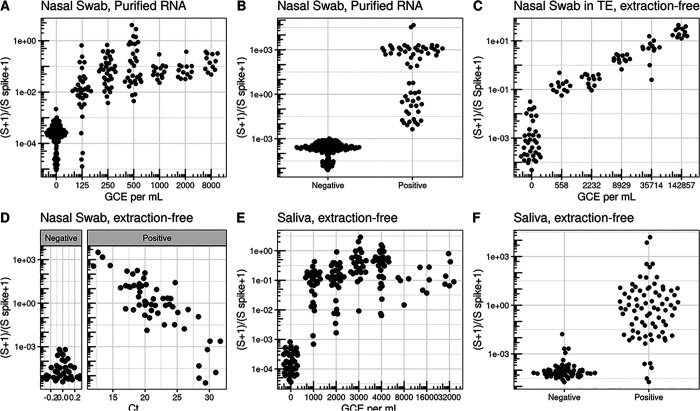
Figure 2. Validation in clinical specimens demonstrate a limit of detection equivalent to sensitive RT-qPCR reactions.
A) Limit of Detection in nasal swab samples with no SARS-CoV2 were pooled and ATCC inactivated virus was added at different concentrations. Nasal Swab sample was RNA purified and using SwabSeq showed a limit of detection of 250 genome copy equivalents (GCE) per mL. B) RNA-purified clinical nasal swab specimens obtained through the UCLA Health Clinical Microbiology Laboratory were tested based on clinical protocols using FDA authorized platforms and then also tested using SwabSeq. This represents a subset of the total purified RNA samples used in our validation. We show 100% agreement with samples that tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 (n=63) and negative for SARS-CoV-2 (n=159). C) We also tested RNA purified samples from extraction-free nasopharyngeal swab and showed a limit of detection of 558 GCE/mL. D) Relationship between Ct from RT-qPCR targeting the S gene (x-axis) and SwabSeq ratio for extract-free swabs into normal saline or Tris-EDTA (y-axis) for patient samples classified as testing positive or negative for SARS-CoV-2 by the UCLA Clinical Microbiology Laboratory. Samples with no virus detected were assigned a Ct of 0 for this visualization. E) Extraction- free processing of saliva specimens show a limit or detection down to 1000 GCE per mL. F) Extraction-free processing of saliva clinical specimens using swabseq (y-axis) compared to classification of SARS-CoV-2 status from RNA-purified clinical nasal swab specimens for matched samples (x-axis).