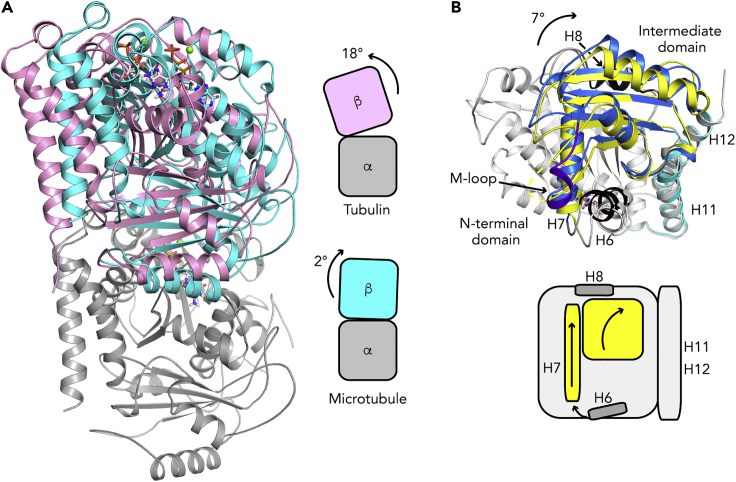
Figure 2.
Tubulin Conformational Changes Associated with Microtubule Assembly
(A) Relative orientation of tubulin subunits in soluble and in microtubular tubulins. (Left) The structure of tubulin bound to an αRep (pdb id 6GWC, β-tubulin in pink) is compared with that of tubulin in GMPCPP-microtubules (pdb id 6DPU, cyan). The N-terminal domains of the α subunits have been superposed on their secondary structural elements and only α-tubulin of 6GWC is shown (gray). (Right) Schematic illustration of the rotation angles needed to align the α and β subunits in these two structures.
(B) Structural changes in the β subunit. (Top) The β-tubulin N-terminal domains of soluble tubulin (pdb id 6S8K) and of the microtubule (pdb id 6DPU) have been superposed using their secondary structural elements; only that of soluble tubulin is shown. The C-terminal helices coincide, whereas the intermediate domains are misaligned by about 7°, which also leads to a translation of the H7 helix. Soluble tubulin is in gray, except for its intermediate domain, which is in yellow. Microtubular tubulin is colored blue (intermediate domain, with the M-loop in purple blue), black (H6 and H8 helices), and cyan (C-terminal helices). (Bottom) Schematic illustration of the movements.