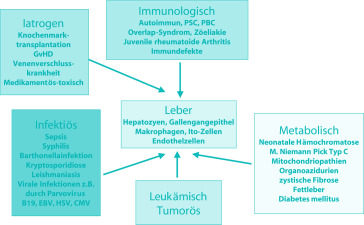
Abstract
Systemerkrankungen als Ursache einer Lebererkrankung sind häufig, ohne dass man genaue Zahlen angeben kann. Die verschiedenen Grunderkrankungen sind für sich betrachtet zwar selten, nur dadurch, dass viele Erkrankungen in Betracht gezogen werden müssen, ergibt sich eine relative Häufung. Durch Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der molekularbiologischen Diagnostik insbesondere bei den Stoffwechselerkrankungen lassen sich heute bereits viele der in Frage kommenden Grunderkrankungen eindeutig nachweisen. Allerdings ist bei keiner der Erkrankungen ein hundertprozentiger molekularbiologischer Nachweis möglich. Damit ergibt sich eine sichere Diagnose nur bei einem positiven Nachweis. Bei fehlendem Nachweis einer bisher bekannten für die Erkrankung spezifischen Mutation bleibt die Zuordnung entweder enzymatischen Tests oder klinischer Diagnose vorbehalten. Insbesondere bei der Manifestation als akutes Leberversagen ist die für die Diagnosesicherung erforderliche Zeit damit oft nicht vorhanden.
Literatur
Literatur zu Abschn. 20.1
- Davison S. Coeliac disease and liver function. Arch Dis Child. 2002;87:293–296. doi: 10.1136/adc.87.4.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn DM, Mohan N, McKiernan P, et al. Progress in treatment and outcome for children with neonatal hemochromatosis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal. 2003;88:F124–127. doi: 10.1136/fn.88.2.F124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasle H, Niemeyer CM, Chessels JM, et al. A pediatric approach to the WHO classification of myelodysplastic and myoloproliferative diseases. Leukemia. 2003;17:2531–2532. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henter JI, Arico M, Elinder G, Imashuku S, Janka G. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohisziocytosis. Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1998;12:417–433. doi: 10.1016/S0889-8588(05)70520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the pediatric population. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8:549–558. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2004.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton HM, Yates K, Unalp-Arida A, et al. Association between metabolic syndrome and liver histology among children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2093–2102. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand EB, Karper SJ, Kelly S, et al. Treatment of neonatal hemochromatosis with exchange transfusion and intravenous immunoglobulins. J Pediatr. 2009;155:566–571. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C, Kelleher D, Keeling PW. Hepatic manifestations of gastrointestinal diseases. inflammatory bowel diease, celiac disease and Whipple’s disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6:1013–1032. doi: 10.1016/S1089-3261(02)00055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschnitt 20.2
- Bor O, Dinleyici EC, Kebapci M, Aydogdu SD. Ceftriaxone-associated biliary sludge and pseudocholelithiasis during childhood: a prospective study. Pediatr Int. 2004;46:322–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1328-0867.2004.01884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruch SW, Ein SH, Rocchi C, Kim PC. The management of nonpigmented gallstones in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35:729–732. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2000.6044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalane MJ, Neubrand MW, Carey MC. Physical chemical pathogenesis of pigment stones. Semin Liver Dis. 1988;8:317–328. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport M. Laparoscopic surgery in children. Ann R Surg Engl. 2003;85:324–330. doi: 10.1308/003588403769162440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davit-Spraul A, Gonzales E, Baussan C, Jacquemin E. The spectrum of liver diseases related to ABCB4 gene mutations: pathophysiology and clinical aspects. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30(2):134–146. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1253223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Caluwe D, Akl U, Corbally M. Cholecystectomy versus cholecystolithotomy for cholelithiasis in childhood: long term outcome. J Pediatr Surg. 2001;36:1518–1521. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2001.27035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen CA, Roberts CC. Cholelithiasis: clinical characteristics in children. Clin Pediatr. 1989;7:294–298. doi: 10.1177/000992288902800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamba PG, Zancan Midrio LP, et al. Is there a place for medical treatment in children with gallstones? J Pediatr Surg. 1997;32:476–478. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3468(97)90610-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern Z, Vinograd Z, Laufer H, et al. Characteristics of gallbladder bile of infants and children. JPGN. 1996;23:147–150. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199608000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heubi JE, Lewis LG. Diseases of the gallbladder in infancy, childhood and adolescence. In: Suchy FJ, editor. Liver disease in children. St Louis: Mosby Year Book; 1994. pp. 605–621. [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb GW, Jr, Holcomb GW. Cholelithiasis in infants, children, and adolecents. Pediatr Rev. 1991;11:268–274. doi: 10.1542/pir.11-9-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston DE, Kaplan MM. Pathogenesis and treatment of gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:412–421. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302113280608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jüngst D, Lang T, Ritter v. C, Paumgartner G. Cholesterol nucleation time in gallbladder bile of patients with multiple or solitary cholesterol gallstones. Hepatology. 1988;15:804–808. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe TE. Cholelithiasis and cholecystitis in children. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2000;9:170–176. doi: 10.1053/spsu.2000.18838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif S, Sloven DG, Lebenthal E. Gallstones in children. AJDC. 1991;145:105–108. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160010111028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer WJ, Grisoni ER, Gauderer WL. The spectrum of cholelithiasis in the first year of life. J Pediatr Surg. 1989;24:1064–1067. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3468(89)80216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer P, Lenz MP, Kirschner HJ. Pathogenesis and symptomatology of cholelithiasis in childhood. A prospective study. Dig Surg. 2000;17:459–467. doi: 10.1159/000051941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer EA. Gallbladder disease. In: Walker EA, Durie PR, Hamilton JR, Walker-Smith JA, Watkins JB, editors. Pediatric gastrointestinal disease. St Louis: Mosby Year Book; 1996. pp. 1399–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Stringer MD, Taylor DR, Soloway RD. Gallstone composition: are children different? J Pediatr. 2003;142:435–440. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2003.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topal B, Van de Moortel M, Fieuws S, et al. The value of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in predicting common bile duct stones in patients with gallstone disease. Br J Surg. 2003;90:42–47. doi: 10.1002/bjs.4025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ure BM, Jesch NK, Nustede R. Postcholecytectomy syndrome with special regard to children. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2004;14:221–225. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-821066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesdorp I, Bosman D, de Graaff A, et al. Clinical presentations and predisposing factors of cholelithiasis and sludge in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000;31:411–417. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200010000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zargar SA, Javid G, Khan BA, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy in the management of bile duct stones in children. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:586–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschn. 20.3
- Alvarez F, Bernard O, Brunelle F. Congenital hepatic fibrosis in children. J Pediatr. 1981;99:370–375. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(81)80320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando H, Kaneko K, Ito F, Seo T, Ito T. Operative treatment of congenital stenoses of the intrahepatic bile ducts in patients with choledochal cysts. Am J Surg. 1997;173:491–494. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)00013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselah T, Ernst O, Sergent G, et al. Caroli’s disease: A magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography diagnosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:109. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.109_c.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babitt DP, Starshak RJ, Clemett AR. Choledochal cyst: a concept of etiology. AJR. 1973;119:57–62. doi: 10.2214/ajr.119.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J, Slovis TL. Polycystic disease of the kidney. In: Edelman CM, editor. Pediatric kidney disease. Boston: Little Brown; 1992. pp. 1139–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow C. Cystic disease of the liver associated with a similar disease of the kidneys. Trans Pathol Soc Lond. 1856;7:229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Calvet JP, Grantham JJ. The genetics and physiology of polycystic kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 2001;21:107. doi: 10.1053/snep.2001.20929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet VJ. What is congenital hepatic fibrosis? Histopathology. 1992;20:465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb01031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet VJ. Ludwig symposium on biliary disorders, part I. Pathogenesis of ductal plate abnormalities. Mayo Clin Proc. 1998;73:80. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)63624-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan MJ, Kozakewich H, Perez-Atayde A. Solitary non parasitic cysts of the liver. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med. 1995;15:419–428. doi: 10.3109/15513819509026977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabow PA. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:322–342. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307293290508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay-Woodford LM, Mucher G, Hopkins SD. The severe perinatal form of autosomal rezessive polycystic kidney disease maps to chromosome 6p21.1-p12: implications for genetic counceling. Am J Hum Genet. 1995;56:1101–1107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harjai MM, Bal RK. Caroli syndrome. Pediatr Surg Int. 2000;16:431. doi: 10.1007/s003839900323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman MB, Shapiro HA, Thaler MM. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography in the diagnosis of biliary malformations in infants. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988;34:449–453. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5107(88)71432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi T, Kasahara K, Yasuda Y, et al. Malignant change in biliary tract after excision of choledochal cyst. Br J Surg. 1997;84:1687–1691. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800841212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer FM, Hall RJ, Steward BA, Lilly JR. Congenital biliary tract disease. Surg Clin North Am. 1990;70:1403–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)45291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr DNS, Harrison CV, Sherlock S. Congenital hepatic fibrosis. Q J Med. 1961;30:91–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim MJ, Han SJ, Yoon CS, et al. Using MR cholangiopancreatography to reveal anomalous pancreaticobiliary ductal union in infants and children with choledochal cysts. Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:209. doi: 10.2214/ajr.179.1.1790209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim SH, Lim JH, Yoon HK, et al. Choledochal cyst: Comparison of MR and conventional cholangiography. Clin Radiol. 2000;55:378. doi: 10.1053/crad.2000.0438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koperna T, Vogl S, Satzinger U, Schulz F. Nonparasitic cysts of the liver: Results and options of surgical treatment. World J Surg. 1997;21:850. doi: 10.1007/s002689900316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman E, Salinas-Madrigal L, Gwinn JL. Infantile polycystic kidney disease of the kidney and the liver: clinical pathologic and radiologic correlations and comparison with congenital hepatic fibrosis. Medicine. 1971;50:277–318. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197107000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H, Oya N, Suzuki Y, et al. Is it possible to differentiate between choledochal cyst and congenital biliary atresia (type I cyst) by antenatal ultrasonography? Fetal Diagn Ther. 1997;12:306–308. doi: 10.1159/000264493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyano T, Yamataka A, Kato Y, et al. Hepaticoenterostomy after excision of choledochal cysts in children: a 30-year experience with 180 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 1996;31:1417–1421. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3468(96)90843-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyano T, Yamataka A. Choledochal cysts. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1997;9:283–288. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199706000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T, Yamashita Y, Tang Y, et al. Single-shot MR cholangiopancreaticography of neonates, infants, and young children. Am J Roentgenol. 1998;170:33–37. doi: 10.2214/ajr.170.1.9423593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros E, Navarro S, Bru C, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment of primary hepatolithiasis in Caroli’s syndrome. Lancet. 1993;342:404. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92817-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saing H, Han H, Chan KL, et al. Early and late results of excision of choledochal cysts. J Pediatr Surg. 1997;32:1563–1566. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3468(97)90453-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela-Herman S, Scharschmidt BF. Choledochal cyst, a disease for all ages. Lancet. 1996;23:779. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)90864-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma AK. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticography in the management of choledochal cysts in children. J Pediatr Surg. 1995;30:65–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(95)90612-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P, Kolster E, Davies C, Stringer D, Weber J. Choledochal cysts: clinical presentation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986;5:867–872. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198611000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todani T, Urushihara N, Morotomi Y, et al. Characteristics of choledochal cysts in neonates and early infants. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1995;5:143–145. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1066189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno K, Tsuchida Y, Karawasaki H, Ohmiya H, Honna T. Development of intrahepatic cholelithiasis long after primary excision of choledochal cysts. J Am Coll Surg. 1996;183:583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward CJ, Hogan MC, Rossetti S, et al. The gene mutated in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease encodes a large, receptor-like protein. Nat Genet. 2002;30:259. doi: 10.1038/ng833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M. Congenital choledochal cyst: analysis of 1,433 patients in the Japanese literature. Am J Surg. 1980;140:653–657. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Literatur zu Abschn. 20.4
- Chang MH, Chen C-J, Lai MS, et al. Universal hepatitis B vaccination in Taiwan and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in children. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1855–1859. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199706263362602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czauderna P, Mackinlay G, Perilongo G, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in children: results of the first prospective study of the International Society of Pediatric Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:2798–2804. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.06.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häberle B, Bode U, von Schweinitz D. Differenzierte Therapieansätze für Hoch- und Standardrisiko Hepatoblastome. Klin Pädiatr. 2003;215:159–165. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-39375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers RL, Aronson DC, von Schweinitz D, et al. Pediatric liver tumors. In: Pizzo PA, Poplack DG, et al., editors. Principles and practice of pediatric oncology. 5. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. pp. 838–860. [Google Scholar]
- Perilongo G, Maibach R, Shafford E, et al. Cisplatin versus cisplatin plus doxorubicin for standard risk hepatoblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1662–1670. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard J, Brown J, Shafford E, et al. Cisplatin, doxorubicin, and delayed surgery for childhood heaptoblastoma: a successful approach – results of the first prospective study of the International Society of Pediatric Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3819–3828. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.22.3819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte JB, Aronson DC, Brown J, et al. Liver transplantation for hepatoblastoma: results from the International Society of Pediatric Oncology (SIOP) study SIOPEL-1 and review of the world experience. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2004;42:74–83. doi: 10.1002/pbc.10376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid I, Häberle B, Albert M, et al. Sorafenib and cisplatin/doxorubicin (PLADO) in pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;58:539–544. doi: 10.1002/pbc.23295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schweinitz D. Lebertumoren. In: Gadner H, Gaedicke G, Niemeyer C, Ritter J, editors. Pädiatrische Hämatologie und Onkologie. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer; 2005. pp. 911–921. [Google Scholar]
- von Schweinitz D. Management of liver tumors in childhood. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2006;15:17–24. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2005.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schweinitz DTH, Till H. Maligne viszerale Tumoren des Kindes. In: Siewert JR, editor. Praxis der Viszeralchirurgie. Onkologische Chirurgie. 2. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer; 2010. pp. 813–839. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A, Perilongo G, Malogolowkin M, von Schweinitz D, editors. Pediatric liver tumors. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zsiros J, Maibach R, Shafford E, et al. Successful treatment of childhood high risk hepatoblastoma with dose intensive multiagent chemotherapy and surgery – final results of the SIOPEL-3HR study of the childhood liver tumor strategy group. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2584–2590. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.4857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]