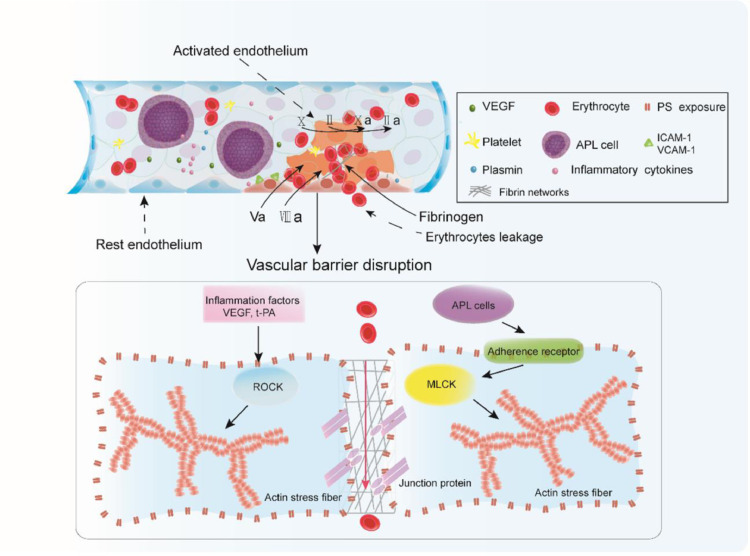
Fig. 7.
Intercellular fibrin networks prevent erythrocyte leakage. VEGF, inflammatory cytokines, and APL blasts interact with ECs. Cellular factors activate ROCK signaling, whereas APL cells adhere to the adherence receptors ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 and trigger the MLCK pathway, resulting in stress fiber formation, EC retraction, and junction protein dissociation. The gaps among dissociated junctions are large enough to permit RBC transmigration. PS exposure on the activated ECs provides a catalytic surface for FV and FVIII, resulting in coagulation pathway activation and fibrin formation among the openings. Intercellular fibrin works to repair the integrity of the endothelium. Plasmin activated through the overexpression of t-PA from APL blasts acts to weaken the fibrin network, allowing RBCs to leak into the extravascular space.