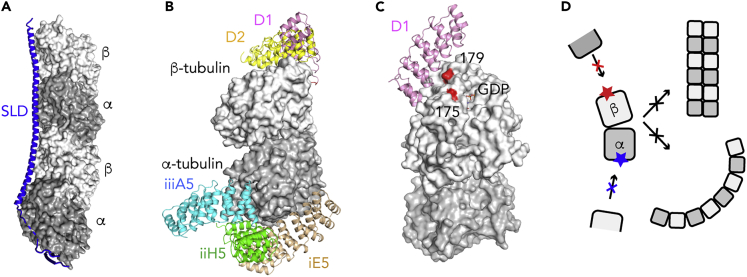
Figure 1.
Crystallization Helpers Prevent Tubulin Self-Assembly
(A) The T2R complex, composed of two tubulin heterodimers, with the α subunits in dark gray and the β subunits in light gray, and one SLD of the RB3 protein (blue).
(B) The binding site of tubulin crystallization chaperones selected from libraries of artificial proteins to target either the β subunit (e.g., D1 and D2 DARPins) or the α subunit (e.g., iE5, iiH5, and iiiA5 αReps).
(C) Assembly-blocked mutants of tubulin. In yeast tubulin, the T175R, V179R double mutation in β-tubulin impairs longitudinal contacts between tubulin molecules, favoring crystallization. The position of the mutated residues is shown on mammalian tubulin, because residue 175 was not traced in the yeast tubulin model. The D1 binding site is shown as a reference.
(D) The crystallization helpers target tubulin surfaces (red and blue stars) to prevent the tubulin self-association into straight (top, right) or curved (bottom, right) assemblies.