Abstract
Previously, I suggested that arachidonic acid (AA, 20:4 n-6) and similar bioactive lipids (BALs) inactivate SARS-CoV-2 and thus, may be of benefit in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. This proposal is supported by the observation that (i) macrophages and T cells (including NK cells, cytotoxic killer cells and other immunocytes) release AA and other BALs especially in the lungs to inactivate various microbes; (ii) pro-inflammatory metabolites prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and leukotrienes (LTs) and anti-inflammatory lipoxin A4 (LXA4) derived from AA (similarly, resolvins, protectins and maresins derived from eicosapentaenoic acid: EPA and docosahexaenoic acid: DHA) facilitate the generation of M1 (pro-inflammatory) and M2 (anti-inflammatory) macrophages respectively; (iii) AA, PGE2, LXA4 and other BALs inhibit interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) synthesis; (iv) mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that are of benefit in COVID-19 elaborate LXA4 to bring about their beneficial actions and (v) subjects with insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease and the elderly have significantly low plasma concentrations of AA and LXA4 that may render them more susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection and cytokine storm that is associated with increased mortality seen in COVID-19. Statins, colchicine, and corticosteroids that appear to be of benefit in COVID-19 can influence BALs metabolism. AA, and other BALs influence cell membrane fluidity and thus, regulate ACE-2 (angiotensin converting enzyme-2) receptors (the ligand through which SARS-CoV2 enters the cell) receptors. These observations lend support to the contention that administration of BALs especially, AA could be of significant benefit in prevention and management of COVI-19 and other enveloped viruses.
Key Words: COVID-19, Inflammation, Bioactive lipids, SARS-CoV-2, Arachidonic acid, Cytokines
Introduction
Enormous efforts are being made to develop both preventive and therapeutic strategies to stem the pandemic of COVID-19. An effective vaccine is likely but takes considerable time. Similarly, drugs that inhibit the replication of SARS-CoV-2, prevent its ability to infect human cells/tissues and nullify the clinical manifestations of COVID-19 may take time and a timeline of success of these efforts are not clear. In this scenario, it is noteworthy that little attention has been paid to the possibility that bioactive lipids (BALs) are likely to be benefit in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 have largely been ignored. Previously, I suggested that BALs especially, AA and LXA4 may have the potential to inactivate SARS-CoV-2 and other similar enveloped viruses and thus, could be employed to prevent and manage COVID-19 (1,3, 4, 5, 6, 7). In continuation of this argument, further evidence is presented here as to the potential benefit of AA and LXA4 and related BALs in COVID-19.
Alveolar Macrophages Release AA to Suppress Microbial Infections
Alveolar macrophages (and macrophages elsewhere), peripheral leukocytes, T, B, NK cells and other immunocytes release AA and other BALs and their metabolites such as eicosanoids that could be considered as one of the innate immune responses needed to prevent and protect from various microbial infections. Alveolar macrophages and other immunocytes in the lungs release AA and other BALs into the surrounding tissues (including alveolar fluid) to inactivate invading microbes (8,9). It is noteworthy that alveolar fluid donates AA and other BALs to be utilized by alveolar macrophages to bring about their anti-microbial action. This interaction between alveolar macrophages and their milieu is interesting and suggests crosstalk between various cells to eliminate microbes and protect the tissues from infections. Based on this, it is suggested that administration of appropriate amounts of AA, EPA and DHA (the most effective BALs) direct to lungs or intravenously will be of significant benefit in the management of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), SARS and MERS (3,4). Furthermore, AA and other BALs by their ability to alter cell membrane fluidity can alter the expression of ACE-2 and TMPRSS2 and thus, prevent the ability of SARS-CoV-2 to enter the target cells to infect them.
BALs Facilitate Generation of M1 and M2 Macrophages
Macrophages of inflammatory phenotype (M1-like) secrete prostaglandins (PGs), leukotrienes (LTs) and thromboxanes (TXs), which have pro-inflammatory action to initiate and perpetuate inflammation whereas anti-inflammatory lipoxin A4 from AA, PGE1 from dihomo-GLA (DGLA), D- and E-series resolvins from EPA and DHA, respectively, and protectins and maresins from DHA facilitate generation of the M2 macrophages to suppress inflammation (3,10, 11, 12, 13). The balance between M1 and M2-like macrophages determines the outcome of inflammation. Both pro- and anti-inflammatory BALs need to be synthesized and secreted in a coordinated and orderly fashion to induce and resolve inflammation and restore homeostasis for which adequate amounts of AA and other BALs and the formation of their respective pro- and anti-inflammatory metabolites are needed. Supplementation of AA during an acute inflammatory process augments the formation of LXA4, an anti-inflammatory molecule, with little or no change in the synthesis of PGE2, a pro-inflammatory molecule. Thus, provision of AA tilts the balance more towards resolution of inflammation by facilitating generation of M2-like macrophages that leads to resolution of inflammation. This process of switching between M1 and M2-like macrophages and generation and maintenance of balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory bioactive lipids (especially between LXA4 and PGE2) is closely regulated by an interaction that occurs between BALs and pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines such that a smooth transmission from inflammation to resolution of inflammation occurs (3,13).
BALs and Cytokine Storm
AA, EPA, DHA, lipoxins, resolvins, protectins and maresins are potent inhibitors of pro-inflammatory IL-6 and TNF-α synthesis (3,13,14). In contrast, TNF-α and IL-6 inhibit the activities of desaturases (15) that are essential for the formation of AA, EPA and DHA from dietary LA and ALA (3,6,13, 14, 15). Hence, increased production of IL-6 and TNF- α that occurs during SARS-CoV-2 infection (and other infections) can induce a deficiency of AA, EPA and DHA. This, in turn, could result in a reduction in the synthesis of anti-inflammatory LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins. In such an instance, further increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines occurs due to the absence of negative feedback regulatory control exerted by AA, EPA, DHA and their metabolites LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins. Hence, it is predicted that administration of adequate amounts of AA, EPA and DHA and their anti-inflammatory metabolites suppress excess generation and release of IL-6 and TNF-α and other pro-inflammatory cytokines and prevent cytokine storm seen in severe cases of COVID-19 and sepsis and restore homeostasis. In addition, subjects with obesity, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease have low plasma concentrations of AA., whereas elderly have decreased activity of desaturases that results in low plasma levels of AA and low LXA4 levels (14,16,17). This may explain why these subjects have severe COVID-19 and are more prone to cytokine storm and resultant mortality.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secrete LXA4
It is noteworthy that the beneficial action of mesenchymal stem cells in the management of COVID-19 reported (18) can also be attributed to their ability to produce LXA4 that mediates their (mesenchymal stem cells) anti-inflammatory action (19, 20, 21).
Th strongest support to the involvement of BALs in CVID-19 is derived from the recent reports (22,23) that when human cells are exposed to SARS-Co-V-2 and/or human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E), they (human cells) release large amounts of AA and LA and both these fatty acids inactivate the viruses (Figure 1, Figure 2 ). Interestingly, Yan B, et al. (23) reported that supplementation of LA and AA to HCoV-229E and MERS-CoV infected Huh-7 cells significantly suppressed virus replication implying that BALs can inactivate SARS-oV-2 and related viruses. This implies that when the human cells are exposed to SARS-CoV-2 and other similar viruses, there will be activation of PLA2 that induces the release of AA and other BALs. If the released BALs are adequate, they would inactivate the viruses and recovery ensues. In the event the cells are unable to release sufficient amounts of specific BALs, the virus replicates and produces COVID-19. These results are in direct support of the proposal that BALs have a significant role in the pathobiology of SARS-CoV-2 and other corona virus-induced diseases (1,3,6). This implies that (BALs, especially AA) could be useful in the prevention and management of COVID-19. The advantage with AA is that it is a natural, endogenous lipid that can be given orally or parenterally (24,25) without any significant side effects. AA is recognized by FDA as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) and can be given even to children.
Figure 1.
(A) Plasma levels of AA in those infected with SARS-Co-V-2. These results emphasize the proposal that healthy people have adequate amounts of AA whereas severe COVID-19 patients have a deficiency of AA. This data is taken from reference (22). a,b,cp <0.05 compared to respective controls as shown in the Figure.
Figure 2.
Ability of LA and AA and other fatty acids to inactivate HCoV-229E and MERS-CoV viruses. HuH-7 cells were infected with HCoV-229E or MERS-CoV viruses. After one hour of inoculation with the virus, the cells were treated with 50 mmol or 100 mmol of fatty acids for 24 h. Both supernatant and cell lysates were collected and analyzed using RT-qPCR technique. p <0.05.
This data (Figure 3, Figure 4) is taken from reference (23).
Corticosteroids, BALs and COVID-19
The recent reports that corticosteroids (given as dexamethasone, 6 mg/d for 10 days) and GM-CSF blockade with mavrilimumab (6 mg/kg i.v.) are of benefit in severe COVID-19 pneumonia and systemic hyperinflammation (26,27) can also be attributed to their ability to block the formation of excess of pro-inflammatory PGE2 and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) from AA and cytokines. Corticosteroids inhibit the activity of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) (thus, inhibit the release of AA and other PUFAs from the cell membrane), desaturases (that are needed for the conversion of dietary LA and ALA–AA and EPA and DHA respectively), and COX-2 and LOX enzymes leading to decreased formation of prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes and thus, ameliorate inflammation. Thus, corticosteroids induce AA, EPA and DHA deficiency state due to their inhibitory action on desaturases. Corticosteroids also inhibit LXA4 synthesis (from AA) and possibly, resolvins, protectins and maresins (from EPA and DHA) due to their inhibitory action on COX-2 and LOX enzymes. The inhibitory action of corticosteroids on LXA4 is much stronger compared to its action on PGE2 and LTB4 synthesis (28). This results in suppression of inflammation but at the same time corticosteroids interfere with resolution of inflammation and wound healing process for which LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins are needed. Thus, corticosteroids have both beneficial and harmful actions: suppress acute inflammation and interfere with wound healing process. In the initial stages, corticosteroids suppress inflammation but as a result of AA/EPA/DHA deficiency and an imbalance between LTB4 vs. LXA4 can lead to impaired wound healing (13,28, 29, 30, 31). In addition, enhanced production of TNF-α and IL-6 seen during active COVID-19 also causes an EFAs (PUFAs) deficiency state due to their inhibitory action on desaturases (15). Hence, in order to bypass this block in the activity of desaturases and augment LXA4 formation supplementation of AA is needed that is known to enhance LXA4 with little or no change in PGE2 formation (32, 33, 34, 35). In such an EFAs (PUFAs) deficiency state, AA supplementation results in inhibition of IL-6 and TNF-α synthesis, enhances the formation of LXA4 and suppresses PGE2 production and initiates the much-needed anti-inflammatory events and appropriate wound healing. This may explain why only 1/3rd of those with COVID-19 showed response to dexamethasone since the other 2/3rd might have had significant EFAs (PUFAs) deficiency state, especially when they are sicker than those who responded to dexamethasone. Hence, it is suggested that a combined administration of dexamethasone + AA/EPA/DHA will be highly beneficial and more patients are likely to respond compared to dexamethasone alone. This argument is in tune with the recent observation that those with high plasma cortisol concentrations have increased mortality and a reduced median survival (36), probably not only because of the severity of illness but also since they are likely to have significant reduction in the activity of desaturases, COX-2, LOX and PLA2 resulting in significant EFAs (PUFAs) deficiency. This implies that these patients with high plasma cortisol levels may benefit from supplementation of AA and other PUFAs. This suggestion can be verified by measuring plasma concentrations of various PUFAs, PGs, LTs, LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins and various cytokines and correlating the same to plasma cortisol levels and the severity of the illness and their survival.
In addition to their inhibitory action on the expression of PLA2, COX-2, LOX, and desaturases glucocorticoids enhance the expression of annexin-1 (also called as lipocortin 1). Annexin-1 shows all the actions of glucocorticoids and induces the production of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Annexin-1 suppresses the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and other cytokines (37). For the anti-inflammatory action of annexin-1, there is an essential role for LXA4. Both LXA4 and/or annexin-1 seem to enhance the production of IL-10, which suppresses TNF-α action and the consequent tissue injury and lethality (38). Thus, there is a complex and inter-dependent interaction among PLA2, COX-2, desaturases, annexin-1 and LXA4 in the anti-inflammatory action of corticosteroids (Figure 3 ).
Figure 3.
Scheme showing possible relationship between bioactive lipids and SARS-CoV-2. PLA2 = Phospholipase A2 enzyme that is needed for the release of AA, EPA and HA from the cell membrane lipid pool. GM-CSF = Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. COX = Cyclo-oxygenase enzyme COX-1 and COX-2) that is needed for the synthesis of PGs. LOX = Lipoxygenase enzyme (5-, 12-, 15-LOX enzymes) that is needed for the formation of LTs, lipoxins, resolvins, protectins and maresins form their precursors. Desaturases are needed for the conversion of dietary LA and ALA to form their long-chain metabolites such as GLA (γ-linolenic acid), dihomo-GLA (dihomo-γ-linolenic acid) and arachidonic acid from LA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) from ALA. HMGB1 = high-mobility group box-1, a pro-inflammatory cytokine. LXs = lipoxins; RSvs = resolvins; PRTs = protectins; MaRs = maresins; LTs = leukotrienes. PGE2 = prostaglandin E2; COX-2 = cyclo-oxygenase; LOX = lipoxygenase. MSCs = mesenchymal stem cells.
AA Supplementation Does Not Enhance Inflammation and May, in Fact, Suppress Inflammation
In general, it is believed that AA is pro-inflammatory in nature since it forms the precursor to PGE2, LTB4 and TXB2 which are pro-inflammatory molecules. Interestingly, LXA4, a potent anti-inflammatory molecule, is also derived from AA. This implies that AA can have both pro- and anti-inflammatory actions depending on the products that are formed from it in a given situation. In a systematic review of randomised controlled trials (RCT) of increased intake of AA by adults revealed that 80 and 2000 mg AA per day for 1-12 weeks did increase the AA content in different blood fractions with no adverse effects on blood lipids, platelet aggregation and blood clotting, immune function, inflammation or urinary excretion of AA metabolites (39). These result are supported by other studies which showed that dietary supplementation with 1.5 g/d AA (n = 9, 24 ± 1.5 years) or placebo (n = 10, 26 ± 1.3 years) for 4 weeks did increase plasma content of AA and GLA accompanied by a decrease in LA, EPA and DGLA content in plasma compared to placebo. Surprisingly, AA supplementation decreased the mRNA expression of the immune cell surface markers; neutrophil elastase/CD66b and IL-1β in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with no effect on immune cell markers or inflammatory cytokines, suggesting that AA supplementation is safe and does not increase basal systemic or intramuscular inflammation (40).
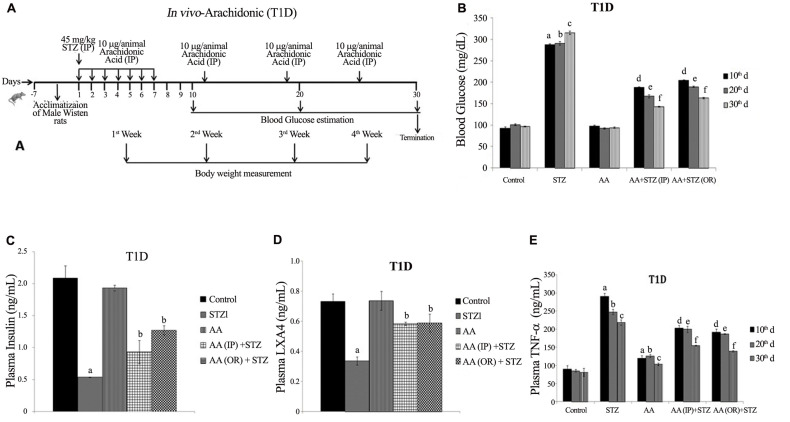
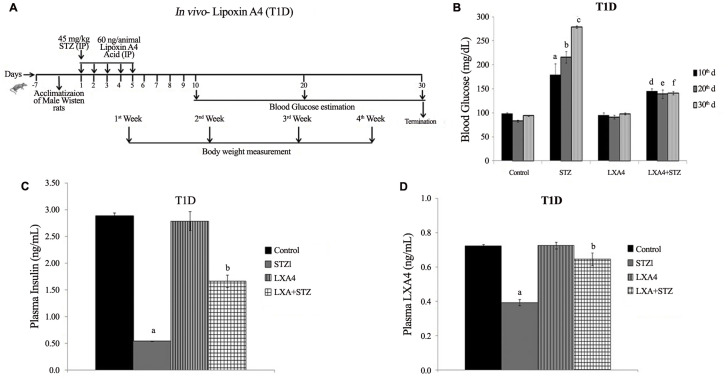
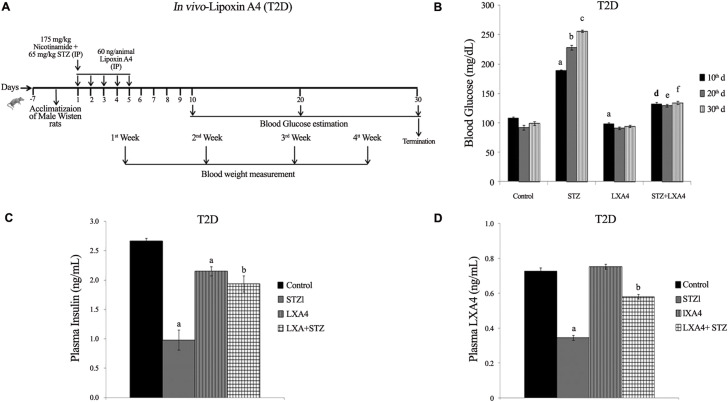
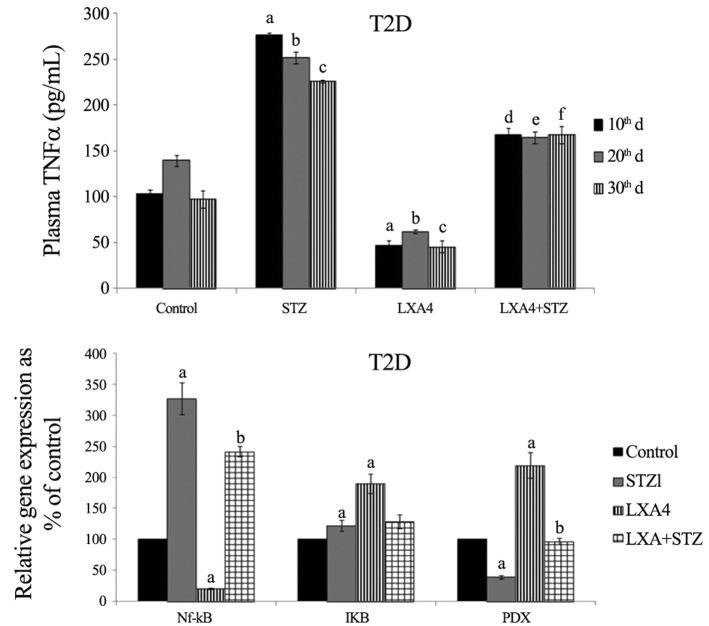
Our studies revealed that alloxan and other chemicals-induced apoptosis of pancreatic β cells and type 1 diabetes mellitus can be prevented by various BALs, especially AA and is not dependent on its (AA) metabolism to PGs (prostaglandins), LTs (leukotrienes) or TXs (thromboxanes) suggesting that the fatty acid by itself is active. Of all the fatty acids tested, AA was found to be the best. In vivo studies showed that alloxan-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus can be prevented to some extent by all the fatty acids (especially GLA, DGLA, AA, EPA and DHA) but again of all, AA was found to be the most effective (Table 1 ). It is noteworthy that alloxan-induced a significant decrease in the GLA, DGLA, and AA of n-6 series with inconsistence changes in EPA and DHA of n-3 series in the plasma, hepatic, and muscle tissues (Table 2 , and Supplementary Tables 1–3). These changes reverted to normal in AA-treated animals in addition to amelioration of alloxan-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (42, 43, 44, 45, 46). In a further extension of these studies, it was noted that both alloxan and streptozotocin-induced apoptosis of RIN (rat insulinoma pancreatic β) cells and alloxan and streptozotocin (STZ)- induced type 1 and type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus respectively in Wistar rats could be completely prevented by AA and its anti-inflammatory metabolite lipoxin A4 (LXA4) (41,47, 48, 49). It was noted that STZ-induced increase in plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α levels and enhanced expression of pro-inflammatory genes NF-kB and COX-2 and iNOS can be suppressed by AA and LXA4 (Supplementary Figures 1–4) in addition to their (AA and LXA4) ability to prevent development of diabetes mellitus (41,47, 48, 49). It is noteworthy that both COX-2 (cycli-oxygenase-2) and LOX (lipoxygenase) inhibitors did not block the beneficial actions of AA against STZ-induce type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. This suggests that PGs LTs and TXs are not involved in the beneficial actions of AA (42,44, 45, 46). These results also indicate that the COX and LOX inhibitors used in our study cannot block the activity of these enzymes completely and minimal activity of these enzymes is sufficient to augment LXA4 formation from AA used these studies (41,42,44, 45, 46). In addition, it was also noted that resolvins and protectins, anti-inflammatory metabolites of EPA and DHA, though were effective in preventing cytotoxic action of alloxan and STZ in vitro and type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in vivo, were still much less effective compared to AA and LXA4 (45, and unpublished data). These results emphasize the anti-inflammatory actions of AA and LXA4 compared to perceived anti-inflammatory BALs such as EPA and DHA, resolvins and protectins. It is noteworthy that oral AA supplementation is as effective as that of i.p. method of delivery in preventing the development of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in experimental animals that was accompanied by restoration of decreased LXA4 to normal (47, 48, 49). These results suggest that oral supplementation of AA is adequate to prevent chemical-induced diabetes mellitus that was accompanied by formation of LXA4 in adequate amounts (41). Based on these results, it can be proposed that pro-inflammatory stimuli induced increase in the formation of PGE2 and decreased levels of LXA4 (as revealed by our studies with alloxan and STZ-induced diabetes studies) and increased expression of NF-kB, COX-2, iNOS and plasma and tissue levels of IL-6 and TNF-α can be suppressed and restored to normal by AA (41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50). Thus, AA need to be considered as a potent endogenous anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective molecule, at least in part, due to its ability to give rise to LXA4.
Table 1.
Incidence of type 1 diabetes in Wistar rats treated with alloxan and various polyunsaturated fatty acids
| Fatty acid | Alloxan only (n = 10) | Alloxan + simultaenous fatty acid treatment (n = 10) | Alloxan + pre-treatment with fatty acid (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LA | 9 | 4 | 3 |
| GLA | 9 | 5 | 0 |
| DGLA | 10 | 5 | 2 |
| AA | 10 | 1 | 0 |
| ALA | 9 | 7 | 1 |
| EPA | 10 | 7 | 0 |
| DHA | 10 | 3 | 0 |
| SA | 10 | n.d. | 10 |
| OA | 10 | n.d. | 10 |
n.d. = not done; LA = linoleic acid (18:2 n-6); GLA = γ-linolenic acid (18:3 n-6); DGLA = dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (20:3 n-6); AA = arachidonic acid (20”4 n-6); ALA = α-linolenic acid (18:3 n-3); EPA = eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5 n-3); DHA = docosahexaenoic acid (22:6, n-3).
It is evident from these results that though all fatty acids are effective to some extent in preventing alloxan-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus, AA is the most effective. This data is taken from ref. (41).
Table 2.
Fatty acid analysis of plasma phospholipid fraction of experimental animals treated with alloxan to induce type 1 diabetes mellitus and their treatment with AA
| Fatty acid | Untreated control | Alloxan | AA only | Pre-AA + alloxan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA 14:0 | 1.03 ± 0.07 | 3.54 ± 0.05a | 1.02 ± 0.16 | 1.36 ± 0.23b |
| PA 16:0 | 23.09 ± 0.6 | 29.3 ± 0.7a | 22.9 ± 0.5b | 23.1 ± 0.62b |
| POA 16:1 | 21.57 ± 1.48 | 29.4 ± 2.1a | 17.9 ± 0.7b | 16.4 ± 2.01b |
| SA 18:0 | 14.0 ± 1.2 | 15.24 ± 1.63 | 18.36 ± 2.16 | 19.57 ± 2.15 |
| OA 18:1 n-9 | 9.54 ± 0.46 | 6.3 ± 0.056a | 10.77 ± 0.38b | 11.8 ± 0.58a,b |
| LA 18:2 n-6 | 21.28 ± 0.8 | 11.74 ± 0.63a | 20.66 ± 1.3b | 21.72 ± 1.16b |
| GLA 18:3 n-6 | 1.28 ± 0.092 | 0.61 ± 0.049a | 1.7 ± 0.33b | 1.48 ± 0.22b |
| DGLA 20:3 n-6 | 1.49 ± 0.14 | 0.49 ± 0.053a | 1.45 ± 0.22b | 0.84 ± 0.16a |
| AA 20:4 n-6 | 0.96 ± 0.07 | 0.52 ± 0.04a | 1.54 ± 0.07a,b | 1.22 ± 1.07a,b |
| ALA 18:3 n-3 | 2.56 ± 0.16 | 1.8 ± 0.06 | 2.46 ± 0.08 | 1.97 ± 0.13 |
| EPA 20:5 n-3 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 0.3 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.08 |
| DHA 22:6 n-3 | 0.86 ± 0.07 | 1.39 ± 0.61a | 0.85 ± 0.07b | 0.77 ± 0.06b |
All values are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 10).
ap <0.05 compared to untreated control; bp <0.05 compared to alloxan group.
It is evident from this data that in alloxan treated Wistar animals there is a significant decrease in the plasma levels of LA, GLA, DGLA and AA that were restored to normal in alloxan + AA treated animals. There were no significant alterations in n-3 fatty acids (ALA, EPA) except that DHA was significantly increased in alloxan treated animals that was restored to normal in alloxan + AA treated animals. This data is taken from ref. (42).
It has been suggested that increased consumption of dietary LA and ALA (that are essential fatty acids, EFAs) might increase the formation of their long-chain metabolites such as AA (from LA) and EPA and DHA (from ALA) respectively. This is unlikely to happen since only a small percentage of dietary LA and ALA are converted to AA and EPA and DHA due to low activity of desaturase enzymes. It is known that no more than 5% of consumed ALA is converted to EPA and approximately <0.5% to DHA, whereas the formation of AA in many tissues is no more than 0.5% of the total consumed LA (51). In view of this, it is imperative that to overcome the deficiency of GLA, DGLA, AA, EPA and DHA in many diseases it is necessary to provide GLA/DGLA/AA/EPA/DHA directly.
AA and LXA4 Have Antioxidant Action and Suppress Oxidative Stress
There is evidence to suggest that COVID-19 is associated with exacerbated oxidative stress (52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57). Nox2 is activated whenever there is excess production of reactive oxidant species that leads to enhanced oxidative stress. Several RNA viruses are known to activate Nox2. In patients with COVID-19, Nox2 activation has been reported with much higher Nox2 activation in those with thrombotic events compared to those who did not have thrombotic events suggesting that oxidative stress is present in those with severe disease and thrombotic events. The high neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio observed in critically ill patients with COVID-19 is likely to be another reason for excessive levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in them. It is possible that enhanced ROS generation may promote a cascade of biological events that could induce tissue damage, thrombosis and red blood cell dysfunction seen in COVID-19. These results are supported by the finding that activation of Nrf2, a transcription factor that regulates cellular redox balance and the expression of genes involved in immunity and inflammation, downregulates ACE2 and TMPRSS2 mRNA expression, including IL-1-beta, IL-6, TNF-α, the cell adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin, and a group of IFN-γ-induced genes. Many of these cytokines are involved in the development of “cytokine storm” that is responsible for increased fatality in COVID-19. This suggests that in fatal cases of COVID-19 Nrf2 activation is impaired and its activation may be of significant benefit in this condition (56). In fact, the potential involvement of ROS and oxidative stress in COVID-19 led to the suggestion that elderly age subjects, and patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at higher risk of mortality since they already have increased oxidative stress (58) (Table 3 ). Based on the results presented in Supplementary Figures 1–4, it is evident that both AA and LXA4 have potent anti-inflammatory actions by virtue of their ability to inhibit the production of IL-6 and TNF-α; inhibit iNOS, NF-kB, and COX-2 and enhance NRF2 genes expression and thus, suppress oxidative stress that may account for their (AA and LXA4) potential beneficial action in COVID-19 as suggested previously (1,3). Our earlier studies showed that AA and LXA4 can restore altered antioxidant enzymes due to alloxan and STZ to normal (41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49) lending further support to the suggestion that these two BALs (AA and LXA4) and possibly, other BALs have potent antioxidant actions as well (41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49,60).
Table 3.
Lipid peroxides in the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, CHD, diabetic nephropathy, pneumonia, septicemia, RA and lupus determined by TBA reaction
| S. No. | Group | MDA-eq (nmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control (n = 10) | 1.56 ± 0.36 |
| 2. | Pneumonia (n = 13) | 1.80 ± 0.58 |
| 3. | Septicemia (n = 14) | 2.37 ± 0.6a |
| 4. | RA (n = 12) | 1.61 ± 0.35 |
| 5. | Lupus (n = 5) | 1.73 ± 0.49 |
| 6. | Control (n = 20) | 1.27 ± 0.23 |
| 7. | Type 2 DM (n = 10) | 2.4 ± 0.6a |
| 8. | Diabetic nephropathy (n = 10) | 3.0 ± 1.1a |
| 9. | HTN (n = 30) | 3.4 ± 0.4a |
| 10. | CHD (n = 14) | 2.4 ± 1.1a |
All values are expressed as mean ± SEM; ap <0.05 compared to control.
This data is taken from ref. (59).
BALs and Adaptive Immunity
In this context, it is noteworthy that both innate immunity and adaptive immunity are modulated by BALs. Innate immunity (also called natural or native immunity) is responsible for the early line of defense against microbes. It consists of cellular and biochemical defense mechanisms and responds rapidly to infections. Some of the principal components of innate immunity include: (i) physical and chemical barriers, such as epithelia and antimicrobial chemicals produced at epithelial surfaces. As already discussed above (8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14), BALs could be secreted by epithelial cells to inactivate SARS-CoV-2; (ii) neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer (NK) cells and other innate lymphoid cells phagocyte microbes (including SARS-CoV-2); (iii) members of the complement system and other mediators of inflammation.
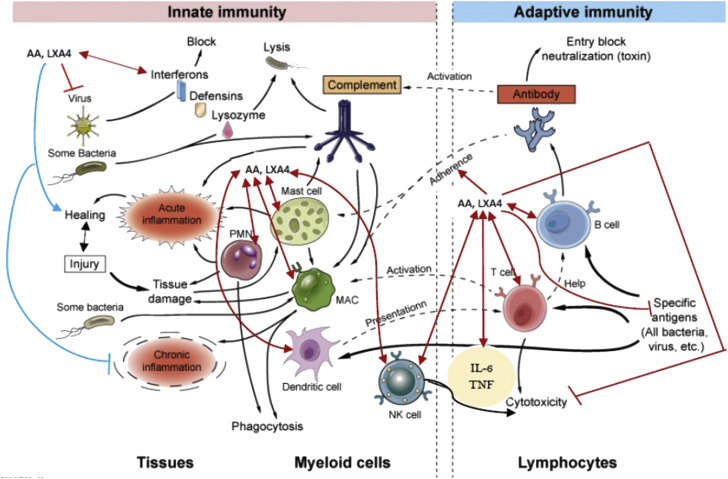
In contrast to this, adaptive immunity (also called specific or acquired immunity) system recognizes and reacts to microbial and nonmicrobial substances. Adaptive immunity distinguishes different substances and responds more vigorously to repeated exposures to the same microbe, known as memory. The major components of adaptive immunity are lymphocytes and antibodies. Innate immunity is activated when pattern recognition receptor(s) (PRR) are activated that recognize different types of microbes including viruses that leads to their phagocytosis and release of interferons (IFNs). Adaptive immunity is based on the special properties of lymphocytes (T and B cells) that respond selectively to non-self-antigens resulting in the development of specific memory. Thus, both innate and adaptive immune responses are components of an integrated system of host defense and function cooperatively. The innate immune response to microbes stimulates adaptive immune responses and thus, adaptive immune responses often enhance the action(s) of innate immunity, making them more effective (Figure 4 ).
Figure 4.
Scheme showing the components of innate and adaptive immune responses and the involvement of BALs (especially GLA, DGLA, AA, EPA, DHA, LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins) in their modulation. Cells of the innate and adaptive immune systems release various BALs (especially AA and LXA4) to regulate their action and bring about the elimination of invading microbes. AA and LXA4 can enhance the phagocytosis of PMNLs, macrophages, T cells, and NK cells to induce the inactivation of invading microbes and regulate the secretion of various cytokines. BALs are needed to induce inflammation and induce resolution of inflammation and enhance wound healing. It may be noted here that BALs (especially AA and LXA4) inhibit the cytotoxic action of IL-6 and TNF-α on normal cells but enhances their cytotoxic action on tumor cells. GLA, DGLA, EPA, DHA, resolvins, protectins and maresins may also have similar actions but are likely to be less potent compared to AA/LXA4. For details see text and ref. (61).
There is reasonable evidence to suggest that inflammation, immune reactions, secretion of cytokines (both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines), resolution of inflammation, and restoration of homoeostasis are regulated by various BALs (Figure 4) especially in the pathobiology of rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, lupus, and multiple sclerosis (7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,16,25,31,33, 34, 35,41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51,55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65). In fact, our studies revealed that in majority of these diseases, there is a deficiency of GLA, DGLA, AA, ALA, EPA and DHA) and LXA4 implying that altered levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory BALs (the balance being tilted more towards pro-inflammatory molecules) may account for their pathobiology suggesting that administration of AA and LXA4 could be of benefit in their resolution (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 , and Supplementary Tables 1–3). In view of the immunomodulatory actions (both innate and adaptive immune responses) of BALs, it is likely that the altered CD8+ T cells and CD4+/CD8+ ratio as a result of the inflammatory status seen in COVID-19 (64) could be restored to normal by AA and LXA4 and other BALs (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 , and Supplementary Figures 1-4) (65).
Table 4.
Fatty acid analysis of the plasma PL (phospholipid) fraction in patients with pneumonia, septicemia, RA, and lupus
| Fatty acid | Control (n = 10) | Pneumonia (n = 12) | Septicemia (n = 14) | RA (n = 12) | SLE (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16:0 | 24.8 ± 3.4 | 32.5 ± 3.6 | 26.95 ± 4.1 | 30.2 ± 3.0 | 32.0 ± 3.75 |
| 18:0 | 23.3 ± 4.1 | 21.4 ± 7.1 | 24.58 ± 6.0 | 19.0 ± 6.1 | 14.6 ± 5.82 |
| 18:1 n-9 | 13.1 ± 2.3 | 15.6 ± 3.2 | 16.5 ± 3.3b | 14.8 ± 2.1 | 16.0 ± 2.76 |
| 18:2 n-6 | 17.7 ± 3.1 | 14,2 ± 0.3b | 16.3 ± 2.4 | 17.5 ± 2.7 | 20.8 ± 2.2 |
| 18:3 n-6 | 0.13 ± 0.09 | 0.13 ± 0.08 | 0.04 ± 0.05b | 0.02 ± 0.04a | 0.01 ± 0.01a |
| 20:3 n-6 | 3.2 ± 0.79 | 1.5 ± 0.4b | 0.46 ± 0.54b | 2.5 ± 0.58 | 2.12 ± 0.52 |
| 20:4 n-6 | 8.8 ± 2.0 | 5.1 ± 0.4b | 5.8 ± 1.6b | 9.5 ± 2.2 | 8.93 ± 2.0 |
| 22:4 n-6 | 0.42 ± 0.23 | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 0.34 ± 0.28 | 0.26 ± 0.37a | 0.18 ± 0.18a |
| 22:5 n-6 | 0.73 ± 0.55 | 0.45 ± 0.63 | 1.5 ± 1.02b | 0.6 ± 0.7 | 0.8 ± 1.0 |
| 18:3 n-6/18:2 n-6 | 0.007 | 0.0092 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.004 |
| 20:4 n-6/18:2 n-6 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.5 | 0.54 | 0.44 |
| 20:4 n-6/20:3 n-6 | 4.01 | 3.4 | 2.75 | 3.8 | 4.2 |
| 18:3 n-3 | 0.27 ± 0.12 | 0.09 ± 0.04b | 0.16 ± 0.11b | 0.12 ± 0.16b | 0.1 ± 0.1b |
| 20:5 n-3 | 0.25 ± 0.26 | 0.23 ± 0.24 | 0.01 ± 0.01b | 0.05 ± 0.14a | 0.04 ± 0.04a |
| 22:5 n-3 | 0.54 ± 0.16 | 0.44 ± 0.53 | 0.29 ± 0.12b | 0.69 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.35b |
| 22:6 n-3 | 1.43 ± 0.43 | 0.54 ± 0.43b | 1.2 ± 1.14 | 0.62 ± 0.56b | 0.88 ± 0.75b |
| 20:5 n-3/18:3 n-3 | 0.92 | 1.55 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.40 |
All values ae expressed as mean ± S.D; ap <0.001 compared to control; bp <0.05 compared to control.
18:3 n-6/18:2 n-6 ratio denotes the activity of Δ6 desaturase; 20:4 n-6/20:3 n-6 ratio denotes the activity of Δ5 desaturase; 20:4 n-6/18:2 n-6 and 20:5 n-3/18:3 n-3 ratios denote the activity of both Δ6 and Δ5 desaturases; It is interesting to note that lipid peroxides are increased in sepsis, pneumonia and lupus and RA (Table 6). Both sepsis and COVID-19 are characterized by pneumonia. There are some specific changes in the levels of various fatty acids in sepsis, pneumonia, RA, and lupus. Sepsis is characterized by deficiency of GLA/DGLA/AA/EPA compared to other inflammatory conditions such as pneumonia, RA and lupus. A similar deficiency of these fatty acids is predicted in COVID-19. Data for Tables 6 and 7 is taken from (reference 59: Das UN, Ramesh G, Kumar SG, et al. Free radicals, lipid peroxidation and essential fatty acids in patients with pneumonia, septicemia and collagen vascular diseases. J Nutr Med 1992;3:117–127).
Table 5.
The percentage of distribution of fatty acids from plasma phospholipid fraction in patients with hypertension (HTN), coronary heart disease (CHD), type 2 diabetes mellitus, and diabetic nephropathy
| Fatty acid | Control | HTN | CHD | Type 2 DM | Diabetic nephropathy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16:0 | 25.9 ± 3.0 | 29.3 ± 2.7a | 27.8 ± 3.5 | 26.6 ± 5.2 | 26.8 ± 2.7 |
| 18:0 | 20.9 ± 3.6 | 23.2 ± 4.9a | 18:0 ± 10.7 | 14.6 ± 4.1 | 11.6 ± 3.6a |
| 18:1 n-9 | 13.0 ± 2.3 | 12.1 ± 1.5 | 11.5 ± 3.1 | 12.0 ± 2.6 | 14.5 ± 3.1 |
| 18:2 n-6 | 18.6 ± 3.1 | 14.5 ± 3.1a | 17.8 ± 5.0 | 13.9 ± 5.3 | 15.1 ± 3.1 |
| 18:3 n-6 | 0.14 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.3a | 0.1 ± 0.1a | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.2 |
| 20:3 n-6 | 3.4 ± 1.0 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 1.1 | 1.7 ± 1.0a | 2.0 ± 0.8a |
| 20:4 n-6 | 9.4 ± 1.8 | 7.8 ± 2.0a | 7.0 ± 2.1a | 4.6 ± 1.8a | 6.6 ± 2.6a |
| 22:5 n-6 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.4a | 1.0 ± 0.9 | 2.1 ± 0.6a | 1.3 ± 0.5a |
| 18:3 n-6/18:2 n-6 | 0.008 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.017 | 0.008 |
| 20:4 n-6/18:2 n-6 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.43 |
| 20:4 n-6/20:3 -6 | 2.8 | 2.53 | 2,59 | 2.8 | 3.3 |
| 18:3 n-3 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.2a | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.2a | 0.1 ± 0.1a |
| 20:5 n-3 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.2a | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.2 ± 0.3 |
| 22:5 n-3 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.3a | 1.6 ± 1.3 | 1.7 ± 1.1 |
| 22:6 n-3 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 0.8 ± 0.4a | 0.5 ± 0.4a | 0.5 ± 0.3a |
| 20:5 n-3/18:3 n-3 | 1.8 | 1.39 | 0.41 | 3.2 | 4.0 |
All values are expressed as mean ± SD. ap <0.05 compared to control.
This data is taken from ref. (16).
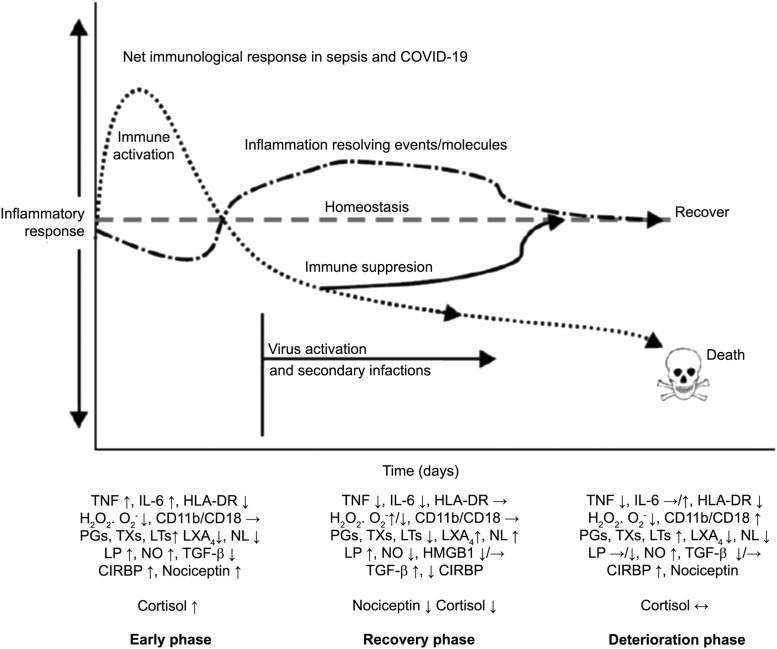
Figure 5.
Scheme showing potential changes in the plasma levels of various cytokines and other markers in COVID-19 (and sepsis) and the two phases of cytokine response. The first phase consists of hyperinflammation as a result of release of excess of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the second phase is characterized by decreased or even normal levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and even immunosuppression. During the first phase, dexamethasone and anti-TNF or anti-IL-6 and other cytokine antagonists are indicated. During the second phase, efforts need to be made to restore homeostasis. In both the phases BALs are expected to be of significant benefit.
This figure is modified from Das UN. Arch Med Sci 2014;10:325–335.
Figure 6.
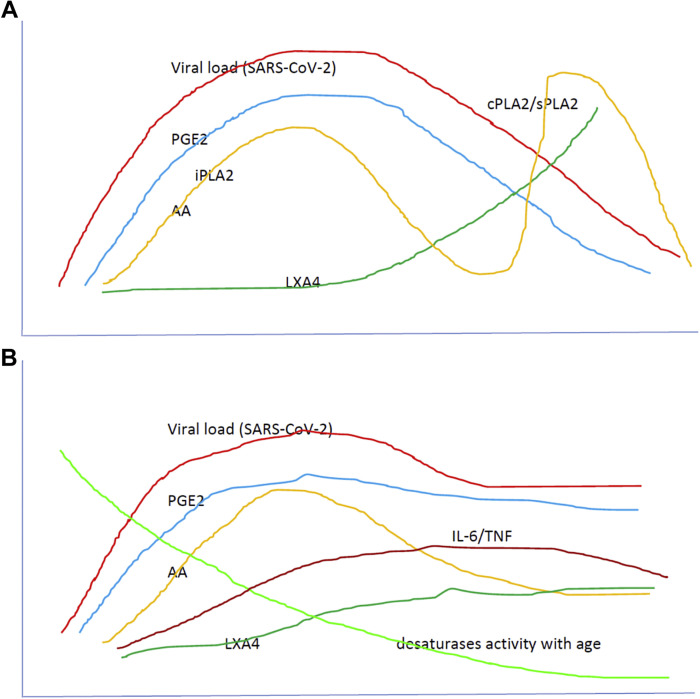
A. Scheme showing potential relationship among AA, PGE2, LXA4 and viral load in a COVID-19 patient who recovers. AA is likely to be released from the cell membrane in two phases, first phase is used for PGE2 synthesis, whereas the second phase is meant for LXA4 synthesis. Once PGE2 concentration reaches its peak, LXA4 synthesis is triggered that induces resolution of inflammation. AA release is triggered by SARS-CoV-2 and other infections. AA released due to the action of iPLA2 inactivates SARS-CoV-2, is sued for the synthesis of PGE2, whereas the second phase pf release of AA induced by cPLA2/sPLA2 is used for the formation of LXA4 and to induce resolution of inflammation. B. Scheme showing possible relationship among various BALs and viral load in a COVID-19 patient who succumbs to the disease. In these subjects, the second phase of release of AA by the action of cPLA2/sPLA2 is truncated, and consequently the formation of LXA4 is suboptimal and hence, the recovery process is delayed or not seen. Due to the absence of negative feedback control exerted by AA (due to the absence of second phase of release of AA), IL-6 and TNF levels continue to remain high and usher in cytokine storm and consequent mortality. It is predicted that as the viral load increases so also the plasma levels of PGE2. But, once PGE2 reaches its peak, it triggers the generation of LXA4 to initiate the resolution of inflammation simultaneously with a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines. To achieve this aim of initial increase in PGE2 levels and subsequent enhancement of LXA4 production, there could occur two phases of release of DGLA/AA/EPA/DHA from the cell membrane lipid pool (as shown in Figure 6A) that is not seen in those with severe COVID-19. This failure of biphasic phase of release of DGLA/AA/EPA/DHA leads to heightened mortality. As a result, PGE2 fails to reach its peak to trigger LXA4 synthesis it leads to failure of resolution of inflammation. Plasma IL-6 and TNF levels increase in parallel with viral load but either may remain high or fall depending on the robustness of the immunocytes and thus, there could be hyperinflammation in the initial stages followed by immunosuppression. Both IL-6 and TNF can activate PLA2 and induce the release of DGLA/AA/EPA/DHA to ensure formation of adequate amounts of PGE2 and LXA4 depending on the context and necessity. Thus, there is a complex set of interactions and negative and positive feedback among BALs, cytokines, and PLA2 activity. For further details see the text.
This figure is modified from Das UN. Arch Med Sci 2014;10:325–335.
GM-CSF, Colchicine and BALs
The recent report (27) that GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factor) blockade with mavrilimumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia and systemic hyperinflammation is beneficial can also be explained in terms of their action on BALs. GM-CSF is a potent stimulant of LTB4 production and inducer of AA release (66,67). Hence, when GM-CSF action is blocked by mavrilimumab, the induced release of AA is utilized for the production of LXA4 that, in turn, induces its (mavrilimumab) ant-inflammatory action (67). Similarly, the beneficial action of colchicine reported in COVID-19 (68) can also be explained in terms of its action on BALs. Colchicine is known to modulate the metabolism of BALs such as enhancement in the action of PGE1 (69,70). The property of colchicine to potentiate the actions of PGE1 is especially interesting since both PGE1 and LXA4 have similar actions (Table 6 ).
Table 6.
Comparison between PGE1 and LXA4
| Property/action | LXA4 | PGE1 |
|---|---|---|
| Derived from | Arachidonic acid (AA) | Di-homo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA) |
| Rate limiting step in AA/DGLA synthesis | δ-6- and δ-5-desaturases | δ-6-desaturase |
| Platelet anti-aggregator | ++ | + |
| Vasodilator | ++ | + |
| Anti-inflammatory action | ++ | + |
| Suppresses IL-6 and TNF-α | ++ | + |
| Cytoprotective action | +++ | ++ |
| Geno-protective action | +/– | ++ |
| Anti-diabetic action | ++ | + |
| Suppresses ROS generation | ++ | + |
| Suppression of PGE2 production | ++ | Not known |
| Inflammation resolution action | ++ | + |
| Wound healing action | ++ | ++ |
| Blood pressure lowering action | + | + |
| Anti-arrhythmic action | +/– | +/– |
| Protects endothelium | ++ | ++ |
| PGE2 can trigger synthesis | Yes | Not known |
| Anti-microbial action | ++ | + |
| Has a specific receptor | Yes-ALX | Yes-EP1 and EP3 |
| Half-life | Few seconds | 5–30 min |
In view of the similarities in their actions, it is possible that PGE1 may also be effective in suppressing inflammation, cytokine storm, and thrombotic manifestations in COVID-19 similar to LXA4 as discussed in the text. It is interesting to note that PGE1 is derived from DGLA, the precursor of AA whereas LXA4 is derived from AA.
A recent report indicated that circulating levels of IL-2, IL-4, TNF-α, IFN-γ and C- reactive protein may not be associated with severity of COVID-19 symptoms. This implies that there are two phases in the pathobiology of COVID-19, the first one is characterized by hyperinflammation that may happen in the beginning of COVID-19 and the second phase could result in immunosuppression with little or no change in the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines as in sepsis (71,72). This suggests that one need to measure plasma levels of various cytokines in order to establish whether COVID-19 is in the first or the second phase and accordingly tailor the administer dexamethasone, anti-cytokine, and other therapies. Hence, one need to exercise caution in rushing to administer immunosuppressive therapies without measuring plasma cytokines levels (Figure 6).
Summary and Conclusions
It is evident from the preceding discussion that BALs (i) can inactivate enveloped viruses including SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), SARS, MERS, HCV, HBV, influenza, chikungunya, dengue and zika (1,3, 4, 5, 6, 7,19).; (ii) have the dual function of initiating and perpetuating inflammation (especially by PGs, LTs, TXs) and suppressing inflammation and initiate resolution of inflammation and restoration of homeostasis (especially by LXA4. resolvins, protectins and maresins); (iii) the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory M1 and M2-like macrophages depends on the way AA, EPA and DHA, the precursors of pro- and anti-inflammatory metabolites, are handled by immunocytes; and (iv) anti-GM-CSF, corticosteroids, and colchicine bring about their beneficial actions by modulating the metabolism of BALs. Based on these evidences, it is evident that use of appropriate amounts of AA/EPA/DHA may result in the formation of adequate amounts of pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines and BALs in an orderly and cohesive fashion to fight SARS-CoV-2 and other infections. It is suggested that a deficiency of DGLA, AA, EPA and DHA may predispose an individual to develop COVID-19. This is further supported by the observation that sepsis that is remarkably similar to serious COVID-19 is associated with a deficiency of GLA/DGLA/AA/EPA and enhanced levels of lipid peroxides and free radicals (Table 3, Table 4). The higher degree of morality due to COVID-19 seen in those with diabetes mellitus, hypertension and coronary heart disease can also be attributed to their deficiency of GLA, DGLA, AA, ALA, EPA and DHA (Table 5).
The less frequent and mild disease seen in children and decreased incidence of COVID-19 in women can be ascribed to relatively higher amounts of BALs in them, especially of AA and LXA4. For instance, the activity of desaturases decreases with age whereas children have a relatively higher activity of desaturases (Figure 6), whereas estrogen stimulates LXA4 synthesis (73, 74, 75, 76). Thus, it is anticipated that children have a higher capacity to generate GLA, DGLA, AA, EPA and DHA that can be converted to form beneficial LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins to fight SARS-CoV-2. On the other hand, pre-menopausal women generate significantly higher amounts of LXA4 due to the stimulatory action of estrogen and thus, are resistant and less likely to develop severe COVID-19.
The observation that when human cells are exposed to SARS-Co-V-2 and/or human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E), they release large amounts of AA and LA and both these fatty acids inactivate the viruses (Figure 1, Figure 2) (22,23) implies that activation of PLA2 in order to release sufficient amounts of AA and LA is of paramount importance. Adequate activity of PLA2 is needed not only to release appropriate amounts of DGLA/AA/EPA/DHA to inactivate SARS-CoV-2 but also to trigger formation of PGE2 for the initial inflammation and LXA4 for subsequent resolution of inflammation. In the event the cells are deficient in these fatty acids, the virus replicates and produces COVID-19 lending direct support to the proposal that BALs have a significant role in the pathobiology of SARS-CoV-2 and other corona virus-induced diseases (1,3). It is known that deficiency of AA/EPA/DHA (especially that of ALA, the precursor of EPA and DHA) enhances the expression of angiotensin-II receptors (77,78), which serves as a receptor for SARS-CoV-2 (79). It is evident from the data presented in Supplementary Figures 1–4 and Supplementary Tables 1–3, and Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 that diabetes mellitus hypertension, CHD, and inflammatory conditions such as RA, lupus and pneumonia have deficiency of GLA, DGLA, AA, EPA and DHA that, in turn, could lead to decreased formation of anti-inflammatory LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins due to substrate deficiency and thus, enhance their susceptibility to COVID-19. This may explain the high degree of mortality noted in the elderly and those with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and CHD and other diseases. Since AA and LXA4 have cytoprotective action (41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49), their deficiency could make various cells/tissues more vulnerable to the cytotoxic action of SARS-CoV-2. In view of the evidences presented here, an in-depth study of BALs, especially AA, in the prevention and management of COVID-19 is warranted.
Definition of bioactive lipids and eicosanoids: Linolenic acid (LA), alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), γ-linolenic acid (GLA), dihomo-GLA (DGLA), arachidonic acid (AA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes (TXs), leukotrienes (LTs), lipoxins (LXs), resolvins, protectins and maresins are all considered as bioactive lipids; whereas PGs, LTs, TXs, LXA4, resolvins, protectins and maresins are called as eicosanoids.
LA and ALA are Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs).
LA, GLA, DGLA, AA, EPA and DHA are Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs).
(ARCMED_2020_1166)
Footnotes
Supplementary digital content available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.09.006.
Supplementary data
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2A–D.
Supplementary Figure 2E–G.
Supplementary Figure 3A–D.
Supplementary Figure 4A–D.
Supplementary Figure 4E–F.
References
- 2.Das U.N. Can bioactive lipids inactivate Coronavirus (COVID-19)? Arch Med Res. 2020;51:282–286. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Das U.N. Bioactive lipids and Coronavirus (COVID-19)-further discussion. Arch Med Res. 2020;51:445–449. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kohn A., Gitelman J., Inbar M. Unsaturated free fatty acids inactivate animal enveloped viruses. Arch Virol. 1980;66:301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF01320626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Huang H., Chen Y., Ye J. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication by peroxidation of arachidonate and restoration by vitamin E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:1866–1870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708423104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Das U.N. Arachidonic acid and other unsaturated fatty acids and some of their metabolites function as endogenous antimicrobial molecules: a review. J Adv Res. 2018;11:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Das U.N. Do unsaturated fatty acids function as endogenous anti-bacterial and anti-viral molecules? Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83:390–391. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/83.2.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Territo M.C., Golde D.W. The function of human alveolar macrophages. Res J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979;25:111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Juers J.A., Rogers R.M., McCurdy J.B. Enhancement of bactericidal capacity of alveolar macrophages by human alveolar lining material. J Clin Invest. 1976;58:271–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI108468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang Q., Xu Q.Y., Wu H.M. Effect of lipid-induced macrophage M1/M2 polarization on lipid metabolism in hepatocytes. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018;26:276–281. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Simões R.L., De-Brito N.M., Cunha-Costa H. Lipoxin A4 selectively programs the profile of M2 tumor-associated macrophages which favour control of tumor progression. Int J Cancer. 2017;140:346–357. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ramon S., Dalli J., Sanger J.M. The protectin PCTR1 is produced by human M2 macrophages and enhances resolution of infectious inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2016;186:962–973. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.12.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Das U.N. Current and emerging strategies for the treatment and management of systemic lupus erythematosus based on molecular signatures of acute and chronic inflammation. J Inflammation Res. 2010;3:143–170. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S9425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Das U.N. Bioactive lipids in age-related disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1260:33–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-42667-5_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mayer K., Schmidt R., Muhly-Reinholz M. In vitro mimicry of essential fatty acid deficiency in human endothelial cells by TNFα impact of ω-3 versus ω-6 fatty acids. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:944–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Das U.N. Essential fatty acid metabolism in patients with essential hypertension, diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease. Prostaglandins Leukot Essen Fatty Acids. 1995;52:387–391. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(95)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gangemi S., Pescara L., D'Urbano E. Aging is characterized by a profound reduction in anti-inflammatory lipoxin A4 levels. Exp Gerontol. 2005;40:612–614. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2005.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Leng Z., Zhu R., Hou W. Transplantation of ACE2- mesenchymal stem cells improves the outcome of patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Aging Dis. 2020;11:216–228. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Das U.N. Bioactive lipids as mediators of the beneficial action(s) of mesenchymal stem cells in COVID-19. Aging Dis. 2020;11:746–755. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bai Y., Wang J., He Z. Mesenchymal stem cells reverse diabetic nephropathy disease via lipoxin A4 by targeting transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/smad pathway and pro-Inflammatory cytokines. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:3069–3076. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fang X., Abbott J., Cheng L. Human mesenchymal stem (stromal) cells promote the resolution of acute lung injury in part through lipoxin A4. J Immunol. 2015;195:875–881. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shen B., Yi X., Sun Y. Proteomic and metabolomic characterization of 2 COVID-19 patient sera. Cell. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yan B., Chu H., Yang D. Characterization of the lipidomic profile of human coronavirus-infected cells: Implications for lipid metabolism remodeling upon coronavirus replication. Viruses. 2019;11:73. doi: 10.3390/v11010073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hatziantoniou S., Giamarellos-Bourboulis E.J., Skiathitis S. Rapid alterations of serum fatty acids with the intravenous administration of an arachidonate solution. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2004;70:465–468. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2003.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Giamarellos-Bourboulis E.J., Mouktaroudi M., Adamis T. n-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids enhance the activities of ceftazidime and amikacin in experimental sepsis caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:4713–4717. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4713-4717.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ledford H. Steroid is first drug showing to prevent deaths from COVID-19. Nature. 2020;582:469. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01824-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.De Luca G., Cavalli G., Campochiaro C. GM-CSF blockade with mavrilimumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia and systemic hyperinflammation: a single-centre, prospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2:E465–E473. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30170-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bhavsar P.K., Levy B.D., Hew M.J. Corticosteroid suppression of lipoxin A4 and leukotriene B4 from alveolar macrophages in severe asthma. Respir Res. 2010;11:71. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fuller R.W., Kelsey C.R., Cole P.J. Dexamethasone inhibits the production of thromboxane B2 and leukotriene B4 by human alveolar and peritoneal macrophages in culture. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984;67:653–656. doi: 10.1042/cs0670653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang D., Li Y., Peng H. Glucocorticoids sensitize rat placental inflammatory responses via inhibiting lipoxin A4 biosynthesis. Biol Reprod. 2014;90:74. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.116384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Das U.N. Springer; New York: 2011. Molecular Basis of Health and Disease. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tateishi N., Kakutani S., Kawashima H. Dietary supplementation of arachidonic acid increases arachidonic acid and lipoxin A4 contents in colon but does not affect severity or prostaglandin E2 content in murine colitis model. Lipids Health Dis. 2014;13:30. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tateishi N., Kaneda Y., Kakutani S. Dietary supplementation with arachidonic acid increases arachidonic acid content in paw but does not affect arthritis severity or prostaglandin E2 content in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis model. Lipids Health Dis. 2015;14:3. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-14-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kakutani S., Ishikura Y., Tateishi N. Supplementation of arachidonic acid-enriched oil increases arachidonic acid contents in plasma phospholipids but does not increase their metabolites and clinical parameters in Japanese healthy elderly individuals: a randomized controlled study. Lipids Health Dis. 2011;10:241. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Das U.N. Beneficial role of bioactive lipids in the pathobiology, prevention, and management of HBV, HCV and alcoholic hepatitis, NAFLD, and liver cirrhosis: A review. J Adv Res. 2019;17:17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tan T., Khoo B., Mills E.G. Association between high serum total cortisol concentrations and mortality from COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30216-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yang Y.H., Aeberli D., Dacumos A. Annexin-1 regulates macrophage IL-6 and TNF via glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper. J Immunol. 2009;183:1435–1445. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Souza D.G., Fagundes C.T., Amaral F.A. The Required Role of Endogenously Produced Lipoxin A4 and annexin-1 for the production of IL-10 and inflammatory hyporesponsiveness in Mice. J Immunol. 2007;179:8533–8543. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.12.8533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Calder P.C., Campoy C., Eilander A. A systematic review of the effects of increasing arachidonic acid intake on PUFA status, metabolism and health-related outcomes in humans. Br J Nutr. 2019;121:1201–1214. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519000692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Markworth J.F., Mitchell C.J., D'Souza R.F. Arachidonic acid supplementation modulates blood and skeletal muscle lipid profile with no effect on basal inflammation in resistance exercise trained men. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018;128:74–86. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2017.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Naveen K.V.G., Naidu V.G.M., Das U.N. Arachidonic acid and lipoxin A4 attenuate alloxan-induced cytotoxicity to RIN5F cells in vitro and type 1 diabetes mellitus in vivo. BioFactors. 2017;43:251–271. doi: 10.1002/biof.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Suresh Y., Das U.N. Protective action of arachidonic acid against alloxan-induced cytotoxicity and diabetes mellitus. Prostaglandins Leukot Essen Fatty Acids. 2001;64:37–52. doi: 10.1054/plef.2000.0236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mohan I.K., Das U.N. Prevention of chemically-induced diabetes mellitus in experimental animals by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nutrition. 2001;17:126–151. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(00)00468-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Suresh Y., Das U.N. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and chemically-induced diabetes mellitus: Effect of ω-3 fatty acids. Nutrition. 2003;19:213–228. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(02)00855-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Suresh Y., Das U.N. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and chemically-induced diabetes mellitus. Effect of ω-6 fatty acids. Nutrition. 2003;19:93–114. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(02)00856-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Suresh Y., Das U.N. Differential effect of saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids on alloxan-induced diabetes mellitus. Prostaglandins Leukot Essen Fatty Acids. 2006;74:199–213. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2005.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Naveen K.V.G., Naidu V.G.M., Das U.N. Arachidonic acid and lipoxin A4 attenuate streptozotocin-induced cytotoxicity to RIN5F cells in vitro and type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in vivo. Nutrition. 2017;35:61–80. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Naveen K.V.G., Naidu V.G.M., Das U.N. Amelioration of streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in Wistar rats by arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496:105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Naveen K.V.G., Das U.N. Arachidonic acid rich ARASCO oil has anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic actions against high fat diet-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in Wistar rats. Nutrition. 2019;66:203–218. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Das U.N. Arachidonic acid and lipoxin A4 as possible endogenous anti-diabetic molecules. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2013;88:201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2012.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Poorani R., Bhatt A.N., Dwarakanath B.S., Das U.N. COX-2, aspirin and metabolism of arachidonic, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids and their physiological and clinical significance. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;785:116–132. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Violi F., Oliva A., Cangemi R. Nox2 activation in Covid-19 Redox. Biol. 2020;36:101655. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Laforge M., Elbim C., Frère C. Tissue damage from neutrophil-induced oxidative stress in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:515–516. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Panfoli I. Potential role of endothelial cell surface ectopic redox complexes in COVID-19 disease pathogenesis. Clin Med (Lond) 2020 doi: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Thomas T., Stefanoni D., Reisz J.A. COVID-19 infection alters kynurenine and fatty acid metabolism, correlating with IL-6 levels and renal status. JCI Insight. 2020;5:140327. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.140327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.McCord J.M., Hybertson B.M., Cota-Gomez A. Nrf2 activator PB125® as a potential therapeutic agent against COVID-19. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020;9:518. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Delgado-Roche L., Mesta F. Oxidative stress as key player in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection. Arch Med Res. 2020;51:384–387. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sawalha A.H., Zhao M., Coit P. Epigenetic dysregulation of ACE2 and interferon-regulated genes might suggest increased COVID-19 susceptibility and severity in lupus patients. Clin Immunol. 2020;215:108410. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Das U.N., Ramesh G., Kumar S.G. Free radicals, lipid peroxidation and essential fatty acids in patients with pneumonia, septicemia and collagen vascular diseases. J Nutr Med. 1992;3:117–127. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Leuti A., Maccarrone M., Chiurchiù V. Proresolving lipid mediators: Endogenous modulators of oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8107265. doi: 10.1155/2019/8107265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Panigrahy D., Gilligan M.M., Huang S. Inflammation resolution: a dual-pronged approach to averting cytokine storms in COVID-19? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020;39:337–340. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09889-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chiurchiù V., Leuti A., Maccarrone M. Bioactive lipids and chronic Inflammation: managing the fire within. Front Immunol. 2018;9:38. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chiurchiù V., Leuti A., Dalli J. Proresolving lipid mediators resolvin D1, resolvin D2, and maresin 1 are critical in modulating T cell responses. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf7483. 353ra111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wang F., Nie J., Wang H. Characteristics of peripheral lymphocyte subset alteration in COVID-19 Pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 2020;221:1762–1769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Das U.N. Humana Press; New York: 2020. Molecular Biochemical Aspects of Cancer. [Google Scholar]
- 66.DiPersio J.F., Billing P., Williams R. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines prime human neutrophils for enhanced arachidonic acid release and leukotriene B4 synthesis. J Immunol. 1988;140:4315–4322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Starosta V., Pazdrak K., Boldogh I. Lipoxin A4 counter regulates GM-CSF signaling in eosinophilic granulocytes. J Immunol. 2008;181:8688–8699. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Deftereos S.G., Giannopoulos G., Vrachatis D.A., GRECCO-19 Investigators Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3:e2013136. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gemsa D., Kramer W., Brenner M. Induction of prostaglandin E release from macrophages by colchicine. J Immunol. 1980;124:376–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Peters-Golden M., McNish R.W., Davis J.A. Colchicine inhibits arachidonate release and 5-lipoxygenase action in alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol. 1996;271(6 Pt 1):L1004–L1013. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1996.271.6.L1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mehta P., McAuley D.F., Brown M. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395:1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Das U.N. HLA-DR expression, cytokines and bioactive lipids in sepsis. Arch Med Sci. 2014;10:325–335. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2014.42586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Das U.N. Oestrogen, statins and essential fatty acids: similarity in their actions and benefits-is there a common link? Nutrition. 2002;18:178–188. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(01)00719-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Das U.N. Nitric oxide as the mediator of the anti-osteoporotic actions of oestrogen, statins and essential fatty acids. Exp Biol Med. 2002;227:88–93. doi: 10.1177/153537020222700202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kumar R., Clerc A.C., Gori I. Lipoxin A₄ prevents the progression of de novo and established endometriosis in a mouse model by attenuating prostaglandin E₂ production and estrogen signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Russell R., Gori I., Pellegrini C. Lipoxin A4 is a novel estrogen receptor modulator. FASEB J. 2011;25:4326–4337. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-187658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Begg D.P., Puskás L.G., Kitajka K. Hypothalamic gene expression in ω-3 PUFA-deficient male rats before, and following, development of hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2012;35:381–387. doi: 10.1038/hr.2011.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Das U.N. Pre(peri)-natal ω-3 PUFA deficiency-induced hypertension and its broader implications. Hypertens Res. 2012;35:375–379. doi: 10.1038/hr.2011.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Samavati L., Uhal B.D. ACE2, much more than just a receptor for SARS-COV-2. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:317. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.