To the editor
The majority of Philadelphia-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients carry a t(9;22) translocation characterized by chromosomal breakpoints located on exon 13 or 14 of the BCR gene and exon 2 of the ABL1 gene (e13a2 or e14a2). This translocation generates a fusion gene whose epidemiology has been recently evaluated by the International BCR-ABL1 Study Group.1 It has been reported that the type of transcript influences the rate of complete cytogenetic response, the rate of major/deep molecular response, and the time needed to obtain major molecular response (MMR) during first-line imatinib or nilotinib treatment. Worldwide experiences also report inferior overall survival, leukemia related survival, progression-free survival and transformation-free survival in e13a2 patients, but this statement has not been confirmed in all studies.2–5
Type of transcript is of interest also in the field of treatment-free remission (TFR), which is the current goal of all hematologists who treat CML, although not all reports on discontinuation take into consideration this variable.
In rare cases of CML, breakpoints on chromosomes 9 and 22 occur in unusual regions, giving rise to atypical fusion transcripts. These transcripts, including e13a3, e14a3, e1a3, e19a2, e8a2, are not amplified by quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR), which is the standardized and recommended method of molecular response evaluation. Current recommendations and guidelines consider the possibility to perform RT-qPCR on BCR-ABL1 as one of the criteria to meet to pursue tyrosine kinases inhibitors (TKI) stop both in clinical trials and in everyday practice as well.6, 7
Nowadays, disease monitoring in atypical transcripts patients is performed routinely by non-quantitative Nested PCR, providing only an idea of their minimal residual disease (MRD) status.
Not having certainties about their biological behavior, due to their rarity, the lack of quantitative information about their molecular response automatically excludes patients with atypical transcripts from prospective protocols on TKI discontinuation.
We retrospectively collected seven patients with chronic-phase CML carrying rare atypical transcripts, identified by Sanger sequencing,8 who discontinued TKI for various reasons, such as severe comorbidities, toxicity, or patient request (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patients’ features.
| Patient | Transcript | Time on TKI before stop (months) | Treatment | Duration of MMR before stop (months) | Loss of MMR | TFR (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | b2a3 | 66 | Dasatinib | 48 | No | 55+ |
| 2 | b3a3 | 195 | Imatinib | 92 | No | 19+ |
| 3 | b3a3 | 46 | Imatinib, Nilotinib | 33 | No | 22+ |
| 4 | b3a3 | 34 | Imatinib | 30 | No | 77+ |
| 5 | e8a2 | 107 | Nilotinib, Imatinib | 93 | No | 5+ |
| 6 | e19a2 | 71 | Imatinib, Nilotinib | 38 | No | 28+ |
| 7 | e19a2 | 71 | Imatinib, Nilotinib | 43 | Yes | 2 |
TKI = Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; MMR = Major molecular response; TFR = Treatment free remission.
For this study, we defined stable Major Molecular Response (MMR) as an undetectable transcript at nested PCR in all follow-ups in the last 24 months before discontinuation. Molecular monitoring was usually performed every three months during treatment and every month for the first six months after TKI discontinuation, followed by evaluation every six weeks for the remaining six months and every three months after then.8
Patients showed a stable MMR, and the median duration of treatment with TKI was 71 months (range: 34–195), the median duration of MMR at nested PCR before discontinuation was 43 months (range: 30–93). Only one patient resumed TKI therapy two months after stopping due to nested PCR positivity in two consecutive controls. The other six patients remained off-treatment at last observation after a median follow-up of 25 months (range: 5–77). Among these, five patients remained negative, with an undetectable transcript in all samples after discontinuation. Patient 3, who stopped the second line Nilotinib for intolerance, showed a fluctuation after stopping TKI between negative PCR and low-level positivity at the second step of nested PCR (2 out of 13 samples). No progressions occurred. All patients, including the one that resumed therapy, are in MMR at the last follow-up.
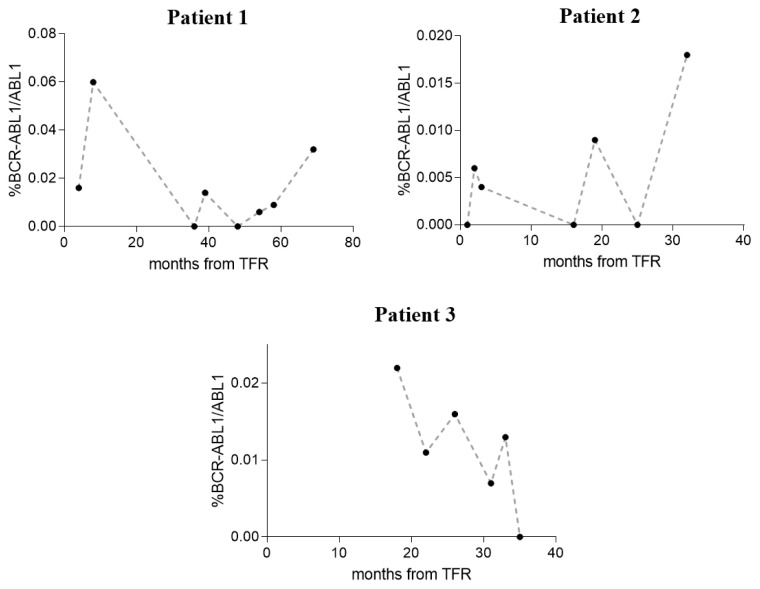
Although nowadays nested PCR represents the only routinely accepted method to monitor molecular response in CML patients with atypical transcripts, the qualitative nature of its results is not enough in an era of quantitative analysis. For this reason, we used recently published droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) assays9 to quantify the BCR-ABL1 levels in 3 of 6 collected patients in TFR (unfortunately, for 3 of these, RNA samples were not available after routine diagnostic tests). Twenty-one follow-ups were tested after TKI suspension (7 for the patient 1, 8 for the patient 2, and 6 for the patient 3), and results were reported in Figure 1 and Table 2.
Figure 1.
Monitoring by ddPCR of BCR-ABL1 levels in 3 CML patients with atypical transcripts during the treatment-free remission (TFR) phase. Percentage of BCR-ABL1/ABL1 was reported on y-axis, while the time of follow-up after TFR was on x-axis and was indicated in months.
Table 2.
%BCR-ABL1/ABL1 levels in 3 CML patients with atypical transcript monitored with ddPCR.
| Sample | Months after TFR | ddPCR %BCR-ABL1/ABL1 |
|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 4 | 0.016 |
| Patient 1 | 8 | 0.060 |
| Patient 1 | 36 | 0.000 |
| Patient 1 | 39 | 0.014 |
| Patient 1 | 48 | 0.000 |
| Patient 1 | 54 | 0.006 |
| Patient 1 | 58 | 0.009 |
| Patient 1 | 69 | 0.032 |
|
| ||
| Patient 2 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Patient 2 | 2 | 0.006 |
| Patient 2 | 3 | 0.004 |
| Patient 2 | 16 | 0.000 |
| Patient 2 | 19 | 0.009 |
| Patient 2 | 25 | 0.000 |
| Patient 2 | 32 | 0.018 |
|
| ||
| Patient 3 | 18 | 0.022 |
| Patient 3 | 22 | 0.011 |
| Patient 3 | 26 | 0.016 |
| Patient 3 | 31 | 0.007 |
| Patient 3 | 33 | 0.013 |
| Patient 3 | 35 | 0.000 |
TFR: Treatment free remission.
All the tested follow-ups showed a BCR-ABL1/ABL1 percentage lower than 0.1% during all the TFR periods; in some points, %BCR-ABL1/ABL1 achieve values lower than 0.01%, and in 6 follow-ups BCR-ABL1 levels resulted undetectable (0%). Our data in these three patients confirmed with quantitative information the achievement of a stable MMR, previously defined only by qualitative data (nested PCR).
To our knowledge, there are no reports in the literature about patients with atypical transcripts who discontinued therapy. Although current guidelines do not recommend discontinuation for patients lacking a standardized quantitative method for response monitoring, we observed that our small cohort stopped the treatment successfully.
In this particular moment where CML care is focused on TKI discontinuation, it seems rather important to us to raise consciousness on the possibility to extend the policy of withdrawing TKI even in carefully selected patients harboring atypical transcripts. The rapid evolution of molecular technologies in the last years, in particular the use of ddPCR, could help the exploration of TFR opportunity also in these rare cases and could pave the way to study how the atypical transcripts affect treatment response.
In our opinion, this leads to two important matters of debate: first, may qualitative analysis suffice, at least in a specific setting, for MRD monitoring? This could be of interest to all low-income countries that cannot afford to perform RT-qPCR during treatment nor discontinuation. Second, is it plausible to assume that patients who carried the atypical transcript may also have the opportunity to stop treatment? Although our cohort is limited, these patients behave as “standard breakpoints carriers” in terms of survival and progression during therapy. Furthermore, among our cases was also present one patient with fluctuation of BCR-ABL1 levels during the TFR phase, which was not at the end associated with relapse. Although the definition of fluctuation cannot be the same of the A-STIM due to the lacking of the MMR threshold to consider, we observed that, as in the mentioned study, the occurring of this pattern of positive values of BCR-ABL1 did not impair the successfulness of discontinuation.10
Although our data are encouraging and represent a preliminary step to consider the possibility of TKI discontinuation also for these patients, further reports are of course needed to make our observations more reliable: the increase in the number of cases we were able to collect, as well as the application of new quantitative technologies, such as digital PCR, for the MRD quantification.
To date, there are no standardized primers and probes set to monitor patients with atypical BCR-ABL1 transcripts with qRT-PCR, thus it is impossible to compare the two methods, and it is difficult to define a priori which is the best technique between qRT-PCR and ddPCR. Based on our experience and literature, ddPCR technology provides absolute quantification of target copies, without the need for standard curves; the massive sample partitioning enables the reliable measurement of small copy numbers of transcript, and error rates are reduced by removing the amplification efficiency reliance of qRT-PCR. Furthermore, recently published works, that compare qRT-PCR and ddPCR methods for the monitoring of canonical BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts, suggest that ddPCR could be a reliable and promising tool and conclude that ddPCR has a good agreement with qRT-PCR, but it is more precise and reproducible in the quantification of very low BCR-ABL1 transcript levels.11–14 Lastly, a standardization process of BCR–ABL1 molecular monitoring for CML patients with rare variants by harmonization to an International Scale could be useful to define MRD levels better, compare results, and establish a better therapeutic strategy.
Footnotes
Competing interests: The authors declare no conflict of Interest.
References
- 1.Baccarani M, Castagnetti F, Gugliotta G, et al. The proportion of different BCR-ABL1 transcript types in chronic myeloid leukemia. An international overview. Leukemia. 2019 May;33(5):1173–1183. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pfirrmann M, Evtimova D, Saussele S, et al. No influence of BCR-ABL1 transcript types e13a2 and e14a2 on long-term survival: results in 1494 patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with imatinib. Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology. 2017 May;143(5):843–850. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jain P, Kantarjian H, Patel KP, et al. Impact of BCR-ABL transcript type on outcome in patients with chronic-phase CML treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Blood. 2016 Mar 10;127(10):1269–75. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-674242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Castagnetti F, Gugliotta G, Breccia M, et al. The BCR-ABL1 transcript type influences response and outcome in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated frontline with imatinib. American journal of hematology. 2017 Aug;92(8):797–805. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pagnano KBB, Miranda EC, Delamain MT, et al. Influence of BCR-ABL Transcript Type on Outcome in Patients With Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated With Imatinib. Clinical lymphoma, myeloma & leukemia. 2017 Nov;17(11):728–733. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hochhaus A, Saussele S, Rosti G, et al. Chronic myeloid leukaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology. 2017 Jul 1;28(suppl_4):iv41–iv51. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Radich JP, Deininger M, Abboud CN, et al. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, Version 1.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network : JNCCN. 2018 Sep;16(9):1108–1135. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.van Dongen JJ, Macintyre EA, Gabert JA, et al. Standardized RT-PCR analysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease. Report of the BIOMED-1 Concerted Action: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Leukemia. 1999 Dec;13(12):1901–28. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Petiti J, Lo Iacono M, Dragani M, et al. Novel Multiplex Droplet Digital PCR Assays to Monitor Minimal Residual Disease in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Showing Atypical BCR-ABL1 Transcripts. Journal of clinical medicine. 2020 May 13;9(5) doi: 10.3390/jcm9051457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.van Dongen JJ, Macintyre EA, Gabert JA, et al. Standardized RT-PCR analysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease. Report of the BIOMED-1 Concerted Action: investigation of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Leukemia. 1999 Dec;13(12):1901–28. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bernardi S, et al. Variant-specific discrepancy when quantitating BCR-ABL1 e13a2 and e14a2 transcripts using the Europe Against Cancer qPCR assay. Is dPCR the key? European journal of haematology. 103:272–273. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chung HJ, et al. Performance Evaluation of the QXDx BCR-ABL %IS Droplet Digital PCR Assay. Ann Lab Med. 40:72–75. doi: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fava C, et al. A Comparison of Droplet Digital PCR and RT-qPCR for BCR-ABL1 Monitoring in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood. 134:2092–2092. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-125614. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Franke GN, et al. Comparison of Real-Time Quantitative PCR and Digital Droplet PCR for BCR-ABL1 Monitoring in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. The Journal of molecular diagnostics: JMD. 22:81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]