Abstract
The cryopreservation of sperm and embryos is useful to efficiently archive valuable resources of genetically engineered mice. Till date, more than 60,000 strains of genetically engineered mice have been archived in mouse banks worldwide. Researchers can request for the archived mouse strains for their research projects. The research infrastructure of mouse banks improves the availability of mouse resources, the productivity of research projects, and the reproducibility of animal experiments. Our research team manages the mouse bank at the Center for Animal Resources and Development in Kumamoto University and continuously develops new techniques in mouse reproductive technology to efficiently improve the system of mouse banking. In this review, we introduce the activities of mouse banks and the latest techniques used in mouse reproductive technology.
Keywords: Genetically engineered mice, Mouse bank, Reproductive technology, Sperm, Embryo, Cryopreservation, In vitro fertilization, Cold storage, Hands-on workshop
Introduction
A genetically engineered mouse is a powerful tool to elucidate the complex communications between genes or organs in health and diseases [1]. Moreover, humanized mouse models derived from immunosuppressed mice are helpful to bridge the gap of discovery and the development of new medicines between human and animal experiments [2]. Therefore, it is important to enhance the availability and accessibility of mouse resources to conduct research projects efficiently using valuable mouse models.
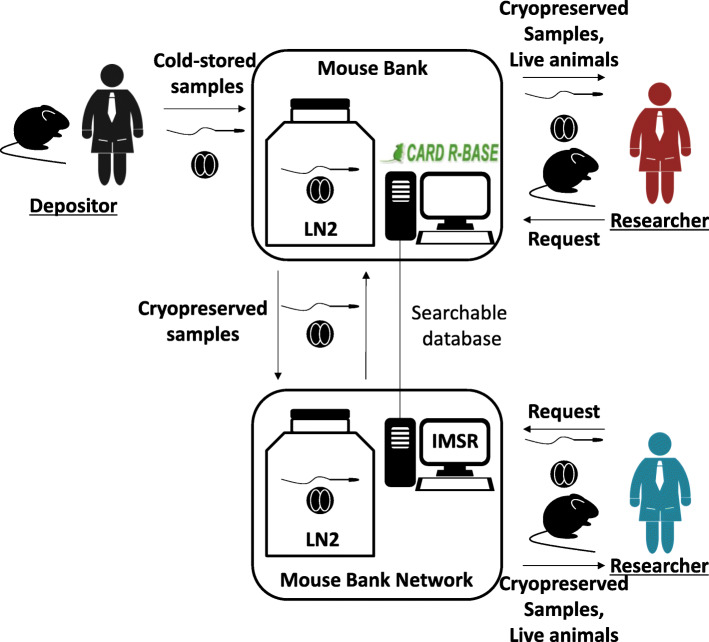
A mouse bank plays a vital role in archiving and supplying mouse resources [3]. In Kumamoto University, the Center for Animal Resources and Development (CARD) was established as a research center for genetics and biomedical science using genetically engineered mice and as a quality center of mouse resources as a mouse bank in 1998 [4, 5]. The CARD provides services of production, cryopreservation, and supply of genetically engineered mice and established a searchable database of the archived mouse strains known as the CARD Resource Database (CARD R-BASE, http://cardb.cc.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/transgenic/). Till date, the international collaboration of mouse banks (International Mouse Strain Resource: IMSR) has successfully collected more than 60,000 strains of genetically engineered mice (Table 1). The archived mouse strains can be browsed through the IMSR website (http://www.findmice.org/) [6]. Researchers can obtain live mice, cryopreserved embryos, or the sperm of choice from those mouse banks.
Table 1.
Mouse Banks (date as of August 4, 2020)
| Repository | Region | Mouse strain |
|---|---|---|
| Australian Phenome Bank (APB) | Australia | 1619 |
| Animal Resources Centre (ARC) | Australia | 16 |
| Center for Animal Resources and Development (CARD) | Japan | 1757 |
| Cornell Heart Lung Blood Resource for Optogenetic Mouse Signaling (CHROMus) | USA | 8 |
| Canadian Mouse Mutant Repository (CMMR) | Canada | 845 |
| Charles River Laboratories (CRL) | USA | 56 |
| Cystic Fibrosis Mouse Model Core (CWR) | USA | 10 |
| Dr. Elizabeth M. Simpson, Ph.D. (EMS) | Canada | 4 |
| European Mouse Mutant Archive (EMMA) | Germany | 7062 |
| genOway (GENO) | France | 9 |
| GemPharmatech (GPT) | China | 9889 |
| MRC Harwell (HAR) | UK | 1491 |
| JAX Mice and Services (JAX) | USA | 11,161 |
| Korea Mouse Phenotyping Center (KMPC) | Korea | 157 |
| Mutant Mouse Regional Resource Centers (MMRRC) | USA | 17,223 |
| MUGEN Mouse Database (MUGEN) | Greece | 75 |
| National Cancer Institute at Frederick (NCIMR) | USA | 139 |
| National Institute of Genetics (NIG) | Japan | 142 |
| Oriental BioService, Inc. (OBS) | Japan | 29 |
| Oak Ridge Collection at JAX (ORNL) | USA | 908 |
| RIKEN BioResource Research Center (RBRC) | Japan | 5357 |
| National Applied Research Laboratories (RMRC-NLAC) | Taiwan | 351 |
| Shanghai Model Organisms Center, Inc. (SMOC) | China | 2954 |
| Taconic Biosciences (TAC) | USA | 2725 |
| Texas A&M Institute for Genomic Medicine (TIGM) | USA | 195 |
| University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill - Systems Genetics Core (UNC) | USA | 75 |
| Total | 64,257 |
In Asia, an international association of mouse research centers and mouse banks known as the Asian Mouse Mutagenesis and Resource Association (AMMRA, http://ammra.info/) was organized and has been functioning since 2006 [7]. The AMMRA aims at producing original mouse resources and promoting international collaboration in Asia. At the AMMRA conference, strategies are discussed to improve science using our resources, technology, and network, and workshops are held to educate students, technicians, and young researchers. Furthermore, the AMMRA participates in the Global Mouse Models for COVID-19 Consortium to support research fighting the coronavirus pandemic.
In a mouse bank, reproductive technology plays key roles in the efficient production, preservation, and transport of genetically engineered mice. Our center continuously refines the mouse reproductive technology to enhance the function of the mouse bank system. Till date, we have overcome several problems in mouse reproductive technology and have efficiently archived mouse resources by sperm and embryo cryopreservation to produce eggs and embryos using the techniques of ultrasuperovulation and in vitro fertilization and to establish the worldwide shipment of cryopreserved or cold-stored embryos and sperm [5]. Our techniques are used widely in mouse repositories and transgenic facilities [8–11]. In this review, we introduce the latest techniques used in the CARD mouse bank.
Mouse reproductive technology
Sperm cryopreservation
Sperm cryopreservation is the most cost-effective method to preserve mouse strains [12, 13]. Cryopreserved sperm can be preserved permanently in a liquid nitrogen tank and animals can be reproduced using in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer techniques. Potentially, more than 2000 pups can be produced from the cryopreserved sperm collected from a male mouse. Cryopreserved sperm can be transported in a dry shipper at − 196 °C or a shipment box containing dry ice at − 79 °C [14]. Prof. Nakagata developed the fundamental system of mouse sperm cryopreservation using a cryoprotectant composed of 18% raffinose pentahydrate and 3% skim milk (Nakagata method) [15].
However, there was a critical problem concerning the low fertility (0–20%) of cryopreserved sperm in C57BL/6 mice [16, 17]. To overcome this problem, we improved the raffinose- and skim-milk-based cryoprotectant by adding 100 mM l-glutamine (modified R18S3) [18]. We also developed a system of in vitro fertilization using frozen–thawed sperm to enhance the fertilization rate by treating with methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MBCD) and reduced glutathione (GSH). During sperm preincubation, MBCD (0.75 mM) increased the fertilization rate of frozen–thawed mouse sperm by stimulating cholesterol efflux from the sperm membrane [19]. In the fertilization medium, 1.0 mM of GSH or cysteine analogs supported sperm penetration through the zona pellucida and increased the fertilization rate by dissecting the disulfide bonds of the zona pellucida [20, 21]. Combining these techniques, we developed an optimized protocol for the cryopreservation of mouse sperm and in vitro fertilization using the frozen–thawed sperm [22]. A review describing the history of technology development in mouse sperm cryopreservation was written by Prof. Sztein [23].
Embryo and oocyte vitrification
The vitrification of mouse embryos is useful to preserve mouse resources and readily reanimate homozygote mutant mice [24, 25]. Vitrified embryos can be preserved permanently in a liquid nitrogen tank at − 196 °C [26]. A standardized protocol in mice consists of a simple vitrification method using 1 M dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and a mixture of 2 M DMSO, 1 M acetoamide, and 3 M propanediol (DAP213) used as the vitrification solution [27]. More than 90% of vitrified–warmed embryos can survive and 30–50% of the survived embryos can develop into pups via embryo transfer.
The vitrification of mouse oocytes is helpful for the emergent use of in vitro fertilization when there is a shortage of oocytes owing to superovulation failure or the delayed transport of cold-stored sperm. The simple vitrification method is also applicable to the cryopreservation of mouse oocytes [28, 29]. However, it has been observed that the prolonged exposure of hyaluronidase to remove cumulus cells from oocytes decreased the fertilization rate of cryopreserved mouse oocytes [30]. Treatment with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) was found to recover the fertilizing ability of vitrified–warmed mouse oocytes by alleviating zona hardening [31].
The vitrification of mouse oocytes in the pronuclear stage was found to be useful for the production of genetically modified mice by genome editing techniques. Fertilized oocytes were produced by in vitro fertilization. At 6.5 h after insemination, the fertilized oocytes were cryopreserved by the simple vitrification method [32]. After warming, the oocytes can be readily used for microinjection or electroporation to edit the target gene using the TALEN or CRISPR-Cas9 system [32–36].
Superovulation
Superovulation is a useful technique to obtain a large number of oocytes via the administration of hormones [37]. Ovulated oocytes are used for cryopreservation, in vitro fertilization, or mating to obtain fertilized oocytes in vivo. To induce superovulation, equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) are administered routinely to female mice [38]. The average yield using the eCG and hCG method is 25 oocytes/female mouse [39]. In 2015, we refined the superovulation technique by the coadministration of inhibin antiserum (IAS) and eCG (IASe or ultrasuperovulation), which was able to produce more than 100 oocytes/female mouse [40]. IAS blocked the negative feedback of inhibin on the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), resulting in the production of excess levels of FSH and the promotion of follicular development [41, 42]. The coadministration of IAS and eCG was found to be effective in stimulating follicular development by endogenous and exogenous FSH. The ultrasuperovulation technique was helpful in reducing the number of oocyte donors and achieved a rapid and mass production of genetically engineered mice. With IASe treatment, 4-week-old C57BL/6 J female mice produced the largest number of oocytes at the age between 3 and 50 weeks [43]. The yield of ovulated oocytes using the IASe treatment was different between inbred mice (A/J: 24.9 oocytes/female; BALB/cByJ: 90.3 oocytes/female; C3HeJ: 52.0 oocytes/female; DBA/2 J: 68.8 oocytes/female; and FVB/NJ: 25.6 oocytes/female) and outbred mice (CD1: 33.7 oocytes/female) [44]. Among the highly immunosuppressed mouse (nonobese diabetic/Shi-scid IL2rγnull mouse), female mice aged 12 weeks produced the largest number of oocytes (70.0 oocytes/female) [45]. Therefore, the optimal age of female mice to induce ultrasuperovulation using IASe treatment also depends on the mouse strain.
Cold storage of sperm
The cold storage of sperm is applicable to the shipment of genetically engineered mice as an alternative to the shipment of live animals [46]. The shipment of cold-stored sperm can be done easily using inexpensive shipment and avoids the risks of spreading infectious diseases and the escape or death of live animals during the shipment. Regarding the shipment of sperm, we collected the cauda epididymis in a preservation solution and shipped it in a cold-transport kit [46]. We observed that the fertilizing ability of cold-stored mouse sperm decreased in a time-dependent manner [47]. However, the preservation solution of Lifor perfusion medium and in vitro fertilization using MBCD and GSH were found to be effective in preventing the reduction of the fertilizing ability of cold-stored sperm [46, 48]. Furthermore, the addition of DMSO and quercetin to the preservation medium prolonged the storage period of cold-stored sperm for 10 days [49]. The cold-stored sperm could be cryopreserved and later used to recover animals by in vitro fertilization and by embryo transfer [50]. Today, we generally receive cold-stored sperm to produce embryos or live animals or to archive cryopreserved sperm in the CARD mouse bank. The new transport system using the cold-stored sperm facilitated the domestic and international transportation of mouse resources.
Cold storage of two-cell embryos
The cold storage of two-cell embryos has also been found to be useful for the shipment of genetically engineered mice [51]. The transported two-cell embryos can be used to produce animals by embryo transfer at the receiving facility. An advantage of the cold-transport of embryos is that it is a simple procedure without the need for cryopreservation and avoids the potential risks involved in the shipment of live animals. The developmental ability of cold-stored embryos could decline in a time-dependent manner. The preservation M2 medium containing 1.5 mM NAC was found to prolong the storage period of cold-stored embryos for 4 days [51–53]. Cold-stored embryos can also be cryopreserved using the simple vitrification method [54]. The shipment of cold-stored embryos is practical for performing embryo transfer beyond the facility or when there is a lack of mice recipients on the date of embryo transfer.
Mouse reproductive technology workshop
To share our knowledge and techniques of mouse reproductive technology with our community, we have been organizing the CARD Mouse Reproductive Technology Workshop in Japan and abroad since 2000 (Table 2). In this workshop, we provide lectures, demonstrate the latest techniques, and perform hands-on training on the preparation of glass pipettes, oocyte handling, sperm cryopreservation, cold storage of sperm, in vitro fertilization using fresh, frozen–thawed, and cold-stored sperm, oocyte washing and observation, cryopreservation of oocytes and in vitro fertilization using vitrified–warmed oocytes, two-cell embryo collection, embryo cryopreservation, cold storage of embryos, operation of vasectomized mice, surgery of embryo transfer, and nonsurgical transportation of embryos. More than 700 students have participated in our workshops. Owing to the prevailing coronavirus pandemic, we have postponed the hands-on training and plan to set up an online course to overcome the limitations of international travel. Moreover, we intend to update new techniques on our website regarding the online manual of mouse reproductive technology (http://card.medic.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/card/english/sigen/manual/onlinemanual.html).
Table 2.
Venues of CARD Mouse Reproductive Technology Workshop
| Venue | Region |
|---|---|
| CARD, Kumamoto University | Japan |
| Asahikawa Medical University | Japan |
| Central Institute for Experimental Animals (CIEA) | Japan |
| Shanghai Laboratory Animal Center (SLAC) | China |
| National Laboratory Animal Center (NLAC) | Taiwan |
| The National Institute for Food and Drug Control (NIFDC) | China |
| Biological Resource Centre at A*STAR | Singapore |
| National Centre for Biotechnology at Spanish National Research Council (CNB-CSIC) | Spain |
| Roswell Park Cancer Institute | USA |
| Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & BioTechnology (KRIBB) | Korea |
| Institute Pasteur | France |
| Texas A&M Institute of Genomic Medicine | USA |
| Jackson Laboratory | USA |
Conclusions
The cryopreservation of mouse resources is an important strategy to accumulate valuable mouse characteristics useful for the scientific community. The optimal combination of reproductive technology will provide the best standards of cryopreserved mouse resources to researchers. We have provided a picture of the mouse bank system in Fig. 1. The advanced mouse bank system will provide a seamless archive and supply of mouse resources beyond facilities and countries. In addition, an international resource network will provide a robust research infrastructure to facilitate international collaborations. We have described the latest techniques of mouse reproductive technology in this review article. Details of the techniques can be mastered via the hands-on workshop or our online manuals. We hope that this review article would be helpful in improving the management and availability of mouse resources at your facility.
Fig. 1.
Application of advanced mouse reproductive technology in a mouse bank
Acknowledgments
We thank our technical staff Tomoko Kondo, Kiyoko Yamashita, Eri Ishida, Maki Sakaguchi, and Yuka Deshimaru; our graduate students Yuta Ishizuka, Hidetaka Yoshimoto, Ayumi Mukunoki, Yuka Horikoshi (CARD, Kumamoto University), and Kristy Kinchen Williams (Mouse Biology Program, University of California Davis) for the helpful support and discussion; and the organizers of the hands-on workshops Norihiko Shimizu (Asahikawa Medical University, Japan), Dr. Minesuke Yokoyama (CIEA, Japan), Dr. Xu Ping (SLAC, China), Dr. Arun Kumar (BRC, Singapore), Dr. Leo Wang (NLAC, Taiwan), Dr. Fan Changfa (NIFDC, China), Dr. Lluis Montoliu (CNB-CSIC, Spain), Dr. Aimee Stablewski (Roswell Park Cancer Institute, USA), Dr. Jan Parker-Thornburg (MD Anderson Cancer Institute, USA), Dr. Hyoung-Chin Kim (KRIBB, Korea), Dr. Jean Jaubert (Institute Pasteur, France), Dr. Benjamin Morpurgo (TIGM, USA), Dr. Andrei Golovko (TIGM, USA), Dr. William Shawlot (University of Texas at Austin, USA), Dr. Robert Taft (Jackson Laboratory), and Dr. Jennifer Corrigan (Jackson Laboratory).
Abbreviations
- CARD
Center for Animal Resources and Development
- IMSR
International Mouse Strain Resource
- AMMRA
Asian Mouse Mutagenesis and Resource Association
- MBCD
Methyl-β-cyclodextrin
- GSH
Reduced glutathione
- DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DAP213
2 M DMSO, 1 M acetoamide, and 3 M propanediol
- NAC
N-acetyl cysteine
- TALEN
Transcription activator-like effector nuclease
- CRISPR
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- Cas9
CRISPR-associated nuclease 9
- eCG
Equine chorionic gonadotropin
- hCG
Human chorionic gonadotropin
- IAS
Inhibin antiserum
- IASe
Inhibin antiserum and equine chorionic gonadotropin
- FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone
Authors’ contributions
TT, SN, YN, JS, and NN contributed to writing the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants for the Research on Development of New Drugs (Project ID: 167698659) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), the Fundamental Technologies Upgrading Program, National BioResource Project (NBRP), of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), and JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP26860039, JP16K08239, and JP15H04606.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Competing interests
There is no competing interest associated with this article.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Rosenthal N, Brown S. The mouse ascending: perspectives for human-disease models. Nat Cell Biol 2007;9:993–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Ito M, Hiramatsu H, Kobayashi K, Suzue K, Kawahata M, Hioki K, et al. NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mouse: an excellent recipient mouse model for engraftment of human cells. Blood. 2002;100:3175–3182. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-12-0207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Donahue LR, Hrabe de Angelis M, Hagn M, Franklin C, Lloyd KC, Magnuson T, et al. Centralized mouse repositories. Mamm Genome. 2012;23:559–571. doi: 10.1007/s00335-012-9420-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nakagata N, Yamamura K. Current activities of CARD as an international core center for mouse resources. Exp Anim. 2009;58:343–350. doi: 10.1538/expanim.58.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nakagata N, Takeo T. Basic mouse reproductive techniques developed and modified at the Center for Animal Resources and Development (CARD), Kumamoto University. Exp Anim. 2019;68:391–395. doi: 10.1538/expanim.19-0070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Eppig JT, Motenko H, Richardson JE, Richards-Smith B, Smith CL. The international mouse strain resource (IMSR): cataloging worldwide mouse and ES cell line resources. Mamm Genome. 2015;26:448–455. doi: 10.1007/s00335-015-9600-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ayadi A, Birling MC, Bottomley J, Bussell J, Fuchs H, Fray M, et al. Mouse large-scale phenotyping initiatives: overview of the European mouse disease clinic (EUMODIC) and of the Wellcome Trust sanger institute mouse genetics project. Mamm Genome. 2012;23:600–610. doi: 10.1007/s00335-012-9418-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guan M, Bogani D, Marschall S, Raspa M, Takeo T, Nakagata N, et al. In vitro fertilization in mice using the MBCD-GSH protocol. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2014;4:67–83. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo140059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Guan M, Bogani D, Marschall S, Raspa M, Takeo T, Nakagata N, et al. Conservation of mouse models through embryo freezing. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2014;4:205–227. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo140082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guan M, Bogani D, Marschall S, Raspa M, Takeo T, Nakagata N, et al. Contemporary techniques for freezing mouse spermatozoa. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2014;4:85–104. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo140065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kenyon J, Guan M, Bogani D, Marschall S, Raspa M, Pickard A, et al. Transporting mouse embryos and germplasm as frozen or unfrozen materials. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2014;4:47–65. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo140064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Critser JK, Mobraaten LE. Cryopreservation of murine spermatozoa. ILAR J. 2000;41:197–206. doi: 10.1093/ilar.41.4.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Marschall S, Hrabe de Angelis M. Cryopreservation of mouse spermatozoa: double your mouse space. Trends Genet. 1999;15:128–131. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(99)01715-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Okamoto M, Nakagata N, Toyoda Y. Cryopreservation and transport of mouse spermatozoa at −79 degrees C. Exp Anim. 2001;50:83–86. doi: 10.1538/expanim.50.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nakagata N. Cryopreservation of mouse spermatozoa. Mamm Genome. 2000;11:572–576. doi: 10.1007/s003350010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sztein JM, Farley JS, Mobraaten LE. In vitro fertilization with cryopreserved inbred mouse sperm. Biol Reprod. 2000;63:1774–1780. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod63.6.1774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nishizono H, Shioda M, Takeo T, Irie T, Nakagata N. Decrease of fertilizing ability of mouse spermatozoa after freezing and thawing is related to cellular injury. Biol Reprod. 2004;71:973–978. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.024422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Takeo T, Nakagata N. Combination medium of cryoprotective agents containing L-glutamine and methyl-{beta}-cyclodextrin in a preincubation medium yields a high fertilization rate for cryopreserved C57BL/6J mouse sperm. Lab Anim. 2010;44:132–137. doi: 10.1258/la.2009.009074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takeo T, Hoshii T, Kondo Y, Toyodome H, Arima H, Yamamura K, et al. Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin improves fertilizing ability of C57BL/6 mouse sperm after freezing and thawing by facilitating cholesterol efflux from the cells. Biol Reprod. 2008;78:546–551. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.065359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Takeo T, Nakagata N. Reduced glutathione enhances fertility of frozen/thawed C57BL/6 mouse sperm after exposure to methyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Biol Reprod. 2011;85:1066–1072. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.092536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Takeo T, Horikoshi Y, Nakao S, Sakoh K, Ishizuka Y, Tsutsumi A, et al. Cysteine analogs with a free thiol group promote fertilization by reducing disulfide bonds in the zona pellucida of mice. Biol Reprod. 2015;92:90. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.114.125443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Takeo T, Nakagata N. Mouse sperm cryopreservation using cryoprotectant containing l-glutamine. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2018;2018:pdb prot094516. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 23.Sztein JM, Takeo T, Nakagata N. History of cryobiology, with special emphasis in evolution of mouse sperm cryopreservation. Cryobiology. 2018;82:57–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2018.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Whittingham DG, Leibo SP, Mazur P. Survival of mouse embryos frozen to −196 degrees and −269 degrees C. Science. 1972;178:411–414. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4059.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mobraaten LE. Mouse embryo cryobanking. J In Vitro Fert Embryo Transf. 1986;3:28–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01131377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lyon MF, Whittingham DG, Glenister P. Long-term storage of frozen mouse embryos under increased background irradiation. CIBA Found Symp. 1977:273–90. 10.1002/9780470720332.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Nakao K, Nakagata N, Katsuki M. Simple and efficient vitrification procedure for cryopreservation of mouse embryos. Exp Anim. 1997;46:231–234. doi: 10.1538/expanim.46.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nakagata N. High survival rate of unfertilized mouse oocytes after vitrification. J Reprod Fertil. 1989;87:479–483. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0870479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nakagata N, Takeo T, Fukumoto K, Kondo T, Haruguchi Y, Takeshita Y, et al. Applications of cryopreserved unfertilized mouse oocytes for in vitro fertilization. Cryobiology. 2013;67:188–192. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2013.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ishizuka Y, Takeo T, Nakao S, Yoshimoto H, Hirose Y, Sakai Y, et al. Prolonged exposure to hyaluronidase decreases the fertilization and development rates of fresh and cryopreserved mouse oocytes. J Reprod Dev. 2014;60:454–459. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2014-045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mukunoki A, Takeo T, Nakagata N. N-acetyl cysteine restores the fertility of vitrified-warmed mouse oocytes derived through ultrasuperovulation. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0224087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nakagawa Y, Sakuma T, Takeo T, Nakagata N, Yamamoto T. Electroporation-mediated genome editing in vitrified/warmed mouse zygotes created by IVF via ultra-superovulation. Exp Anim. 2018;67:535–543. doi: 10.1538/expanim.18-0062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nakagawa Y, Sakuma T, Nakagata N, Yamasaki S, Takeda N, Ohmuraya M, et al. Application of oocyte cryopreservation technology in TALEN-mediated mouse genome editing. Exp Anim. 2014;63:349–355. doi: 10.1538/expanim.63.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nakagawa Y, Sakuma T, Sakamoto T, Ohmuraya M, Nakagata N, Yamamoto T. Production of knockout mice by DNA microinjection of various CRISPR/Cas9 vectors into freeze-thawed fertilized oocytes. BMC Biotechnol. 2015;15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12896-015-0144-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nakagawa Y, Sakuma T, Nishimichi N, Yokosaki Y, Yanaka N, Takeo T, et al. Ultra-superovulation for the CRISPR-Cas9-mediated production of gene-knockout, single-amino-acid-substituted, and floxed mice. Biol Open. 2016;5:1142–1148. doi: 10.1242/bio.019349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nakagawa Y, Sakuma T, Nishimichi N, Yokosaki Y, Takeo T, Nakagata N, et al. Culture time of vitrified/warmed zygotes before microinjection affects the production efficiency of CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knock-in mice. Biol Open. 2017;6:706–713. doi: 10.1242/bio.025122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Luo C, Zuniga J, Edison E, Palla S, Dong W, Parker-Thornburg J. Superovulation strategies for 6 commonly used mouse strains. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2011;50:471–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gates AH. Viability and developmental capacity of eggs from immature mice treated with gonadotrophins. Nature. 1956;177:754–755. doi: 10.1038/177754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Byers SL, Payson SJ, Taft RA. Performance of ten inbred mouse strains following assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) Theriogenology. 2006;65:1716–1726. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2005.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Takeo T, Nakagata N. Superovulation using the combined administration of inhibin antiserum and equine chorionic gonadotropin increases the number of ovulated oocytes in C57BL/6 female mice. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0128330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kishi H, Taya K, Watanabe G, Sasamoto S. Follicular dynamics and secretion of inhibin and oestradiol-17 beta during the oestrous cycle of the hamster. J Endocrinol. 1995;146:169–176. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1460169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang H, Herath CB, Xia G, Watanabe G, Taya K. Superovulation, fertilization and in vitro embryo development in mice after administration of an inhibin-neutralizing antiserum. Reproduction. 2001;122:809–816. doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1220809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Takeo T, Mukunoki A, Nakagata N. Ovulation of juvenile, mature, and aged female C57BL/6 mice following coadministration of inhibin antiserum and equine chorionic gonadotropin. Theriogenology. 2019;135:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Takeo T, Nakagata N. Immunotherapy using inhibin antiserum enhanced the efficacy of equine chorionic gonadotropin on superovulation in major inbred and outbred mice strains. Theriogenology. 2016;86:1341–1346. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.04.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Goto M, Takeo T, Takahashi R, Nakagata N. Efficient production of immunodeficient non-obese diabetic/Shi-scid IL2rgamma(null) mice via the superovulation technique using inhibin antiserum and gonadotropin. Lab Anim. 2020. 10.1177/0023677220928091. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Takeo T, Tsutsumi A, Omaru T, Fukumoto K, Haruguchi Y, Kondo T, et al. Establishment of a transport system for mouse epididymal sperm at refrigerated temperatures. Cryobiology. 2012;65:163–168. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2012.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kaneko T, Fukumoto K, Haruguchi Y, Kondo T, Machida H, Koga M, et al. Fertilization of C57BL/6 mouse sperm collected from cauda epididymides after preservation or transportation at 4 degrees C using laser-microdissected oocytes. Cryobiology. 2009;59:59–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2009.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yoshimoto H, Takeo T, Irie T, Nakagata N. Fertility of cold-stored mouse sperm is recovered by promoting acrosome reaction and hyperactivation after cholesterol efflux by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Biol Reprod. 2017;96:446–455. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.142901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yoshimoto H, Takeo T, Nakagata N. Dimethyl sulfoxide and quercetin prolong the survival, motility, and fertility of cold-stored mouse sperm for 10 days. Biol Reprod. 2017;97:883–891. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Takeo T, Fukumoto K, Kondo T, Haruguchi Y, Takeshita Y, Nakamuta Y, et al. Investigations of motility and fertilization potential in thawed cryopreserved mouse sperm from cold-stored epididymides. Cryobiology. 2014;68:12–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2013.10.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Takeo T, Kaneko T, Haruguchi Y, Fukumoto K, Machida H, Koga M, et al. Birth of mice from vitrified/warmed 2-cell embryos transported at a cold temperature. Cryobiology. 2009;58:196–202. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2008.12.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Takeo T, Kondo T, Haruguchi Y, Fukumoto K, Nakagawa Y, Takeshita Y, et al. Short-term storage and transport at cold temperatures of 2-cell mouse embryos produced by cryopreserved sperm. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2010;49:415–419. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Horikoshi Y, Takeo T, Nakagata N. N-acetyl cysteine prolonged the developmental ability of mouse two-cell embryos against oxidative stress at refrigerated temperatures. Cryobiology. 2016;72:198–204. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2016.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mukunoki A, Takeo T, Nakao S, Tamura K, Horikoshi Y, Nakagata N. Simple transport and cryopreservation of cold-stored mouse embryos. Exp Anim. 2020. 10.1538/expanim.20-0042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.