Abstract
Background
Walker-Warburg syndrome (WWS) is a rare form of alpha-dystroglycanopathy characterized by muscular dystrophy and severe malformations of the CNS and eyes. Bi-allelic pathogenic variants in POMK are the cause of a broad spectrum of alpha-dystroglycanopathies. POMK encodes protein-O-mannose kinase, which is required for proper glycosylation and function of the dystroglycan complex and is crucial for extracellular matrix composition.
Results
Here, we report on male monozygotic twins with severe CNS malformations (hydrocephalus, cortical malformation, hypoplastic cerebellum, and most prominently occipital meningocele), eye malformations and highly elevated creatine kinase, indicating the clinical diagnosis of a congenital muscular dystrophy (alpha-dystroglycanopathy). Both twins were found to harbor a homozygous nonsense mutation c.640C>T, p.214* in POMK, confirming the clinical diagnosis and supporting the concept that POMK mutations can be causative of WWS.
Conclusion
Our combined data suggest a more important role for POMK in the pathogenesis of meningoencephalocele. Only eight different pathogenic POMK variants have been published so far, detected in eight families; only five showed the severe WWS phenotype, suggesting that POMK-associated WWS is an extremely rare disease. We expand the phenotypic and mutational spectrum of POMK-associated WWS and provide evidence of the broad phenotypic variability of POMK-associated disease.
Keywords: POMK, Protein O-mannose kinase, Walker-Warburg syndrome, Alpha-dystroglycanopathy, Congenital muscular dystrophy, Meningoencephalocele
Background
Encephalocele is a congenital malformation in which herniated meninges (with or without brain tissue) protrude outside the skull. The underlying cause has still not been completely elucidated [1]. Encephalocele is characteristic for some syndromal diseases, such as Knobloch syndrome (COL18A1), as well as certain ciliopathies such as Meckel-Gruber and Joubert syndromes, and several chromosomal aberrations [2]. Regarding diseases affecting proper glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan, the manifestation of a meningoencephalocele has only rarely been associated with defects in known genes such as POMT1 and ISPD [3, 4]. Geis and colleagues discussed the presence of an encephalocele as possibly an indicator of the presence of pathogenic POMT1 mutations in terms of a phenotype-genotype correlation [3].
The protein-O-mannosyl kinase gene (POMK, OMIM *615247) encodes a protein involved in the glycosylation of the laminin-binding O-coupled carbohydrate chain of alpha-dystroglycan (α-DG). The α-DG in turn links the dystrophin complex via the sarcolemma to the extracellular matrix. POMK is expressed in various tissues including muscle, brain, retina, heart and kidney and is equally abundant in fetal and adult brain, heart and kidney tissues but reduced in skeletal muscle, with reduced expression at the end of the fetal period and an expression pattern predominantly in interstitial cells and blood vessels [5]. It is suspected that POMK plays an important role in the fetal development of myocytes, and indeed, embryonic pomk knockout zebrafish showed reduced embryonic motility and muscular dystrophy 3 days post fertilization [5]. In addition, Pomk-deficient zebrafish embryos showed small heads, delayed eye development, shortened and thickened tails and U-shaped somites as well as reduced embryo motility [5]. Notably, Pomk-deficient mouse models show severe, often lethal phenotypes with neuronal heterotopias in some brain areas, possibly as a consequence of defective neuronal migration [6]. The phenotypic presentation of both animal models accords with the hypothesis that POMK plays a significant role in muscle and nervous tissue, impacting on the differentiation of the respective cell types, and is in line with the concept of POMK as a gene occasionally associated with manifestation of brain malformations.
In humans, mutations within the POMK gene can lead to different alpha-dystroglycanopathy phenotypes ranging from the milder form (type MDDGC12 [7], OMIM #616094) to the most severe form, named Walker-Warburg syndrome (WWS, also named MDDGA12, OMIM #615249), which is a congenital muscular dystrophy associated with central nervous system and eye malformations. Variants in POMT1 are the main cause of WWS. Like POMK, the POMT1 gene also codes for an enzyme involved in the O-mannosylation pathway. The clinical picture of patients with POMT1 variants includes neural tube defects ranging from meningocele to meningoencephalocele [8]. Compared to POMT1, POMK variants leading to WWS are rarer and either result in the expression of a shortened, incorrectly folded protein or interfere with catalytic function [9]. POMK genotype-phenotype correlations are complex because even mutations leading to expression of a (massively) shortened protein can result in a mild phenotype. However, the functional and physiological mechanisms explaining the phenotypic variability still remain unclear [5].
To date, only 14 patients with POMK-associated alpha-dystroglycanopathy due to 8 different mutations have been described [5, 7, 10–13] and two additional pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants are listed in the POMK database [https://databases.lovd.nl/shared/view/POMK; accessed 7 April 2020] . An encephalocele was reported for only one patient, a 19-week fetus (termination of pregnancy; TOP) by Jae and colleagues [11]. Here, we describe monozygotic twins each with occipital meningoencephalocele and homozygous nonsense mutation in POMK.
Results
Clinical details
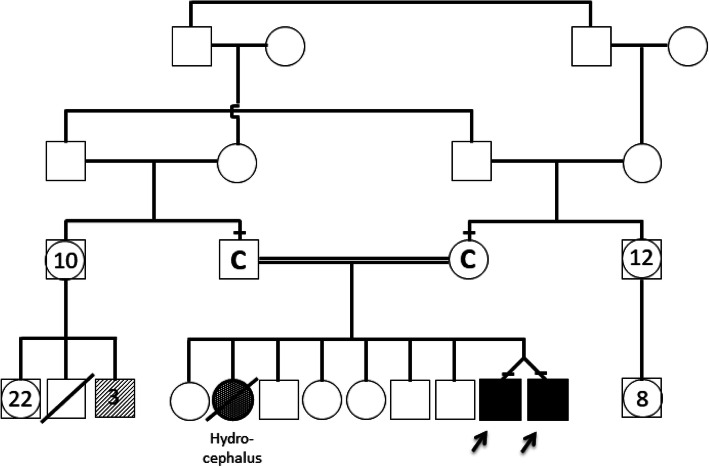
The mother and father are healthy consanguineous parents (first cousins) having in total nine children: six are healthy and one died postnatally due to complications of hydrocephalus (no further data or material available). Further family history was unremarkable apart from three paternal nephews with unspecific developmental delay of unknown origin (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Pedigree. Healthy consanguineous parents. Six healthy siblings – one sibling died postnatally (congenital hydrocephalus). Three paternal first cousins (males) are affected by developmental delay (grey squares – no further information available)
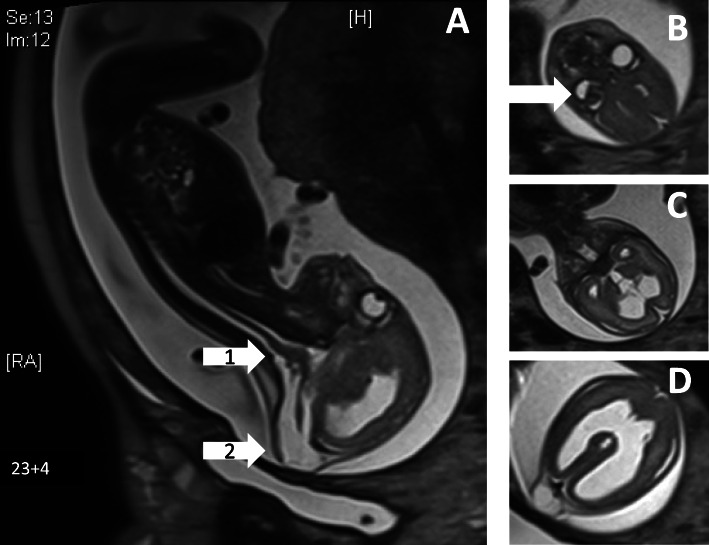
Prenatal ultrasonography screening in the 23rd week of pregnancy revealed the presence of occipital encephaloceles, hydrocephalus and cerebellar hypoplasia in both twins (Fig. 2). Prenatal MRI scans confirmed these findings (Fig. 3). Monochorionic-diamniotic male twins were born in gestational week 35 + 2 by planned caesarean section and because of progressive contractions. Birth parameters were in the normal range. Gemini 1 (G1): weight 2330 g (− 0.6 SD, 20th percentile), length 47 cm (30th percentile, − 0.3 SD), and occipitofrontal circumference 31 cm (8th percentile, − 1.3 SD). - Gemini 2 (G2): weight 2230 g (15th percentile, − 0.9 SD), length 47 cm (30th percentile, − 0.3 SD), and occipitofrontal circumference 30.5 cm (4th percentile, − 1.6 SD). Postnatally, additional eye malformations were observed by ultrasound and posterior ophthalmoscopy in both siblings and lissencephaly (Fig. 4). G1 showed a microphthalmos of the right eye and a coloboma dorsolateral of the left bulbus. G2 showed a bilateral persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous body and a posterior staphyloma of the left eye. The eye malformations led to blindness in both twins.
Fig. 2.
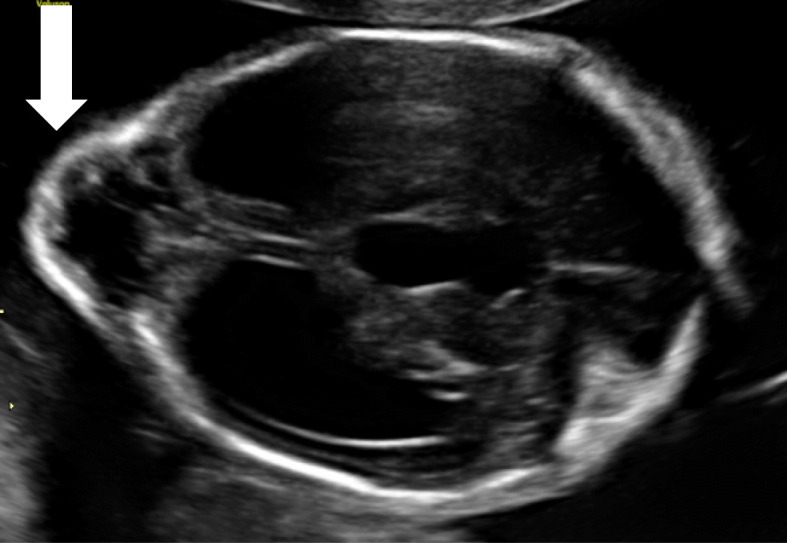
Prenatal ultrasound of the brain (22th week of pregnancy): occipital encephalocele (white arrow) and hydrocephalus
Fig. 3.
Prenatal MRI scan at 23 + 4 weeks of gestation; a hypoplastic cerebellum (white arrow 1), occipital meningocele (white arrow 2); b persistent hypoplastic primary vitreous body (white arrow); c + d internal hydrocephalus
Fig. 4.
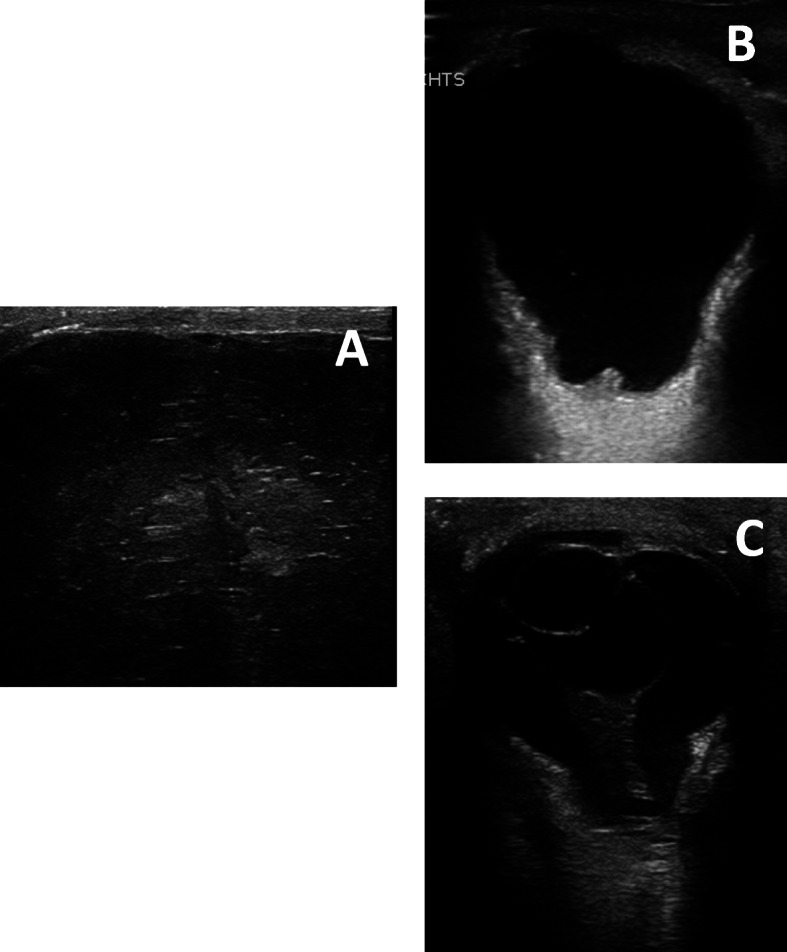
Postnatal ultrasound of the brain / eyes; A lissencephaly with polymicrogyria; b staphyloma; c persistent hypoplastic primary vitreous body
Brainstem evoked response audiometry (BERA) diagnosed severe sensorineural hearing loss in both patients.
Neuropediatric examination showed floppy infants with severe generalized muscle hypotonia, hyporeflexia, decreased spontaneous motor activity and muscular weakness observed when moving the muscles of the extremities against gravity. In addition to the ocular malformation, a prominent occipital protuberance was detected (histologically diagnosed as a meningoencephalocele) (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.

a-b postnatal examination of both twins revealed prominent occipital meningocele (white arrows)
Laboratory analysis showed a significant increase of the creatine kinase level to 7159 U/l (G1) and 8769 U/l (G2), respectively, with an accompanying elevation of transaminase levels and LDH.
MRI of the brain (Fig. 6) and spine, each performed on the 2nd/3rd day of life, showed a median occipital meningocele with dorsally opened fourth ventricle and hypo- to aplastic cerebellar vermis, a long narrowed thoracic myelon with dorsal attachment of single caudal fibers, internal hydrocephalus as well as dysgyria with generalized polymicrogyria-like cobblestone malformations and bi-temporo-occipital subcortical band heterotopia.
Fig. 6.
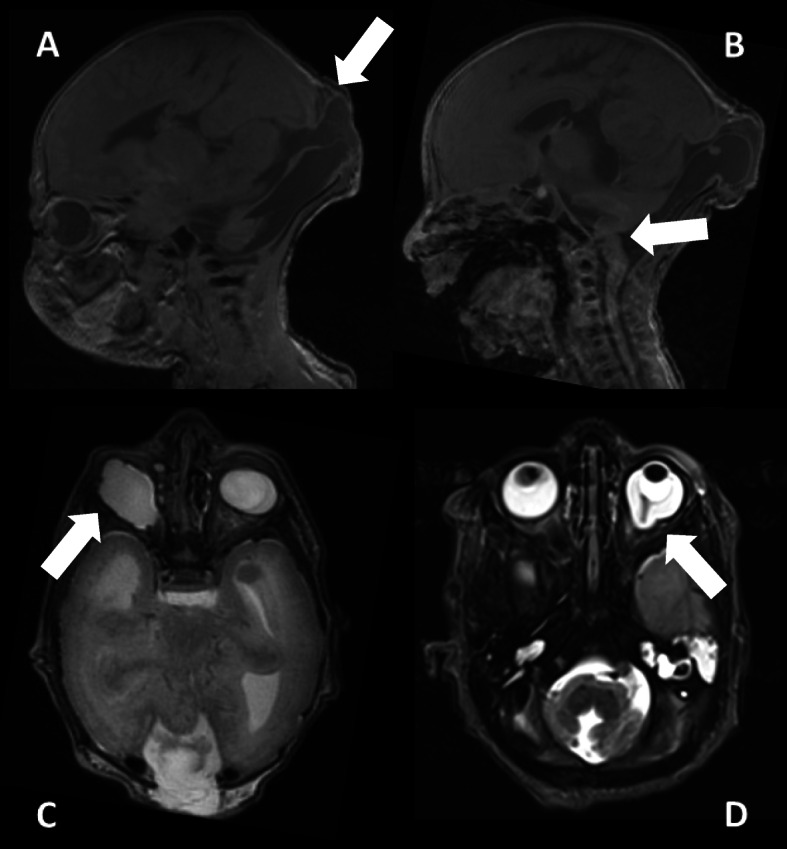
Postnatal cranial MRI scan (performed at 2nd / 3rd day); clinical findings: occipital meningocele with dorsal enlarged 4th ventricle (white arrow picture a), vermis hypo−/aplasia (white arrow picture b), generalized polymicrogyria-like cobblestone malformation, temporo-occipital subcortical band heterotopia, eye malformations (G1: microphthalmia with coloboma and caudal cyst, G2: persistent hypoplastic primary vitreous body and posterior staphyloma). a/c = G1, b/d = G2
During the perinatal period, the meningoencephalocele was treated with neurosurgery and the hydrocephalus was treated with a ventriculo-peritoneal (VP) shunt. Both twins developed structural epilepsy with generalized seizures; G1 had repeated seizures with epileptic status refractory to antiepileptic therapy.
Both boys were provided with hearing aids. They received supportive therapy including physiotherapy and early remedial education and were cared for by our palliative care team. They had repeated hospitalizations due to therapy refractory epileptic seizures and severe respiratory infections. Psychomotor development was severely retarded and typical developmental milestones were not reached (even head control was not possible). Both boys could spontaneously move their heads, but the other extremities were tetraplegic. G2 was last measured at the age of 6 months [weight: 8430 g (0.44 SD), length 65.5 cm (− 0.95 SD)]. At the age of 17 months, G2 died of cardiorespiratory failure due to aspiration. Currently, at the age of 30 months, G1 continues to show no psychomotor development [weight: 16000 g (1.38 SD), length 94 cm (0.43 SD), occipitofrontal circumference: 44 cm (− 5.0 SD)].
Molecular genetic analysis
In consideration of the clinical findings, a molecular panel analysis for genes related to WWS was performed including FKRP, FKTN, ISPD, B3GNT1, COL4A1, LARGE, POMK and TMEM5.
Due to the combination of severe CNS- and eye-malformations in combination with high CK-levels in these floppy infants, an alpha-dystroglycanopathy was considered. This assumption was supported by the presence of elevated serum CK levels. Panel sequencing resulted in the identification of a homozygous nonsense mutation [c.640C>T; p.Gln214*; NM_032237.4, OMIM: 615247] within the POMK gene in both twins. Sanger sequencing confirmed the homozygous POMK variant in both siblings and showed the parents to be heterozygous mutation carriers. Unfortunately, no material of the deceased sibling presenting with a hydrocephalus was available for mutational screening.
Discussion
Walker-Warburg syndrome is a rare form of congenital muscular dystrophy (prevalence approximately 1:60,500) [14] with currently 18 known causative genes (POMT1, POMT2, POMGNT1, FKTN, FKRP, LARGE1, ISPD, POMGNT2, GMPPB, DAG1, TMEM5, B3GALNT2, POMK, B3GNT1, DOLK, DPM1, DPM2, DPM3) [15]. So far, only five families with WWS caused by variants in POMK have been described (in total eight individuals of whom four are terminated pregnancies; for details see families 3–7 in Table 1). All causative variants reported affected or diminished POMK activity, either by truncating the protein or impacting on the catalytic protein domain [5, 10–15].
Table 1.
Clinical presentation and diagnostic characterization of individuals with pathogenic POMK mutations
| this study | Di Constanzo et al. [5], | Renesse et al. [10], | Jae et al. [11], | Preiksaitiene et al. [12], | Ardicli et al. [13], | Strang-Karlsson et al. [7], | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| family 1 patient 1# |
family 1 patient 2# |
family 2 patient 3 |
family 2 patient 4 |
family 3 patient 5* |
family 4 patient 6* |
family 4 patient 7* |
family 5 patient 8* |
family 5 patient 9# |
family 6 patient 10* |
family 6 patient 11* |
family 6 patient 12* |
family 7 patient 13* |
family 8 patient 14 |
family 9 patient 15 |
family 9 patient 16 |
|
| c-DNA mutation | c.640C>T | c.640C>T | c.325C>T | c.325C>T |
c.286delT c.905T>A |
c.325C>T | c.325C>T |
c.410T>G c.773A>G |
c.410T>G c.773A>G |
c.136C>T | c.136C >T | c.136C>T | c.136C>T | c.401T>G |
c.965C>T c.136C>T |
c.965C>T c.136C>T |
| protein mutation | p.Gln214* | p.Gln214* | p.Gln109* | p.Gln109* |
p.Phe96Phefs*19 p.Val302Asp |
p.Gln109* | p.Gln109* |
p.Leu13Arg p.258Arg |
p.Leu13Arg p.258Arg |
p.Arg46Ter | p.Arg46Ter | p.Arg46Ter | p.Arg46Ter | p.V134G |
p.Pro322Leu p.Arg46Ter |
p.Pro322Leu p.Arg46Ter |
| age of onset | neonatal | neonatal | infancy | infancy | neonatal | infancy | neonatal | neonatal | neonatal | neonatal | neonatal | neonatal | neonatal | childhood | childhood | childhood |
| first signs | in utero: cerebral malformation, opened dorsal 4th ventricle, encephalocele | in utero: cerebral malformation, agyri, encephalocele | floppiness and delayed walking at 18 months | floppiness and delayed walking at 18 months | in utero: macrocephaly, hydrocephalus | feeding problems, motoric development delayed | proximal weakness, little antigravity movements, hyporeflexia | typical WWS |
in utero: ventriculomegaly/ hydrocephalus, absence of the falx cerebri and cerebellar tentorium, occipital encephalocele |
in utero: ventriculo-megaly, thin cortex, hydro-cephalus, macro-cephaly | in utero: ventriculo-megaly | in utero: ventriculo-megaly (lateral / 4th ventricle) | in utero: hydrocephalus, ventriculo-megaly, suspected aplasia of cerebellar vermis | muscle weakness, easy fatigue, clumsiness, difficulty running and climbing | hip / neck cramps, growing pain | thigh stiffness, cramps thigh/neck |
| muscle weakness (locali-sation) | CMD, postnatal reduced spontaneous motor movement, lifting limbs against gravity | CMD, postnatal reduced spontaneous motor movement, lifting arms against gravity | proximal weakness, calf pseudo-hypertrophy, mild facial weakness | posture and gait affected | CMD, spontaneous motility absent at 7 months | CMD, proximal weakness (difficulties climbing stairs and running) | proximal weakness, never able to sit, roll on the side with 2 years | typical WWS | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | CMD, muscle weakness age of 12), calf hypertrophy, proximal muscle weakness, Gowers sign | CMD, proximal weakness, calf hyper-trophy | CMD, proximal weakness |
| CK level | 7159 U/l | 8769 U/l | 1090 U/l | 1420 U/l | 3985 U/l | 1238 U/l | 1810 U/l | typical WWS | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2400 U/l | 1000-4000 U/l | 6800 U/l |
| biopsy findings | n/a | n/a | n/a | dystrophic, cell death and regeneration positive for all markers tested dystrophin, utrophin, merosin, dysferlin, sarco-glycans and b-dystro-glycan | muscle fibers are absent | myopathic pattern with normal dystrophin expression (9 months) re-biopsy (age of 4): laminin, alpha 2, merosin reduced | myopathic pattern and merosin deficiency | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | mild dystrophic changes, increase in nuclei, degenerating and regenerating fibers, focal endomysal fibrosis immunofluorescent analysis: laminin alpha 2 pos., alpha-dystroglycan neg., dystrophin/ sarcoglycan pos. | normal | moderate chronic myopathic changes, small groups of regenerating fibers, sparse inflammatory cell infiltrates, alpha-dystroglycan deficiency, normal merosin immunolabelling |
| MRI findings | meningocele, opened 4th ventricle, hypoplastic vermis cerebellum, small myelon, arachnoid cyst | meningocele, opened 4th ventricle, hypoplastic vermis, lissencephaly, small myelon, arachnoid cyst | cysterna magna | temporal lobe arachnoid cyst | cobblestone lissencephaly, agenesis of the corpus, severe cerebellar vermis hypoplasia | symmetric cerebral white matter changes (15 months) | hypomyelination | aquaeductal stenosis, hydrocephalus, agyria, cerebellar and brainstem hypoplasia, Arnold-Chiari malformation | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | cerebellar hypoplasia, cortical disorganization, brainstem hypoplasia, cerebellar cortical microcysts, bilateral hippocampal incomplete rotation | n/a | n/a |
| ocular findings | anophthalmus (right eye), blindness, cataract (left), staphyloma (left) | congenital cataract, bilateral hypoplastic corpus vitreum, lagophthalmos bilateral | none | none | glaucoma (right eye), bilateral retinal degeneration | eyes appeared large (corneal diameter 11,5 mm) – no criteria for megalo-cornea | reduced visual acuity | micro-ophthalmia, persistent hyperplasic primary vitreous body, myopia, cataract | cataract, coloboma | none | none | none | none | none | none | none |
| additional information | pathological EEG with delta-waves, tonic-clonic seizures, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss | pathological EEG with multifocal pathological EEG-potentials, seizures, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, patent foramen ovale | hyporeflexia | hypotonia, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss,delayed psycho-motor development, tonic seizures | sensorineural hearing loss | BERA: moderate hearing impairment, contractures knees/hips | mirror movements (hands) since infancy | birth asphyxia due to placental abruption, high frequency hearing loss | preterm birth (placenta previa) Weakened function of left ventricle (age 12) | |||||||
| latest check up | 30 months: severe motor and verbal developmental disorder: hypersalivation, no movement of the head, no active movement of the extremities or active language | 17 months: cardiopulmonary resuscitation with exitus letalis due to an aspiration | still ambulatory at 25 | at the age of 13 years: climbs stairs without support | death at the age of 4 years | at the age of 17 years: wheelchair, at the age of 21 years: lost ambulation, not able to stand, eat or drink without support | at the age of 10 years: scoliosis, pathologic pulmonary function (VC:36%) | death at the age of 3 years | TOP (19 weeks of gestation) | died during labor (32 weeks of gestation, TOP) | TOP (16 weeks of gestation) | TOP (14/15 weeks of gestation) |
TOP (19 weeks and 6 days of gestation) autopsy: massive hydrocephalus, aplasia of the cerebellar vermis |
at the age of 19 years: mild learning difficulties, reduced deep tendon reflexes, pes cavus deformity | calf hypertrophy, mild lumbar lordosis, slightly winged scapulae, brisk tendon reflexes in upper extremities | calf hypertrophy, mild lumbar lordosis, slightly winged scapulae, brisk tendon reflexes in upper extremities, problems walking on heels |
Columns of individuals with severe WWS phenotype are marked *; #: WWS+ encephalocele
The clinical manifestation of patients with pathogenic variants in POMK is rather broad (see introduction) and a varying spectrum of clinical manifestations and severity can even be observed within the subgroup of POMK-related WWS (classified as such by the authors/clinicians).
Renesse et al. described two siblings of a consanguineous family with a homozygous POMK nonsense mutation (c.325C>T, p.Q109X). Both siblings had secondary microcephaly, muscular hypotonia, feeding problems and developmental delay. In addition, they presented with hypomyelinization of the brain, mild hearing loss and intellectual disability [10]. The 15-year-old sibling has developed joint contractures, neuromuscular scoliosis and nocturnal hypoventilation. The 22-year-old sibling has used a wheelchair since the age of 17 and is dependent on comprehensive help in her everyday life. Ocular abnormalities were found in the form of large bulbi with reduced visual acuity, but did not meet the criteria of a megalocornea in this patient [10]. Given that the clinical presentation of these POMK siblings manifests in the spectrum between the milder MDDGC12 and the most severe MDDGA12 phenotype, these cases might be classified as MDDGB12.
Di Costanzo et al. reported on three patients from two different families with pathogenic POMK mutations. Patients from one family presented with the same homozygous POMK nonsense mutation (c.325C>T, p.Q109X) as the patients described by Von Renesse et al. [5, 10]. However, clinically, the patients described by Di Costanzo et al. had a milder limb-girdle muscular dystrophy phenotype in line with MDDGC12: both patients showed their first symptoms in infancy but are still able to walk at the age of 25 and 13 years, respectively. They show no ocular malformations and their IQ is slightly below average (IQ 80 and 83) [5]. In contrast, the second family characterized by Di Costanzo et al. had a compound heterozygous mutation (combination of frame shift and missense mutation, c.286delT, p.Phe96Phefs*19 and c.905T>A, p.Val302Asp) and presented clinically with WWS, similar to our two cases. The affected child was diagnosed in utero with macrocephaly and hydrocephalus. Postnatally, muscular hypotonia was present, as well as other CNS malformations including cobblestone lissencephaly, corpus callosum agenesis, vermis aplasia further complicated by eye malformations (glaucoma, retinal degeneration) and severe sensorineural hearing loss. The child showed a severe psychomotor developmental disorder, developed tonic seizures and died at the age of 4 years [5]. Jae et al. described additional compound heterozygous missense mutations in the POMK gene (p.Leu137Arg, p.Gln258Arg) in a patient with typical symptoms of WWS [11]. The second child of the family had severe brain malformations as well as an occipital encephalocele and died prenatally [11].
Very recently, Preiksaitiene et al. reported on two families with in total four WWS patients of which three were TOPs: brain malformations with hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly due to a POMK nonsense mutation were detected in utero [12]. One mildly affected POMK patient (caused by a homozygous missense mutation) presenting with mirror movements of the hands was described by Ardicli et al.: the initial symptoms manifested during childhood with muscle weakness, easy fatigability, clumsiness and difficulties running and climbing. At the age of 12, proximal muscle weakness with calf hypertrophy was detected. On the MRI scan, several brain malformations were identified – surprisingly only associated with mild learning difficulties [13]. In addition, Strang-Karlsson et al. reported on a family with two siblings with a homozygous POMK missense mutation resulting in mild congenital muscular dystrophy: during childhood hip and neck cramps (triggered by yawning) were described together with proximal muscle weakness with calf hypertrophy. Investigation of a muscle biopsy obtained from one patient revealed normal histological findings whereas the biopsy from the sibling showed moderate chronic myopathic changes with small groups of regenerating fibers and sparse inflammatory cell infiltrates [7].
Based on our findings as well as previous findings of meningoencephaloceles in patients with POMT1 and ISPD mutations, we recommend an initial laboratory analysis of CK in newborns which present clinically with the combined symptoms of muscular weakness and meningoencephalocele [3, 4].
POMK is an atypical kinase that phosphorylates the 6-position of O-mannose after mannose has been modified by both GTDC2 and B3GALNT2 (two proteins encoded by genes leading to overlapping neurological phenotypes). The glycan structure resulting from POMK-modulated phosphorylation appears to be relevant for binding to the extracellular matrix (ECM) [10, 16]. Although the basic biochemical function of POMK is well understood, further research on larger POMK patient populations is needed to improve understanding of the phenotypic variability, which might be caused by the activation of compensatory mechanisms (warranting proper protein glycosylation and ECM assembly) and/ or the presence of further molecular genetic alterations of relevance as modifiers.
Conclusion
Given that encephaloceles are occasionally associated with other genetic defects causative of alpha-dystroglycanopathies, including genes encoding for proteins involved in O-mannosylation of α-DG such as POMT1 [3], the presence of a meningoencephalocele in our POMK patients supports the concept that perturbed post-translational modification of α-DG has a detrimental impact on α-DG-function and affects correct maturation of the neural tube during fetal development. Our combined clinical and genetic findings thus expand the clinical spectrum of POMK patients and classify POMK as candidate gene for meningoencephalocele.
Methods
Study aim, design and setting of the study
The study aimed to combine clinical and diagnostical findings obtained in different patients with POMK mutations. The study took place at the university hospital Essen.
Characteristics of participitans
We analysed two monozygous twins with a mutation in POMK. We compared different patients published before and focused on mutations in c-DNA and protein level, age of onset, first symptoms, muscle weakness (localisation), CK level, biopsy findings, MRI findings, ocular findings, additional information and latest check-up.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Rachel Thompson for proofreading the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- a-DG
alpha-dystroglycan
- BERA
Brainstem evoked response audiometry
- B3GALNT2
Beta-1,3-N-Acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2
- B3GNT1
N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
- CDG
Congenital disorder of glycosylation
- CK
Creatine kinase
- CMD
Congenital muscle dystrophy
- CNS
Central nervous system
- COL18A1
Collagen type XVIII alpha 1 chain
- COL4A1
Collagen type IV alpha 1 chain
- DAG1
Dystroglycan 1
- DOLK
Dolichol kinase
- DPM1
Dolichyl-Phosphate Beta-D-Mannosyltransferase Subunit 1
- DPM2
Dolichyl-Phosphate Beta-D-Mannosyltransferase Subunit 2
- DPM3
Dolichyl-Phosphate Beta-D-Mannosyltransferase Subunit 3
- ECM
Extraceullar matrix
- FKRP
Fukutin-related protein
- FKTN
Fukutin
- GMPPB
GDP-Mannose Pyrophosphorylase B
- GTDC2
Glycosyltransferase-like domain containing 2
- ISPD
Isoprenoid synthase domain-containing protein
- LARGE
Like-glycosyltransferase
- MDDGA12
Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy Type A 12
- MDDGC12
Muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy Type C 12
- OMIM
Online mendelian inheritance in man
- POMGNT1
Protein O-linked mannose N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1
- POMGNT2
Protein O-linked mannose N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2
- POMK
Protein-O-Mannose Kinase
- POMT1
Protein-O-mannosyltransferase 1
- POMT2
Protein-O-mannosyltransferase 2
- SHH
Sonig hedgehog gene
- TMEM5
Transmembrane protein 5
- TOP
Termination of pregnancy
- VC
Vital capacity
- VP
Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt
- WWS
Walker-Warburg syndrome
Authors’ contributions
USS, KR, HK, LP and ADM performed the clinical examination of the patients. UH conducted the genetic testing. AKu and ME performed the human genetic consultation and counselling. AKö, AI, AS examined the patients with ultrasound. BS generated the MRI-report. USS, AR, LP, AKu and FK drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was not supported by funding.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The parents of the twins consented to publication of clinical, diagnostical and molecular findings.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Rolo A, Galea GL, Savery D, Greene NDE, Copp AJ. Novel mouse model of encephalocele: post-neurulation origin and relationship to open neural tube defects. Dis Models Mechan. 2019;12:dmm040683. doi: 10.1242/dmm.040683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Seidahmed MZ, et al. Genetic, chromosomal, and syndromic causes of neural tube defects. Saudi Med J. 2014;35(Suppl 1):49–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Geis T, et al. Clinical long-time course, novel mutations and genotype-phenotype correlation in a cohort of 27 families with POMT1-related disorders. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019;14:179. doi: 10.1186/s13023-019-1119-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bönnemann CG, et al. Diagnostic approach to the congenital muscular dystrophies. Neuromuscul Disord. 2014;24:289–311. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2013.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Di Costanzo S, et al. POMK mutations disrupt muscle development leading to a spectrum of neuromuscular presentations. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:5781–5792. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moore SA, et al. Deletion of brain dystroglycan recapitulates aspects of congenital muscular dystrophy. Nature. 2002;418:422–425. doi: 10.1038/nature00838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Strang-Karlsson S, et al. A novel compound heterozygous mutation in the POMK gene causing limb-girdle muscular dystrophy-dystroglycanopathy in a sib pair. Neuromuscul Disord. 2018;28:614–618. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2018.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Devisme L, et al. Cobblestone lissencephaly: neuropathological subtypes and correlations with genes of dystroglycanopathies. Brain. 2012;135:469–482. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nagae M, et al. 3D structural analysis of protein O-mannosyl kinase, POMK, a causative gene product of dystroglycanopathy. Genes Cells. 2017;22:348–359. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.von Renesse A, et al. POMK mutation in a family with congenital muscular dystrophy with merosin deficiency, hypomyelination, mild hearing deficit and intellectual disability. J Med Genet. 2014;51:275. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-102236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jae LT, et al. Deciphering the Glycosylome of Dystroglycanopathies using haploid screens for Lassa virus entry. Science. 2013;340:479. doi: 10.1126/science.1233675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Preiksaitiene E, et al. Pathogenic homozygous variant in POMK gene is the cause of prenatally detected severe ventriculomegaly in two Lithuanian families. Am J Med Genet. 2020;182:536–542. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ardicli D, et al. Congenital mirror movements in a patient with alpha-dystroglycanopathy due to a novel POMK mutation. Neuromuscul Disord. 2017;27:239–242. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2016.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Genetics Home References . Walker-Warburg-syndrome. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Johnson K, et al. Detection of variants in dystroglycanopathy-associated genes through the application of targeted whole-exome sequencing analysis to a large cohort of patients with unexplained limb-girdle muscle weakness. Skelet Muscle. 2018;8:23. doi: 10.1186/s13395-018-0170-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yoshida-Moriguchi T, et al. SGK196 is a glycosylation-specific O-mannose kinase required for Dystroglycan function. Science. 2013;341:896. doi: 10.1126/science.1239951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.