Abstract
This chapter describes the clinical features, and diagnosis of complications in AECHB including secondary bacterial infections, coagulation disorder, water electrolyte disorder, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatopulmonary syndrome and endotoxemia
Patients with severe hepatitis have impaired immunity and are therefore vulnerable to all kinds of infections. After infection, these patients may experience shock, DIC and multiple organ failure, all of which seriously affect their prognosis and are major causes of death. Concurrent infections consist primarily of infections of the lungs, intestines, biliary tract, and urinary tract, as well as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and sepsis.
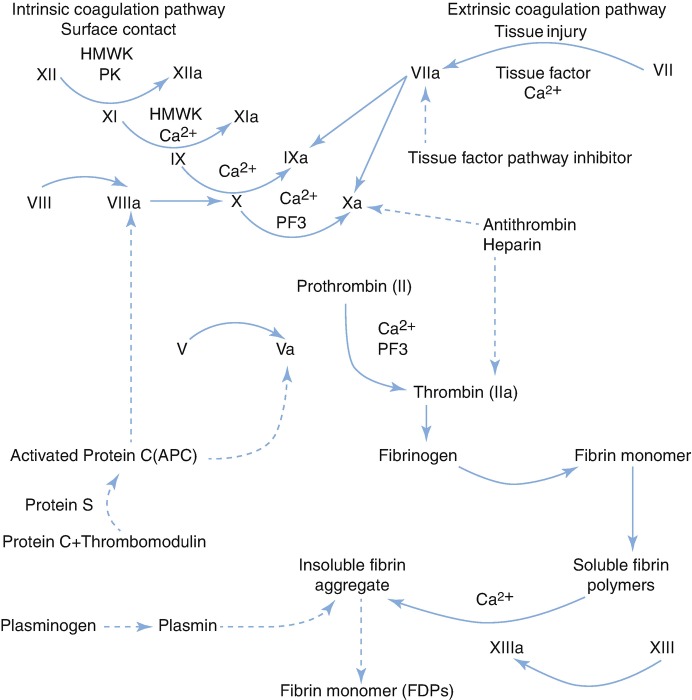
Severe hepatitis may reduce the synthesis of coagulation factors and enhance their dysfunction and increase anticoagulants and platelet abnormalities, leading to coagulopathy. Infection, hepatorenal syndrome and complications can further aggravate coagulopathy, resulting in DIC and seriously affecting patient prognosis.
Hepatorenal syndrome, which is characterized by renal failure, hemodynamic changes in arterial circulation and abnormalities in the endogenous vascular system, is a common clinical complication of end-stage liver disease, and one of the important indicators for the prognosis of patients with severe hepatitis.
Water electrolyte disorder (water retention, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hyperkalaemia) and acid-base imbalance are common in patients with severe hepatitis. These internal environment disorders can lead to exacerbation and complication of the illness.
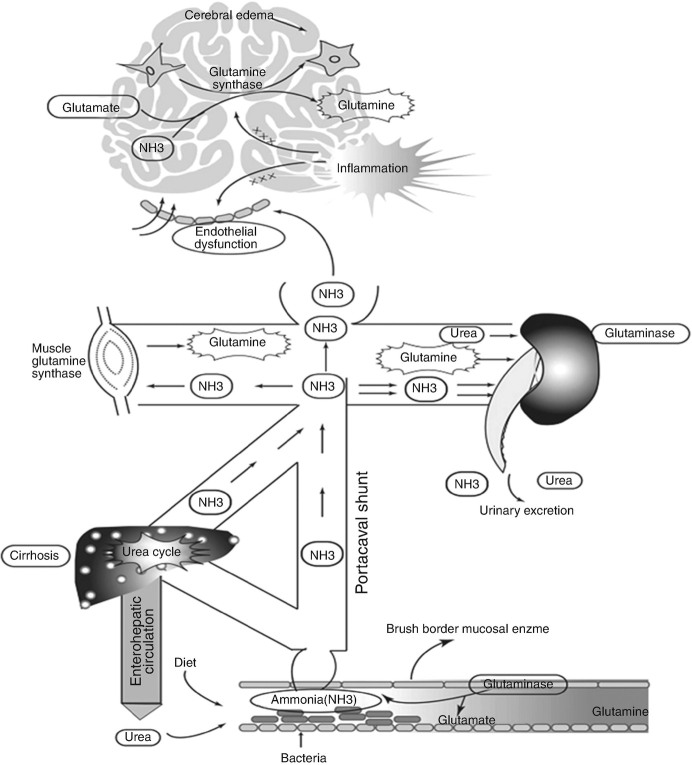
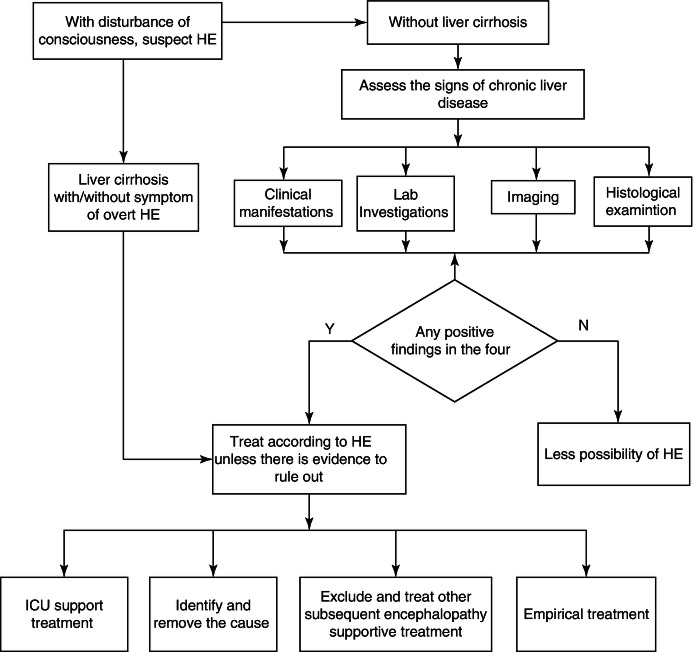
Hepatic encephalopathy is a neurological and psychiatric anomaly syndrome based on metabolic disorder, and an important prognostic indicator for patients with severe hepatitis.
The hepatopulmonary syndrome is an important vascular complication in lungs due to systemic hypoxemia in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. The majority of patients with HPS are asymptomatic. Long-term oxygen therapy remains the most frequently recommended therapy for symptoms in patients with severe hypoxemia.
Endotoxemia, an important complication of severe hepatitis, is not only a second hit to the liver, but also leads to other complications including SIRS and MODS.
References
- 1.Bajaj JS, O’Leary JG, Reddy KR, Wong F, Biggins SW, Patton H, Fallon MB, Garcia-Tsao G, Maliakkal B, Malik R, Subramanian RM, Thacker LR, Kamath PS, North American Consortium For The Study Of End-Stage Liver Disease N Survival in infection-related acute-on-chronic liver failure is defined by extrahepatic organ failures. Hepatology. 2014;60:250–256. doi: 10.1002/hep.27077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang Z, Lu J, Liu M, Wang Y, Qu G, Li H, Wang J, Pang Y, Liu C, Zhao Y. Genotyping and molecular characteristics of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from China. J Infect. 2015;70:335–345. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Godbole G, Shanmugam N, Dhawan A, Verma A. Infectious complications in pediatric acute liver failure. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;53:320–325. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318222b0cd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bilzer M, Roggel F, Gerbes AL. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int. 2006;26:1175–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Acharya SK, Dasarathy S, Irshad M. Prospective study of plasma fibronectin in fulminant hepatitis: association with infection and mortality. J Hepatol. 1995;23:8–13. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(95)80304-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Qin X, Gao B. The complement system in liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2006;3:333–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wyke RJ, Yousif-Kadaru AG, Rajkovic IA, Eddleston AL, Williams R. Serum stimulatory activity and polymorphonuclear leucocyte movement in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982;50:442–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sun S, Guo Y, Zhao G, Zhou X, Li J, Hu J, Yu H, Chen Y, Song H, Qiao F, Xu G, Yang F, Wu Y, Tomlinson S, Duan Z, Zhou Y. Complement and the alternative pathway play an important role in LPS/D-GalN-induced fulminant hepatic failure. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Taylor NJ, Manakkat Vijay GK, Abeles RD, Auzinger G, Bernal W, Ma Y, Wendon JA, Shawcross DL. The severity of circulating neutrophil dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis is associated with 90-day and 1-year mortality. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:705–715. doi: 10.1111/apt.12886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Taylor NJ, Nishtala A, Manakkat Vijay GK, Abeles RD, Auzinger G, Bernal W, Ma Y, Wendon JA, Shawcross DL. Circulating neutrophil dysfunction in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2013;57:1142–1152. doi: 10.1002/hep.26102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liu H, Zhang H, Wan G, Sang Y, Chang Y, Wang X, Zeng H. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: a novel predictor for short-term prognosis in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. J Viral Hepat. 2014;21:499–507. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Metelitsa LS, Naidenko OV, Kant A, Wu HW, Loza MJ, Perussia B, Kronenberg M, Seeger RC. Human NKT cells mediate antitumor cytotoxicity directly by recognizing target cell CD1d with bound ligand or indirectly by producing IL-2 to activate NK cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:3114–3122. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.6.3114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Notas G, Kisseleva T, Brenner D. NK and NKT cells in liver injury and fibrosis. Clin Immunol. 2009;130:16–26. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2008.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tripathy AS, Das R, Chadha MS, Arankalle VA. Epidemic of hepatitis B with high mortality in India: association of fulminant disease with lack of CCL4 and natural killer T cells. J Viral Hepat. 2011;18:e415–e422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dong X, Gong Y, Zeng H, Hao Y, Wang X, Hou J, Wang J, Li J, Zhu Y, Liu H, Han J, Zhou H, Shen L, Gao T, Zhou T, Yang S, Li S, Chen Y, Meng Q, Li H. Imbalance between circulating CD4+ regulatory T and conventional T lymphocytes in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver Int. 2013;33:1517–1526. doi: 10.1111/liv.12248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zou Z, Xu D, Li B, Xin S, Zhang Z, Huang L, Fu J, Yang Y, Jin L, Zhao JM, Shi M, Zhou G, Sun Y, Wang FS. Compartmentalization and its implication for peripheral immunologically-competent cells to the liver in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol Res. 2009;39:1198–1207. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2009.00571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, Purcell RH, Chisari FV. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol. 2003;77:68–76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.1.68-76.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ye Y, Liu J, Lai Q, Zhao Q, Peng L, Xie C, Zhang G, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Zhu J, Huang Y, Hu Z, Xie D, Lin B, Gao Z. Decreases in activated CD8+ T cells in patients with severe hepatitis B are related to outcomes. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:136–145. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang JY, Zhang Z, Lin F, Zou ZS, Xu RN, Jin L, Fu JL, Shi F, Shi M, Wang HF, Wang FS. Interleukin-17-producing CD4(+) T cells increase with severity of liver damage in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2010;51:81–91. doi: 10.1002/hep.23273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fernandez J, Acevedo J, Castro M, Garcia O, de Lope CR, Roca D, Pavesi M, Sola E, Moreira L, Silva A, Seva-Pereira T, Corradi F, Mensa J, Gines P, Arroyo V. Prevalence and risk factors of infections by multiresistant bacteria in cirrhosis: a prospective study. Hepatology. 2012;55:1551–1561. doi: 10.1002/hep.25532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pinzone MR, Celesia BM, Di Rosa M, Cacopardo B, Nunnari G. Microbial translocation in chronic liver diseases. Int J Microbiol. 2012;2012:694629. doi: 10.1155/2012/694629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rai R, Saraswat VA, Dhiman RK. Gut microbiota: its role in hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2015;5:S29–S36. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bauer TM, Schwacha H, Steinbruckner B, Brinkmann FE, Ditzen AK, Aponte JJ, Pelz K, Berger D, Kist M, Blum HE. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in human cirrhosis is associated with systemic endotoxemia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:2364–2370. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang XD, Soltesz V, Andersson R, Bengmark S. Bacterial translocation in acute liver failure induced by 90 per cent hepatectomy in the rat. Br J Surg. 1993;80:66–71. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Verbeke L, Nevens F, Laleman W. Bench-to-beside review: acute-on-chronic liver failure - linking the gut, liver and systemic circulation. Crit Care. 2011;15:233. doi: 10.1186/cc10424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fukui H. Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:425–442. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Su HB, Wang HF, Lin F, Xu HM, Zhao H, Li L, Yan T, Mou JS, Li C. Retrospective study of liver failure complicated with bacterium and fungous infection. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2007;21:229–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang XH, Zhang GH, Man CJ, He FM. Clinical study on the severe hepatitis with nosocomial fungal infections and risk factors. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2004;12:389–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koulaouzidis A. Diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: an update on leucocyte esterase reagent strips. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1091–1094. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i9.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Koulaouzidis A, Bhat S, Saeed AA. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:1042–1049. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Madrid AM, Cumsille F, Defilippi C. Altered small bowel motility in patients with liver cirrhosis depends on severity of liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42:738–742. doi: 10.1023/a:1018899611006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chiva M, Guarner C, Peralta C, Llovet T, Gomez G, Soriano G, Balanzo J. Intestinal mucosal oxidative damage and bacterial translocation in cirrhotic rats. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15:145–150. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200302000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ramachandran A, Prabhu R, Thomas S, Reddy JB, Pulimood A, Balasubramanian KA. Intestinal mucosal alterations in experimental cirrhosis in the rat: role of oxygen free radicals. Hepatology. 2002;35:622–629. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.European Association for the Study of the Liver EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2010;53:397–417. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Runyon BA. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012. Hepatology. 2013;57:1651–1653. doi: 10.1002/hep.26359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rimola A, Garcia-Tsao G, Navasa M, Piddock LJ, Planas R, Bernard B, Inadomi JM. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a consensus document. International Ascites Club. J Hepatol. 2000;32:142–153. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(00)80201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Eccles S, Pincus C, Higgins B, Woodhead M. Diagnosis and management of community and hospital acquired pneumonia in adults: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2014;349:g6722. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mandell LA. Community-acquired pneumonia: An overview. Postgrad Med. 2015;127:607–615. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2015.1074030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Caly WR, Strauss E. A prospective study of bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 1993;18:353–358. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rolando N, Kramer DJ. Scenario number one: sepsis and ARDS before liver transplantation. Liver Transpl Surg. 1997;3:60–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rolando N, Harvey F, Brahm J, Philpott-Howard J, Alexander G, Casewell M, Fagan E, Williams R. Fungal infection: a common, unrecognised complication of acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 1991;12:1–9. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90900-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hassan EA, Abd El-Rehim AS, Hassany SM, Ahmed AO, Elsherbiny NM, Mohammed MH. Fungal infection in patients with end-stage liver disease: low frequency or low index of suspicion. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;23:69–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2013.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kups J, Wozniakowska-Gesicka T, al-Batool K. Fungal infection in the course of acute liver failure. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002;13:165–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chen J, Yang Q, Huang J, Li L. Risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and hospital mortality in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients: a retrospective-cohort study. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10:1625–1631. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shroff S, Shroff GS, Yust-Katz S, Olar A, Tummala S, Tremont-Lukats IW. The CT halo sign in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Case Rep. 2014;2:113–114. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Deeren DH. The Importance of Previous CT Scans in the Diagnosis of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Ther Adv Hematol. 2011;2:121–122. doi: 10.1177/2040620711402416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Caillot D, Latrabe V, Thiebaut A, Herbrecht R, De Botton S, Pigneux A, Monchecourt F, Mahi L, Alfandari S, Couaillier JF. Computer tomography in pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in hematological patients with neutropenia: an useful tool for diagnosis and assessment of outcome in clinical trials. Eur J Radiol. 2010;74:e172–e175. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.05.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Docke WD, Prosch S, Fietze E, Kimel V, Zuckermann H, Klug C, Syrbe U, Kruger DH, von Baehr R, Volk HD. Cytomegalovirus reactivation and tumour necrosis factor. Lancet. 1994;343:268–269. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Varani S, Lazzarotto T, Margotti M, Masi L, Gramantieri L, Bolondi L, Landini MP. Laboratory signs of acute or recent cytomegalovirus infection are common in cirrhosis of the liver. J Med Virol. 2000;62:25–28. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(200009)62:1<25::aid-jmv4>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Knollmann FD, Maurer J, Bechstein WO, Vogl TJ, Neuhaus P, Felix R. Pulmonary disease in liver transplant recipients. Spectrum of CT features. Acta Radiol. 2000;41:230–236. doi: 10.1080/028418500127345406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dhiman RK, Saraswat VA, Rajekar H, Reddy C, Chawla YK. A guide to the management of tuberculosis in patients with chronic liver disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2012;2:260–270. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2012.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Menzies D, Pai M, Comstock G. Meta-analysis: new tests for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: areas of uncertainty and recommendations for research. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:340–354. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-146-5-200703060-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pai M, Zwerling A, Menzies D. Systematic review: T-cell-based assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection: an update. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:177–184. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-149-3-200808050-00241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ferrara G, Losi M, Meacci M, Meccugni B, Piro R, Roversi P, Bergamini BM, D’Amico R, Marchegiano P, Rumpianesi F, Fabbri LM, Richeldi L. Routine hospital use of a new commercial whole blood interferon-gamma assay for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:631–635. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200502-196OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gangadharam PR. Microbiology of nontuberculosis mycobacteria. Semin Respir Infect. 1996;11:231–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Atilla A, Aydin S, Demirdoven AN, Kilic SS. Severe toxoplasmic hepatitis in an immunocompetent patient. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2015; [DOI] [PubMed]
- 57.Bartelt LA, Sartor RB. Advances in understanding Giardia: determinants and mechanisms of chronic sequelae. F1000Prime Rep. 2015;7:62. doi: 10.12703/P7-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Buonfrate D, Formenti F, Perandin F, Bisoffi Z. Novel approaches to the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21:543–552. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Nakajima T. Roles of sulfur metabolism and rhodanese in detoxification and anti-oxidative stress functions in the liver: responses to radiation exposure. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1721–1725. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Muciñobermejo J, Carrilloesper R, Uribe M, et al. Coagulation abnormalities in the cirrhotic patient. Ann Hepatol. 2013;12:713–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Mihaila R, Dragomir I. Advances of knowledge on coagulation disorders in liver cirrhosis and their clinical consequences. Biomed Res. 2015;26:625–632. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mirsaeva GK, Mironchuk NN. Features of coagulation hemostasis and anticoagulation system in patients with chronic heart failure due to ischemic heart disease. Kazan Med J. 2015;96(5):716–722. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Valla DC, Rautou PE. The coagulation system in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Int. 2015;35(Suppl 1):139–144. doi: 10.1111/liv.12723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jeon YJ, Kim YR, Bo EL, et al. Association of five common polymorphisms in the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene with primary ovarian insufficiency. Fertil Steril. 2014;101:825–832. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Okafor ON, Gorog DA. Endogenous fibrinolysis: an important mediator of thrombus formation and cardiovascular risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1683–1699. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.02.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pallister CJ, Watson MS. Haematology. Banbury: Scion; 2010. pp. 336–347. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Heinz S, Braspenning J. Measurement of blood coagulation factor synthesis in cultures of human hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1250:309–316. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2074-7_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kopec AK, Luyendyk JP. Coagulation in liver toxicity and disease: Role of hepatocyte tissue factor. Thromb Res. 2014;133:S57–S59. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.03.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Valla DC, Rautou PE. The coagulation system in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Int. 2015;35(Suppl 1):139–144. doi: 10.1111/liv.12723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gutenberg P. Coagulation factor V deficiency. Phlebology. 2016;34:160–166. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pluta A, Gutkowski K, Hartleb M. Treatment of coagulopathies in severe liver disease. Postepy Nauk Medycznych. 2010:63–8.
- 72.Jin YH, Wang MS, Zheng FX, et al. Molecular genetics and clinical features of nine patients with inherited coagulation factor VII deficiency. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2012;29:404–407. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2012.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Math SK, Sanders MA, Hollensead SC. Unexpected laboratory diagnosis: Acquired dysfibrinogenemia in a bleeding patient with liver disease. MLO Med Lab Obs. 2010;42 [PubMed]
- 74.Chen W, Wang D, Ni N, et al. A fast and simple approach to the quantitative evaluation of fibrinogen coagulation. Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36:337–340. doi: 10.1007/s10529-013-1365-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Schroeder V, Handrková H, Dodt J, et al. Free factor XIII activation peptide affects factor XIII function. Br J Haematol. 2014;168:757–759. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Komáromi I, Bagoly Z, Muszbek L. Factor XIII: novel structural and functional aspects. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Samis JA, Stewart KA, Nesheim ME, et al. Factor V cleavage and inactivation are temporally associated with elevated elastase during experimental sepsis. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:2559–2561. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Wheeler AP, Gailani D. The intrinsic pathway of coagulation as a target for antithrombotic therapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2016;30:1099–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2016.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kozarcanin H, Lood C, Munthe-Fog L, et al. The lectin complement pathway serine proteases (MASPs) represent a possible crossroad between the coagulation and complement systems in thromboinflammation. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:802–807. doi: 10.1111/jth.13208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Annich G. M. Extracorporeal life support: the precarious balance of hemostasis. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2015;13:S336–S342. doi: 10.1111/jth.12963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chalupa P, Holub M. Favorable Outcome of Severe Acute Hepatitis B in a Patient Treated with Antithrombin III and Antiviral Therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:481. doi: 10.1086/600822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Huang N, Rodriguez R L, Hagie F E, et al. Monocot seed product comprising a human serum albumin protein: US, US 8158857 B2[P]. 2012.
- 83.Kutcher ME, Ferguson AR, Cohen MJ. A principal component analysis of coagulation after trauma. J Trauma Injury Infect Crit Care. 2013;74:1223–1229. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31828b7fa1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Okamoto K, Tamura T, Yamaguchi K. Clinical trials of anticoagulants and anticoagulant factor concentrates for the management of DIC in Japan. Rinsho Byori. 2011;Suppl 147:95–103. [PubMed]
- 85.Mann HJ, Short MA, Schlichting DE. Protein C in critical illness. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009;66:1089–1096. doi: 10.2146/ajhp080276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kruithof EK, Dunoyer-Geindre S. Human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Thromb Haemost. 2014;112:243–254. doi: 10.1160/TH13-06-0517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jankun J, Aleem AM, Selman SH, et al. Highly stable plasminogen activator inhibitor type one (VLHL PAI-1) protects fibrin clots from tissue plasminogen activator-mediated fibrinolysis. Int J Mol Med. 2007;20:683–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Martí-Carvajal AJ, Cardona AF, Simancas D. Treatment for disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with acute and chronic leukemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;66:1–2. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008562.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Frith D, Brohi K. The pathophysiology of trauma-induced coagulopathy. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2012;18(6):631–636. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0b013e3283599ab9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Agren A, Wiman B, Schulman S. Laboratory evidence of hyperfibrinolysis in association with low PAI-1 activity. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2007;18:657–660. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e3282dded21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Carvalho M, Rodrigues A, Gomes M, et al. Interventional algorithms for the control of coagulopathic bleeding in surgical, trauma, and postpartum settings: recommendations from the Share Network Group. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016;22:1593–1600. doi: 10.1177/1076029614559773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Surawong A, Rojnuckarin P, Juntiang J, et al. Hyperfibrinolysis and the risk of hemorrhage in stable cirrhotic patients. Asian Biomed. 2010;4:199–206. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Fohlen-Walter A, Maistre ED, Mulot A, et al. Does negative heparin-platelet factor 4 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay effectively exclude heparin-induced thrombocytopenia? J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:1844–1845. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lehmann JP. Endogenous plasma activated protein C levels and the effect of enoxaparin and drotrecogin alfa (activated) on markers of coagulation activation and fibrinolysis in pulmonary embolism. Crit Care. 2011;15:1–10. doi: 10.1186/cc9968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yousif M., Hassanein O., Salim I., Said N. 774 ROLE OF ENDOGENOUS HEPARINOIDS AND BACERIAL INFECTION IN BLEEDING FROM ESOPHAGEAL VARICES COMPLICATING LIVER CIRRHOSIS. Journal of Hepatology. 2009;50:S284. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Blich M, Golan A, Arvatz G, et al. Macrophages activation by heparanase is mediated by TLR-2 and TLR-4 and associates with plaque progression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:e56–e65. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.254961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lentz BR. Exposure of platelet membrane phosphatidylserine regulates blood coagulation. Prog Lipid Res. 2003;42:423–438. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7827(03)00025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kuharsky AL, Fogelson AL. Surface-mediated control of blood coagulation: the role of binding site densities and platelet deposition. Biophys J. 2001;80:1050–1074. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76085-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Crow AR, Leytin V, Starkey AF, et al. CD154 (CD40 ligand)-deficient mice exhibit prolonged bleeding time and decreased shear-induced platelet aggregates. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:850–852. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.t01-1-00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Jiang XW, Fei G, Yan M, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation in the spleen for treatment of hypersplenism in cirrhosis patients. Digest Dis Sci. 2015;61:1–6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3732-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Tomikawa M, Akahoshi T, Sugimachi K, et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy may be a superior supportive intervention for cirrhotic patients with hypersplenism. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:397–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kuter DJ, Gernsheimer TB. Thrombopoietin and platelet production in chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:1193–1211. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2009.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bachman DE, Forman MA, Hostutler RA, et al. Prospective diagnostic accuracy evaluation and clinical utilization of a modified assay for platelet-associated immunoglobulin in thrombocytopenic and nonthrombocytopenic dogs. Vet Clin Pathol. 2015;44:355–368. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Melissa V. Chan, Rebecca B. M. Knowles, Lundberg M H, et al. P2Y 12, receptor blockade synergises strongly with nitric oxide and prostacyclin to inhibit platelet activation. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2015, 81:621–633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 105.De Haas CJC, Weeterings C, Vughs MM, et al. Staphylococcal superantigen-like 5 activates platelets and supports platelet adhesion under flow conditions, which involves glycoprotein Ibα and α IIb β 3. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7:1867–1874. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Soares CV, Lima A, et al. Liver disease and gastrointestinal bleeding in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia - case report. Jornal Português De Gastrenterologia. 2010:213–6.
- 107.Philips C, Mukhopadhyay P. Hemostasis, disorders of coagulation and transfusion in cirrhosis. J Franklin Inst. 2015;64:123–124. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Arroyo V, Fernandez J, Ginès P. Pathogenesis and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:81–95. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Tandon P, Garcia-Tsao G. Bacterial infections, sepsis, and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:26–42. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Cho J, Sun MC, Yu SJ, et al. Bleeding complications in critically ill patients with liver cirrhosis. Korean J Intern Med. 2013;31:288–295. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2014.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Sillermatula JM, Schwameis M, Blann A, et al. Thrombin as a multi-functional enzyme. Focus on in vitro and in vivo effects. Thromb Haemost. 2011;106:1020–1033. doi: 10.1160/TH10-11-0711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Tripodi A, Anstee QM, Sogaard KK, et al. Hypercoagulability in cirrhosis: causes and consequences 1. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:1713–1723. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Presseizen K, Friedman Z, Shapiro H, et al. Phosphatidylserine expression on the platelet membrane of patients with myeloproliferative disorders and its effect on platelet-dependent thrombin formation. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2002;8:33–39. doi: 10.1177/107602960200800104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Ali M, Ananthakrishnan AN, Mcginley EL, et al. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis: a nationwide analysis. Digest Dis Sci. 2011;56:2152–2159. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Kamran BL, Katayon H, Dorna M, et al. Risk factors for portal vein thrombosis in patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation in Shiraz, Iran. Hepat Mon. 2015;15:e26407. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.26407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Jacobs BS, Levine SR. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2012;2:449–457. doi: 10.1007/s11940-000-0043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Soule HR, Brunck TK. Blood coagulation protein antagonists and uses therefor: EP, US 6221659 B1[P] 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Weingarten MA, Sande AA. Acute liver failure in dogs and cats. J Vet Emerg Crit Care. 2015;25:455–473. doi: 10.1111/vec.12304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Asakura H. Classifying types of disseminated intravascular coagulation: clinical and animal models. J Intensive Care. 2014;2:1–7. doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-2-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Seth D, Haber PS, Syn WK, et al. Pathogenesis of alcohol-induced liver disease: classical concepts and recent advances. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:1089–1105. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Collen D. Thrombin-antithrombin III and plasmin-antiplasmin complexes as indicators of in vivo activation of the coagulation and/or fibrinolytic systems. Pier Working Paper Archive. 2006;32:398–402. doi: 10.1080/17843286.1977.11717894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Giannoni P, Pietra G, Travaini G, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia nurse-like cells express hepatocyte growth factor receptor (c-MET) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and display features of immunosuppressive type 2 skewed macrophages. Haematologica. 2014;99:1078–1087. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.091405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Pluta A, Gutkowski K, Hartleb M. Coagulopathy in liver diseases. Adv Med Sci. 2010;55:16–21. doi: 10.2478/v10039-010-0018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Jablonka W, Kotsyfakis M, Mizurini DM, et al. Identification and mechanistic analysis of a novel tick-derived inhibitor of thrombin. PLoS One. 2014;10:e0133991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gajos G, Zalewski J, Undas A. Low fasting glucose is associated with enhanced thrombin generation and unfavorable fibrin clot properties in diabetics with high cardiovascular risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:476–480. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0207-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Weijers EM, Wijhe MHV, Joosten L, et al. Molecular weight fibrinogen variants alter gene expression and functional characteristics of human endothelial cells. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8:2800–2809. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Chen CS, Cumbler EU, Triebling AT. Coagulopathy due to celiac disease presenting as intramuscular hemorrhage. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22:1608–1612. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0297-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Birchall J, Doree C, Gill R, et al. Recombinant factor VIIa for the prevention and treatment of bleeding in patients without haemophilia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;20:93–103. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005011.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Wang L, Bastarache JA, Ware LB. The coagulation cascade in sepsis. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14:1860–1869. doi: 10.2174/138161208784980581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Abdel-Razik A, Mousa N, Elhelaly R, et al. De-novo portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis: risk factors and correlation with the model for end-stage liver disease scoring system. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27:585–592. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Baumann Kreuziger LM, Datta YH, Johnson AD, et al. Monitoring anticoagulation in patients with an unreliable PT/INR: factor II versus chromogenic factor X testing. Am J Hematol. 2014;87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 132.Tripodi A, Chantarangkul V, Primignani M, et al. The international normalized ratio calibrated for cirrhosis (INR liver) normalizes prothrombin time results for model for end-stage liver disease calculation †. Hepatology. 2007;46(2):520–527. doi: 10.1002/hep.21732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Shiozawa Y, Fujita H, Fujimura J, et al. A fetal case of transient abnormal myelopoiesis with severe liver failure in Down syndrome: prognostic value of serum markers. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2004;21:273–278. doi: 10.1080/08880010490277088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Liu XY, Hu JH, Wang HF. Analysis of prognostic factors for patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Chin J Hepatol. 2009;17:607–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Lippi G, Favaloro EJ. Activated partial thromboplastin time: new tricks for an old dogma. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2008;34:604–611. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1104539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Wu SJ, Yan HD, Zheng ZX, et al. Establishment and validation of ALPH-Q score to predict mortality risk in patients with acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure: a prospective cohort study. Medicine. 2015;94:e403. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Tobias JD, Berkenbosch JW. Synthetic factor VIIa concentrate to treat coagulopathy and gastrointestinal bleeding in an infant with end-stage liver disease. Clin Pediatr. 2002;41:613–616. doi: 10.1177/000992280204100810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Chen J, Duan ZP, Bai L, et al. Changing characteristic of blood coagulation factors and their correlation with blood coagulation status in different hepatic diseases. Chin J Hepatol. 2012;20:206–210. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2012.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Berkessy S. The plasma-protamine-paracoagulation-(3-P-) test. Zeitschrift Für Die Gesamte Innere Medizin Und Ihre Grenzgebiete. 1974;29:491–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Timan IS, Aulia D, Enny. The use of ethanol gelation test to screen the activation of coagulation and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Lab Med Qual Assur, 2003, 25:231–235.
- 141.Venkata NRE, Divakar G. An overview on microbial fibrinolytic proteases. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2014;5:643–656. [Google Scholar]
- 142.Nair GB, Lajin M, Muslimani A. A cirrhotic patient with spontaneous intramuscular hematoma due to primary hyperfibrinolysis. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2011;9:249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Sartori MT, Spiezia L, Cesaro S, et al. Role of fibrinolytic and clotting parameters in the diagnosis of liver veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a pediatric population. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:682–689. doi: 10.1160/TH04-09-0621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Koyama K, Madoiwa S, Nunomiya S, et al. Combination of thrombin-antithrombin complex, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and protein C activity for early identification of severe coagulopathy in initial phase of sepsis: a prospective observational study. Crit Care. 2014;18:1–11. doi: 10.1186/cc13190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Seto WK, Lai CL, Yuen MF. Acute-on-chronic liver failure in chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:662–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Zanetto A, Senzolo M, Ferrarese A, et al. Assessment of bleeding risk in patients with cirrhosis. Curr Hepatol Rep. 2015;14:9–18. [Google Scholar]
- 147.Bailey MA, Griffin KJ, Sohrabi S, et al. Plasma thrombin-antithrombin complex, prothrombin fragments 1 and 2, and D-dimer levels are elevated after endovascular but not open repair of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57:1512–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Lisman T, Bakhtiari K, Adelmeijer J, et al. Intact thrombin generation and decreased fibrinolytic capacity in patients with acute liver injury or acute liver failure. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10:1312–1319. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Aso Y, Matsumoto S, Fujiwara Y, et al. Impaired fibrinolytic compensation for hypercoagulability in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: association with increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Metabolism. 2002;51:471–476. doi: 10.1053/meta.2002.31334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Levi M, De JE, Meijers J. The diagnosis of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood Rev. 2003;16:217–223. doi: 10.1016/s0268-960x(02)00032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Kawasugi K, Wada H, Hatada T, et al. Prospective evaluation of hemostatic abnormalities in overt DIC due to various underlying diseases. Thromb Res. 2011;128:186–190. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Tang XH, Qiang LI, Lin WH, et al. Establishment and evaluation of a modified plasma protamine paracoagulation test. J Southern Med Univ. 2011;31:1626–1628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Olson JD. D-dimer: an overview of hemostasis and fibrinolysis, assays, and clinical applications. Adv Clin Chem. 2015;69:1–46. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Lippi G, Favaloro EJ, Cervellin G. Massive posttraumatic bleeding: epidemiology, causes, clinical features, and therapeutic management. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2013;39:83–93. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Bhalla A, Suri V, Singh V. Malarial hepatopathy. J Postgrad Med. 2006;52:315–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Wada H, Matsumoto T, Yamashita Y. Diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) according to four DIC guidelines. J Intensive Care. 2014;2:15. doi: 10.1186/2052-0492-2-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Heuft MM, Houba SM, Ge VDB, et al. Protective effect of hepatitis B virus-active antiretroviral therapy against primary hepatitis B virus infection. AIDS. 2014;28:999–1005. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kozeklangenecker SA. Fluids and coagulation. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2015;21:517–524. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Bhatia V, Lodha R. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Indian J Pediatr. 2011;78:227–233. doi: 10.1007/s12098-010-0296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Seo YS, Kim YH, Ahn SH, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis. J Korean Med Sci. 2008;23:635–643. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Franchis RD. Somatostatin, somatostatin analogues and other vasoactive drugs in the treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36(Suppl 1):S93–S100. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2003.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Barkun AN, Sarvee M, Myriam M. Topical hemostatic agents: a systematic review with particular emphasis on endoscopic application in GI bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;77:692–700. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Olsen KM. Use of acid-suppression therapy for treatment of non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005;62:18–23. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/62.10_Supplement_2.S18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, et al. Portal hypertension and gastrointestinal bleeding. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:3–25. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Tan XP. Observed the effect of Improved three-balloon catheter tube method in cirrhotic patients with gastrointestinal bleeding. Today Nurse. 2014;
- 166.Barkun A, Sabbah S, Enns R, et al. The Canadian Registry on Nonvariceal Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding and Endoscopy (RUGBE): Endoscopic hemostasis and proton pump inhibition are associated with improved outcomes in a real-life setting. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1238–1246. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Jovanovic I, Vormbrock K, Wilcox CM, et al. Therapeutic and interventional endoscopy for gastrointestinal bleeding. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2011;37:339–351. doi: 10.1007/s00068-011-0125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Dempfle CE, Borggrefe M. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Intensivmedizin Und Notfallmedizin. 2006;43:103–110. [Google Scholar]
- 169.Saito H, Maruyama I, Shimazaki S, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (ART-123) in disseminated intravascular coagulation: results of a phase III, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Yamanouchi M, Ubara Y, Mise K, et al. Hemodialysis without Anticoagulation for a Patient with Chronic Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Case Rep Nephrol Urol. 2014;4:25–30. doi: 10.1159/000358269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Alessandria C, Ozdogan O, Guevara M, Restuccia T, Jimenez W, Arroyo V, et al. MELD score and clinical type predict prognosis in hepatorenal syndrome: relevance to liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2005;41:1282–1289. doi: 10.1002/hep.20687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Ginės P, Guevara M, Arroyo V, et al. Hepatorenal syndrome. Lancet. 2003;362:1819–1827. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.O’Grady JG. Clinical disorders of renal function in acute liver failure. In: Gines P, Arroyo V, Rodes J, Schrier RW, editors. Ascites and renal dysfunction in liver disease. 2. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2005. pp. 383–393. [Google Scholar]
- 174.Flint A. Clinical report on hydroperitoneum based on analysis of 46 cases. Am J MedSci. 1963;45:306e39. [Google Scholar]
- 175.Bartoli E, Chiandussi L, editors. Hepato-Renal Syndrome. Padua: Piccin Medical Books; 1979. [Google Scholar]
- 176.Arroyo V, Gines P, Gerbes AL, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Int Ascites Club Hepatol. 1996;23:164e76. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Salerno F, Gerbes A, Gines P, Wong F, Arroyo V. Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Gut. 2007;56:1310–1318. doi: 10.1136/gut.2006.107789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Wong F, Nadim MK, Kellum JA, Salerno F, Bellomo R, Gerbes A, Angeli P, et al. Working Party proposal for a revised classification system of renal dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 2011;60:702–709. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.236133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Davis CL, Feng S, Sung R, Wong F, Goodrich NP, Melton LB, Reddy KR, et al. Simultaneous liver-kidney transplantation: evaluation to decision making. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:1702–1709. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Laleman W. Role of vasoactive substances and cellular effectors in the pathophysiology of cirrhotic portal hypertension: the past, the present and the future--Georges Brohe’e Lecture. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2009;72:9e16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Colle I, Geerts AM, Van Steenkiste C, et al. Hemodynamic changes in splanchnic blood vessels in portal hypertension. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2008;291:699e713. doi: 10.1002/ar.20667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Rodrìguez-Vilarrupla A, Fernàndez M, Bosch J, et al. Current concepts on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension. Ann Hepatol. 2007;6:28e36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Blendis L, Wong F. The hyperdynamic circulation in cirrhosis: an overview. Pharmacol Ther. 2001;89:221e31. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(01)00124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Wong F, Pantea L, Sniderman K. Midodrine, octreotide, albumin, and TIPS in selected patients with cirrhosis and type 1 hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatology. 2004;40:55e64. doi: 10.1002/hep.20262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Wong F, Sniderman K, Liu P, et al. The effects of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on systemic and renal hemodynamics and sodium homeostasis in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122:816e22. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-11-199506010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Arroyo V, Terra C, Gines P. Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of type-1 and type-2 hepatorenal syndrome. J Hepatol. 2007;46:935e46. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Bernadich C, Bandi JC, Piera C, et al. Circulatory effects of graded diversion of portal blood flow to the systemic circulation in rats: role of nitric oxide. Hepatology. 1997;26:262e7. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Bosch J, Pizcueta MP, Fernandez M, et al. Hepatic, splanchnic and systemic haemodynamic abnormalities in portal hypertension. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1992;6:425e36. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(92)90030-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Garcia-Tsao G, Parikh CR, Viola A. Acute kidney injury in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:2064–2077. doi: 10.1002/hep.22605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Schrier RW, Arroyo V, Bernardi M, Epstein M, Henriksen JH, Rodes J. Peripheral arterial vasodilation hypothesis: a proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988;8:1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Iwakiri Y, Groszmann RJ. The hyperdynamic circulation of chronic liver diseases: from the patient to the molecule. Hepatology. 2006;43:S121–S131. doi: 10.1002/hep.20993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Ginès A, Escorsell A, Ginès P, et al. Incidence, predictive factors, and prognosis of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis with ascites. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:229–236. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Lata J. Hepatorenal syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:4978–4984. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Salerno F, Cazzaniga M, Merli M, Spinzi G, Saibeni S, Salmi A, Fagiuoli S, et al. Diagnosis, treatment and survival of patients with hepatorenal syndrome: a survey on daily medical practice. J Hepatol. 2011;55:1241–1248. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Zakim B, et al. Hepatology [M]. 6th ed: Elsevier Medicine; 2011.
- 196.Seu P, Wilkinson AH, Shaked A, et al. The hepatorenal syndrome in liver transplant recipients. Ann Surg. 1991;57:806–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Sanyal AJ, Boyer T, Garcia-Tsao G, Regenstein F, et al. A randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of terlipressin for type 1 hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1360–1368. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Martin-Llahi M, Pepin MN, Guevara M, Diaz F, Torre A, Monescillo A, Soriano G, et al. Terlipressin and albumin vs albumin in patients with cirrhosis and hepatorenal syndrome: a randomized study. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1352–1359. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Moreau R, Durand F, Poynard T, et al. Terlipressin in patients with cirrhosis and type 1 hepatorenal syndrome: a retrospective multicenter study. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:923–930. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.32364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Solanki P, Chawla A, Garg R, et al. Beneficial effects of terlipressin in hepatorenal syndrome: a prospective, randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18:152–156. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.02934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Lavayssiere L, Kallab S, Cardeau-Desangles I, et al. Impact of molecular adsorbent recirculating system on renal recovery in type-1 hepatorenal syndrome patients with chronic liver failure. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:1019–1024. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Wong F, Raina N, Richardson R. Molecular adsorbent recirculating system is ineffective in the management of type 1 hepatorenal syndrome in patients with cirrhosis and ascites who have failed vasoconstrictor treatment. Gut. 2010;59:381–386. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.174615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Mitzner SR, Stange J, Klammt S, et al. Improvement of hepatorenal syndrome with extracorporeal albumin dialysis MARS: Results of a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Liver Transpl. 2000;6:277–286. doi: 10.1002/lt.500060326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Heemann U, Treichel U, Loock J, et al. A dialysis in cirrhosis with superimposed acute liver injury: a prospective, controlled study. Hepatology. 2002;36:949–958. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.36130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Ochs A, Rössle M, Haag K, Hauenstein KH, et al. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for refractory ascites. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1192–1197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199505043321803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Somberg KA, Lake JR, Tomlanovich SJ, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts for refractory ascites: assessment of clinical and hormonal response and renal function. Hepatology. 1995;21:709–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Ginès P, Uriz J, Calahorra B, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting versus paracentesis plus albumin for refractory ascites in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1839–1847. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.37073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Michl P, Gulberg V, Bilzer M, Waggershauser T, Reiser M, Gerbes AL. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for cirrhosis and ascites: effects in patients with organic or functional renal failure. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000;35:654–658. doi: 10.1080/003655200750023642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Marcela K. Hepatorenal syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(36):4978–4984. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i36.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Fasolato S, Angeli P, Dallagnese L, et al. Renal failure and bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis: epidemiology and clinical features. Hepatology. 2007;45:223–229. doi: 10.1002/hep.21443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Thabut D, Massard J, Gangloff A, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease score and systemic inflammatory response are major prognostic factors in patients with cirrhosis and acute functional renal failure. Hepatology. 2007;46:1872–1882. doi: 10.1002/hep.21920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Dundar HZ, Yılmazlar T, et al. Management of hepatorenal syndrome. World J Nephrol. 2015;4(2):277–286. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Fernandez J, Navasa M, Planas R, et al. Primary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis delays hepatorenal syndrome and improves survival in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:818–824. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.06.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Huang K, Hu JH, Wang HF, He WP, Chen J, Duan XZ, Zhang AM, Liu XY. Survival and prognostic factors in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(29):3448–3452. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i29.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Kaufman CE, Mckee PA. Essentials of pathophysiology. 1. Beijing: Peaking Union Medical College Press; 2002. p. 547. [Google Scholar]
- 216.Jianzhi W, Huiming J. Textbook of pathophysiology. 1. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2007. p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- 217.Juha P Kokko. Disorder of fluid volume, electrolyte, and acid-base balance. J Claude Bennett, FredPlum. Cecil textbook of medicine. 20th ed. W.B.Saunders company, 1996, 525.
- 218.Henriksen JH, Bendtsen F, Møller S. Acid-base disturbance in patients with cirrhosis: relation to hemodynamic dysfunction. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27(8):920–927. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Benjaminov FS. The pathophysiology of ascites formation in cirrhosis of the liver. Harefuah. 2002;141(8):721–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Korzelius C, Schrier RW, Sterns RH, Thompson CJ. Diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of hyponatremia: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. 2013;126(10 Suppl 1):S1–42. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Cárdenas A, Solà E, Rodríguez E, Barreto R, Graupera I, Pavesi M, Saliba F, Welzel T, Martinez-Gonzalez J, Gustot T, Bernardi M, Arroyo V, Ginès P; CANONIC study investigators of the EASL-CLIF Consortium. Hyponatremia influences the outcome of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure: an analysis of the CANONIC study. Crit Care. 2014, 18(6):700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 222.Diercks DB, Shumaik GM, Harrigan RA, Brady WJ, Chan TC. Electrocardiographic manifestations: electrolyte abnormalities. J Emerg Med. 2004;27(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2004.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Li XM, Li YX, Meng QH, Duan ZH, Hou W, Li J. Characteristics of acid-base balance in patients with chronic severe hepatitis: analysis of 126 cases. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Aug 15;86(30):2131–3(in Chinese). [PubMed]
- 224.Kaufman CE, Mckee PA. Essentials of pathophysiology. 1. Beijing: Peaking Union Medical College Press; 2002. p. 569. [Google Scholar]
- 225.Abelow B. Understanding acid-base. 1. Baltimore: Lippincott, Williams&Wilkins; 1998. p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- 226.Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy--definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;35:716–721. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.31250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.(2013) [Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 21: 641–651. [PubMed]
- 228.Bajaj JS, Cordoba J, Mullen KD, Amodio P, Shawcross DL, et al. Review article: the design of clinical trials in hepatic encephalopathy--an International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism (ISHEN) consensus statement. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33:739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04590.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Lauridsen MM, Poulsen L, Rasmussen CK, Hogild M, Nielsen MK, et al. Effects of common chronic medical conditions on psychometric tests used to diagnose minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2016;31:267–272. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9741-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Tripathi S, Tripathi YB. Hepatic encephalopathy: cause and possible management with botanicals. Recent Patents Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2014;8:185–191. doi: 10.2174/1872213x08666141107164418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Butterworth RF. Pathophysiology of brain dysfunction in hyperammonemic syndromes: The many faces of glutamine. Mol Genet Metab. 2014;113:113–117. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Prakash R, Mullen KD. Mechanisms, diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:515–525. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Ott P, Vilstrup H. Cerebral effects of ammonia in liver disease: current hypotheses. Metab Brain Dis. 2014;29:901–911. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9494-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Jones EA, Mullen KD. Theories of the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2012;16:7–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2011.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Gooday R, Hayes PC, Bzeizi K, O’Carroll RE. Benzodiazepine receptor antagonism improves reaction time in latent hepatic encephalopathy. Psychopharmacology. 1995;119:295–298. doi: 10.1007/BF02246294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Jones EA. Ammonia, the GABA neurotransmitter system, and hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2002;17:275–281. doi: 10.1023/a:1021949616422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Montana V, Verkhratsky A, Parpura V. Pathological role for exocytotic glutamate release from astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014;12:324–333. doi: 10.2174/1570159X12666140903094700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Ding S, Yang J, Liu L, Ye Y, Wang X, et al. Elevated dopamine induces minimal hepatic encephalopathy by activation of astrocytic NADPH oxidase and astrocytic protein tyrosine nitration. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;55:252–263. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Holecek M. Evidence of a vicious cycle in glutamine synthesis and breakdown in pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy-therapeutic perspectives. Metab Brain Dis. 2014;29:9–17. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9428-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Kobtan AA, El-Kalla FS, Soliman HH, Zakaria SS, Goda MA. Higher Grades and Repeated Recurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy May Be Related to High Serum Manganese Levels. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;169:153–158. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Holecek M. Ammonia and amino acid profiles in liver cirrhosis: effects of variables leading to hepatic encephalopathy. Nutrition. 2015;31:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Shawcross DL, Wright G, Olde Damink SW, Jalan R. Role of ammonia and inflammation in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2007;22:125–138. doi: 10.1007/s11011-006-9042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Shawcross DL, Davies NA, Williams R, Jalan R. Systemic inflammatory response exacerbates the neuropsychological effects of induced hyperammonemia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2004;40:247–254. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2003.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Merola J, Chaudhary N, Qian M, Jow A, Barboza K, et al. Hyponatremia: a risk factor for early overt encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation. J Clin Med. 2014;3:359–372. doi: 10.3390/jcm3020359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Gaduputi V, Chandrala C, Abbas N, Tariq H, Chilimuri S, et al. Prognostic significance of hypokalemia in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2014;61:1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Tsai CF, Chen MH, Wang YP, Chu CJ, Huang YH, et al. Proton pump inhibitors increase risk for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis in population study. Gastroenterology. 2016; [DOI] [PubMed]
- 247.Jepsen P, Christensen J, Weissenborn K, Watson H, Vilstrup H. Epilepsy as a risk factor for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016;16:77. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0487-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Casadaban LC, Parvinian A, Minocha J, Lakhoo J, Grant CW, et al. Clearing the confusion over hepatic encephalopathy after tips creation: incidence, prognostic factors, and clinical outcomes. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:1059–1066. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Wang JY, Zhang NP, Chi BR, Mi YQ, Meng LN, et al. Prevalence of minimal hepatic encephalopathy and quality of life evaluations in hospitalized cirrhotic patients in China. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:4984–4991. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Borentain P, Soussan J, Resseguier N, Botta-Fridlund D, Dufour JC, et al. The presence of spontaneous portosystemic shunts increases the risk of complications after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2016;97:643–650. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2016.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Nardelli S, Gioia S, Pasquale C, Pentassuglio I, Farcomeni A, et al. Cognitive impairment predicts the occurrence of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111:523–528. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Brenner M, Butz M, May ES, Kahlbrock N, Kircheis G, et al. Patients with manifest hepatic encephalopathy can reveal impaired thermal perception. Acta Neurol Scand. 2015;132:156–163. doi: 10.1111/ane.12376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Kircheis G, Fleig WE, Gortelmeyer R, Grafe S, Haussinger D. Assessment of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy: a critical analysis. J Hepatol. 2007;47:642–650. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Hassanein TI, Hilsabeck RC, Perry W. Introduction to the Hepatic Encephalopathy Scoring Algorithm (HESA) Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:529–538. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-9895-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Ong JP, Aggarwal A, Krieger D, Easley KA, Karafa MT, et al. Correlation between ammonia levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Med. 2003;114:188–193. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Qureshi MO, Khokhar N, Shafqat F. Ammonia levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014;24:160–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Haussinger D, Schliess F. Pathogenetic mechanisms of hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 2008;57:1156–1165. doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.122176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Dabos KJ, Parkinson JA, Sadler IH, Plevris JN, Hayes PC. (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-based metabonomic study in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:1701–1707. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i12.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Amodio P, Campagna F, Olianas S, Iannizzi P, Mapelli D, et al. Detection of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: normalization and optimization of the Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score. A neuropsychological and quantified EEG study. J Hepatol. 2008;49:346–353. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Sharma P, Sharma BC, Puri V, Sarin SK. Critical flicker frequency: diagnostic tool for minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2007;47:67–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Romero-Gomez M, Cordoba J, Jover R, del Olmo JA, Ramirez M, et al. Value of the critical flicker frequency in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2007;45:879–885. doi: 10.1002/hep.21586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Olesen SS, Gram M, Jackson CD, Halliday E, Sandberg TH, et al. Electroencephalogram variability in patients with cirrhosis associates with the presence and severity of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2016;65:517–523. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 263.Jackson CD, Gram M, Halliday E, Olesen SS, Sandberg TH, et al. New spectral thresholds improve the utility of the electroencephalogram for the diagnosis of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;127:2933–2941. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2016.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Bajaj JS, Wade JB, Sanyal AJ. Spectrum of neurocognitive impairment in cirrhosis: Implications for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2009;50:2014–2021. doi: 10.1002/hep.23216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Maharshi S, Sharma BC, Sachdeva S, Srivastava S, Sharma P. Efficacy of nutritional therapy for patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy in a randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:454–460. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.09.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Amodio P, Canesso F, Montagnese S. Dietary management of hepatic encephalopathy revisited. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014;17:448–452. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Sawhney R, Jalan R. Liver: the gut is a key target of therapy in hepatic encephalopathy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12:7–8. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Rahimi RS, Singal AG, Cuthbert JA, Rockey DC. Lactulose vs polyethylene glycol 3350--electrolyte solution for treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy: the HELP randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:1727–1733. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Rahimi RS, Rockey DC. Novel ammonia-lowering agents for hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2015;19:539–549. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Rai R, Ahuja CK, Agrawal S, Kalra N, Duseja A, et al. Reversal of low-grade cerebral edema after lactulose/rifaximin therapy in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2015;6:e111. doi: 10.1038/ctg.2015.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 271.Shavakhi A, Hashemi H, Tabesh E, Derakhshan Z, Farzamnia S, et al. Multistrain probiotic and lactulose in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Res Med Sci. 2014;19:703–708. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Morgan MY, Hawley KE. Lactitol vs. lactulose in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients: a double-blind, randomized trial. Hepatology. 1987;7:1278–1284. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 273.Agrawal A, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: an open-label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:1043–1050. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2012.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Paik YH, Lee KS, Han KH, Song KH, Kim MH, et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactulose for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective randomized study. Yonsei Med J. 2005;46:399–407. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Bajaj JS, Barrett AC, Bortey E, Paterson C, Forbes WP. Prolonged remission from hepatic encephalopathy with rifaximin: results of a placebo crossover analysis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41:39–45. doi: 10.1111/apt.12993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Kimer N, Krag A, Moller S, Bendtsen F, Gluud LL. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of rifaximin in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:123–132. doi: 10.1111/apt.12803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Mullen KD, Sanyal AJ, Bass NM, Poordad FF, Sheikh MY, et al. Rifaximin is safe and well tolerated for long-term maintenance of remission from overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;e12392:1390–1397. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Sidhu SS, Goyal O, Parker RA, Kishore H, Sood A. Rifaximin vs. lactulose in treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int. 2016;36:378–385. doi: 10.1111/liv.12921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 279.Lunia MK, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sachdeva S, Srivastava S. Probiotics prevent hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1003–1008.e1001. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Saab S, Suraweera D, Au J, Saab EG, Alper TS, et al. Probiotics are helpful in hepatic encephalopathy: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Liver Int. 2016;36:986–993. doi: 10.1111/liv.13005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 281.Sharma P, Sharma BC, Puri V, Sarin SK. An open-label randomized controlled trial of lactulose and probiotics in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20:506–511. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f3e6f5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 282.Dhiman RK, Rana B, Agrawal S, Garg A, Chopra M, et al. Probiotic VSL#3 reduces liver disease severity and hospitalization in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized, controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:1327–1337. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 283.Matoori S, Leroux JC. Recent advances in the treatment of hyperammonemia. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;90:55–68. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 284.Diaz-Herrero MM, del Campo JA, Carbonero-Aguilar P, Vega-Perez JM, Iglesias-Guerra F, et al. THDP17 decreases ammonia production through glutaminase inhibition. A new drug for hepatic encephalopathy therapy. PLoS One. 2014;9:e109787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 285.Gluud LL, Vilstrup H, Morgan MY (2016) Non-absorbable disaccharides versus placebo/no intervention and lactulose versus lactitol for the prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: Cd003044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 286.Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Piedrafita B, Boix J, Felipo V. Inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy: ibuprofen restores learning ability in rats with portacaval shunts. Hepatology. 2007;46:514–519. doi: 10.1002/hep.21734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 287.Poo JL, Gongora J, Sanchez-Avila F, Aguilar-Castillo S, Garcia-Ramos G, et al. Efficacy of oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate in cirrhotic patients with hyperammonemic hepatic encephalopathy. Results of a randomized, lactulose-controlled study. Ann Hepatol. 2006;5:281–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 288.Rockey DC, Vierling JM, Mantry P, Ghabril M, Brown RS, Jr, et al. Randomized, double-blind, controlled study of glycerol phenylbutyrate in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2014;59:1073–1083. doi: 10.1002/hep.26611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 289.Mousa N, Abdel-Razik A, Zaher A, Hamed M, Shiha G, et al. The role of antioxidants and zinc in minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized trial. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2016;9:684–691. doi: 10.1177/1756283X16645049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 290.Abdelaziz RR, Elkashef WF, Said E. Tranilast reduces serum IL-6 and IL-13 and protects against thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury and hepatic encephalopathy. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;40:259–267. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 291.Blei AT. Is it worth removing albumin-bound substances in hepatic encephalopathy? Z Gastroenterol. 2001;39(Suppl 2):8. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-919027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 292.Gluud LL, Dam G, Les I, Cordoba J, Marchesini G, et al. (2015) Branched-chain amino acids for people with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: Cd001939. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 293.Morgan MY, Blei A, Grungreiff K, Jalan R, Kircheis G, et al. The treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2007;22:389–405. doi: 10.1007/s11011-007-9060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 294.Ahboucha S, Butterworth RF. The neurosteroid system: implication in the pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Int. 2008;52:575–587. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 295.Torres-Vega MA, Vargas-Jeronimo RY, Montiel-Martinez AG, Munoz-Fuentes RM, Zamorano-Carrillo A, et al. Delivery of glutamine synthetase gene by baculovirus vectors: a proof of concept for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia. Gene Ther. 2015;22:58–64. doi: 10.1038/gt.2014.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 296.Bai M, He C, Yin Z, Niu J, Wang Z, et al. Randomised clinical trial: L-ornithine-L-aspartate reduces significantly the increase of venous ammonia concentration after TIPSS. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:63–71. doi: 10.1111/apt.12795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 297.Luo L, Fu S, Zhang Y, Wang J. Early diet intervention to reduce the incidence of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis patients: post-Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) findings. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2016;25:497–503. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.092015.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 298.Lynn AM, Singh S, Congly SE, Khemani D, Johnson DH, et al. Embolization of portosystemic shunts for treatment of medically refractory hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Transpl. 2016;22:723–731. doi: 10.1002/lt.24440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 299.Hung PC, Wang HS, Hsia SH, Wong AM. Plasmapheresis as adjuvant therapy in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and hepatic encephalopathy. Brain and Development. 2014;36:356–358. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2013.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 300.Wong RJ, Gish RG, Ahmed A. Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with significantly increased mortality among patients awaiting liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2014;20:1454–1461. doi: 10.1002/lt.23981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 301.Atluri DK, Asgeri M, Mullen KD. Reversibility of hepatic encephalopathy after liver transplantation. Metab Brain Dis. 2010;25:111–113. doi: 10.1007/s11011-010-9178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 302.Fallon MB, Abrams GA. Pulmonary dysfunction in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2000;32(4):859–865. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.7519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 303.Lange PA, Stoller JK. The hepatopulmonary syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122(7):521–529. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-7-199504010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 304.Ford RM, Sakaria SS, Subramanian RM. Critical care management of patients before liver transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 2010;24(4):190–206. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2010.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 305.Fuhrmann V, Jager B, Zubkova A, Drolz A. Hypoxic hepatitis - epidemiology, pathophysiology and clinical management. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2010;122(5–6):129–139. doi: 10.1007/s00508-010-1357-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 306.Breuer O, Shteyer E, Wilschanski M, Perles Z, Cohen-Cymberknoh M, Kerem E, Shoseyov D. Hepatopulmonary Syndrome in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis and Liver Disease. Chest. 2016;149(2):e35–e38. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2015.10.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 307.Pouriki S, Alexopoulou A, Chrysochoou C, Raftopoulos L, Papatheodoridis G, Stefanadis C, Pectasides D. Left ventricle enlargement and increased systolic velocity in the mitral valve are indirect markers of the hepatopulmonary syndrome. Liver Int. 2011;31(9):1388–1394. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 308.Rodriguez-Roisin R, Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome--a liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(22):2378–2387. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0707185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 309.Zhang ZJ, Yang CQ. Progress in investigating the pathogenesis of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2010;9(4):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 310.Schenk P, Schoniger-Hekele M, Fuhrmann V, Madl C, Silberhumer G, Muller C. Prognostic significance of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2003;125(4):1042–1052. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)01207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 311.Swanson KL, Wiesner RH, Krowka MJ. Natural history of hepatopulmonary syndrome: Impact of liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2005;41(5):1122–1129. doi: 10.1002/hep.20658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 312.Hoeper MM, Krowka MJ, Strassburg CP. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet. 2004;363(9419):1461–1468. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 313.Schenk P, Fuhrmann V, Madl C, Funk G, Lehr S, Kandel O, Muller C. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: prevalence and predictive value of various cut offs for arterial oxygenation and their clinical consequences. Gut. 2002;51(6):853–859. doi: 10.1136/gut.51.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 314.Krowka MJ, Fallon MB, Kawut SM, Fuhrmann V, Heimbach JK, Ramsay MA, Sitbon O, Sokol RJ. International Liver Transplant Society Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Hepatopulmonary Syndrome and Portopulmonary Hypertension. Transplantation. 2016;100(7):1440–1452. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 315.Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: monitoring at your fingertip. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(6):1599–1600. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1675-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 316.Naeije R. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension. Swiss Med Wkly. 2003;133(11–12):163–169. doi: 10.4414/smw.2003.10016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 317.Goldberg DS, Fallon MB. The Art and Science of Diagnosing and Treating Lung and Heart Disease Secondary to Liver Disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(12):2118–2127. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.04.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 318.Cuadrado A, Diaz A, Iruzubieta P, Salcines JR, Crespo J. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;38(6):398–408. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2015.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 319.Mukaida N, Ishikawa Y, Ikeda N, Fujioka N, Watanabe S, Kuno K, Matsushima K. Novel insight into molecular mechanism of endotoxin shock: biochemical analysis of LPS receptor signaling in a cell-free system targeting NF-kappaB and regulation of cytokine production/action through beta2 integrin in vivo. J Leukoc Biol. 1996;59(2):145–151. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 320.Raetz CR, Ulevitch RJ, Wright SD, Sibley CH, Ding A, Nathan CF. Gram-negative endotoxin: an extraordinary lipid with profound effects on eukaryotic signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991;5:2652–2660. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 321.Medzhitov R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature. 2007;449(7164):819–826. doi: 10.1038/nature06246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 322.Raetz CRH. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 323.Giuliani A, Pirri G, Rinaldi AC. Antimicrobial peptides: the LPS connection. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;618:137–154. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-594-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 324.Magalhães PO, Lopes AM, Mazzola PG, Rangel-Yagui C, Penna TC, Pessoa A., Jr Methods of endotoxin removal from biological preparations: a review. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2007;10(3):388–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 325.Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science. 2005;308:1635–1638. doi: 10.1126/science.1110591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 326.Cullen TW, Schofield WB, Barry NA, Putnam EE, Rundell EA, Trent MS, Degnan PH, Booth CJ, Yu H, Goodman AL. Gut microbiota. Antimicrobial peptide resistance mediates resilience of prominent gut commensals during inflammation. Science. 2015;347(6218):170–175. doi: 10.1126/science.1260580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 327.Janelsins B. M., Lu M., Datta S. K. Altered inactivation of commensal LPS due to acyloxyacyl hydrolase deficiency in colonic dendritic cells impairs mucosal Th17 immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2013;111(1):373–378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311987111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 328.Landsberger M, Zhou J, Wilk S, Thaumüller C, Pavlovic D, Otto M, Whynot S, Hung O, Murphy MF, Cerny V, Felix SB, Lehmann C. Inhibition of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 reduces leukocyte adhesion within the intestinal microcirculation in experimental endotoxemia in rats. Crit Care. 2010;14(6):R223. doi: 10.1186/cc9367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 329.Griffiths KL, Tan JK, O’Neill HC. Characterization of the effect of LPS on dendritic cell subset discrimination in spleen. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(9):1908–1912. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 330.Nguyen DN, Jiang P, Jacobsen S, Sangild PT, Bendixen E, Chatterton DE. Protective effects of transforming growth factor β2 in intestinal epithelial cells by regulation of proteins associated with stress and endotoxin responses. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0117608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 331.Thompson PA, Kitchens RL. Native high-density lipoprotein augments monocyte responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by suppressing the inhibitory activity of LPS-binding protein. J Immunol. 2006;177(7):4880–4887. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 332.Strandberg KL, Richards SM, Tamayo R, Reeves LT, Gunn JS. An altered immune response, but not individual cationic antimicrobial peptides, is associated with the oral attenuation of Ara4N-deficient Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 333.Mehrzad J, Dosogne H, De Spiegeleer B, Duchateau L, Burvenich C. Bovine blood neutrophil acyloxyacyl hydrolase (AOAH) activity during endotoxin and coliform mastitis. Vet Res. 2007;38(5):655–668. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2007024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 334.Schmiel DH, Moran EE, Keiser PB, Brandt BL, Zollinger WD. Importance of antibodies to lipopolysaccharide in natural and vaccine-induced serum bactericidal activity against Neisseria meningitidis group B. Infect Immun. 2011;79(10):4146–4156. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05125-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 335.Ravikumar Vilwanathan, Shivashangari Kanchi Subramanian, Devaki Thiruvengadam. Effect of Tridax procumbens on liver antioxidant defense system during lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatitis in D-galactosamine sensitised rats. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2005;269(1):131–136. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-3443-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 336.Zhou H, Liang H, Li ZF, Xiang H, Liu W, Li JG. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates intestinal epithelial tight junctions disruption in endotoxemic mice through α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Shock. 2013;40(2):144–151. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318299e9c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 337.Hayani KC, Guerrero ML, Ruiz-Palacios GM, Gomez HF, Cleary TG. Evidence for long-term memory of the mucosal immune system: milk secretory immunoglobulin A against Shigella lipopolysaccharides. J ClinMicrobiol. 1991;29(11):2599–2603. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2599-2603.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 338.Wang JH, Bose S, Kim GC, Hong SU, Kim JH, Kim JE, Kim H. Flos Lonicera ameliorates obesity and associated endotoxemia in rats through modulation of gut permeability and intestinal microbiota. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 339.Wang H, Xu DX, Lv JW, Ning H, Wei W. Melatonin attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced apoptotic liver damage in D-galactosamine-sensitized mice. Toxicology. 2007;237(1–3):49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2007.04.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 340.JeralaR. Structural biology of the LPS recognition. Int J Med Microbiol 2007;297(5):353–363. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 341.Wen M, Ma X, Cheng H, Jiang W, Xu X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Yu Y, Xu H, Qian C, Cao X, An H. Stk38 protein kinase preferentially inhibits TLR9-activated inflammatory responses by promoting MEKK2 ubiquitination in macrophages. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7167. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 342.McDonald B, Jenne CN, Zhuo L, Kimata K, Kubes P. Kupffer cells and activation of endothelial TLR4 coordinate neutrophil adhesion within liver sinusoids during endotoxemia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013;305(11):G797–G806. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00058.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 343.Barquero-Calvo E, Mora-Cartín R, Arce-Gorvel V, de Diego JL, Chacón-Díaz C, Chaves-Olarte E, Guzmán-Verri C, Buret AG, Gorvel JP, Moreno E. Brucella abortus induces the premature death of human neutrophils through the action of its lipopolysaccharide. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11(5):e1004853. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 344.Zullo JA, Nadel EP, Rabadi MM, Baskind MJ, Rajdev MA, Demaree CM, Vasko R, Chugh SS, Lamba R, Goligorsky MS, Ratliff BB. The secretome of hydrogel-coembedded endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells instructs macrophage polarization in endotoxemia. Stem Cells Transl Med 2015 May 6. pii: sctm.2014-0111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 345.Zhang Y, Lu Y, Ma L, Cao X, Xiao J, Chen J, Jiao S, Gao Y, Liu C, Duan Z, Li D, He Y, Wei B, Wang H. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in macrophages restrains TLR4-NF-κB signaling and protects against endotoxin shock. Immunity. 2014;40(4):501–514. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 346.Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Pilcher D, Cooper DJ, Bellomo R. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria in defining severe sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(17):1629–1638. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1415236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 347.La Mura V, Pasarín M, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, García-Pagán JC, Bosch J, Abraldes JG. Liver sinusoidal endothelial dysfunction after LPS administration: a role for inducible-nitric oxide synthase. J Hepatol. 2014;61(6):1321–1327. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 348.Feng A, Zhou G, Yuan X, Huang X, Zhang Z, Zhang T. Inhibitory effect of baicalin on iNOS and NO expression in intestinal mucosa of rats with acute endotoxemia. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e80997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 349.Han DW. Intestinal endotoxemia as a pathogenetic mechanism in liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2002;8(6):961–965. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 350.Lv X, Song JG, Li HH, Ao JP, Zhang P, Li YS, Song SL, Wang XR. Decreased hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ contributes to increased sensitivity to endotoxin in obstructive jaundice. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(48):5267–5273. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i48.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 351.Armstrong MT, Rickles FR, Armstrong PB. Capture of lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) by the blood clot: a comparative study. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e80192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 352.Tarao K. So K, Moroi T, Ikeuchi T, Suyama T. Detection of endotoxin in plasma and ascitic fluid of patients with cirrhosis: its clinical significance. Gastroenterology. 1977;73(3):539–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 353.Zijlstra JG, Tulleken JE, Ligtenberg JJ, de Boer P, van der Werf TS. p38-MAPK inhibition and endotoxin induced tubular dysfunction in men. J Endotoxin Res. 2004;10(6):402–405. doi: 10.1179/096805104225005869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 354.Chastre A, Bélanger M, Nguyen BN, Butterworth RF. Lipopolysaccharide precipitates hepatic encephalopathy and increases blood-brain barrier permeability in mice with acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2014;34(3):353–361. doi: 10.1111/liv.12252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 355.Cruz DN, Antonelli M, Fumagalli R, Foltran F, Brienza N, Donati A, Malcangi V, Petrini F, Volta G, BobbioPallavicini FM, Rottoli F, Giunta F, Ronco C. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: The EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301:2445–2452. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 356.Yoshino N, Endo M, Kanno H, et al. Polymyxins as novel and safe mucosal adjuvants to induce humoral immune responses in mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 357.Verhoef J, Visser MR. Neutrophil phagocytosis and killing: normal function and microbial evasion. The neutrophil. 1993. pp. 109–137. [Google Scholar]
- 358.Baumberger C, Ulevitch RJ, Dayer JM. Modulation of endotoxic activity of lipopolysaccharide by high-density lipoprotein. Pathobiology. 1991;59:378–383. doi: 10.1159/000163681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 359.Wittebole X, Castanares-Zapatero D, Laterre PF. Toll-like receptor 4 modulation as a strategy to treat sepsis. Mediat Inflamm. 2010;2010:568396. doi: 10.1155/2010/568396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 360.Zanoni I, Ostuni R, Marek LR, et al. CD14 controls the LPS-induced endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4. Cell. 2011;147(4):868–880. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 361.Michlewska S, Dransfield I, Megson IL, et al. Macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils is critically regulated by the opposing actions of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory agents: key role for TNF-α. FASEB J. 2009;23(3):844–854. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-121228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 362.Baue AE. MOF, MODS, and SIRS: what is in a name or an acronym? Shock. 2006;26(5):438–449. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000228172.32587.7a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 363.Bone RC, Sibbald WJ, Sprung CL. The ACCP-SCCM consensus conference on sepsis and organ failure. Chest J. 1992;101(6):1481–1483. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 364.Hunter JD, Doddi M. Sepsis and the heart. Br J Anaesth. 2010;104(1):3–11. doi: 10.1093/bja/aep339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 365.Brigham KL, Meyrick B. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133(5):913–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 366.Nolan JP. The role of intestinal endotoxin in liver injury: a long and evolving history. Hepatology. 2010;52(5):1829–1835. doi: 10.1002/hep.23917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 367.Wan L, Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C, Saotome T, May C, Bellomo R. Pathophysiology of septic acute kidney injury: What do we really know? Crit Care Med. 2008;36:S198–S203. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318168ccd5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 368.Semeraro N, Ammollo CT, Semeraro F, et al. Sepsis, thrombosis and organ dysfunction. Thromb Res. 2012;129(3):290–295. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 369.Yang R, Miki K, Oksala N, et al. Bile high-mobility group box 1 contributes to gut barrier dysfunction in experimental endotoxemia. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys. 2009;297(2):R362–R369. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00184.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]