Figure 7. Co-targeting PRMT5 and AKT by GSK3326595 and AKT inhibitor V in DLBCL.
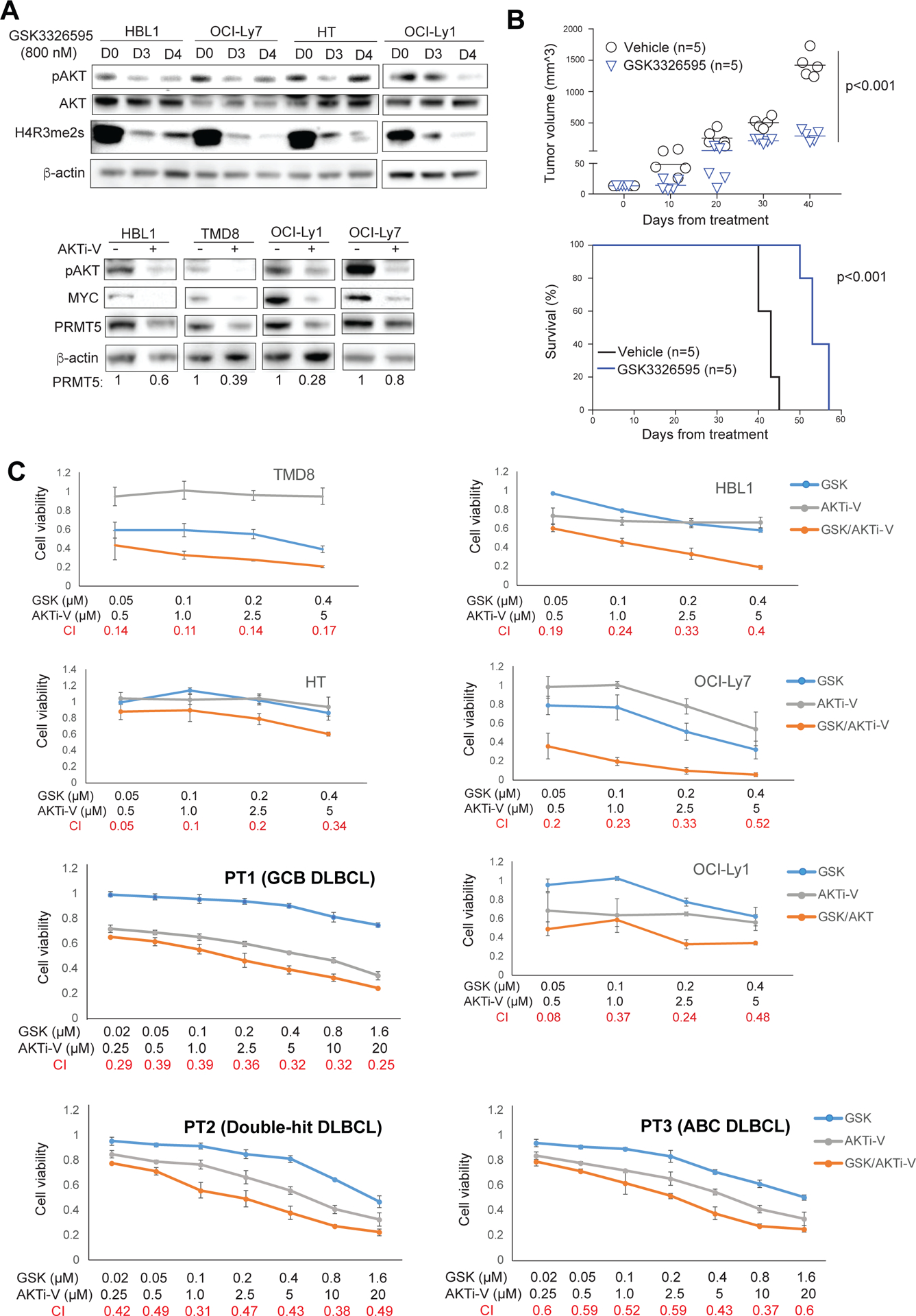
(A, top panel) Treatment of the indicated DLBCL cell lines for 3 or 4 days with 800 nM of the PRMT5 inhibitor GSK3326595 led to reduced Phospho-AKT and symmetric dimethylation of histone H4R3. β-actin served as a loading control. (A, bottom panel) Treatment of the indicated DLBCL cell lines for 2 days with 20 μM of AKT inhibitor V led to reduced phospho-AKT, MYC and PRMT5. β-actin served as a loading control. (B) DLBCL patient derived xenografts (PDX). 5 × 106 freshly isolated ABC DLBCL cells were directly injected into fetal bone chip of NSG-hu mice after the mice were anesthetized with 5% isoflurane vaporizer. Once tumor growth was detected in the first generation, tumor mass was monitored and then passaged. The passaged tumor equally grew and mice were assigned as 5 mice/group for in vivo treatment. Mice were administered vehicle control or GSK3226595 100mg/kg, oral gavage, twice per day for 35 consecutive days after 3 days of tumor engraftment. Tumor burden was calculated by measuring tumor volume (N=5; GSK3226595 vs vehicle, p=0.0000023). Survival curve was analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method (N=5; GSK3226595 vs vehicle, p=0.00001). (C) CellTiter-Glo™ Luminescent Cell Viability Assay of the indicated DLBCL cell lines after 6-day treatment of the indicated concentrations of AKT inhibitor V or GSK3326595, or both, and CellTiter-Glo™ Luminescent Cell Viability Assay of primary cancer cells from 3 DLBCL patients after 3-day treatment of the indicated concentrations of AKT inhibitor V or GSK3326595, or both. Data indicate mean ± SD of triplicates. Combination index (CI) was calculated with CompuSyn software.
