Abstract
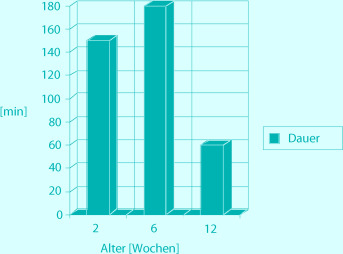
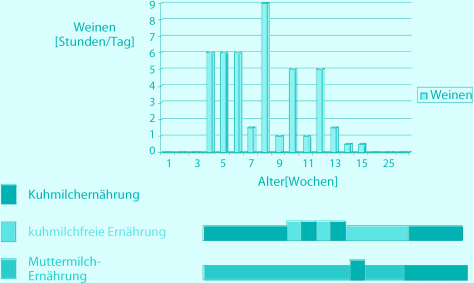
Säuglingskoliken stellen das häufigste gastroenterologische Problem in den ersten Lebensmonaten dar. Sie sind gekennzeichnet durch starkes und lang anhaltendes Schreien bei ansonsten gesunden Säuglingen. Die Abgrenzung vom „normalen“ Schreien folgt international der sog. 3er-Regel, die auf die frühe Untersuchung von Wessel et al. (1954) zurückgeht: - Intermittierendes und ansonsten nicht erklärbares Schreien über mehr als 3 h am Tag, - das an zumindest 3 Tagen pro Woche - über einen Zeitraum von 3 Wochen oder länger auftritt.
Literatur
Literatur zu Abschn. 8.1
- Barr RG. Colic and crying syndromes in infants. Pediatrics. 1998;102:1282–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand PL, Engelbert RH, Helders PJ, Offringa M. Systematic review of the effects of therapy in infants with the KISS-syndrome (kinetic imbalance due to suboccipital strain) Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005;26:703–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazelton TB. Crying in infancy. Pediatrics. 1962;29:579–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowcroft NS, Strachan DP. The social origins of infantile colic: questionnaire study covering 76747 infants. BMJ. 1997;314:1325–1328. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7090.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst E. Chiropractic spinal manipulation for infant colic: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials. Int J Clin Pract. 2009;63:1351–1353. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta SK. Is colic a gastrointestinal disorder? Curr Opin Pedaitr. 2002;14:588–592. doi: 10.1097/00008480-200210000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson I, Lindberg T. Cow’s milk as cause of infantile colic in breast fed infants. Lancet. 1979;2:437–439. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletzko S, Niggemann B, Friedrichs F, Koletzko B. Vorgehen bei Säuglingen mit Verdacht auf Kuhmilchproteinallergie. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 2009;157:687–691. doi: 10.1007/s00112-009-2014-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lucassen PLBJ, Assendelft WJJ, van Eijk TM, et al. Systematic review of the occurrence of infantile colic in the community. Arch Dis Child. 2001;84:398–403. doi: 10.1136/adc.84.5.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R, Hunt K, Ernst E. Nutritional supplements and other complementary medicines for infantile colic: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2011;127:720–733. doi: 10.1542/peds.2010-2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino F, Cresi F, Castagno E, et al. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of a standardized extract of Matricariae recutita, Foeniculum vulgare and Melissa officinalis (ColiMil) in the treatment of breastfed colicky infants. Phytother Res. 2005;19:335–340. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino F, Cordisco L, Tarasco V, et al. Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 in infantile colic: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2010;126(e533):e526. doi: 10.1542/peds.2010-0433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanessa ED, Brown M-J. Maternal smoking and infantile gastrointestinal dysregulation: the case of colic. Pediatrics. 2004;114:497–505. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade S, Kilgour T. Infantile colic. BMJ. 2001;323:437–440. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7310.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel MA, Cobb JC, Jacobsen EB, et al. Paroxysmal fussing in infancy, sometimes called „colic“. Pediatrics. 1954;14:241–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschn. 8.2
- Besedovsky A, Li UK. Across the developmental continuum of irritable bowel syndrome: clinical and pathophysiological considerations. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004;6:247–253. doi: 10.1007/s11894-004-0015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroccio A, Iacono G, Cottone M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of fecal calprotectin assay in distinguishing organic causes of chronic diarrhea from irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective study in adults and children. Clin Chem. 2003;49:861–867. doi: 10.1373/49.6.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou E, Nurko S. Management of functional abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome in children and adolescents. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;4:293–304. doi: 10.1586/egh.10.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Matary W, Spray C, Sandhu B. Irritable bowel syndrome: the commonest cause of recurrent abdominal pain in children. Eur J Pediatr. 2004;163:584–588. doi: 10.1007/s00431-004-1437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. Functional gastrointestinal disorders. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1999;11:375–378. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199910000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman PE, Milla PJ, Benninga MA, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: neonate/toddler. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1519–1526. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joishy M, Davies I, Ahmed M, et al. Fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin as noninvasive markers of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009;48:48–54. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31816533d3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane SV, Sandborn WJ, Rufo PA, et al. Fecal lactoferrin is a sensitive and specific marker in identifying intestinal inflammation. Am J Gastro. 2003;98:1309–1314. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneepkens CMF, Hoekstra Chronic non-specific diarrhea of childhood. Pathophysiology and management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1996;43:375–390. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70411-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layer P, Andresen V, Pehl C, et al. S3-Leitlinie Reizdarmsyndrom: Definition, Pathophysiologie, Diagnostik und Therapie. Z Gastroenterol. 2011;49:237–293. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1245976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele E, Simeone D, Marino A, et al. Functional gastrointestinal disorders in children: an Italian prospective study. Pediatrics. 2004;114:73–78. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primavera G, Amoroso B, Barresi A, et al. Clinical utility of Rome criteria managing functional gastrointestinal disorders in pediatric primary care. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e155–161. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasquin-Weber A, Hyman PE, Cucchiara S, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut. 1999;45(SII):II60–II68. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.2008.ii60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasquin A, Di Lorenzo C, Forbes D, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1527–1537. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.08.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschn. 8.3
- Chicella MF, Batres LA, Heesters MS, Dice JE. Prokinetic drug therapy in children: a review of current options. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39(4):706–711. doi: 10.1345/aph.1E411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitkara DK, Di Lorenzo C. From the bench to the „crib“-side: implications of scientific advances to paediatric neurogastroenterology and motility. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006;18(4):251–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2005.00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo C, Youssef NN. Diagnosis and management of intestinal motility disorders. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010;19(1):50–58. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2009.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C, Goulet O, Ategbo S, et al. Chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction syndrome: clinical analysis, outcome, and prognosis in 105 children. French-Speaking Group of Pediatric Gastroenterology. Dig Dis Sci. 1999;44(5):953–959. doi: 10.1023/A:1026656513463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles CH, De GR, Kapur RP, et al. Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: guidelines for histological techniques and reporting on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working Group. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118(2):271–301. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0527-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles CH, De GR, Kapur RP, et al. The London Classification of gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: report on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working Group. Gut. 2010;59(7):882–887. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.200444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletzko S, Schwarzer A, et al. Intestinal dysmotilities including chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. In: Kleinman RE, Goulet O-J, Mieli-Vergani G, et al., editors. Walker’s pediatric gastrointestinal disease. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 5. Hamilton: Decker; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koletzko S, Jesch I, Faus-Keßler T, et al. Rectal biopsy for diagnosis of intestinal neuronal dysplasia in children: a prospective multicentre study on interobserver variation and clinical outcome. Gut. 1999;44:853–861. doi: 10.1136/gut.44.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousa H, Hyman PE, Cocjin J, Flores AF, Di Lorenzo C. Long-term outcome of congenital intestinal pseudoobstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47(10):2298–2305. doi: 10.1023/A:1020199614102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas J, Sachs P, Ament ME. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in pediatrics. Results of a national survey by members of the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. J Ped Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988;7:323–332. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198805000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
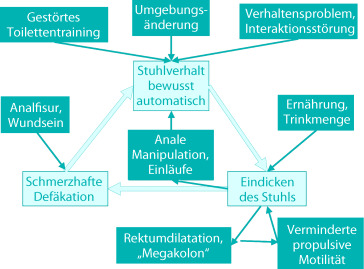
Literatur zu Abschn. 8.4
- Baker SS, Liptak GS, Colletti RB, et al. Constipation in infants and children: evaluation and treatment. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;29:612–626. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199911000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo C. Childhood constipation: finally some hard data about hard stools! J Pediatr. 2000;136:4–7. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(00)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issenman RM, Filmer RB, Gorski PA. A review of bowel and bladder control development in children: how gastrointestinal and urologic problems relate to problems in toilet training. Pediatrics. 1999;103(Suppl):146–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshtgar AS, Ward HC, Sanei A, Clayden GS. Botulinum toxin, a new treatment modality for chronic idiopathic constipation in children: long-term follow-up of a double-blind randomized trial. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:672–680. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2006.12.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michail S, Gendy E, Preud'Homme D, Mezoff A. Polyethylene glycol for constipation in children younger than eighteen months old. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;39:197–199. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200408000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pashankar DS, Loening-Baucke V, Bishop WP. Safety of polyethylene glycol 3350 for the treatment of chronic constipation in children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003;157:661–664. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.157.7.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somnez K, Demirogullari B, Ekingen G, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled treatment of anal fissure by lidocaine, EMLA, and GTN in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2002;37:1313–1316. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2002.34997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschn. 8.5
- Amiel J, Lyonnet S. Hirschsprung disease, associated syndromes, and genetics: a review. J Med Genet. 2001;38:729–739. doi: 10.1136/jmg.38.11.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks AS, Oostra BA, Hofstra RM. Studying the genetics of Hirschsprung’s disease: unraveling an oligogenic disorder. Clin Genet. 2005;67:6–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croffie JM, Davis MM, Faught PR, et al. At what age is a suction rectal biopsy less likely to provide adequate tissue for identification of ganglion cells? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007;44(2):198–202. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000252188.12793.ee. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Torre L, Langer JC. Transanal endorectal pull-through for Hirschsprung disease: technique, controversies, pearls, pitfalls, and an organized approach to the management of postoperative obstructive symptoms. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010;19(2):96–106. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2009.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engum SA, Grosfeld JL. Long-term results of treatment of Hirschsprung’s disease. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2004;13(4):273–285. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2004.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gath R, Goessling A, Keller KM, et al. Analysis of the RET, GDNF, EDN3, and EDNRB genes in patients with intestinal neuronal dysplasia and Hirschsprung disease. Gut. 2001;48(5):671–675. doi: 10.1136/gut.48.5.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsdottir A, Sandblom G, Arnbjornsson E, Larsson LT. Quality of life in adults operated on for Hirschsprung disease in childhood. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010;51(2):160–166. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181cac1b6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch BZ, Angelides AG, Goode SP, Garb JL. Rectal biopsies obtained with jumbo biopsy forceps in the evaluation of Hirschsprung disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52(4):429–432. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181ecd644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imseis E, Gariepy C, et al. Hirschsprung’s disease. In: Kleinman RE, Goulet O, Mieli-Vergani G, et al., editors. Walker’s pediatric gastrointestinal disease. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 5. Hamilton: Decker; 2008. pp. 683–692. [Google Scholar]
- Knowles CH, De GR, Kapur RP, et al. Gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: guidelines for histological techniques and reporting on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working Group. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118(2):271–301. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0527-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles CH, De GR, Kapur RP, et al. The London Classification of gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: report on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working Group. Gut. 2010;59(7):882–887. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.200444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorijn F, Reitsma JB, Voskuijl WP, et al. Diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s disease: a prospective, comparative accuracy study of common tests. J Pediatr. 2005;146(6):787–792. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2005.01.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan M, Kapur RP. Counting myenteric ganglion cells in histologic sections: an empirical approach. Hum Pathol. 2010;41(8):1097–1108. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sribudiani Y, Metzger M, Osinga J, et al. Variants in RET associated with Hirschsprung's disease affect binding of transcription factors and gene expression. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(2):572–582. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.10.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieten D, Spicer R. Enterocolitis complicating Hirschsprung’s disease. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2004;13(4):263–272. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2004.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschn. 8.6
- Bufler P, Gross M, Uhlig HH. Chronische Bauchschmerzen bei Kindern und Jugendlichen. Dtsch Ärztebl. 2011;108(17):295–303. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2011.0295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou E, Nurko S. Functional abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome in children an adolescents. Therapy. 2011;8(3):315–331. doi: 10.2217/thy.11.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams JS, Burke G, Davis PM, Rzepski B, Andrulonis PA. Abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome in adolescents: a community based study. J Pediatr. 1996;129(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(96)70246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman PE, Milla PJ, Benninga MA, et al. Childhood functional disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(5):1519–1526. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HowellS, Poulton R, Talley NJ. The natural history of childhood abdominal pain and its association with adult irritable bowel syndrome: birth-cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;1000(9):2071–2078. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasquin A, Di Lorenzo C, Forbes D, et al. Childhood functional disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(5):1527–1537. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.08.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starfield B, Hoekelman RA, McCormick M, et al. Who provides health care to children and adolescents in the United States? Pediatrics. 1984;74(6):991–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]