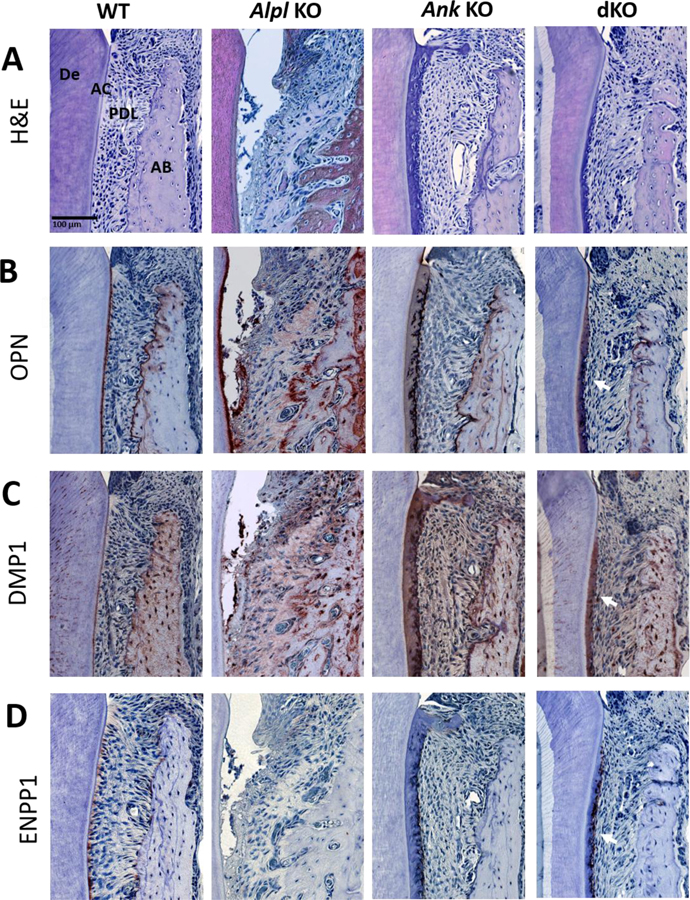
Figure 2. Acellular Cementum Growth Is Inversely Proportional to PPi Levels.
H&E staining (A) shows a layer of acellular cementum (AC) covering root dentin (De) in WT mice, lack of AC in Alpl KO mice, and increased AC in Ank KO mice at 26 dpn. In Alpl, Ank dKO mice, AC is reestablished along the root surface and exhibits increased width (arrowheads). (B) OPN serves as a marker for AC on root surfaces. (C) DMP1 immunolocalization increases with thick AC in Ank KO and Alpl, Ank dKO mice. (D) ENPP1 is expressed by cementoblasts lining root surfaces and is reduced in Alpl KO tissues and elevated in Ank KO samples (arrows). In areas of hypercementosis, Alpl, Ank dKO samples exhibit increased Enpp1 expression (arrows). AB: Alveolar bone; PDL: Periodontal ligament.