Abstract
Cell migration is essential for regulating many biological processes in physiological or pathological conditions, including embryonic development and cancer invasion. In vitro and in silico studies suggest that collective cell migration is associated with some biomechanical particularities such as restructuring of extracellular matrix (ECM), stress and force distribution profiles, and reorganization of the cytoskeleton. Therefore, the phenomenon could be understood by an in-depth study of cells’ behavior determinants, including but not limited to mechanical cues from the environment and from fellow “travelers”. This review article aims to cover the recent development of experimental and computational methods for studying the biomechanics of collective cell migration during cancer progression and invasion. We also summarized the tested hypotheses regarding the mechanism underlying collective cell migration enabled by these methods. Together, the paper enables a broad overview on the methods and tools currently available to unravel the biophysical mechanisms pertinent to cell collective migration as well as providing perspectives on future development toward eventually deciphering the key mechanisms behind the most lethal feature of cancer.
Keywords: cell mechanics, cancer biophysics, unjamming, collective cell dynamics, cancer invasion, epithelial–mesenchymal transition
Graphical Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
While single cell migration has been well-studied, the mechanism of collective migration still remains elusive. Cell collectives are not simply a collection of single cells, and as such, collective migration involves much more mechanically and dynamically complex intra- and interactivities.1,2 Collective cell migration involves a group of cells traveling together under certain patterns with a degree of coordination among the movement of each individual.3 Despite the involvement of such phenomenon in several physiological processes, the underlying biophysical mechanisms are far from being thoroughly understood.
During embryogenesis, certain phenomena such as neural tube closing, ventral closure, or eyelid closure4–6 rely on neighboring epithelial cells collectively migrating from stem cell niches and proliferative zones to the target functioning area,7 consequently forming a continuous monolayer.8 Differ-ent levels of development of embryos show distinct patterns of collective migration. For example, early embryos employ sheet migration where cells remain tight and close while moving forward together.7,9 Tracheal system shows branching morpho-genesis, as it generates a limited number of tip cells and forms elaborate cellular structures.3,7 Border cells in Drosophila ovary migrate as a free group consisting of leaders (cells receiving constitutive epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor signaling) and followers.3,7,10 The lateral line in zebrafish has a slug-like migration.7,11 Mechanical forces in all these processes depend not only on actomyosin contractions which form a purse-string structure5,8 but also on cell crawling driven by lamellipodia and filopodia extrusions.12,13
Collective migration is involved in different stages of wound healing as well. During the generation of epithelial monolayers, leader cells are believed to drag follower cells to migrate, depending on the cell–substrate traction forces localized to the leading edge.14,15 However, evidence supporting that not leader cells but rather an integrative process of transforming local forces into a general tension in the monolayer by each cell was presented as well.16,17 In re-epithelialization of epidermal cells, keratinocytes migrate collectively across the provisional wound bed which is filled with ECM. This sheet migration results in epidermal wound closure.15,18,19 In the regeneration of endothelial cells, collective strands of endothelial cells migrate as vascular sprouting with a leading sprout and penetrate the provisional wound matrix to regenerate vessels.3,7,20 Researchers have been working on modeling the collective migration during wound healing using a continuum model and free boundary system.21 However, the specific mechanism(s) and the determinants of migration and the migration mode still remain unclear.
Cancer invasion, mostly for epithelial-like tumor cells,7 displays many hallmarks of collective cell migration. First, cell– cell junctions suggesting cell–cell couplings are observed among cancer cells.3,22 Second, cell–cell adhesion molecules such as E-cadherin and homophilic cell–cell adhesion receptors are expressed within invasive zones.3, 23 Third, tumor cells display structural ECM remodeling on early movement, suggesting their capability of morphogenesis.3 Lastly, cancer cells migrate from invasive zones to the surrounding matrix as chains or sprouts.7,24 Cancers that display collective invasion include partially dedifferentiated forms of rhabdomyosarcoma, oral squamous cell carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, melanoma, and breast cancer.19,23– 25 While the molecular mechanism of cancer collective invasion is not completely understood, several interesting findings have gradually been made. Understanding the biomechanical determinants of cancer cells before or during collective migration can help identify medical targets. Investigating diseases from a biomechanical point of view has been an important tool for elucidating pathophysiology and patho-genesis of a variety of ailments26 and has helped in developing diagnosis and therapeutic strategies.26,27 These have allowed for the recognition of several differences between cancer cells and corresponding normal cells from a biomechanical perspective. Some notable distinct biomechanical character-istics of tumor cells, at a single-cell level, include their higher stretchability,26 greater softness,28 and loss of stiffness sensing abilities in the case of some malignant cells28 that might have implications on their collective behavior as well.
In epithelial cancers, cells migrate collectively from the main mass to surrounding tissues.29 In metastasis of other cancer types besides those of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and migratory phenotypes,30 cells also exhibit collective migration to spread to other tissues.29,31 As a result, controlling collective migration might be an effective strategy of dealing with cancer spread.
Different from the review by Hakim and Silberzan,32 this review paper focuses on both the experimental and computa-tional methods employed to study collective cell migration, highlighting some of the key discoveries that add to our understanding of the phenomenon. A brief overview of the mechanistic basis is given in Section 2, followed by the review of most commonly used experimental and computational methods, as well as the identification of the unresolved questions regarding collective cell migration during cancer progression and invasion. A more detailed review on the cell– matrix related mechanobiological changes during cell migra-tion can be found elsewhere.33
2. MECHANISMS OF COLLECTIVE CELL MIGRATION
Cues for Collective Cell Migration.
Before going into the mechanism of collective cell migration, it is important to identify the cues that trigger the process. Cues for solitary cell migration are well-studied, as it has been shown that cells can move along a gradient of chemoattractant (chemotaxis), adhesive substrate (haptoaxis), or rigidity (duroaxis) or move in response to electric fields or topography.34 However, more complex molecular pathways are often involved in converting external guiding factors into migration events for cell collectives. For example, the recent work by Barriga et al. has shown that a change in substrate stiffness can trigger collective cell migration,35 and in this pathway, TWIST1 is the key mechano-mediator: upon sensing the high matrix stiffness, TWIST1 is released from its binding partner and translocated to the nucleus to induce constitutive TWIST1 nuclear translocation and EMT.36 While extrinsic factors such as chemoattractants, electric fields, or topography can single-handedly dominate and guide the migration of single cells, collective cell migration requires both the integration of these regulators among the collective and a cohesive response.34,37,38 Although many methods to study the chemical and electrical cues for migration have been developed, studying mechanical cues other than stiffness remains challenging due to a lack of techniques to effectively identify and quantify the mechanical signals. In addition to external chemicals, intrinsic factors among the cell collective also play a role by potentially affecting migration direction, velocity, and capability. Within the migrating cell collective, integrated intrinsic cell–cell interactions like mechanocoupling and polarization guide the overall movement, but cells can also sense and respond to extrinsic cues on the individual level.34,35 Traction force, which directs cell migration, is regulated by cell shapes and substrate stiffness.39,40 Differences in expression profiles between cells in the same migrating collective have been identified and consequently support the hypothesis of leader-follower cell dynamics.41
Leader-Follower Cell Dynamics.
“Swarm-like” behavior of cancer cells proposed by Deisboeck et al. presents the paradigm of tumors as units with multiple individuals (cells) among which we find capabilities of leadership, conflict, and cooperation.42 While in the case of single-cell migration one could discuss the polarization of a cell to yield a leading edge and a trailing one, in the case of collective cell migration, the occurrence of leader cells and follower cells has been observed to coordinate a collectively polarized group of cells.43 The occurrence of the polarization is assumed to be caused by the change of cadherin-mediated contacts due to pulling forces within the monolayer.1 This pressure is hypothesized to encourage actin polymerization at the individual cell front, previously described to enable a push forward of the leading edge of leader cells.44 In addition, it has been suggested that the collective migration of metastatic cells acts in a cooperative manner by exchanging the leadership of the front cells.45 However, the collective movement is sustained not only by the existence of leader cells and follower ones but also by the interactions through the collective that maintain mechanocou-pling and guidance. Cell–cell junctions contribute to supra-cellular adhesion, mechanocoupling sensing, and interpretation of external cues such as soluble factors or ECM topology.43 Their connections are realized through cadherin adhesion proteins, desmosomal proteins, tight junctions, gap junctions, and interactions between immunoglobulin family proteins. Cadherins exert signals along cell–cell junctions, while E-cadherin and N-cadherin levels are often used as markers for cell motility.29,46 Mechanosensitive molecules such as vinculin and filamin play an important role by changing their conformations in response to forces transmitted at cell–cell junctions, triggering signaling events.3,47 Inhibition of the integrin–vinculin–talin complex disturbs the mechanosensing and consequently aborts the collective cell migration.35 Moreover, actomyosin was shown to accumulate at cell–cell adhesion locations, inducing an inner polarization of leader cells, which increases collective migration by creating a permanently tensioned monolayer.48 Because of the difference in traction forces experienced by leader and followers, their interaction has been deemed as resembling a “tug of war”,49 in which the stronger leader cells prevail; however, success is credited partially to the existence of actin cables along the leading edge that help maintain the integrity of cell–cell adhesions29 or to the alignment of forces with the velocity of the collective.50
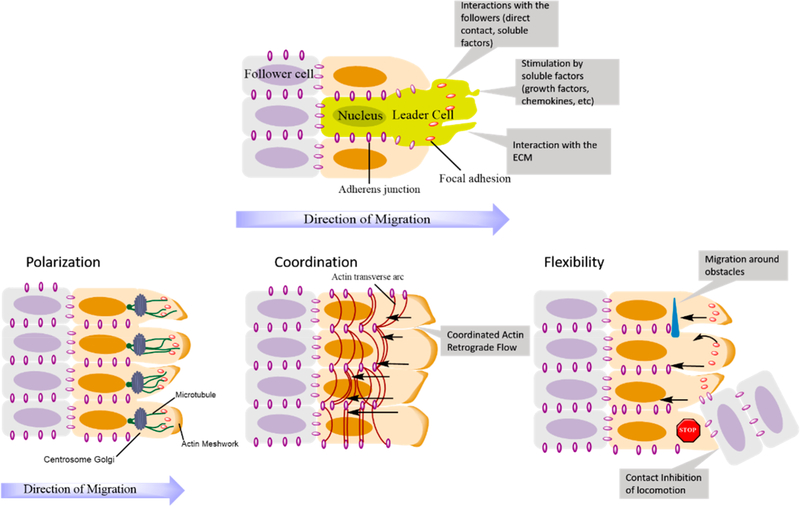
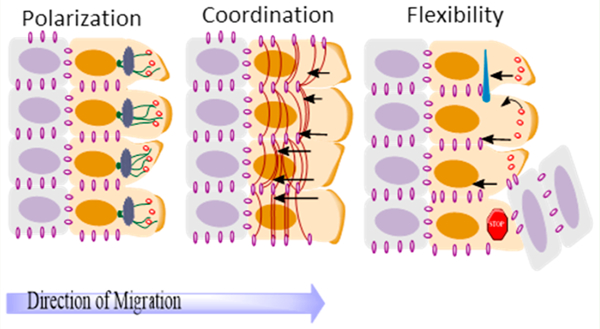
Figure 1 provides a schematic representation of leader-follower cell dynamics during collective migration, together with key factors involved in the migration mechanism. The selection of the leader cells in cell collectives is done by a combination of synergistic mechanisms that aim to maintain a polarized state of the migrating layer consisting of a leading edge and a trailing one while ensuring the integrity of cell–cell contacts and the stability of the tissue geometry.29 Leader cells have been observed to manifest different phenotypes than follower cells, being distinguished by prominent pseudopodia aimed in the direction of migration, as portrayed in the schematic representation in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Top: Representation of the emergence of leader and follower cells within a cell cluster. Bottom: Three key elements of collective cell migration represented with their main components: (a) polarization of cells that leads to the orientation of the cytoskeleton; (b) coordination of actin dynamics between neighboring cells through actin cables; (c) flexibility or dynamic rearrangement of cell–cell contacts due to the retrograde flow of adherens junctions. Adapted with permission from ref 29. Copyright 2016 Springer Nature.
The terminology of “leaders” has been, however, questioned as being deceiving in describing cells that possess the guiding or steering capabilities within a group, as their positioning does not need to be at the front of the collective.51 Furthermore, the existence of a stress coordination among cells17 and the occurrence of plithotaxis among cell collectives, based on mechanical cell–cell contact,52 emphasize that the leader-follower dynamics might be just a subset of a bigger picture to describe the modes of collective migration. The following sections explore this idea, describing the shift from the biochemical-based view of collective migration at a cellular level to a more integrative one which involves factors concerning the mechanical interactions within the collective as a whole.
Glass-like Behavior of Cells.
Introduced in 2001 by Fabry et al.,53 the analogy of cell behavior with that of soft glassy materials (SGM) is a concept that has attracted considerable interest from biomechanics researchers. SGMs include diverse substances such as foams, colloids, emulsions, or slurries and are characterized by their numerous soft elements, aggregated with one another by means of weak interactions and existing away from thermodynamic equilibrium.54 Fabry et al.’s study looked at the dynamics of the cytoskeleton and proposed that the cytoskeleton might undergo aging, rejuvenation, and remodeling events in a similar way to soft glassy materials. This led to the proposition that cells be included in the list of SGMs. Angelini et al. expanded the analogy to compare the fragility analysis of cell layers during collective migration and atomic and molecular glasses.55 Moreover, a study on individual cells showed that compression results in a stiffening of the cytoskeleton to resist it and a decrease in the relaxation time.56 This response of the intracellular space is reminiscent of a repulsive colloidal suspension approaching a glass transition. The projection of this glass-like behavior in cell collectives as well as within the cell is supported by evidence from studies that described structural rearrangements,57,58 kinetic phase transitions shown to occur in cell monolayers,59 and glass-like characteristics during wound closure.60
In the case of inert soft condensed matter, the increase in the size of cell clusters causes a gradual decrease in velocity, which leads to a kinetic arrest phenomena.54 However, the internal structure remains disordered, and the jamming transition requires fine-tuning of temperature, density, and shear stress.61 Similarly, in a cell collectives, with increasing cell density by proliferation, the velocity fields observed become more heterogeneous, reminiscent of a liquid-like to solid-like transition.62
Jamming/Unjamming Transitions.
Further expanding on the existence of solid-like (caged or “jammed”) first proposed by Lenormand et al. in 200763 and liquid-like behaviors of cell collectives (“unjammed”), the existence of a jamming/unjamming transition phenomenon was proposed for epithelial cell collectives.59,64,65 A hypothetical diagram of the transition is shown in Figure 2. In the jammed state, cells are confined in such packing geometry that the thermal fluctuations are insufficient to drive local structural rearrange-ment.66 The jamming phenomenon is similar to the one present in inert matter,67,68 with the particularity that cell collectives contain active particles with a motility of their own and that jamming transitions are encountered at packing densities of 1, such as in confluent monolayers.65
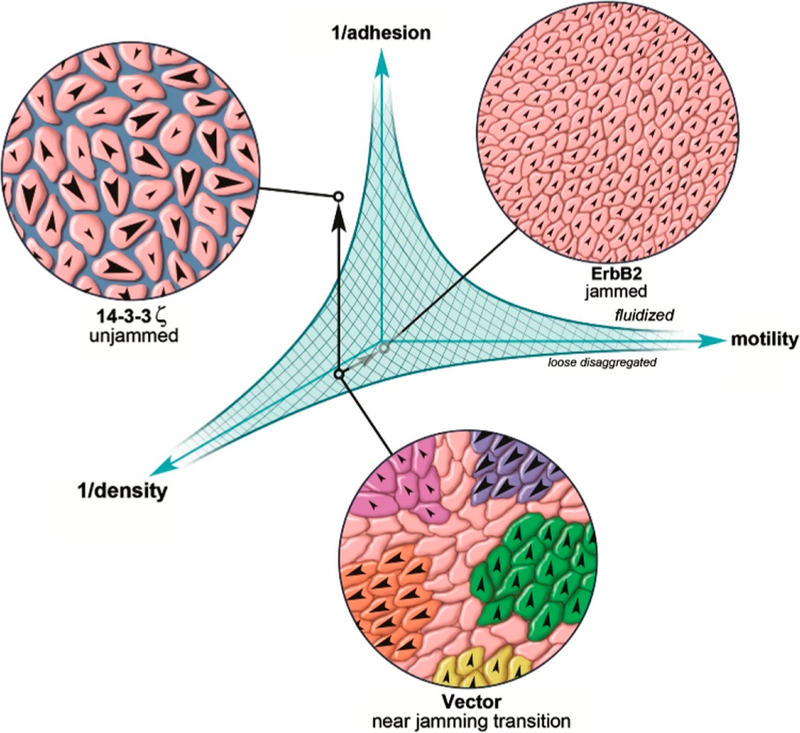
Figure 2.
Hypothetical phase diagram of the jamming/unjamming transition. The shaded area represents the jammed state, which is influenced by the density of cells, the motility of cells in the monolayer, and the cell–cell adhesion strength. Reproduced with permission from ref 69. Copyright 2013 International Society of Differentiation. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Several parameters are considered to have a role in the unjamming/jamming transition such as cell density, cell–cell adhesion, cell motility, and substrate mechanical properties such as stiffness, cell stresses, and their distributions.69 However, the main determinants of a potential jamming/ unjamming phase diagram such as the one in Figure 2 are still being debated, potentially due to the intricacy of the relations between multiple factors. Some authors argue that geometry and the departure from an equilibrium geometry are drivers of unjamming in epithelial cells,70 while others view the increase in mechanical coupling as a prerequisite.71 The density of the cells within a monolayer has been considered as a factor,55 but other works point out that a change in density is not necessary for jamming to occur.72,73 While these viewpoints might seem contradictory, the reader is advised to regard the main results presented within this review as complementary while, alas, potentially incomplete. In a similar fashion, the phase diagram represented here, or in other papers regarding the jamming/unjamming phenomenon in cells, is likely only a partial representation of the reality.
Cellular jamming and unjamming have been observed in experiments by Park et al. with primary epithelial cells from asthmatic and nonasthmatic donors. They showed that after undergoing an unjamming transition caused by external mechanical compression, nonasthmatic tissue would transition back to a jammed state in around 6 days, while their asthmatic counterparts exhibited a delay in reaching this state, taking up to 14 days to become jammed.74 In this context, the unjamming transition in cancerous tissue and other pathologies might be seen as an aberrant behavior of epithelial cells that disturbs the idle, jammed state of these cells.75 Compression-induced unjamming has been observed in human bronchial epithelial cell layer, and the process is associated with certain changes in cell shape, including apical flattening, constriction of apical diameter, cell elongation, and more shape variability. However, whether apical actomycin constriction leads to unjamming remains unclear.66 Unlike inert matter whose boundary conditions do not influence the internal parameters of the system, a wound that changes boundary conditions can slowly lead to decreased density and consequently unjam-ming.76 The jamming/unjamming transition is also affected by the cell type: while proliferation of epithelial cells leads to migration arrest, mesenchymal cells that proliferate slower and migrate faster can impede cell jamming.77 The underlying mechanism of the transition is proposed to be based on mechanical energy barriers to cell rearrangements, contributed by cell–cell junctions, contractile energies, and adhesion energies. As the energy barriers go up, such as due to smaller adhesive with respect to contractile contributions, the systems jams. The opposite happens when the adhesive energy overwhelms the contractile one with cells becoming fluidized and unjammed.78
The response of mesenchymal cells under ECM confine-ment provides evidence for cell jamming being an essential component for the emergence of collective cell migration modes.79 Thus, mesenchymal cells were shown to switch from a single-cell migration mode to a collective one when the microenvironment confinement was large enough to cause cells to jam and reach a large density.79 While collective cell migration is a property of normal epithelial and endothelial collectives,7 observing the phenomenon in mesenchymal cells might have implications on the approach in dealing with cancer metastasis. Given the increased division rates in cancerous tissue that might lead to fluidization, tumors could be inherently prone to unjamming.65 This, together with the new knowledge that EMT is unessential for the development of secondary tumors,80,81 supports the jamming/unjamming transition as a good contender for a triggering mechanism. However, as stated before, current progress in the field does not allow for a definite set of parameters to be accepted as key players in the involved phenomena. Moreover, observations made for a certain cell type, or tissue type, might not necessarily hold true regarding another.
3. EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
An attempt to fully describe the biomechanical mechanisms underlying collective cell migration or cancer invasion will unquestionably involve experiments observing these phenom-ena in a controlled manner. Based mostly on cell culture methods, experimental tools and techniques that were and continue to be used in the study of collective cell migration could be regarded as 2D techniques or 3D techniques with subdivisions for both large categories. This section reviews some of the most commonly used methods that have added to our knowledge of biomechanics of collective cell migration in general and in the case of cancer in particular.
2D Cell Culture Methods.
Migration Assays.
The most commonly used and known migration assay is the Boyden chamber, consisting of a transwell that allows the cells and a chemoattractant agent to be separated by a porous membrane through which cells can migrate.82 Although the setup is fairly easy and accessible and this method has been used to study the effect of several biochemical cues on invasive and migratory behavior of cancer cells,83–85 the method lacks control over geometrical factors and does not offer the possibility of visually inspecting the migration process, thus limiting its applicability. Therefore, the method might be better suited for determining single cell invasion or migration characteristics rather than collective behavior.
To address some of these shortcomings, cell exclusion assays were proposed as an alternative. An example focusing on collective cell behavior is the setup used by Nyegaard et al.86 that has been shown to give reproducible results with high versatility toward ECM types and compatible cells. The principle behind it is to place a barrier before seeding cells and by removing it to allow the cells to migrate into the newly formed void. A drawback of this method was its inability to exclude the effect of proliferation, but by using the lineage-tracing vital stain, one can distinguish migration from proliferation.87 However, in the context of collective cell migration, this technique can be improved using methods of lithography to obtain highly regular substrates and representa-tive microtopographies.88–91
Microstencils obtained by soft lithography allow the confluent cell monolayers to migrate. For instance, Poujade et al. used this technique to validate the triggering of collective motility by the availability of newer space to migrate rather than by an injury of a previously confluent monolayer.23 Petitjean et al. used the same method to study the collective migration of epithelial sheets, particularly identifying the different phenotype of emerging leader cells that were organizing as “finger” structures through particle image velocimetry and particle tracking.91 This study built up to the conclusions by Poujade et al. that employed similar techniques to validate the triggering of collective motility by the availability of newer space to migrate rather than by an injury of a previously confluent monolayer.23
Notbohm et al. used micropatterned masks to investigate the oscillatory behavior of epithelial confined monolayers, and a mechanochemical feedback mechanism was proposed as an explanation for the periodic fluidization and stiffening of the cell monolayer observed.50 In the context of both single and collective cell migration behaviors, topography and anisotropy were shown to influence migration patterns and their orientations, as shown by studies employing micropatterned topographies.93
Wound-Healing Assays.
Unlike migration assays, wound-healing assays usually imply a form of cell injury that results in a cell depleted area.94 In a 2D assay, this is usually obtained by letting cells reach confluence and injure the monolayer through various ways: scratching, stamping, thermal or electric wounding, or laser ablation.
Due to the ease to set up, wound healing assays are useful in the study of collective cell migration in conjunction with various microscopy techniques.95 Interestingly, studies focus-ing on wound-closing have shown that the process is independent of proliferation but is correlated with cell area and persistence,96 which suggest that the cell density is not a determinant in initiating collective cell migration in this context.97 Biochemical pathways of collective migration have been investigated, with Nobes et al. looking at individual contributions of Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 to cell movement in the context of wound healing. Their work revealed a mechanism based on the collaboration of small GTPases Rho, Rac, Cdc42, and Ras, where the first is required to maintain cell adhesion, the second is essential for the protrusion of lamellipodia, Cdc42 regulates cell polarity, and Ras is involved in controlling focal adhesion and stress fiber turnover.98 Additionally, hypoxia and cadherin-22 have been shown to colocalize in human glioblastoma and promote collective cell migration by means of cell–cell adhesions.46
As collective migration heavily relies on cooperation of numerous individuals, the role of cell–cell interactions and their dynamics during migration is a key element to inform a better understanding of the mechanisms involved. Tamada et al. used a circular wound model obtained by laser ablation to study the cell–cell adhesion rearrangement during collective migration as well as to reveal two mechanisms of closing the wound: the actomyosin assembly and contraction that acts on apical edges together with the lamellipodial protrusions into the cell depleted area.99 De Pascalis et al. recently studied glial interfilaments and their influence on astrocytes’ collective migration speed, direction, and persistence. Their study proved that the interfilament network controlled the traction forces distribution in the migrating sheet and held an important role in the organization of actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesions to maintain the structural and functional integrity of the collective.100
3D Cell Culture Methods.
Spheroids.
As by far the most widespread method for studying collective cell migration in three-dimensional culture, the cancer spheroid model can incorporate factors that were not accounted for in the 2D models. Spheroids are constituted by cells, either primary or from cell lines, aggregated in a 3D scaffold, usually from ECM proteins (collagen, fibrin, Matrigel, etc.).101 The main categories of these cancer spheroids are multicellular tumor spheroids, tumorspheres, tissue-derived tumorspheres, and organotypic multicellular spheres.101 Their compositions and applications usually differ: multicellular tumor spheroids are obtained from cell suspensions and used primarily to assess cell migration through ECM; tumorspheres are usually derived from stem cancer cells and employed for studying cancer stemness, and tissue-derived tumor spheres and organotypic spheres are derived from primary cancer tissue and are often used to screen drugs or characterize a patient’s tumor.102 Several key factors were studied in the context of cell migration in tumor spheroids such as matrix density and stiffness,103 ECM reorganization by means of proteases such as MMP, cell–cell adhesion and their dynamics, and microenvironment stresses.104 For example, Labernadie et al. examined the heterophilic E-cadherin/N-cadherin junction in the tumor spheroids made up of cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts to show that these heterotypic junctions serve as force transmitters and mechanotransduction triggers that lead to collective cell migration and invasion.105 Malignant breast cancer cells MDA MB 231 were cocultured in spheroids with MCF-10A epithelial cells by Carey et al. to study the role of leader cells observed in collective cell migration patterns.106 Their findings suggest that malignant cells can “recruit” follower cells from epithelial, nonmalignant cells within the tissue by cell-contractility and proteolysis-dependent matrix remodeling. Also notable are the results of Haeger et al. that studied the response of MV3 melanoma and HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells cultured in spheroids of varying ECM densities. Their findings indicate a plastic response of the cells that involved the shift from single-cell to collective invasive strategies given various degrees of confinement.79
Wound-Healing Assays.
Although less used than the tumor spheroid model, wound-healing assays have been developed for studying collective cell behavior in 3D in vitro. The constructs used in 3D wound healing assays usually consist of layered structures, combining ECM components such as collagen hydrogels and cells.94 Topman et al. used such an assay with a transparent hyaluronic-acid-based hydrogel to calculate the migration rate and directionality of DAPI-stained cells in vitro.107 As studies have shown that the behavior of cells differs from 2D to 3D environments,108,109 the analysis of collective cell migration in 3D environments and the processing of such data is of uttermost importance in revealing the mechanobio-logical mechanisms involved. Particularly, a study by Hakkinen et al. looked at the influence of 2D vs 3D tissue cultures on morphology, adhesion, single-cell migration, and cytoskeleton for human fibroblasts grown in four different ECMs.108 Their work revealed the differences in characteristics such as cell morphology, migration direction and rate, adhesion to ECM, and actin stresses for both 2D vs 3D environments as well as among the different ECMs used. These findings strengthen the need for faithful reproduction of tumor realities within the models used for in vitro testing and justify the use of 3D models such as the ones mentioned above (organoids, 3D wound healing assays) or microfluidics-enabled ones.
Microfluidics-Based Methods.
Advances in microfabri-cation methods made possible the existence of microfluidic devices that mimic the tumor microenvironment and facilitated a better understanding of the micromechanical cues that regulate collective cell behavior.110 Microfluidics-based meth-ods have the advantage of single-cell resolution and tailoring ability, allowing for the study of the complex biomechanical interactions that take place during cell migration, from single-cell migration to collective behavior modes.111 Apart from biochemical cues, cell migration behaviors are informed by the surrounding tissue and ECM properties such as fiber alignment and micro- and nanotopography features, the faithful reproduction of which is difficult in the macroscopic cell culture methods previously discussed.110,111 Some of the common soft-lithography and microfluidics-based methods are shown in Figures 3 and 4.
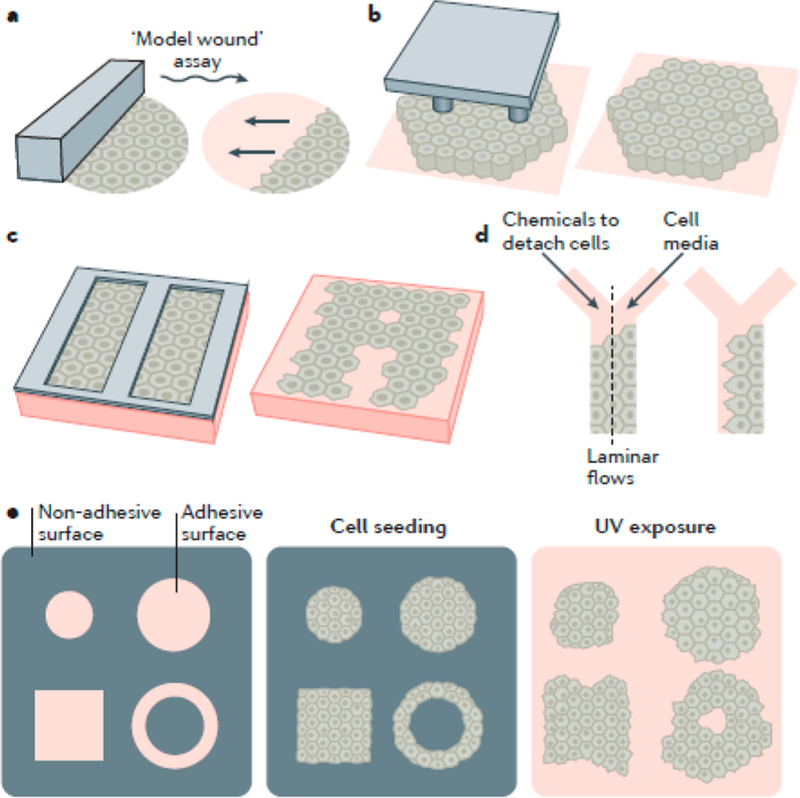
Figure 3.
Example of microfluidics-based methods to study cell migration. (a) Model wound when a microfabricated barrier or mark physically confines cells and is removed to reveal space for monolayers to migrate onto; (b) micropillars; (c) microstencils; (d) microfluidic device for chemically excluding cells; (e) UV-cleavable mask that allows for the confinement of cells and their subsequent release by irradiation. Reproduced with permission from ref 128. Copyright 2017 Springer Nature.
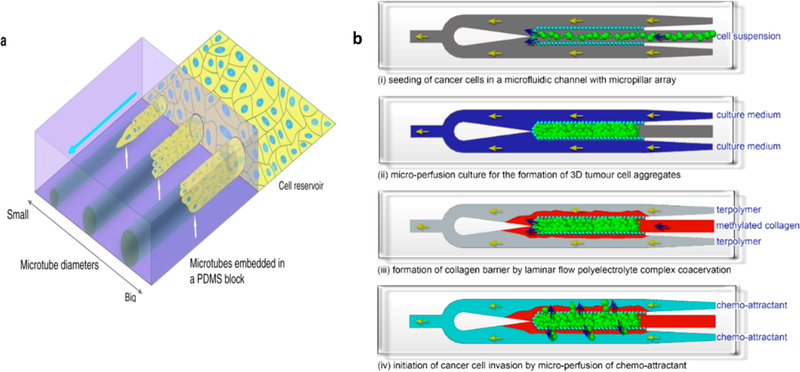
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic of MDCK cells feeding a PDMS block with varying sized microtubes. (b) Schematic of a cancer cell migration assay with a microfluidic device and the steps of studying migration in a 3D environment. (i) Seeding of cancer cells. (ii) Microperfusion culture to allow 3D tumor aggregates to form. (iii) Formation of a collagen barrier around the cellular aggregate by coacervation of positively charged collagen and negatively charged synthetic terpolymer. (iv) Migration of cancer cell by microperfusion of chemoattractant; Panel A reproduced with permission from ref 121. Copyright 2017 Springer Nature. Panel B reproduced with permission from ref 120. Copyright 2018 Yi-Chin Toh, Anju Raja, Hanry Yu, and Danny van Noort.
Studies that proved the cytoskeleton organization,112 focal adhesion assembly,113 or cell alignment114 change as a mechanotransduction response to microtopography stand to show how essential it is to include these type of factors into the study of cell migration. This knowledge might help inform better in vitro prototypes that elucidate the role of mechanical cues in the migratory mode. Wong et al. studied the behavior of cells at the tumor invasion front by employing micropillars to disrupt the cell–cell contacts periodically to enhance individual scattering of cells in a confluent layer.115 Liu et al. developed a microfabricated chip with micropillar arrays as a 3D landscape to investigate the invasiveness of metastatic cells quantitatively.116
Recently, Cui et al. developed a microfluidic device with multiple cell collection microchambers to study the morphol-ogy, cytoskeletal structure, and migration of transepithelial-migrated cells with high specificity, so a fully covered epithelial layer is no longer required for migration.117
Trending toward mimicking tumor microenvironments more closely, cancer models have been developed by means of microfluidic devices. These methods are being employed as a versatile tool to study the influence of several factors on the migration behavior of cells.111,118 The roles of biochemical cues such as AURKA kinase,119 chemoattractants,120 or even mechanical characteristics of the environment such as confinement121 and topology122 have been investigated using such methods. Furthermore, high-throughput microfluidic chip technique has also been utilized to explore tumor–stroma interactions in a 3D microenvironment.123 An important aspect of the tumor microenvironment that might be challenging to capture using the methods described in previous sections is its heterogeneous nature. As previously pointed out in this review, the mechanical environment is a significant determinant of cell migration, and any heterogeneity that appears might be responsible for behaviors observed in in vivo cancer progression.124,125 To that end, an interesting approach by Alobaidi et al. consists of a Diskoid in Geometrically Patterned ECM or “DIGME”, a mechanical-based method that allows control of the shape, microstructure, and heterogeneity of tumor organoids.126
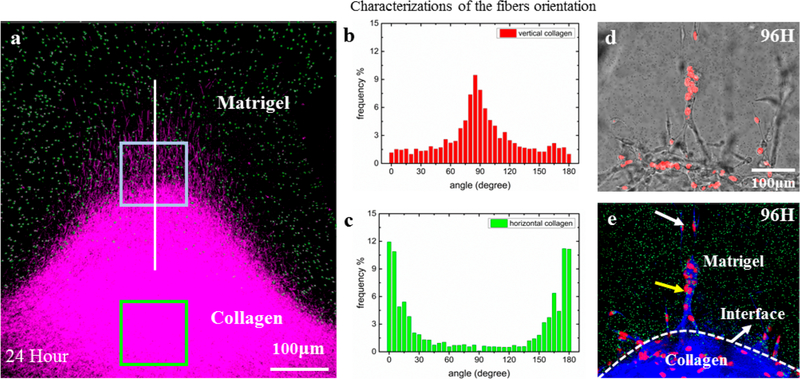
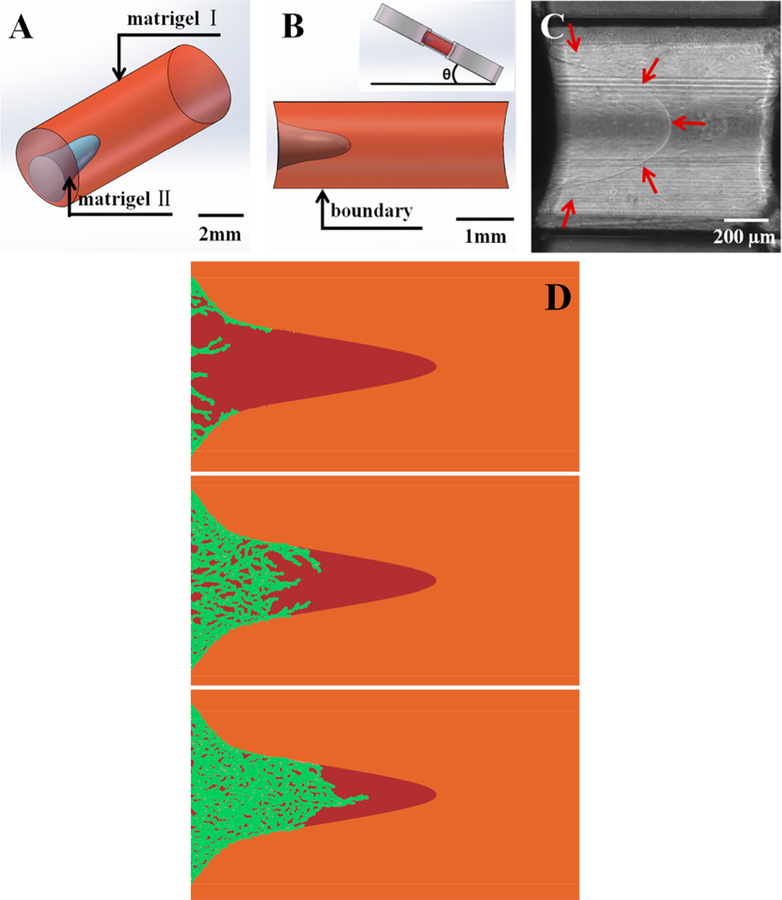
At the later grade of carcinoma tumor, collagen fibers aligned with tumor cells have been observed. To investigate the impact of collagen fibers on the tumor cell invasion, Han et al. designed a sandwiched ECM in a microfluidic chip to create collagen fibers perpendicular to the interface of collagen gel and Matrigel (Figures 5a and 5b). In such a heterogeneous system, the oriented collagen fibers facilitate the invasion of breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) into the 100% Matrigel layer as fast as in 96 h (Figure 5c), while in a homogeneous collagen gel, the cells were unable to invade the Matrigel. In addition, in 144 h, the front cells successfully broke through the entire Matrigel layer, indicating the influence of oriented collagen fibers goes much further than their penetration lengths. The results demonstrate the essential role of collagen fiber orientations in guiding metastatic cell intravasation and assisting the breakage of basement membrane before entering the circulation systems.127
Figure 5.
Oriented collagen fibers direct the metastatic cell invasion into Matrigel. (a) The 3D confocal image reconstruction via image stacking (top view) shows the Matrigel/collagen composite ECM and their interface in three dimensions. (b) The collagen fibers near the interface region possess vertical orientations (red box). (c) The collagen fibers in the centered region possess horizontal orientations (green box). (d) The bright-field images showing snapshots of invading cells at 96 h. (e) The corresponding fluorescent images combined with reflective mode of panel d, which show the Matrigel region with green beads embedded, the collagen region (blue), and the nuclei of invading cells (red). It is clear that, at the 96th hour, guided by oriented collagen fibers, the cells aggregated and strongly invaded into the rigid Matrigel region in single-stream forms. The field of view is the same for panels d and e. Adapted with permission from ref 127. Copyright 2016 Weijing Hana, Shaohua Chen, Wei Yuan, Qihui Fana, Jianxiang Tian, Xiaochen Wang, Longqing Chen, Xixiang Zhang, Weili Wei, Ruchuan Liu, Junle Qu, Yang Jiao, Robert H. Austin, and Liyu Liu.
Measuring Velocities during Collective Cell Migration.
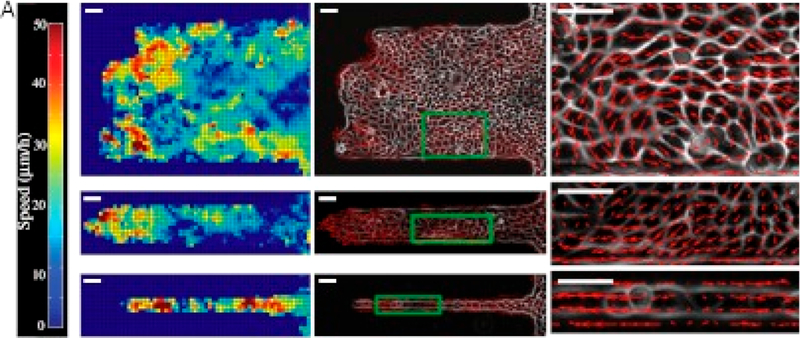
Even in the leader-follower type of organizations for collective cell migration, the front of the migration is not the only motion in monolayers. The bulk of the cell monolayer often experiences swirling that causes “chaotic” motion within the confluent layer.74 The advent of techniques such as particle image velocimetry allows for the characterization of these collective movements in terms of directionality and velocity.92 Heat maps of the velocity fields and displacements in confluent layers such as the ones shown in Figure 6 were used to study the influence of cell density that is believed to lead to a decrease in cellular rearrangements, yielding a jammed state of the epithelia as well as the effects of cell–cell adhesion or cortical tension variants.
Figure 6.
PIV analysis of epithelial sheets migrating on fibronectin strips of varying widths showing the spatial distribution of velocity fields as a heat map (right). A change in the collective behavior is recorded for the larger channels that move by swirling motions compared to the contraction–relaxation-based mode experienced through the narrow channels. Reproduced with permission from ref 128. Copyright 2012 Sri Ram Krishna Vedula, Man Chun Leong, Tan Lei Lai, Pascal Hersen, Alexandre J. Kabla, Chwee Teck Lim, and Benoît Ladoux.
Measuring Forces during Collective Cell Migration.
Another fundamental component toward understanding the biomechanics of collective cell migration is the characterization of forces during the collective behavior. Multiple techniques are employed to infer stresses and forces for both in vitro experiments as well as in vivo, looking at scales between molecular and tissue level.78 One commonly used method consists of mechanical traction force microscopy (TFM), which uses the deformation of soft substrates embedded with fluorescent beads and knowledge of their mechanical proper-ties to infer the traction applied by the cells to the substrate.129 Dembo and Wang first fully developed the method to manifest and quantify the tractions using TFM, and used the method to demonstrate that the ability lamellipodium to generate intense traction stress in 3T3 fibroblast.130 Butler et al. soon improved the method so tractions can be more easily solved from displacements,131 and Trepat et al. applied this method to collective cell migration.16
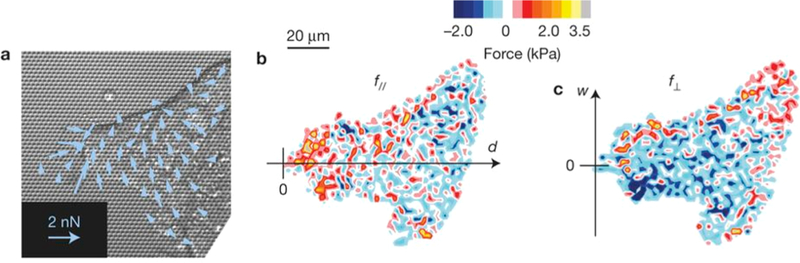
A similar principle is based on seeding cells on a substrate of soft micropillars and inferring the tractions by the pillar deformations. For example, Du Roure et al. used this setup to demonstrate that the highest average traction of a migrating epithelial monolayer is localized at the edge of the layer and oriented toward the bulk of the cell layer.132 Figure 7 shows the results of Reffay et al., who used this method to make similar observations in finger-like formations during the collective migration of MDCK cells.
Figure 7.
Traction force maps obtained in a finger-like formation of MDCK cells migrating on soft micropillars: (a) direction of main forces, (b) intensity of the longitudinal direction, and (c) intensity on the transverse direction. Reproduced with permission from ref 139. Copyright 2014 Springer Nature.
Stresses between cells can be computed from the tractions and the principle of equilibrium.17,133,134 These methods give the tractions and stresses that together bring about collective migration. Details on the relationship between force and motion are still being explored. In their work using computational modeling, Yang et al. explored the possibility of integrating TFM measurements and mechanical inference to account for the nonstatic character of cells.135 Another recent finding is that stress anisotropy produces alignment between local maximal stress within a cell monolayer and the local migration velocity of the cells,17 phenomenon recognized as “phlithotaxis”. Other works have shown a quantitative relation between shear stress and cell alignment136 and the increase in strain rates as a precursor of coordinated motion.137 Integrating these effects, Zaritsky et al. proposed that the mechanism of locally induced coordinated movement relies on the leader cells inducing normal strain on rear neighboring cells and shear strain on adjacent cells.138
Forces can also be assessed by using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) as a tension sensor by incorporating the FRET probes within proteins from the cytoskeleton, cell– cell junctions, or cell–ECM adhesion proteins. For instance, Sarangi et al. combined micropillar substrates with a FRET molecular tension sensor that allowed them to map both the traction forces of each focal adhesion cluster and the molecular tensions experienced within the vinculin molecules in those clusters, showing a strong spatiotemporal correlation between the two.140
Although 2D and 3D assays are helpful in investigating effects of certain factors on collective migration or the biomechanics of cell collectives during the phenomena, the in vivo reality might be different, much as 2D behaviors differ from 3D ones for various types of cells being studied. In this context, it is natural to envision methods to look at the phenomena in vivo. With the ease of fluorescence labeling, either genetically (through FRET sensors or simply fluorescent proteins to allow for detection) or by live-staining methods, and microscopy techniques improving, the hurdle of in vivo experiments strongly lays on the side of data processing rather than data acquisition. Cliffe et. al developed a processing toolbox for investigating collective migration in Drosophila,141 while other studies in vivo have focused on zebrafish142 or Xenopus laevis143 embryos. However, establishing FRET probes for in vivo models remains challenging, as Eder et al. discuss in their paper regarding FRET E-cadherin tension sensors in a Drosophila melanogaster model.144 Moreover, studying collec-tive migration in vivo in the case of cancer brings another set of challenges, as the number of cells is increased dramatically, and imaging procedures are limited by time and field of view.145 Therefore, aspects such as the significance of stress-guided migration patterns or a precise mapping of the forces involved in vivo remain open questions for the moment. An approach to mitigate this type of shortcoming is to produce computational models, versatile and readily available to simulate in vivo behaviors, the highlights of which are described in the following section.
FRET Biosensors.
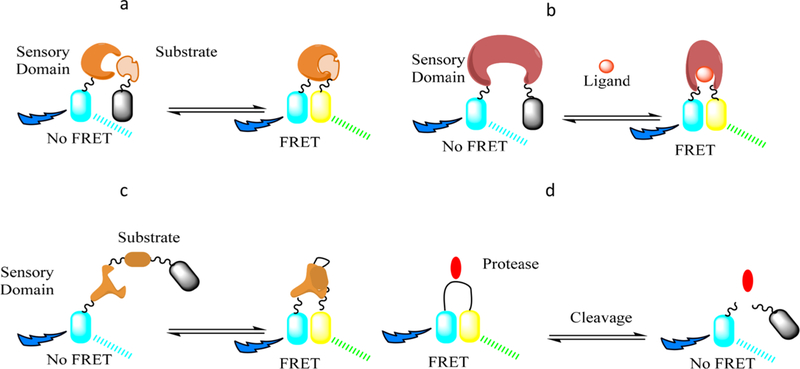
FRET biosensors are based on the interactions of the electromagnetic fields of two fluorescent molecules with overlapping excitation and emission spectra, one of which is deemed the donor and the other the acceptor.146 The connection between the pair is usually made with a spring-like molecule such as a different protein (spectrin, actin)147,148 or even DNA helices.149 These components are then genetically encoded into cells and can yield a detectable FRET signal upon certain biological events that cause the two fluorophores to closely interact, depending on the design of the biosensor. A schematic of the various FRET biosensor strategies is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8.
FRET biosensor design strategies. The two fluorescent molecules are represented by the cyan and yellow cylinders, while the gray color indicats the lack of signal from the respective protein. (a) The donor molecule is attached to a sensory domain, while the acceptor is linked to the corresponding substrate, generating a FRET signal once they are binding. (b) Both proteins are connected to a single sensory domain that changes its conformation upon binding to a particular ligand. (c) Both substrate and sensory domain are linked in a singular probe. (d) An opposite strategy starts with the two proteins connected in close proximity to generate a FRET signal and detects the disappearance of it as the linker is cleaved/ stretched in the biological media.
FRET probes represent a tool that can provide molecular insight when combined with the types of assays described herein (scratch wound assays, migration assays, microfluidics-based methods, etc.), enabling the understanding of underlying molecular mechanisms. For instance, Aoki et al. used a EKAREV-NLS expressing MDCK cells to study the effect of ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) waves, showing that the collective migration direction is facilitated by the propagation of ERK activation in 2D scratch-wound assay cultures.150 Employing the same cell line, MDCK, but this time expressing a FRET vinculin vinculin tension biosensor (TS) tension biosensor, Abdellatef et al. studied the effect of the substrate on cell adhesion and its tension.151 Moreover, Reffay et al. investigated the mechanisms of migration finger formations, showing a strong correlation between single-cell-based RhoA activity gradients and local forces in the structure, by means of Rac1 and RhoA FRET probes.139 Camona-Fontaine et al.152 used FRET to probe for Rac1 activity in neural crest cells from zebrafish (in vivo) during embryo-genesis, as they collectively migrate due to a proposed “coattraction” phenomenon. Using these probes in an in vivo assay provides an interesting possibility of observing factors that might be overlooked or oversimplified by in vitro model assays.
4. COMPUTATIONAL METHODS
4.1. Self-Propelled Particle (SPP) Model.
Out of the SPP models proposed for the study of collective movement and swarming, the Vicsek model proposed in 1995 is perhaps one of the most famous.153,154 Compared to the previously described Boids model, the Vicsek model’s particularity is the rule of the particles aligning themselves with the average direction of neighboring particles. This model was introduced to investigate the transport and phase transition in non-equilibrium systems. Here, a particle within the system possesses a constant absolute velocity whose direction is determined as the average direction of motion of the neighboring particles within a searching radius r with some random perturbation added.153 In particular, the velocity {vi} of the particles is identified at each time step, and the position of the ith particle is determined as
Note that the velocity of a particle vi(t + 1) is calculated to have an absolute value v and a direction determined as the angle θ(t + 1) as
where 〈θ(t)〉r is the average direction of the velocities of neighboring particles within a circle of radius r surrounding the given particle (i.e., ith particle). Also, ∆θ denotes a random number to represent the noise in the system. This model predicted that particles moved either in disordered or ordered motion depending on particle density (or cell packing fraction) and noise level.
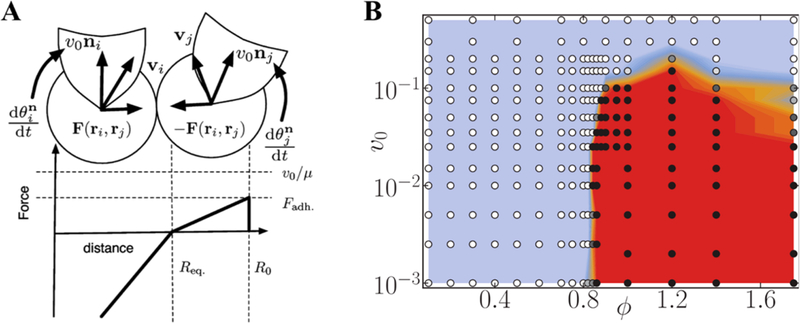
Although this model can simulate collective cell migration, it has several disadvantages as the particles were simply modeled as points, and intercellular interaction was not considered. Researchers then extended and expanded this model to consider this interaction. Specifically, the intercellular force F(ri,rj) between ith and jth cells is considered as piecewise linear force function that is a function of distance between two cells (Figure 9A).59 This force is repulsive if the distance is smaller than Req, whereas it is attractive when the distance is Req ≤ dij ≤ R0, i.e.:
where , , Frep is the maximum repulsive force at dij = 0, and Fadh is the maximum attractive force at dij = R0. Moreover, skewing away from Vicsek’s alignment to neighboring cells behavior, this model includes cells that align to the direction of the net force acting upon them.
Figure 9.
(A) Schematics showing intercellular forces as well as self-propelled velocity directions. (B) Phase diagram showing the transition from the liquid state (blue region) to the solid state (red region). Panel A reprinted with permission from ref 59. Copyright 2006 American Physical Society. Panel B reproduced with permission from ref 156. Copyright 2011 American Physical Society.
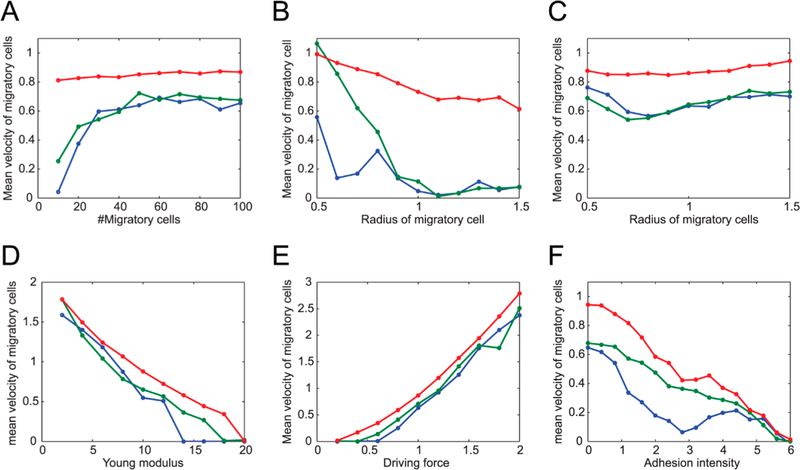
This model was then further improved to investigate the migration behavior of cells.155–158 The results revealed that cell packing fraction, moving velocity, and noise level controlled whether the cells migrated with collective or dispersive behavior. The phase diagram was developed by Henkes et al., who reported that the cells were in liquid- or solid-like state depending on cell packing fraction and velocity (Figure 9B).158 Figure 9B clearly showed a transition from a liquid-like (or unjammed) state to a jammed phase at critical packing fraction of ϕc ≈ 0.842. Yamao et al. concluded that cells migrated with collective, neutral, or dispersive behavior depending on the strength of noise from migratory cells vs nonmigratory ones. Their model used three main components in modeling cell behavior, namely repulsive forces between cells, the driving force of migratory cells together with the reactive forces of neighboring cells via adhesion, and the stochastic forces involved in a random walk. Their study includes the influence of such parameters as the number of migratory cells, their size, elasticity, and the impact of the driving force and adhesion to the environment (Figure 10).155 In 2014, Li and Sun utilized this model to study the coherent rotational motion of 2D confluent cell monolayer.159 They stated that the rotational motion of the cell depends on the geometrical shapes and mechanical properties of the cells. They also concluded that mechanical coupling between cells is necessary to explain this motion. This model has also been used to study the effects of interaction between stromal and cancerous cells, which is important in tumor growth and metastasis,160 on collective migration behavior.161 The authors reported that stromal cell– cancerous cell interactions could play a major role in the generation of collective movement.
Figure 10.
Plots of the collective (green), neutral (blue), and dispersive (red) migration modes of migratory cells in a multicellular environment consisting of both migratory and nonmigratory cells. The average migratory cell speeds are represented against (A) number of migratory cells, migratory cells’ radius (B, C), migration driving force (D), and Young’s modulus for all cells (E). In panel F, an additional attractive force from cell adhesion is included. The “collective” migration mode is herein characterized as a high collective pattern that makes all the cells converge into one stream; the “neutral” mode represents a case in which the migratory cells’ dispersion during migration does not change significantly, while the “dispersive” mode refers to the individual cells migrating. Reproduced under Creative Commons from ref 155. Copyright 2011 Yamao et al.
4.2. Vertex Model.
The SPP model above was able to simulate a jamming/unjamming transition when cell density or packing fraction ϕc < 1. However, the transition can also take place even in nonproliferating confluent biological tissues. In this case, the packing fraction ϕ is close to unity (i.e., there are no gaps between cells). To address this problem, vertex models,73,74,77,159,162–165 which have shown great potential and been extensively applied, were proposed. In the vertex model, each cell is represented by a polygon with several vertices. For a tissue containing N cells, the mechanical energy of the whole tissue is expressed as
| (4) |
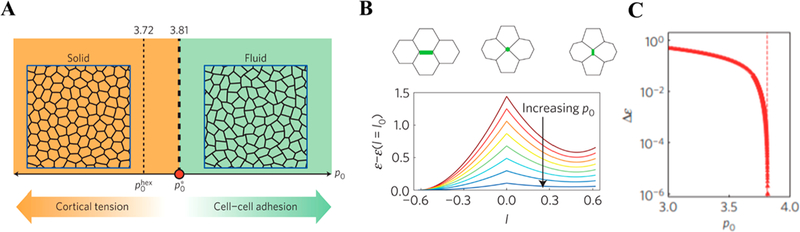
where Ai and Pi are the cross-sectional area and perimeter of the ith cell, respectively, A0 and P0 are the preferred cross- sectional area and perimeter, respectively, and KA and KP are the area and perimeter moduli, respectively. The first term is an elastic term on cell area accounting for a previously apparently elastic behavior observed in cell layers.50,166,167 The second term derives from two terms: the first one is quadratic in the cell perimeter to model the hypothesized active contractility of the actin–myosin subcellular cortex, and the second one is linear in the cell perimeter to simulate an effective line tension resulting from cell–cell adhesion and cortical tension. In addition, a dimensionless effect target shape index is defined as , which the models have assumed to be constant across the whole tissue.
In this model, a critical value of , at which the rigidity transition took place, was determined (Figure 11A).73 Below this critical value, the tissue behaved as an elastic solid-like material with finite shear modulus due to the cortical tension is superior to cell–cell adhesion. In this case, the cells had rounded shape, and the energy barriers for cell rearrangement transitions are finite (Figure 11B). In contrast, above this value, the cells had elongated shape; cell–cell adhesion dominated, and cell rearrangements’ energy barriers vanished (Figure 11C), resulting in zero rigidity and fluid-like behavior.
Figure 11.
(A) Simple phase diagram showing the rigidity transition as a function of p0. When , the tissue was jammed (solid-like tissues), whereas the tissue was unjammed (liquid-like tissue) when . (B) Energy barriers for T1 transition as a function of edge length l for different values of p0, varying from 1.5 to 3.8 in equal increments. (C) Energy barrier height as a function of p0, showing a sharp decrease with the approach of the critical value, , pointed out by a vertical dashed line. Reproduced with permission from ref 73. Copyright 2015 Springer Nature.
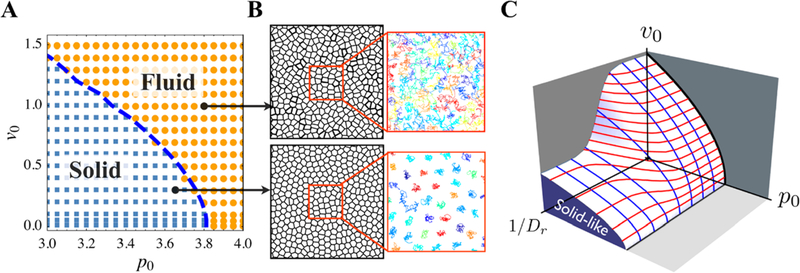
This model was then combined with the SPP model into a so-called self-propelled Voronoi (SPV) model.135,168 This model identifies the cell using only the center (ri) of Voronoi cells in a Voronoi tessellation of space. For a tissue containing N cells, the total mechanical energy of the tissue capturing intercellular interactions is defined by eq 4. The effective mechanical force acting on ith cell is given as F = –∇iE. In addition, cells can move due to self-propelled motility like that of SPP model. The cell center ri is controlled by these forces using the overdamped equation of motion as follows:
where μ is the motility, v0 is the self-propulsion velocity, and is the polarity vector to ith cell.
In this model, Bi et al. used the effective self-diffusivity Deff as one of the criteria to identify glass transition, where Deff was nonzero when the tissue behaved as fluid-like material. Here, Deff refers to the ratio between the total systems’ self-diffusion coefficient and the self-diffusion coefficient of a single, isolated cell. The order parameter chosen this way is unitless and can serve as an identifier of the liquid-like or solid-like state of the represented monolayer. Also, a unitless shape index of the tissue was defined as , which was the averaged shape index of the cells. The authors claimed that in the model where cells were not motile (v0 = 0), q is constant ∼3.81 when p0 < 3.81, and q was increasing linearly with p0 when p0 > 3.81. Interestingly, q could also be used to determine the glass transition for all values of v0. As shown in Figure 12A, the cells were isotropic in the solid phase (blue squares) and anisotropic in the liquid phase (orange circles). In addition, the blue dashed line indicated the boundary defined q = 3.81. The authors developed a 3D phase diagram as shown in Figure 12B to account for the effects of persistence time scale 1/DR for the polarity vector . The jamming transition in their system takes place when the tissue has low motility and cells have a low target shape index and low persistence time.
Figure 12.
(A and B) Phase diagram of glass transition for confluent tissues as a function of cell motility v0 and target shape index p0 when Dr = 1. (C) 3D phase diagram of rigidity transition as a function of cell motility v0, target shape index p0, and persistence 1/Dr. Adapted with permission from ref 168. Copyright 2016 American Physical Society.
4.3. Cellular Potts Model.
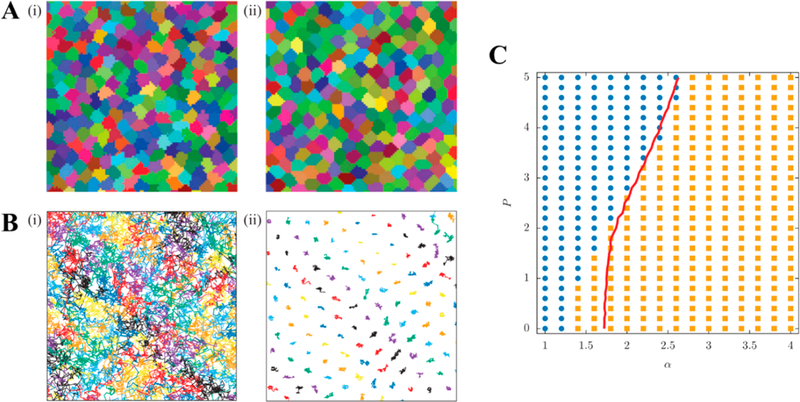
A cellular Potts model is a stochastic model where each cell is represented as a subset of a lattice. This model has been used to study migration of cells through the extracellular matrix169 and through a confluent layer of cells (Figure 13).170 It can be observed that the migratory cells extended (yellow to red gradient) and squeezed between nonmigratory cells by pushing them apart. In addition, Chiang et al. used this model to study the unjamming transition in cell migration.171 The dynamics of the cells were calculated via Monte Carlo algorithm based on a Hamiltonian that allowed for the variation of interfacial effects by means of a interfacial tension parameter and cell motility through a strength of motility parameter. Figures 14A and B show cell shape and trajectories for two different phases which were fluid-like (left panel in Figures 14A and B) and solid-like (right panel in Figures 14A and B). It can be observed that cells had a more rounded shape in the solid-like phase where the cells were caged compared to an elongated shape in liquid-like phase where the cells were flowing. The authors also generated a phase diagram, which is shown in Figure 14C, demonstrating the transition from jammed solid to unjammed phase depending on the interfacial energy α and strength of motility P. In this diagram, the blue circles and yellow square represented diffusive and subdiffusive behavior of the cells. The red curve in this diagram indicated the critical shape index of the cells of pc = 4.9. This value was slightly different from that identified in Vertex and SPV models (i.e., pc = 3.82), which was probably due to discrepancies in cell morphologies in these models. These might arise from the infinite bending rigidity of the vertex’s model edges, while CPM can resolve for more arbitrarily shaped cells. More recently, Hallou et al.198 employed a Cellular Potts method with a self-propelled term to simulate the cells’ active movement and found that cell heterogeneity contributes to metastatic dissemination of cancer cells.
Figure 13.
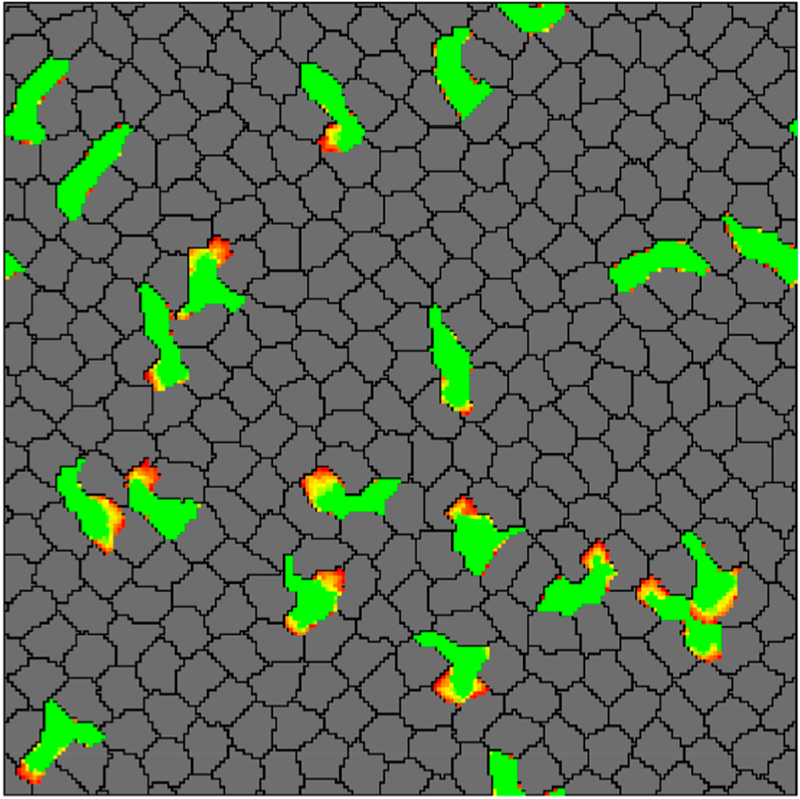
Simulation snapshot showing T cells (green) were squeezing between skin cells (gray) by pushing them apart. The yellow-red regions denote the protrusions extended by T cells. Reproduced with permission from ref 170. Copyright 2015 Ioana Niculescu, Johannes Textor, Rob J. de Boer.
Figure 14.
A snapshot of cell shapes (A) and trajectories of the cell centers (B) for tissues in fluid (α = 1) (i) and solid (α = 4) (ii) state. (C) Phase diagram of rigidity transition as a function of the interfacial energy α and strength of motility P. The blue circles indicated diffusive behavior, whereas the orange squares indicated subdiffusive behavior. The red line corresponds to the condition pairs under which the order parameter (or as previously described, shape index) was equal to its proposed threshold of 4.9. Reproduced with permission from ref 171. Copyright 2016 EPLA.
4.4. Cellular Automaton (CA) Model.
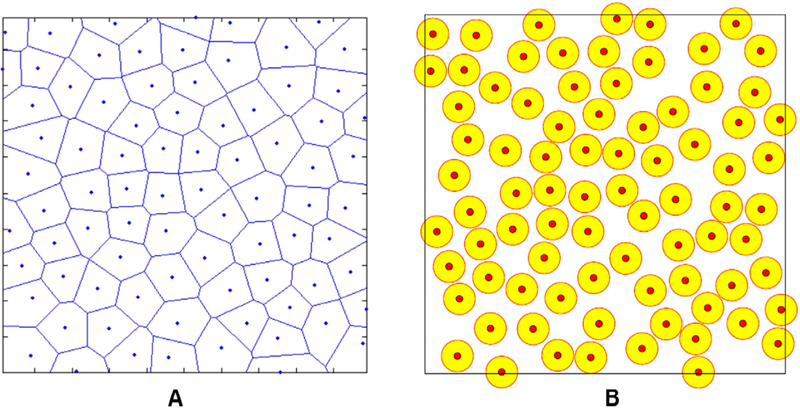
The CA model has been used extensively in theoretical biology. One of the first works applying this method in cancer cell invasion was introduced in 1985 by Duchting and Vogelsaenger.172 This model was greatly improved since then to comprehensively investigate cancer cell invasion. For example, Jiao and Torquato developed a single-cell-based CA model to study the growth dynamics and morphology of invasive solid tumors.173 They first created nonoverlapping spheres using a random sequential addition (RSA) process. The automaton cells were then created using Voronoi tessellation based on the centers of the spheres (Figures 15 and 16).
Figure 15.
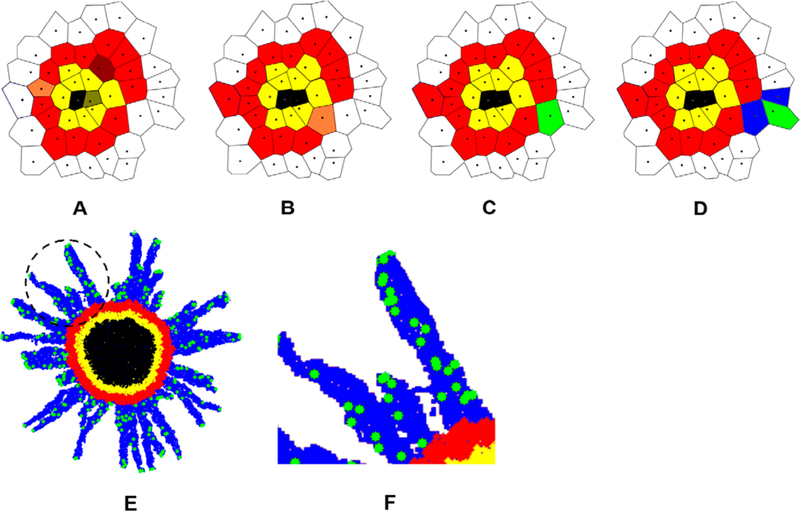
Automaton cells were created using Voronoi tessellation (a) based on the centers of the spheres (b) which were created with RSA process. Reproduced with permission from ref 173. Copyright 2011 Yang Jiao, Salvatore Torquato. In this model, each automaton cell could be either ECM of a specify density, invasive, proliferative, quiescent, or necrotic cell. The microenvironment heterogeneity could easily be considered by varying the distributions of the ECM densities. An invasive cell would degrade the surrounding ECM and migrated from one automaton cell to another if the associated ECM in that cell has a “zero” density (i.e., fully degraded). The detailed rules of this CA model are illustrated in Figure 16. Using this model, the authors successfully captured the cancer cell invasion process by considering various tumor–host interactions (e.g., the mechanical interactions between tumor cells and microenvironment (ECM), degradation of ECM by the tumor cells, and oxygen/nutrient gradient driven cell motions).
Figure 16.
Black: necrotic cells; yellow: quiescent cells; red: proliferative cells; green: invasive tumor cells; white: ECM; blue: degraded ECM. (A) A proliferative cell (dark red) turns into a quiescent cell in panel B because it is too far away from the tumor edge. A quiescent cell (dark yellow) turns into a necrotic cell in panel B because it is too far away from the tumor edge. Another proliferative cell (light red) will create a daughter proliferative cell in panel B. (B) A proliferative cell (light red) will create a mutant invasive daughter cell in panel C. (D) The invasive cell degraded the surrounding ECM and moved to another automaton cell. (E) A snapshot of the CA model simulation showing cancer cell invasion process in a multicellular tumor spheroid at 24 h after initialization. (F) A zoom-in view of the circled region in panel E. Adapted with permission from ref 173. Copyright 2011 Yang Jiao and Salvatore Torquato.
This model was then combined with in vitro cell migration experiments to investigate the effects of ECM heterogeneity on cancer cell invasion.174 The authors developed a heteroge-neous ECM by creating a funnel-like Matrigel interface (Figure 17). The authors claimed that ECM heterogeneity is important in governing the collective cell invasive behaviors and therefore determining metastasis efficiency. Recently, the CA model was improved to investigate 3D tumor growth in heterogeneous environment under chemotherapy.175 The authors concluded that constant dosing is more effective than periodic dosing in suppressing tumor growth. This 3D CA model could help researchers develop efficient tools for prognosis and to optimize cancer treatments.
Figure 17.
(A and B) Diagrams illustrate how funnel-like Matrigel interface is created with Matrigel I and II. (C) The gel interface is indicated by red arrows. (D) Snapshots of CA model simulation showing the collective migration pattern. Reproduced with permission from ref 174, Copyright-free under Creative Commons CC0.
4.5. Finite Element (FE) Model.
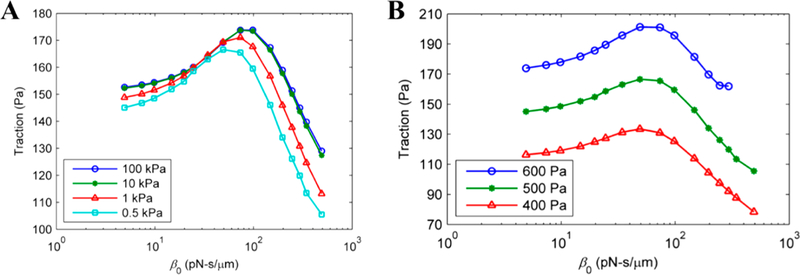
The FE model has been extensively used in cell and tissue mechanics studies.176–183 Recently, this model was used to investigate cell–substrate adhesion as well as cell migration.184–187 Wong and Tang developed a FEA model to investigate the effects of focal adhesion mechanical properties, substrate stiffness, and intracellular stress on cell–matrix interaction during cell migration. The authors reported that cell–matrix traction had a biphasic relationship with respect to frictional coefficient, which could be used to identify focal adhesion properties, as shown in Figure 18.184 The simulation results revealed that both substrate stiffness and intracellular stress affected cell– matrix traction but at different levels. Particularly, traction increased in greater amounts when then intracellular stress was increased from 400 to 600 Pa compared to when substrate stiffness was increased from 0.5 to 100 kPa. Additionally, using a FEM-based mechanochemical coupling model, Zhong et al. show that the competition of cell adhesion stability between the cell front and the cell rear drives individual cell migration.183 While these studies focused mostly on single-cell migration dynamics, Zhao et al. proposed a so-called dynamic cellular finite element model (DyCelFEM) to elucidate biochemical and mechanical cues in regulating cell migration and proliferation that include effects from neighbors in cell collectives (Figure 19).185 The authors concluded that improved directionality and persistence of cell migration was guided by biochemical cues, while mechanical cues played important roles in coordinating collective cell migration. It would be interesting to see whether the findings for single-cell migration determinants hold in the context of large-scale migration, when biochemical cues, geometrical factors, and cell–environment interactions are treated in an integrated manner.
Figure 18.
Maximum cell–substrate traction vs receptor–substrate friction coefficient plots for different substrate mechanical properties (A) and different maximum actomyosin stresses (B) in the case of single cell migration modeling. Reproduced with permission from ref 184. Copyright 2011 Elsevier Ltd.
Figure 19.
(A) Schematics of the skin wound tissue model; schematics showing how biochemical (B) and mechanical (C) cues regulate cell migration. Reproduced with permission from ref 185. Copyright 2017 Jieling Zhao, Youfang Cao, Luisa A. DiPietro, and Jie Liang.
4.6. Deformable Particle Model (DPM).
Recently, a particle-based method (i.e., DPM) was developed to investigate the effect of cell packing density on jamming behavior of cell monolayers.188 A cell is modeled as a polygon composed of a NV edges/particles. Adjacent particles are connected via linear springs with a spring constant of ki and equilibrium length of l0 = p0/NV, where k0 is the target perimeter of the cell/polygon. The total energy of DPM of an N-cell tissue is defined as
where lmi is the length of ith edge of mth cell, ka is the area modulus which is corresponding to the cell’s compressibility, and am and a0 are the mth cell and preferred cross-sectional area, respectively. This is notably similar in form as the fundamental equation of the vertex model. In this equation, Uint is the repulsive interaction between two adjacent cells given by
where kr is the strength of repulsive interaction, δ is the diameter of the disks centered at each of the vertices, vmj is the position vector of the jth particle in cell m, and Θ(…) is the Heaviside step function. The DPM showed that jamming took place at packing fraction of ϕmax ≈ 0.95–0.99. Figure 20 shows the snapshots of cell shape at different packing fraction. The advantage of this model is that it can account for the cell membrane bending as well as its viscoelasticity by integrating both an elastic and a viscous force between each two neighboring points on the membrane.189
Figure 20.
Snapshots of DPM results at different jammed packing fraction determined by a change in particle shape (described by the asphericity factor, A), where (a) A = 1.03, (b) A = 1.08, and (c) A = 1.16. Reproduced with permission from ref 188. Copyright 2018 American Physical Society.
5. CONCLUSIONS AND PERSPECTIVES
Collective cell migration is a hallmark of events such as embryogenesis, wound healing, and cancer tumor invasion.7 Various studies at preclinical stages or using patient-derived samples have agreed on the fact that metastasis can be generated by clusters of cells rather than single cancer cells.190 Moreover, the aggregation of tumor cells during blood circulation or at the distant organ site was shown to be highly inefficient,191 strongly supporting the hypothesis that clusters start as a collective cohort of cells from the primary tumor that migrate together to secondary sites, hence contributing significantly to the lethal nature of cancer.
As described in this review, numerous methods have been developed to study the biomechanical particularities and implications on pathological progression of tumors. Exper-imental procedures, both in vitro and in vivo, alongside computational methods, have uncovered the puzzle pieces of a complex mechanism yet to be appropriately interconnected, which involves a variety of parameters such as cell–cell adhesions, cell–substrate interactions, microenvironment biomechanical behavior, or cytoskeleton rearrangements that inform and regulate the collective cell migration behavior. However, there is still a ways to go to unveil all the intricacies of such mechanism underlying collective cell migration. Experimentally, current limitations include the potential differences between the in vitro models (2- and 3-dimensional) and the in vivo realities, oftentimes difficult to address. Although experimental methods have been adapted for in vivo studies in the case of small organisms, observing collective cell migration triggering in mammals is still challenging.144,145 On the other hand, computational models have not necessarily focused on collective migration in the case of cancer, even if basic principles and uncovered biomechanical factors still hold. Given the differences between cancer cells and their normal counterparts28 as well as the particularities of the interactions within tumor stroma,161 some of the existing modeling strategies remain to be improved to account for such factors. Some advancements in the field have focused on the cell collective–ECM interactions during migration, showing that local stiffness anisotropy influences the migration direction192 or that ECM fibers play an important role in long-distance mechanosignaling in both the single-cell193 and multicellular cases.194,195 These are promising strategies, especially in light of multiple experimental works showing a strong dependency of cell migration and ECM composition, stiffness, and orientation.
From a clinical perspective, proposed methods of targeting collective cancer cell behavior include targeting leader cells42,139 or reducing cell–cell communication.196 However, even if technical hurdles of detection and genetic engineering could be overcome, previous results seem to shade the potential usability of such methods. For example, studies targeting cell–cell communication have shown that tumor aggressiveness increases while collective behavior decreases, indicating a trade-off between collaboration and competitive-ness.42,197 Nonetheless, while the role of collective cell behavior is more evident in cancer metastasis, other features of tumors might be enhanced by it, including drug resistance and the support of stem cell niches.145 Therefore, a better understanding of the mechanisms at play could allow for the right amount of trade-offs as researchers develop new strategies to improve diagnosis or therapeutic efficacy.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Z.C. acknowledges the support from the Branco Weiss-Society in Science fellowship, administered by ETH Zürich. The research was in part supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under Award U01CA202123. L.L. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11474345 and 11674043).
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
REFERENCES
- (1).Rørth P Fellow Travellers: Emergent Properties of Collective Cell Migration. EMBO Rep 2012, 13 (11), 984–991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (2).Doxzen K; Vedula SR; Leong MC; Hirata H; Gov NS; Kabla AJ Guidance of Collective Cell Migration by Substrate Geometry. Integr. Biol 2013, 5 (8), 1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).Friedl P; Gilmour D Collective Cell Migration in Morphogenesis, Regeneration and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2009, 10 (7), 445–457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).Hashimoto H; Robin FB; Sherrard KM; Munro EM Sequential Contraction and Exchange of Apical Junctions Drives Zippering and Neural Tube Closure in a Simple Chordate. Dev. Cell 2015, 32 (2), 241–255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (5).Behrndt M; Salbreux G; Campinho P; Hauschild R; Oswald F; Roensch J Forces Driving Epithelial Spreading in Zebrafish Gastrulation. Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 2012, 338 (6104), 257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (6).Heller E; Kumar KV; Grill SW; Fuchs E Forces Generated by Cell Intercalation Tow Epidermal Sheets in Mammalian Tissue Morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 2014, 28 (6), 617–632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (7).Rorth P Collective Cell Migration. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 2009, 25 (1), 407–429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (8).Begnaud S; Chen T; Delacour D Mechanics of Epithelial Tissues during Gap Closure. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2016, 42, 52–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (9).Solnicakrezel L Conserved Patterns of Cell Movements during Vertebrate Gastrulation. Curr. Biol 2005, 15 (6), R213–R228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).Geisbrecht ER; Montell DJ Myosin vi Is Required for E- Cadherin-Mediated Border Cell Migration. Nat. Cell Biol 2002, 4 (8), 616–620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).Lecaudey V; Cakan-Akdogan G; Norton WH; Gilmour D Dynamic Fgf Signaling Couples Morphogenesis and Migration in the Zebrafish Lateral Line Primordium. Development 2008, 135 (16), 2695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (12).Fenteany G; Janmey PA; Stossel TP Signaling Pathways and Cell Mechanics Involved in Wound Closure by Epithelial Cell Sheets. Curr. Biol 2000, 10 (14), 831–838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (13).Omelchenko T; Vasiliev JM; Gelfand IM; Feder HH; Bonder EM Rho-Dependent Formation of Epithelial “Leader” Cells during Wound Healing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2003, 100 (19), 10788–10793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (14).Lecaudey V; Gilmour D Organizing Moving Groups during Morphogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2006, 18 (1), 102–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (15).Vedula SRK; Hirata H; Nai MH; Brugueś A; Toyama Y; Trepat X; Lim CT; Ladoux B Epithelial Bridges Maintain Tissue Integrity during Collective Cell Migration. Nat. Mater 2014, 13 (2013), 87–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (16).Trepat X; Wasserman MR; Angelini TE; Millet E; Weitz DA; Butler JP; Fredberg JJ Physical Forces during Collective Cell Migration. Nat. Phys 2009, 5 (6), 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- (17).Tambe DT; Hardin CC; Angelini TE; Rajendran K; Park CY; Serra-Picamal X; Zhou EH; Zaman MH; Butler JP; Trepat X Collective Cell Guidance by Cooperative Intercellular Forces. Nat. Mater 2011, 10 (6), 469–475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (18).Raja Sivamani K; Garcia MS; Isseroff RR Wound Re-Epithelialization: Modulating Keratinocyte Migration in Wound Healing. Front. Biosci., Landmark Ed 2007, 12 (8), 2849–2868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (19).Ilina O; Friedl P Mechanisms of Collective Cell Migration at a Glance. J. Cell Sci 2009, 122, 3203–3208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (20).Schmidt M; Paes K; De Maziere A; Smyczek T; Yang S; Gray A; French D; Kasman I; Klumperman J; Ye W EGFL7 Regulates the Collective Migration of Endothelial Cells by Restricting Their Spatial Distribution. Development 2007, 134, 2913–2923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (21).Arciero JC; Mi Q; Branca MF; Hackam DJ; Swigon D Continuum Model of Collective Cell Migration in Wound Healing and Colony Expansion. Biophys. J 2011, 100, 535–543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (22).Czyz J The Stage-Specific Function of Gap Junctions during Tumourigenesis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett 2008, 13 (1), 92–102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (23).Christiansen JJ; Rajasekaran AK Reassessing Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition as a Prerequisite for Carcinoma Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Res 2006, 66 (17), 8319–8326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (24).Friedl P; Noble PB; Walton PA; Laird DW; Chauvin PJ; Tabah RJ; Black M; Zänker K Migration of Coordinated Cell Clusters in Mesenchymal and Epithelial Cancer Explants in Vitro. Cancer Res 1995, 55 (20), 4557–4560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (25).Gaggioli C; Hooper S; Hidalgo-Carcedo C; Grosse R; Marshall JF; Harrington K and Sahai E Fibroblast-Led Collective Invasion of Carcinoma Cells with Differing Roles for RhoGTPases in Leading and Following Cells. Nat. Cell Biol 2007, 9, 1392–1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (26).Lee GYH; Lim CT Biomechanics Approaches to Studying Human Diseases. Trends Biotechnol 2007, 25 (3), 111–118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (27).Suresh S Biomechanics and Biophysics of Cancer Cells. Acta Mater 2007, 55 (12), 3989–4014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (28).Lin H-H; Lin H-K; Lin I-H; Chiou Y-W; Chen H-W; Liu C-Y; Harn HI-C; Chiu W-T; Wang Y-K; Tang M-J Mechanical Phenotype of Cancer Cells: Cell Softening and Loss of Stiffness Sensing. Oncotarget 2015, 6 (25), 20946–20958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (29).Mayor R; Etienne-Manneville S The Front and Rear of Collective Cell Migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2016, 17 (2), 97–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (30).Thiery JP Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Tumour Progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2 (6), 442–454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (31).Collins C; Nelson WJ Running with Neighbors: Coordinating Cell Migration and Cell - Cell Adhesion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 2015, 36, 62–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (32).Hakim V; Silberzan P Collective Cell Migration: A Physics Perspective. Rep. Prog. Phys 2017, 80 (7), 076601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (33).Kurniawan NA; Chaudhuri PK; Lim CT Mechanobiology of Cell Migration in the Context of Dynamic Two-Way Cell-matrix Interactions. J. Biomech 2016, 49 (8), 1355–1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (34).Haeger A; Wolf K; Zegers MM; Friedl P Collective Cell Migration: Guidance Principles and Hierarchies. Trends Cell Biol 2015, 25 (9), 556–566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (35).Barriga EH; Franze K; Charras G; Mayor R Tissue Stiffening Coordinates Morphogenesis by Triggering Collective Cell Migration in Vivo. Nature 2018, 554 (7693), 523–527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (36).Wei SC; Fattet L; Tsai JH; Guo Y; Pai VH; Majeski HE; Chen AC; Sah RL; Taylor SS; Yang J Matrix Stiffness Drives Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Tumour Metastasis through a TWIST1-G3BP2Mechanotransduction Pathway. Nat. Cell Biol 2015, 17 (5), 678–688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (37).Friedl P; Weigelin B Interstitial Leukocyte Migration and Immune Function. Nat. Immunol 2008, 9 (9), 960–969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (38).Cortese B; PalamàI E; D’Amone S; Gigli G Influence of Electrotaxis on Cell Behaviour. Integr. Biol 2014, 6 (9), 817–830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (39).Zhong Y; Ji B Impact of Cell Shape on Cell Migration Behavior on Elastic Substrate. Biofabrication 2013, 5 (1), 015011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (40).He S; Su Y; Ji B; Gao H Some Basic Questions on Mechanosensing in Cell-substrate Interaction. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2014, 70, 116–135. [Google Scholar]
- (41).McLennan R; Schumacher LJ; Morrison JA; Teddy JM; Ridenour DA; Box AC; Semerad CL; Li H; McDowell W; Kulesa PM Neural Crest Migration Is Driven by a Few Trailblazer Cells with a Unique Molecular Signature Narrowly Confined to the Invasive Front. Development 2015, 142 (11), 2014–2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (42).Deisboeck TS; Couzin ID Collective Behavior in Cancer Cell Populations. BioEssays 2009, 31 (2), 190–197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (43).Khalil AA; Friedl P Determinants of Leader Cells in Collective Cell Migration. Integr. Biol 2010, 2 (11–12), 568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (44).Taber L; Shi Y; Yang L; Bayly P A Poroelastic Model for Cell Crawling Including Mechanical Coupling between Cytoskeletal Contraction and Actin Polymerization. J. Mech. Mater. Struct 2011, 6 (1–4), 569–589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (45).Liu L; Duclos G; Sun B; Lee J; Wu A; Kam Y; Sontag ED; Stone HA; Sturm JC; Austin RH Minimization of Thermodynamic Costs in Cancer Cell Invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2013, 110 (5), 1686–1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (46).Kelly NJ; Varga JFA; Specker EJ; Romeo CM; Coomber BL; Uniacke J Hypoxia Activates Cadherin-22 Synthesis via EIF4E2 to Drive Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion and Adhesion. Oncogene 2018, 37 (5), 651–662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (47).van Helvert S; Storm C; Friedl P Mechanoreciprocity in Cell Migration. Nat. Cell Biol 2018, 20 (1), 8–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (48).Venhuizen J-H; Zegers MM Making Heads or Tails of It: Cell-Cell Adhesion in Cellular and Supracellular Polarity in Collective Migration. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol 2017, 9 (11), No. a027854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (49).Tambe DT; Corey Hardin C; Angelini TE; Rajendran K; Park CY; Serra-Picamal X; Zhou EH; Zaman MH; Butler JP; Trepat X Collective Cell Guidance by Cooperative Intercellular Forces. Nat. Mater 2011, 10 (6), 469–475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (50).Notbohm J; Banerjee S; Utuje KJC; Gweon B; Jang H; Park Y; Shin J; Butler JP; Fredberg JJ; Marchetti MC Cellular Contraction and Polarization Drive Collective Cellular Motion. Biophys. J 2016, 110 (12), 2729–2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (51).Theveneau E; Linker C Leaders in Collective Migration: Are Front Cells Really Endowed with a Particular Set of Skills? F1000Research 2017, 6, 1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (52).Trepat X; Fredberg JJ Plithotaxis and Emergent Dynamics in Collective Cellular Migration. Trends Cell Biol 2011, 21 (11), 638–646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (53).Fabry B; Maksym GN; Butler JP; Glogauer M; Navajas D; Fredberg JJ Scaling the Microrheology of Living Cells. Phys. Rev. Lett 2001, 87 (14), 148102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (54).Kollmannsberger P; Fabry B Linear and Nonlinear Rheology of Living Cells. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res 2011, 41 (1), 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- (55).Angelini TE; Hannezo E; Trepat X; Marquez M; Fredberg JJ; Weitz D. a. Glass-like Dynamics of Collective Cell Migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2011, 108 (12), 4714–4719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (56).Zhou EH; Trepat X; Park CY; Lenormand G; Oliver MN; Mijailovich SM; Hardin C; Weitz DA; Butler JP; Fredberg JJ Universal Behavior of the Osmotically Compressed Cell and Its Analogy to the Colloidal Glass Transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2009, 106 (26), 10632–10637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (57).Trepat X; Deng L; An SS; Navajas D; Tschumperlin DJ; Gerthoffer WT; Butler JP; Fredberg JJ Universal Physical Responses to Stretch in the Living Cell. Nature 2007, 447 (7144), 592–595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (58).Nnetu KD; Knorr M; Pawlizak S; Fuhs T; Kas̈ JA Slow and Anomalous Dynamics of an MCF-10A Epithelial Cell Monolayer. Soft Matter 2013, 9 (39), 9335. [Google Scholar]
- (59).Szabó B; Szöllö GJ; Gönci B; Jurányi Z; Selmeczi D; Vicsek T Phase Transition in the Collective Migration of Tissue Cells: Experiment and Model. Phys. Rev. E 2006. 74 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.74.061908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (60).Nnetu KD; Knorr M; Käs J; Zink M The Impact of Jamming on Boundaries of Collectively Moving Weak-Interacting Cells. New J. Phys 2012, 14 (11), 115012. [Google Scholar]
- (61).Liu AJ; Nagel SR The Jamming Transition and the Marginally Jammed Solid. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys 2010, 1 (1), 347–369. [Google Scholar]
- (62).Sadati M; Nourhani A; Fredberg JJ; Taheri Qazvini N Glass-like Dynamics in the Cell and in Cellular Collectives. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med 2014, 6 (2), 137–149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (63).Lenormand G; Chopin J; Bursac P; Fredberg JJ; Butler JP Directional Memory and Caged Dynamics in Cytoskeletal Remodelling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2007, 360 (4), 797–801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (64).Tambe DT; Fredberg JJ And i Hope You like Jamming Too. New J. Phys 2015, 17 (9), 091001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (65).Oswald L; Grosser S; Smith DM; Käs JA Jamming Transitions in Cancer. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys 2017, 50 (48), 483001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (66).Atia L; Bi D; Sharma Y; Mitchel JA; Gweon BA; Koehler S; DeCamp SJ; Lan B; Kim JH; Fredberg JJ Geometric Constraints during Epithelial Jamming. Nat. Phys 2018, 14 (6), 613–620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (67).Silbert LE; Ertas DE; Grest GS; Halsey TC; Levine D Analogies between Granular Jamming and the Liquid-Glass Transition. Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top 2002. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.65.051307. [DOI] [PubMed]
- (68).Cates ME; Wittmer JP; Bouchaud J-P; Claudin P Jamming, Force Chains, and Fragile Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett 1998, 81, 1841. [Google Scholar]
- (69).Sadati M; Taheri Qazvini N; Krishnan R; Park CY; Fredberg JJ Collective Migration and Cell Jamming. Differentiation 2013, 86 (3), 121–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (70).Atia L; Bi D; Sharma Y; Mitchel JA; Gweon B; Koehler S; DeCamp SJ; Lan B; Hirsch R; Fredberg JJ Universal Geometric Constraints during Epithelial Jamming 10.1038/s41567-018-0089-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- (71).Malinverno C; Corallino S; Giavazzi F; Bergert M; Li Q; Leoni M; Disanza A; Frittoli E; Oldani A; Scita G Endocytic Reawakening of Motility in Jammed Epithelia. Nat. Mater 2017, 16 (5), 587–596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (72).Garcia S; Hannezo E; Elgeti J; Joanny J-F; Silberzan P; Gov NS Physics of Active Jamming during Collective Cellular Motion in a Monolayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2015, 112 (50), 15314–15319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (73).Bi D; Lopez JH; Schwarz JM; Manning ML A Density-Independent Rigidity Transition in Biological Tissues. Nat. Phys 2015, 11 (12), 1074–1079. [Google Scholar]
- (74).Park J-A; Kim JH; Bi D; Mitchel JA; Qazvini NT; Tantisira K; Park CY; McGill M; Kim S-H; Fredberg JJ Unjamming and Cell Shape in the Asthmatic Airway Epithelium. Nat. Mater 2015. DOI: 10.1038/nmat4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- (75).Park J-A; Atia L; Mitchel JA; Fredberg JJ; Butler JP Collective Migration and Cell Jamming in Asthma, Cancer and Development. J. Cell Sci 2016, 129 (18), 3375–3383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (76).Chepizhko O; Lionetti MC; Malinverno C; Giampietro C; Scita G; Zapperi S; La Porta CAM From Jamming to Collective Cell Migration through a Boundary Induced Transition. Soft Matter 2018, 14 (19), 3774–3782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (77).Gamboa Castro M; Leggett SE; Wong IY Clustering and Jamming in Epithelial-mesenchymal Co-Cultures. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (78).Pegoraro AF; Fredberg JJ; Park J-A Problems in Biology with Many Scales of Length: Cell–cell Adhesion and Cell Jamming in Collective Cellular Migration. Exp. Cell Res 2016, 343 (1), 54–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (79).Haeger A; Krause M; Wolf K; Friedl P Cell Jamming: Collective Invasion of Mesenchymal Tumor Cells Imposed by Tissue Confinement. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj 2014, 1840 (8), 2386–2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (80).Fischer KR; Durrans A; Lee S; Sheng J; Li F; Wong STC; Choi H; El Rayes T; Ryu S; Gao D Epithelial-to- Mesenchymal Transition Is Not Required for Lung Metastasis but Contributes to Chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527 (7579), 472–476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (81).Zheng X; Carstens JL; Kim J; Scheible M; Kaye J; Sugimoto H; Wu C-C; LeBleu VS; Kalluri R Epithelial-to- Mesenchymal Transition Is Dispensable for Metastasis but Induces Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2015, 527 (7579), 525–530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (82).Valster A; Tran NL; Nakada M; Berens ME; Chan AY; Symons M Cell Migration and Invasion Assays. Methods 2005, 37 (2), 208–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (83).Chen H-C Boyden Chamber Assay. In Cell Migration; Humana Press: NJ, 2005; pp 015–022. [Google Scholar]
- (84).Li Y-H; Zhu C A Modified Boyden Chamber Assay for Tumor Cell Transendothelial Migration in Vitro. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1999, 17 (5), 423–429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (85).Grotendorst GR; Seppa HEJ; Kleinman HK; Martin GR Attachment of Smooth Muscle Cells to Collagen and Their Migration toward Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (Type V Collagen/Substrate Adhesion/Chemotaxis/Mitogens); PNAS, 1981; Vol. 78, 3669–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (86).Nyegaard S; Christensen B; Rasmussen JT An Optimized Method for Accurate Quantification of Cell Migration Using Human Small Intestine Cells. Metab. Eng. Commun 2016, 3, 76–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (87).Glenn HL; Messner J; Meldrum DR A Simple Non-Perturbing Cell Migration Assay Insensitive to Proliferation Effects. Sci. Rep 2016, 6 (1), 31694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (88).Falconnet D; Csucs G; Michelle Grandin H; Textor M Surface Engineering Approaches to Micropattern Surfaces for Cell-Based Assays. Biomaterials 2006, 27 (16), 3044–3063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (89).Lamb BM; Westcott NP; Yousaf MN Microfluidic Lithography to Create Dynamic Gradient SAM Surfaces for Spatio-Temporal Control of Directed Cell Migration. ChemBioChem 2008, 9 (16), 2628–2632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (90).Junkin M; Wong PK Probing Cell Migration in Confined Environments by Plasma Lithography. Biomaterials 2011, 32 (7), 1848–1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (91).Petitjean L; Reffay M; Grasland-Mongrain E; Poujade M; Ladoux B; Buguin A; Silberzan P Velocity Fields in a Collectively Migrating Epithelium. Biophys. J 2010, 98 (9), 1790–1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (92).Poujade M; Grasland-Mongrain E; Hertzog A; Jouanneau J; Chavrier P; Ladoux B; Buguin A; Silberzan P Collective Migration of an Epithelial Monolayer in Response to a Model Wound. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2007, 104, 15988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (93).Nikkhah M; Edalat F; Manoucheri S; Khademhosseini A Engineering Microscale Topographies to Control the Cell-substrate Interface. Biomaterials 2012, 33 (21), 5230–5246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (94).Stamm A; Reimers K; Strauß S; Vogt P; Scheper T; Pepelanova I In Vitro Wound Healing Assays - State of the Art. Bio Nano Materials 2016, 17 (1–2), 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- (95).Liang C-C; Park AY; Guan J-L In Vitro Scratch Assay: A Convenient and Inexpensive Method for Analysis of Cell Migration in Vitro. Nat. Protoc 2007, 2 (2), 329–333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (96).Wickert LE; Pomerenke S; Mitchell I; Masters KS; Kreeger PK Hierarchy of Cellular Decisions in Collective Behavior: Implications for Wound Healing. Sci. Rep 2016, 6 (1), 20139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (97).Farooqui R; Fenteany G Multiple Rows of Cells behind an Epithelial Wound Edge Extend Cryptic Lamellipodia to Collectively Drive Cell-Sheet Movement. J. Cell Sci 2005, 118 (1), 51–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (98).Nobes CD; Hall A Rho GTPases Control Polarity, Protrusion, and Adhesion during Cell Movement. J. Cell Biol 1999, 144 (6), 1235–1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (99).Tamada M; Perez TD; Nelson WJ; Sheetz MP Two Distinct Modes of Myosin Assembly and Dynamics during Epithelial Wound Closure. J. Cell Biol 2007, 176 (1), 27–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (100).De Pascalis C; Péz-González C; Seetharaman S; Boëda B; Vianay B; Burute M; Leduc C; Borghi N; Trepat X; Etienne-Manneville S Intermediate Filaments Control Collective Migration by Restricting Traction Forces and Sustaining Cell-Cell Contacts. J. Cell Biol 2018, 217, 3031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (101).Lintz M; Muñoz A; Reinhart-King CA The Mechanics of Single Cell and Collective Migration of Tumor Cells. J. Biomech. Eng 2017, 139 (2), 021005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (102).Nath S; Devi GR Three-Dimensional Culture Systems in Cancer Research: Focus on Tumor Spheroid Model. Pharmacol. Ther 2016, 163, 94–108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (103).Nguyen-Ngoc K-V; Cheung KJ; Brenot A; Shamir ER; Gray RS; Hines WC; Yaswen P; Werb Z; Ewald AJ ECM Microenvironment Regulates Collective Migration and Local Dissemination in Normal and Malignant Mammary Epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2012, 109, E2595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (104).Cheng G; Tse J; Jain RK; Munn LL Micro-Environmental Mechanical Stress Controls Tumor Spheroid Size and Morphology by Suppressing Proliferation and Inducing Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. PLoS One 2009, 4 (2), No. e4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (105).Labernadie A; Kato T; Brugués A; Serra-Picamal X; Derzsi S; Arwert E; Weston A; González-Tarragó V; Elosegui-Artola A; Trepat X A Mechanically Active Heterotypic E-Cadherin/N-Cadherin Adhesion Enables Fibroblasts to Drive Cancer Cell Invasion. Nat. Cell Biol 2017, 19 (3), 224–237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (106).Carey SP; Starchenko A; McGregor AL; Reinhart-King CA Leading Malignant Cells Initiate Collective Epithelial Cell Invasion in a Three-Dimensional Heterotypic Tumor Spheroid Model. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2013, 30 (5), 615–630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (107).Topman G; Shoham N; Sharabani-Yosef O; Lin F-H; Gefen A A New Technique for Studying Directional Cell Migration in a Hydrogel-Based Three-Dimensional Matrix for Tissue Engineering Model Systems. Micron 2013, 51, 9–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (108).Hakkinen KM; Harunaga JS; Doyle AD; Yamada KM Direct Comparisons of the Morphology, Migration, Cell Adhesions, and Actin Cytoskeleton of Fibroblasts in Four Different Three-Dimensional Extracellular Matrices. Tissue Eng., Part A 2011, 17 (5–6), 713–724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (109).Duval K; Grover H; Han L-H; Mou Y; Pegoraro AF; Fredberg J; Chen Z Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology 2017, 32 (4), 266–277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Research Misconduct Found]
- (110).Huang Y; Agrawal B; Sun D; Kuo JS; Williams JC Microfluidics-Based Devices: New Tools for Studying Cancer and Cancer Stem Cell Migration. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5 (1), 013412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (111).Halldorsson S; Lucumi E; Gómez-Sjöberg R; Fleming RMT Advantages and Challenges of Microfluidic Cell Culture in Polydimethylsiloxane Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron 2015, 63, 218–231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (112).Yim EKF; Darling EM; Kulangara K; Guilak F; Leong KW Nanotopography-Induced Changes in Focal Adhesions, Cytoskeletal Organization, and Mechanical Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31 (6), 1299–1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (113).Biggs MJP; Richards RG; Dalby MJ Nanotopographical Modification: A Regulator of Cellular Function through Focal Adhesions. Nanomedicine 2010, 6 (5), 619–633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (114).Li Y; Huang G; Zhang X; Wang L; Du Y; Lu TJ; Xu F Engineering Cell Alignment in Vitro. Biotechnol. Adv 2014, 32 (2), 347–365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (115).Wong IY; Javaid S; Wong EA; Perk S; Haber DA; Toner M; Irimia D Collective and Individual Migration Following the Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Mater 2014, 13 (11), 1063–1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (116).Liu YJ; Le Berre M; Lautenschlaeger F; Maiuri P; Callan-Jones A; Heuzé M; Takaki T; Voituriez R; Piel M Confinement and Low Adhesion Induce Fast Amoeboid Migration of Slow Mesenchymal Cells. Cell 2015, 160 (4), 659–672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (117).Cui X; Guo W; Sun Y; Sun B; Hu S; Sun D; Lam RH W. A Microfluidic Device for Isolation and Characterization of Transendothelial Migrating Cancer Cells. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11 (1), 014105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (118).Grada A; Otero-Vinas M; Prieto-Castrillo F; Obagi Z; Falanga V Research Techniques Made Simple: Analysis of Collective Cell Migration Using the Wound Healing Assay. J. Invest. Dermatol 2017, 137 (2), e11–e16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (119).Xia J-L; Fan W-J; Zheng F-M; Zhang W-W; Xie J-J; Yang M-Y; Kamran M; Wang P; Teng H-M; Liu Q Inhibition of AURKA Kinase Activity Suppresses Collective Invasion in a Microfluidic Cell Culture Platform. Sci. Rep 2017, 7 (1), 2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (120).Toh Y-C; Raja A; Yu H; van Noort D; Toh Y-C; Raja A; Yu H; van Noort DA 3D Microfluidic Model to Recapitulate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Bioengineering 2018, 5 (2), 29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (121).Xi W; Sonam S; Beng Saw T; Ladoux B; Teck Lim C Emergent Patterns of Collective Cell Migration under Tubular Confinement. Nat. Commun 2017, 8 (1), 1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (122).Dahl JB; Lin J-MG; Muller SJ; Kumar S Microfluidic Strategies for Understanding the Mechanics of Cells and Cell-Mimetic Systems. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng 2015, 6, 293–317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (123).Fan Q; Liu R; Jiao Y; Tian C; Farrell JD; Diao W; Wang X; Zhang F; Yuan W; Liu L A Novel 3-D Bio-Microfluidic System Mimicking in Vivo Heterogeneous Tumour Microstructures Reveals Complex Tumour-stroma Interactions. Lab Chip 2017, 17 (16), 2852–2860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (124).Junttila MR; de Sauvage FJ Influence of Tumour Micro-Environment Heterogeneity on Therapeutic Response. Nature 2013, 501 (7467), 346–354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (125).Krakhmal NV; Zavyalova MV; Denisov EV; Vtorushin SV; Perelmuter VM Cancer Invasion: Patterns and Mechanisms. Acta Naturae 2015, 7 (2), 17–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (126).Alobaidi AA; Sun B Probing Three-Dimensional Collective Cancer Invasion with DIGME. Cancer Converg 2017, 1 (1), 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (127).Han W; Chen S; Yuan W; Fan Q; Tian J; Wang X; Chen L; Zhang X; Wei W; Liu L Oriented Collagen Fibers Direct Tumor Cell Intravasation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2016, 113 (40), 11208–11213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (128).Ladoux B; Mèg R-M Mechanobiology of Collective Cell Behaviours. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2017, 18 (12), 743–757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (129).Colin-York H; Fritzsche M The Future of Traction Force Microscopy. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng 2018, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- (130).Dembo M; Wang Y-L Stresses at the Cell-to-Substrate Interface during Locomotion of Fibroblasts. Biophys. J 1999, 76 (4), 2307–2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (131).Butler JP; Tolićørrelykke IM; Fabry B; Fredberg JJ Traction Fields, Moments, and Strain Energy That Cells Exert on Their Surroundings. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol 2002, 282 (3), C595–C605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (132).Du Roure O; Saez A; Buguin A; Austin RH; Chavrier P; Silberzan P; Ladoux B Force Mapping in Epithelial Cell Migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2005, 102, 2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (133).Tambe DT; Croutelle U; Trepat X; Park CY; Kim JH; Millet E; Butler JP; Fredberg JJ Monolayer Stress Microscopy: Limitations, Artifacts, and Accuracy of Recovered Intercellular Stresses. PLoS One 2013, 8 (2), e55172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (134).Nier V; Jain S; Lim CT; Ishihara S; Ladoux B; Marcq P Inference of Internal Stress in a Cell Monolayer. Biophys. J 2016, 110 (7), 1625–1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (135).Yang X; Bi D; Czajkowski M; Merkel M; Manning ML; Marchetti MC Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2017, 114, 12663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (136).He S; Liu C; Li X; Ma S; Huo B; Ji B Dissecting Collective Cell Behavior in Polarization and Alignment on Micro- patterned Substrates. Biophys. J 2015, 109 (3), 489–500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (137).Zaritsky A; Kaplan D; Hecht I; Natan S; Wolf L; Gov NS; Ben-Jacob E; Tsarfaty I Propagating Waves of Directionality and Coordination Orchestrate Collective Cell Migration. PLoS Comput. Biol 2014, 10 (7), No. e1003747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (138).Zaritsky A; Welf ES; Tseng Y-Y; Rabadań MA; Serra-Picamal X; Trepat X; Danuser G Seeds of Locally Aligned Motion and Stress Coordinate a Collective Cell Migration. Biophys. J 2015, 109, 2492–2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (139).Reffay M; Parrini MC; Cochet-Escartin O; Ladoux B; Buguin A; Coscoy S; Amblard F; Camonis J; Silberzan P Interplay of RhoA and Mechanical Forces in Collective Cell Migration Driven by Leader Cells. Nat. Cell Biol 2014, 16 (3), 217–223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (140).Sarangi BR; Gupta M; Doss BL; Tissot N; Lam F; Mège R-M; Borghi N; Ladoux B Coordination between Intra- and Extracellular Forces Regulates Focal Adhesion Dynamics. Nano Lett 2017, 17 (1), 399–406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (141).Cliffe A; Doupé DP; Sung H; Lim IKH; Ong KH; Cheng L; Yu W Quantitative 3D Analysis of Complex Single Border Cell Behaviors in Coordinated Collective Cell Migration. Nat. Commun 2017. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- (142).Diz-MuñOz A; Krieg M; Bergert M; Ibarlucea-Benitez I; Muller DJ Control of Directed Cell Migration In Vivo by Membrane-to-Cortex Attachment. PLoS Biol 2010, 8 (11), 1000544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (143).Szabó A; Melchionda M; Nastasi G; Woods ML; Campo S; Perris R; Mayor R In Vivo Confinement Promotes Collective Migration of Neural Crest Cells. J. Cell Biol 2016, 213 (5), 543–555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (144).Eder D; Basler K; Aegerter CM Challenging FRET-Based E-Cadherin Force Measurements in Drosophila. Sci. Rep 2017, 7 (1), 13692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (145).Friedl P; Locker J; Sahai E; Segall JE Classifying Collective Cancer Cell Invasion. Nat. Cell Biol 2012, 14 (8), 777–783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (146).Guo J; Sachs F; Meng F Fluorescence-Based Force/ Tension Sensors: A Novel Tool to Visualize Mechanical Forces in Structural Proteins in Live Cells. Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2014, 20 (6), 986–999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (147).Meng F; Sachs F Orientation-Based FRET Sensor for Real-Time Imaging of Cellular Forces. J. Cell Sci 2012, 125 (3), 743–750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (148).Wang Y; Meng F; Sachs F Genetically Encoded Force Sensors for Measuring Mechanical Forces in Proteins. Commun. Integr. Biol 2011, 4 (4), 385–390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (149).Dai N; Kool ET Fluorescent DNA-Based Enzyme Sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40 (12), 5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (150).Aoki K; Kondo Y; Naoki H; Hiratsuka T; Itoh RE; Matsuda M Propagating Wave of ERK Activation Orients Collective Cell Migration. Dev. Cell 2017, 43 (3), 305–317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (151).Abdellatef SA; Nakanishi J Photoactivatable Substrates for Systematic Study of the Impact of an Extracellular Matrix Ligand on Appearance of Leader Cells in Collective Cell Migration. Biomaterials 2018, 169, 72–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (152).Carmona-Fontaine C; Theveneau E; Tzekou A; Tada M; Woods M; Page KM; Parsons M; Lambris JD; Mayor R Complement Fragment C3a Controls Mutual Cell Attraction during Collective Cell Migration. Dev. Cell 2011, 21 (6), 1026–1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (153).Vicsek T; Czirok A; Ben-Jacob E; Cohen I; Shochet O Novel Type of Phase Transition in a System of Self-Driven Particles. Phys. Rev. Lett 1995, 75, 1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (154).Reynolds CW; Reynolds CW; Flocks WC Herds and Schools: A Distributed Behavioral Model. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques - SIGGRAPH ‘87; ACM Press: New York, New York, USA, 1987; Vol. 21, pp 25–34. DOI: 10.1145/37401.37406. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- (155).Yamao M; Naoki H; Ishii S Multi-Cellular Logistics of Collective Cell Migration. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (156).Chaté H; Ginelli F; Grégoire G; Peruani F; Raynaud F Modeling Collective Motion: Variations on the Vicsek Model. Eur. Phys. J. B 2008, 64, 451. [Google Scholar]
- (157).Fily Y; Henkes S; Marchetti MC Freezing and Phase Separation of Self-Propelled Disks. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (158).Henkes S; Fily Y; Marchetti MC Active Jamming: Self-Propelled Soft Particles at High Density. Phys. Rev. E - Stat. Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys 2011. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.84.040301. [DOI] [PubMed]
- (159).Li B; Sun SX Coherent Motions in Confluent Cell Monolayer Sheets. Biophys. J 2014, 107, 1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (160).Yue X; Nguyen TD; Zellmer V; Zhang S; Zorlutuna P Stromal Cell-Laden 3D Hydrogel Microwell Arrays as Tumor Microenvironment Model for Studying Stiffness Dependent Stromal Cell-Cancer Interactions. Biomaterials 2018, 170, 37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (161).Chang WK; Carmona-Fontaine C; Xavier JB Tumour-Stromal Interactions Generate Emergent Persistence in Collective Cancer Cell Migration. Interface Focus 2013, 3, 20130017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (162).Umetsu D; Aigouy B; Aliee M; Sui L; Eaton S; licher F; Dahmann C Local Increases in Mechanical Tension Shape Compartment Boundaries by Biasing Cell Intercalations. Curr. Biol 2014, 24, 1798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (163).Lan H; Wang Q; Fernandez-Gonzalez R; Feng JJ A Biomechanical Model for Cell Polarization and Intercalation during Drosophila Germband Extension. Phys. Biol 2015, 12, 056011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (164).Sussman DM; Schwarz JM; Marchetti MC; Manning ML Soft yet Sharp Interfaces in a Vertex Model of Confluent Tissue. Phys. Rev. Lett 2018. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.058001. [DOI] [PubMed]
- (165).Bi D; Lopez JH; Schwarz JM; Manning ML Energy Barriers and Cell Migration in Densely Packed Tissues. Soft Matter 2014, 10 (12), 1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (166).Zehnder SM; Suaris M; Bellaire MM; Angelini TE Cell Volume Fluctuations in MDCK Monolayers. Biophys. J 2015, 108 (2), 247–250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (167).Vincent R; Bazellières E; Pérez-González C; Uroz M; Serra-Picamal X; Trepat X Active Tensile Modulus of an Epithelial Monolayer. Phys. Rev. Lett 2015, 115 (24), 248103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (168).Bi D; Yang X; Marchetti MC; Manning M L.ys Motility-Driven Glass and Jamming Transitions in Biological Tissues. Phys. Rev. X 2016. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.6.021011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- (169).Scianna M; Preziosi L; Wolf K A Cellular Potts Model Simulating Cell Migration on and in Matrix Environments. Math. Biosci. Eng 2013, 10, 235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (170).Niculescu I; Textor J; de Boer RJ Crawling and Gliding: A Computational Model for Shape-Driven Cell Migration. PLoS Comput. Biol 2015, 11, e1004280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (171).Chiang M; Marenduzzo D Glass Transitions in the Cellular Potts Model. EPL 2016, 116, 28009. [Google Scholar]
- (172).Düchting W; Vogelsaenger Th. Recent Progress in Modelling and Simulation of Three-Dimensional Tumor Growth and Treatment. BioSystems 1985, 18 (1), 79–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (173).Jiao Y; Torquato S Emergent Behaviors from a Cellular Automaton Model for Invasive Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironments. PLoS Comput. Biol 2011, 7 (12), 10–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (174).Zhu J; Liang L; Jiao Y; Liu L Enhanced Invasion of Metastatic Cancer Cells via Extracellular Matrix Interface. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0118058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (175).Xie H; Jiao Y; Fan Q; Hai M; Yang J; Hu Z; Yang Y; Shuai J; Chen G; Liu L Modeling Three-Dimensional Invasive Solid Tumor Growth in Heterogeneous Microenvironment under Chemotherapy. PLoS One 2018, 13 (10), 1–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (176).Nguyen TD; Gu Y Exploration of Mechanisms Underlying the Strain-Rate-Dependent Mechanical Property of Single Chon-drocytes. Appl. Phys. Lett 2014, 104, 183701. [Google Scholar]
- (177).Nguyen TD; Oloyede A; Singh S; Gu YT Microscale Consolidation Analysis of Relaxation Behavior of Single Living Chondrocytes Subjected to Varying Strain-Rates. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater 2015, 49, 343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (178).Laible J; Pflaster D; Krag M; Simon BHL A Poroelastic-Swelling Finite Element Model with Application to the Intervertebral Disc. Spine 1993, 18, 659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (179).Simon BR; Liable JP; Pflaster D; Yuan Y; Krag MH A Poroelastic Finite Element Formulation Including Transport and Swelling in Soft Tissue Structures. J. Biomech. Eng 1996, 118, 1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (180).Simon B; Kaufmann M; McAfee MBA Porohyperelastic Finite Element Analysis of Large Arteries Using ABAQUS. J. Biomech. Eng 1998, 120, 296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (181).Nguyen TD; Oloyede A; Gu Y A Poroviscohyperelastic Model for Numerical Analysis of Mechanical Behavior of Single Chondrocyte. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering 2016, 19, 126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (182).Nguyen TD; Oloyede A; Singh S; Gu Y Investigation of the Effects of Extracellular Osmotic Pressure on Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Individual Chondrocyte. Cell Biochem. Biophys 2016, 74, 229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (183).Zhong Y; He S; Ji B MECHANICS IN MECHANO-SENSITIVITY OF CELL ADHESION AND ITS ROLES IN CELL MIGRATION. Int. J. Comput. Mater. Sci. Eng 2012, 01 (04), 1250032. [Google Scholar]
- (184).Wong HC; Tang WC Finite Element Analysis of the Effects of Focal Adhesion Mechanical Properties and Substrate Stiffness on Cell Migration. J. Biomech 2011, 44, 1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (185).Zhao J; Cao Y; Dipietro LA; Liang J Dynamic Cellular Finite-Element Method for Modelling Large-Scale Cell Migration and Proliferation under the Control of Mechanical and Biochemical Cues: A Study of Re-Epithelialization. J. R. Soc., Interface 2017, 14, 20160959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (186).Nguyen TD; Gu Y Investigation of Cell-Substrate Adhesion Properties of Living Chondrocyte by Measuring Adhesive Shear Force and Detachment Using AFM and Inverse FEA. Sci. Rep 2016. DOI: 10.1038/srep38059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- (187).McGarry JP; McHugh PE Modelling of in Vitro Chondrocyte Detachment. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 1554. [Google Scholar]
- (188).Boromand A; Signoriello A; Ye F; O’Hern CS; Shattuck MD Jamming of Deformable Polygons. Phys. Rev. Lett 2018121 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.248003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (189).Karunasena HCP; Senadeera W; Brown RJ; Gu YT A Particle Based Model to Simulate Microscale Morphological Changes of Plant Tissues during Drying. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (190).Cheung KJ; Ewald AJ A Collective Route to Metastasis: Seeding by Tumor Cell Clusters. Science 2016, 352 (6282), 167–169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (191).Aceto N; Bardia A; Miyamoto DT; Donaldson MC; Wittner BS; Spencer JA; Yu M; Pely A; Engstrom A; Maheswaran S Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters Are Oligoclonal Precursors of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cell 2014, 158 (5), 1110–1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (192).Dietrich M; Le Roy H; ckner DB; Engelke H; Zantl R; Rad̈ler JO; Broedersz CP Guiding 3D Cell Migration in Deformed Synthetic Hydrogel Microstructures. Soft Matter 2018, 14 (15), 2816–2826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (193).Liang L; Jones C; Chen S; Sun B; Jiao Y Heterogeneous Force Network in 3D Cellularized Collagen Networks. Phys. Biol 2016, 13 (6), 066001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (194).Nan H; Liang L; Chen G; Liu L; Liu R; Jiao Y Realizations of Highly Heterogeneous Collagen Networks via Stochastic Reconstruction for Micromechanical Analysis of Tumor Cell Invasion. Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top 2018, 97 (3), 033311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (195).Alobaidi AA; Xu Y; Chen S; Jiao Y; Sun B Probing Cooperative Force Generation in Collective Cancer Invasion. Phys. Biol 2017, 14 (4), 045005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (196).Matesic DF; Ali A; Sidorova TS; Burns TJ A Cell-Cell Communication Marker for Identifying Targeted Tumor Therapies. Curr. Bioact. Compd 2014, 9 (3), 255–262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (197).Oliveira R; Christov C; Guillamo J; DeBoüard S; Palfi S; Venance L; Tardy M; Peschanski M Contribution of Gap Junctional Communication between Tumor Cells and Astroglia to the Invasion of the Brain Parenchyma by Human Glioblastomas. BMC Cell Biol 2005, 6 (1), 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (198).Hallou A; Jennings J; Kabla AJ Tumour heterogeneity promotes collective invasion and cancer metastatic dissemination. R. Soc. Open Sci 2017, 4, 161007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]