Abstract
The sensitizing effect of chromone-derived compounds on UVC-induced proliferation inhibition has not been comprehensively investigated so far. The subject of this study was to examine the proliferation change of oral cancer cells while using the combined treatment of UVC (254 nm) with our previously developed sulfonyl chromen-4-ones (CHW09), namely UVC/CHW09. Cell viability, apoptosis, oxidative stress, and DNA damage for the individual and combined treatments for UVC and/or CHW09 were examined in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells. In 24 h MTS assay, UVC (30 J/m2; UVC30), or CHW09 (25 and 50 µg/mL; namely, CHW09-25 and CHW09-50) show 54%, 59%, and 45% viability. The combined treatment (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) show lower cell viability (45% and 35%). Mechanistically, UVC/CHW09 induced higher apoptosis than individual treatments and untreated control, which were supported by the evidence of flow cytometry for subG1, annexin V/7-aminoactinomycin D, pancaspase and caspases 3/7 activity, and western blotting for cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Moreover, this cleaved PARP expression was downregulated by pancaspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK. UVC/CHW09 showed higher oxidative stress than individual treatments and untreated control in terms of flow cytometry for reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial membrane potential, and mitochondrial mass. Furthermore, UVC/CHW09 showed higher DNA damage than individual treatments and untreated control in terms of flow cytometry for H2A histone family member X and 8-oxo-2’-deoxyguanosine. In conclusion, combined treatment UVC/CHW09 suppresses proliferation, and promotes apoptosis, oxidative stress, and DNA damage against oral cancer cells, providing a novel application of sulfonyl chromen-4-ones in order to sensitize UVC induced proliferation inhibition for oral cancer therapy.
Keywords: UVC, chromone, oral cancer, apoptosis, DNA damage, combined treatment
1. Introduction
Radiotherapy is commonly combined with anticancer drugs to enhance radiosensitivity [1,2] and it has become the standard care for several types of cancer treatment. However, both radiation and anticancer drugs may have side effects. Cytotoxicity to normal cells partly contributes to this side effect. Accordingly, chemical agents with low cytotoxic effects on normal cells are developed as potential radiosensitizers for cancer therapy.
Ultraviolet C (UVC; 200–280 nm) provides an alternative choice to generate non-ionizing radiation, which is more convenient for laboratory and clinical treatments than X-ray. Some drugs can modulate UVC induced proliferation inhibition by its prevention or enhancement, as reported in X-ray studies. For example, pyridoxamine protects UVC-induced apoptosis in HaCaT Cells [3]. Combined treatment of metformin and resveratrol prevents UVC-induced proliferation inhibition in lung cancer A549 cells [4]. In contrast, the combined treatments of cisplatin/UVC [5] and methanolic extracts of Cryptocarya concinna/UVC [6], respectively, suppresses the proliferation of colorectal and oral cancer cells.
Sulfonyl chromen-4-ones (CHW09) is an oxidative stress inducing agent and it suppresses the proliferation of oral cancer cells [7]. By enhancing oxidative stress after CHW09 treatment, the radiosensitizing effect of CHW09 has been reported in X-ray irradiated oral cancer cells [8]. Similarly, UVC can induce oxidative stress [9] and it may have the potential to enhance CHW09-induced oxidative stress for inhibiting oral cancer cell proliferation. However, a detailed investigation for the combined treatment of UVC and CHW09 are warranted.
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the proliferation inhibition ability of CHW09 to UVC (254 nm)-irradiated oral cancer cells. Cell viability, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and oxidative stress, as well as DNA damage were measured in order to explore its possible mechanism.
2. Results
2.1. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High Cell Killing Effect to Oral Cancer Cells
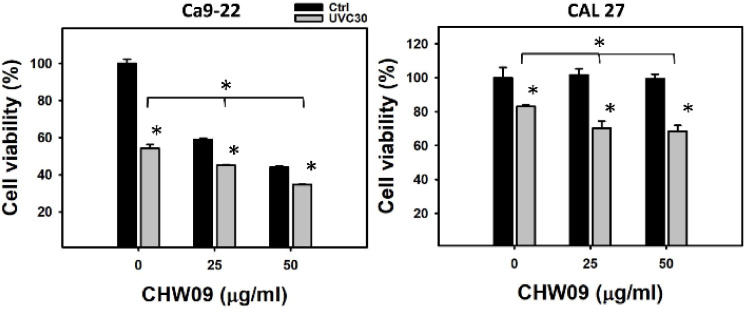
In 24 h MTS assay, individual treatments of UVC (30 J/m2; UVC30) or CHW09 (25 and 50 µg/mL; namely CHW09-25 and CHW09-50) show 54%, 59%, and 45% viability for oral cancer Ca9-22 cells (left, Figure 1). While UVC/CHW09 combined treatment (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) show lower cell viability (45% and 35%) than its individual treatment for Ca9-22 cells. Similarly, UVC30, CHW09-25, or CHW09-50 show 81%, 98%, and 97% viability for oral cancer CAL 27 cells at 24 h MTS assay (right, Figure 1). While, UVC/CHW09 combined treatment (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) showed lower cell viability (70% and 68%) than its individual treatment for CAL 27 cells.
Figure 1.
Cell viability (MTS assay) of oral cancer Ca9-22 and CAL 27 cells after UVC/CHW09 combined treatments. Cells were pretreated with ultraviolet C (UVC) irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
2.2. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High SubG1 Content to Oral Cancer Cells
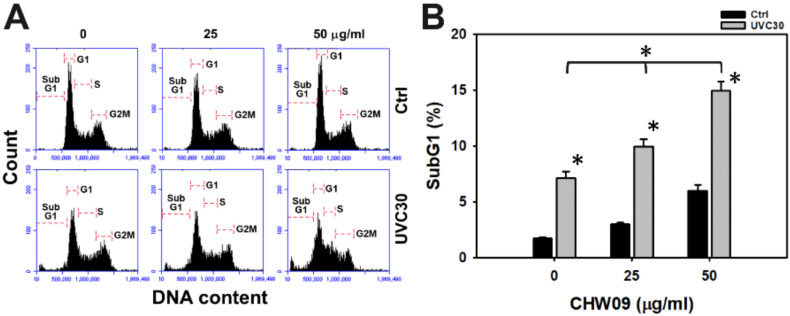
The cell cycle progression status of Ca9-22 cells after UVC and/or CHW09 treatments were evaluated (Figure 2A). In Figure 2B, the individual treatment of UVC or CHW09 show higher subG1 (%) than untreated control. The subG1 (%) of the combined treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) are higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment, especially for UVC30/CHW09-50.
Figure 2.
Change of subG1 percentage in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells after UVC/CHW09 combined treatments. Cells were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of cell cycle analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (B) Statistics in Figure 2A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
2.3. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High Annexin V Content to Oral Cancer Cells
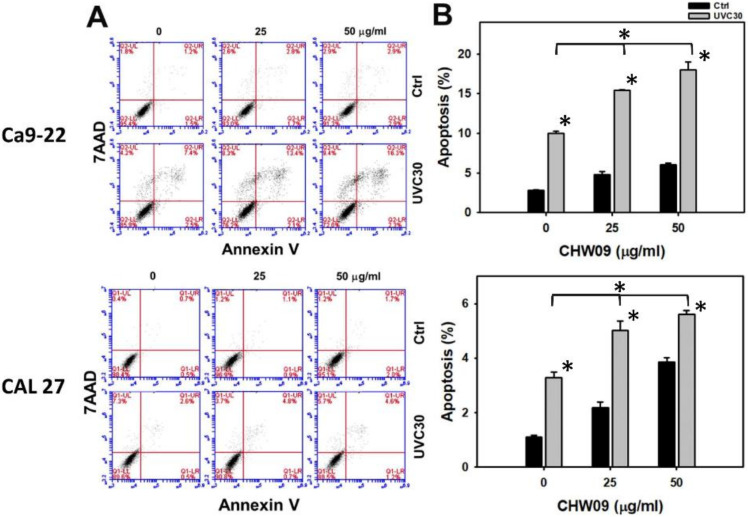
SubG1 accumulation is only one of the indicators for apoptosis, we further performed annexin V/7-aminoactinomycin D (7AAD) patterns after UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in order to evaluate the apoptosis change of oral cancer Ca9-22 and CAL 27 cells (Figure 3A). In Figure 3B, individual treatment of UVC or CHW09 for oral cancer cells shows higher annexin V (+)/7AAD (+ or −) (%), i.e., apoptosis (%), than the control. Annexin V (+)/7AAD (+ or −) percentages of the combined treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) for oral cancer cells were higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment, especially for UVC30/CHW09-50.
Figure 3.
Changes of annexin V/7AAD status of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer cells. Cells (Ca9-22 and CAL 27) were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of annexin V/7AAD analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. Annexin V (+)/7AAD (+ or −) is counted as apoptosis (+) (%) [10]. (B) Statistics in Figure 3A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
2.4. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High Caspase Activity to Oral Cancer Cells
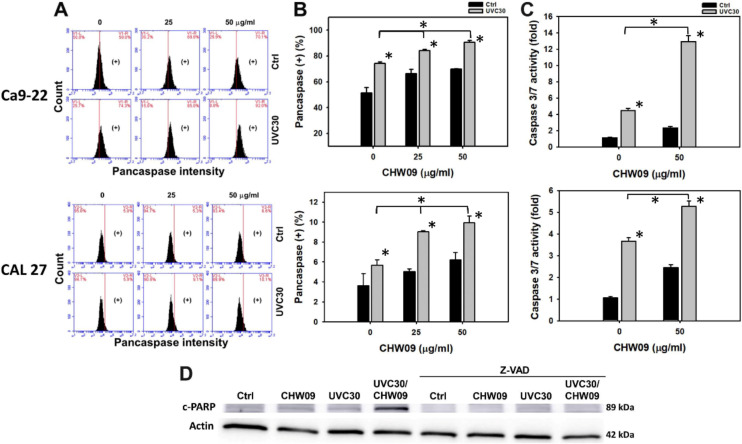
The pancaspase flow cytometry of oral cancer Ca9-22 and CAL 27 cells were analyzed to evaluate the involvement of caspases (Figure 4A). In Figure 4B, individual treatment of UVC or CHW09 for oral cancer cells showed higher pancaspase-positive (%) than the untreated control. The pancaspase-positive (%) of these combined treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) are higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment, especially for UVC30/CHW09-50.
Figure 4.
Changes of apoptosis (caspase activity) of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer cells. Cells (Ca9-22 and CAL 27) were pretreated with UVC irradiation UVC (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of pancaspase analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (+) in the right side of each panel indicates the pancaspase (+) (%). (B) Statistics in Figure 4A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others. (C) Cas 3/7 activity in CHW09 and/or UVC-treated Ca9-22 and CAL 27 cells. Cas 3/7 activity was determined by ELISA assays. (D) Expressions of cleaved form to PARP (c-PARP) in CHW09 and/or UVC-treated Ca9-22 cells in the absence and presence of Z-VAD pretreatment (100 µM for 2 h).
In Figure 4C, the apoptotic protein caspases 3/7 (Cas 3/7) activity of the combined treatment (UVC30/CHW09-50) for oral cancer Ca9-22 and CAL 27 cells were higher than individual treatments and the untreated control after 24 h as indicated by ELISA assays. In Figure 4D and Supplementary Figure S1, the apoptotic protein cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (c-PARP) expression of the combined treatment (UVC30/CHW09-50) are higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment. In contrast, this c-PARP induction was inhibited by pancaspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (Z-VAD) pretreatment.
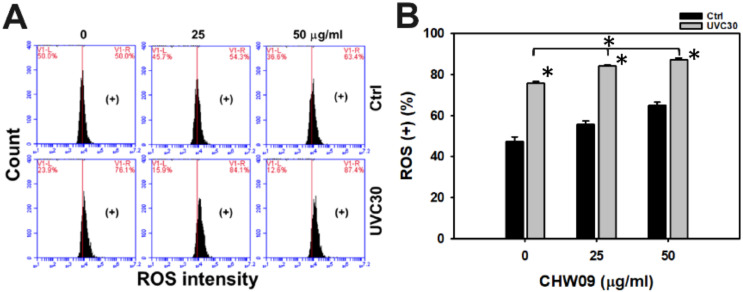
2.5. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation to Oral Cancer Cells
UVC was reported to induce oxidative stress, such as ROS production [11]. Hence, the ROS status of Ca9-22 cells after UVC and/or CHW09 treatments warrants more detailed investigation. Its ROS pattern of flow cytometry was provided (Figure 5A). In Figure 5B, individual treatment of UVC or CHW09 show higher ROS (+) (%) than untreated control. The ROS (+) (%) of the combined treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) are higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after a 16 h treatment.
Figure 5.
Changes of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) generation of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells. Cells were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, 50 µg/mL) for 16 h. (A) Representative pattern of ROS analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (+) in the right side indicates the ROS positive percentage (+) (%). (B) Statistics in Figure 5A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
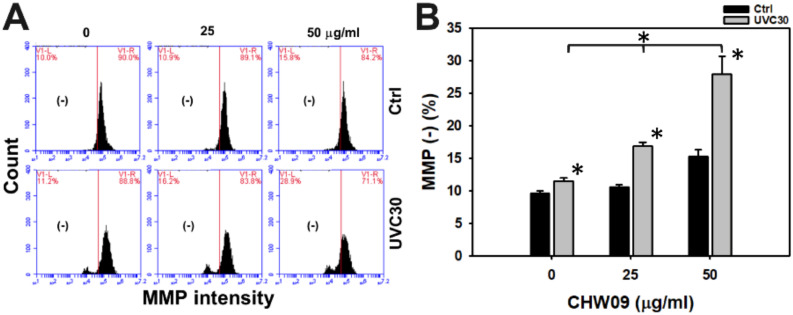
2.6. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Depletion to Oral Cancer Cells
MMP was examined to further check the oxidative stress status. Hence, the MMP status of Ca9-22 cells after UVC and/or CHW09 treatments warrants detailed investigation. Its MMP pattern of flow cytometry was provided (Figure 6A). In Figure 6B, individual treatment of UVC or CHW09 show higher MMP (−) (%) than the untreated control. The MMP (−) (%) of the combined treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) are higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment, especially for UVC30/CHW09-50.
Figure 6.
Changes of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells. Cells were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of MMP analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (-) in the left side of each panel indicates the MMP negative percentage (−) (%). (B) Statistics in Figure 6A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
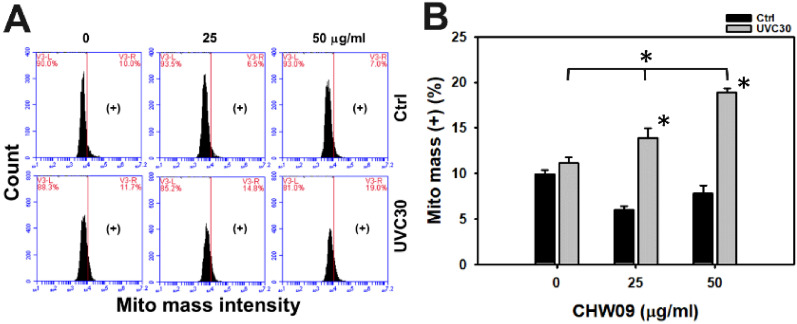
2.7. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High Mitochondrial Mass (Mito Mass) to Oral Cancer Cells
Oxidative stress also enhances mitochondrial mass [12]. Hence, the Mito mass status of Ca9-22 cells after UVC and/or CHW09 treatments warranted detailed investigation. Its Mito mass pattern of flow cytometry was provided (Figure 7A). In Figure 7B, the individual treatment of UVC showed higher MMP (−) (%) than control, but individual treatment of CHW09 showed lower MMP (−) (%) than untreated control. The Mito mass (+) (%) of UVC/CHW09 treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) are higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment, especially for UVC30/CHW09-50.
Figure 7.
Changes of Mito mass of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells. Cells were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of mito mass analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (+) in the right side of each panel indicates the mito mass (+) (%). (B) Statistics in Figure 7A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
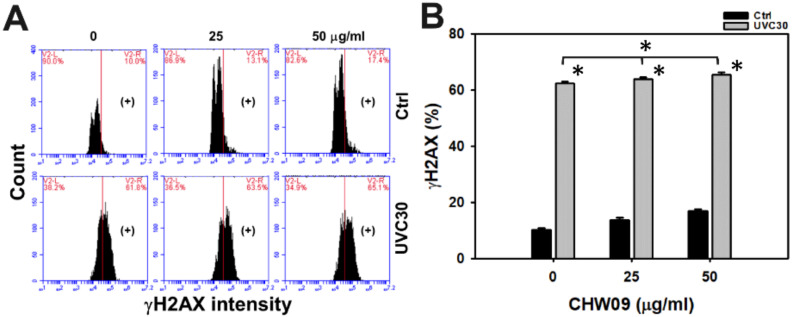
2.8. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Showed High H2A Histone Family Member X (γH2AX) Content to Oral Cancer Cells
Oxidative stress enhances DNA damage [13]. Hence, the DNA damage status of Ca9-22 cells after UVC and/or CHW09 treatments warranted detailed investigation. Its γH2AX-monitoring DNA damage pattern of flow cytometry was provided (Figure 8A). In Figure 8B, individual treatment of UVC showed higher γH2AX (+) (%) than the untreated control. The γH2AX (+) (%) of UVC30/CHW09-50 was mildly higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment.
Figure 8.
Changes of DNA damage of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells. Cells were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of γH2AX analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (+) in the right side indicates the γH2AX (+) (%). (B) Statistics in Figure 8A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
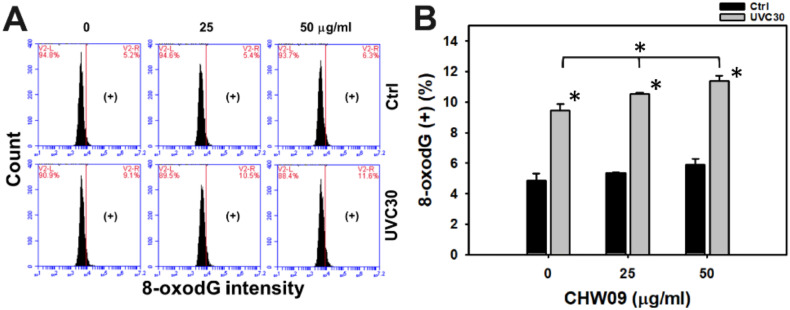
2.9. UVC/CHW09 Combined Treatment Shows High 8-Oxo-2’-Deoxyguanosine (8-OxodG) Content to Oral Cancer Cells
In addition to γH2AX DNA damage, flow cytometry investigated the oxidative DNA damage 8-oxodG (Figure 9A). In Figure 9B, individual treatment of UVC showed higher 8-oxodG (+) (%) than the untreated control. The 8-oxodG (+) (%) of UVC/CHW09 treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) were higher than its individual treatment and untreated control after 24 h treatment, especially for UVC30/CHW09-50.
Figure 9.
Changes of 8-oxodG of UVC and/or CHW09 treatments in oral cancer Ca9-22 cells. Cells were pretreated with UVC irradiation (0 and 30 J/m2) and/or post-treated with CHW09 (control, 25, and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h. (A) Representative pattern of 8-oxodG analysis for UVC and/or CHW09 treatment. (+) in the right side indicates the 8-oxodG (+) (%). (B) Statistics in Figure 9A. Data, mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by one-way ANOVA and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. *, p < 0.0001. * without line indicates the significance between control and UVC30. * with line indicates the significance between UVC30/CHW09 and others.
3. Discussion
The present study evaluated the combined treatment of sulfonyl chromen-4-ones (CHW09) and UVC in oral cancer cells. CHW09 enhanced the UVC-induced proliferation inhibition of oral cancer cells and its possible mechanism was discussed as follows.
3.1. CHW09 Is a Potential UVC Sensitizer
We previously reported that CHW09 is a selective killing agent for oral cancer cells [7]. For its low cytotoxicity to normal oral cells, CHW09 is a potential radiosensitizer to X-ray in inhibiting oral cancer cell proliferation [8]. However, the potential of UVC sensitization of CHW09 has not yet been reported. In the present study, different doses of CHW09 show enhancing effects to UVC-induced inhibitory proliferation against oral cancer cells. In addition to CHW09, different chromone-derived compounds, such as 7-(6-Chloropyridin-2-ylthio)-4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one, showed apoptosis inducible effects to A549 lung cancer cells [14]. It warrants for evaluating UVC sensitizing effect to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells for other non-CHW09 chromone-derived compounds in the future.
When compared to the X-ray irradiation machine, UVC generating devise is more convenient for the physician and dentist to operate in consultation room and medical chair rather than radiation room. Moreover, the CHW09 is less cytotoxic to normal oral cells than oral cancer cells, reducing the side effect [7]. This character provides the benefits for a potential clinical application of UVC/CHW09 treatments for anticancer therapy.
3.2. Oxidative Stress and Mito Mass Contribute to Enhance UVC Induced Proliferation Inhibition of CHW09 to Oral Cancer Cells
Although UVC/CHW09 treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) show slightly higher ROS levels than UVC alone (Figure 5B), it shows a dramatically higher induction of MMP depletion than individual treatments (Figure 6B). These results suggest that UVC/CHW09 treatments may cooperatively enhance oxidative stress in oral cancer cells. Moreover, oxidative stress may trigger Mito mass. For example, efavirenz induces oxidative stress and Mito mass in live cancer Hep3B cells [15]. Similarly, UVC/CHW09 treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) show higher Mito mass than individual treatments (Figure 7B). These results suggest that UVC/CHW09 treatments may cooperatively enhance Mito mass in oral cancer cells.
Oxidative stress is generated when the redox homeostasis gets dysfunctional, which is partly attributed to the downregulation of cellular antioxidant signaling [16]. Moreover, antioxidant response can regulate mitochondrial function and interact with autophagy and apoptosis response [17]. Because UVC/CHW09 treatments induce both oxidative stress and mitochondrial mass changes in oral cancer cells, this warrants a detailed investigation of antioxidant signaling expression upon UVC/CHW09 treatments.
3.3. DNA Damage Contributes to Enhance UVC Induced Inhibitory Proliferation of CHW09 to Oral Cancer Cells
Oxidative stress may trigger DNA damage [18,19]. CHW09 [7] and UVC [20,21] have been reported to induce γH2AX. CHW09 [7] and UVC [22] have been reported to induce 8-oxodG. Although UVC/CHW09 treatment (UVC30/CHW09-50) shows slightly higher γH2AX level than individual treatments (Figure 8B), it shows moderate induction for 8-oxodG generation (Figure 9B). These results suggest that UVC/CHW09 treatments may cooperatively enhance more oxidative DNA damage (8-oxodG) than γH2AX DNA damage in oral cancer cells. Furthermore, mitochondrial DNA damage, such as 4977 bp-deletion, can enhance oxidative stress and Mito mass in human sarcoma ρ0 cells [12]. Moreover, oxidative stress may inhibit DNA repair ability [23,24]. The repair of 8-oxodG is initiated by 8-oxoguanine glycosylase (OGG1) [24]. Therefore, this warrants a detailed examination of DNA repair after UVC/CHW09 treatment in oral cancer cells.
In addition to targeting DNA molecules, oxidative stress also possibly induces protein and lipid peroxidation [25,26]. Therefore, the contribution of protein and lipid peroxidation upon UVC/CHW09 treatment of oral cancer cells cannot be excluded and warrants for further investigation.
3.4. Apoptosis Contributes to Enhance UVC Induced Inhibitory Proliferation of CHW09 to Oral Cancer Cells
Oxidative stress [27,28] and DNA damage [29,30,31] are able to trigger apoptosis. As mentioned above, UVC induces oxidative stress and DNA damage, inducing cell apoptosis. For example, UVC induces apoptosis in human keratinocyte HaCaT Cells [3] and glioblastoma U343 cells [32]. Similarly, UVC/CHW09 treatments (UVC30/CHW09-25 and UVC30/CHW09-50) show higher apoptosis expressions or activity, such as annexin V, pancaspase, Cas 3/7, and c-PARP, than individual treatments (Figure 3 and Figure 4). These results suggest that UVC/CHW09 treatments may cooperatively enhance apoptosis in oral cancer cells.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures, CHW09, Inhibitor, and Antibodies
Human oral cancer cells (Ca9-22) that were obtained from Health Science Research Resources Bank (HSRRB) (Osaka, Japan) were cultured in common medium with supplement for 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco) and antibiotics at 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator, as described previously [33]. The synthesis and structure of CHW09 has been described previously [7]. The pancaspase inhibitor Z-VAD (Selleckchem.com; Houston, TX, USA) was used to inhibit apoptosis [34]. Detailed western blotting analysis was mentioned [35]. Primary antibody for apoptosis included c-PARP (1:1000 dilution) (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA) as well as the control β-actin mouse mAb (1:5000 dilution) (Sigma-Aldrich; St. Louis, MO, USA).
4.2. UVC Irradiation and/or CHW09 Treatment
After medium removal, the cells were irradiated with mock or a germicidal lamp UVC (30 J/m2) at a rate of 1 J/m2/s within the lamina flow for cell culture [36]. Subsequently, the cells were post-treated with control (DMSO only) or CHW09 (25 and 50 µg/mL) for 24 h.
4.3. Cell Viability
After treatment, cell viability was measured by MTS kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) [31] based on its colorimetric change in proportion to mitochondrial enzyme activity.
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
After 75% ethanol fixation overnight, the cells were washed with 1 x PBS and DNA content was measured by 7AAD (Biotium Inc., Hayward, CA, USA) [37] at the condition (1 µg/mL, 30 min, 37 °C) for the analysis of cell cycle distribution. After harvesting, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL3 channel of Accuri™ C6) (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) were used to analyze cell cycle phases. Finally, the subG1 population was used as an indicator for apoptosis.
4.5. Annexin V/7AAD Analysis
Using annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (10 µg/mL) (Strong Biotech Corp., Taipei, Taiwan)/7AAD (1 µg/mL) kit and staining for 30 min. at 37 °C, apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry, as previously described [38]. After harvesting, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1/FL3 channels of Accuri™ C6) were performed to detect and analyze FITC and 7AAD intensities, respectively. Annexin V (+)/7AAD (+ or −) (%) was regarded as apoptosis (+) (%)
4.6. Pancaspase and Cas 3/7 Activity Analysis
Using multiple caspase activity assay kit (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), 500X Tide Fluor™ 2 (TF2)-Val-Ala-Asp (VAD)-fluoromethyl ketone (FMK) at the condition (1:1000 dilution for 2 h incubation at room temperature) was used to detect caspases activity (caspases-1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9), as previously described [39]. After harvesting, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1 channel of Accuri™ C6) was used to measure and analyze pancaspase intensity. Caspase-Glo® 3/7 ELISA Assay (Promega; Madison, WI, USA) was used to detect caspases 3/7 activity according to the user’s instruction.
4.7. ROS Analysis
A ROS sensor dye 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCF-DA) (Sigma-Aldrich) at the condition (100 nM, 30 min, 37 °C) was used to detect cellular ROS, as previously described [40]. After harvesting, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1 channel of Accuri™ C6) were used to measure and analyze intracellular ROS intensity.
4.8. MMP Analysis
MitoProbe™ DiOC2(3) assay kit (Invitrogen, Eugene, OR, USA) at the condition (10 µM DiOC2(3), 20 min, 37 °C) was used to detect MMP, as described previously [30]. After harvesting, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1 channel of Accuri™ C6) were performed to detect and analyze MMP intensity.
4.9. Mito Mass Analysis
MitoTrackerTM Green FM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA) at the condition (300 nM, 30 min, 37 °C) was used to stain mitochondria, regardless of MMP level, which is proportional to Mito mass. After resuspension, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1 channel of Accuri™ C6) were performed to detect and analyze Mito mass intensity.
4.10. γH2AX Analysis
γH2AX marker was measured using antibody coupled with flow cytometry, as previously described [41]. Briefly, the cells were fixed by 75% ethanol overnight before antibody reaction. The primary p-Histone H2A.X (Ser 139) mAb (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) were diluted in 1:500 with 1% bovine serum albumin/0.2% Tween 20 in 1× PBS (BTP) buffer to incubate cells at 4 °C for 1 h. After washing, the secondary antibody tagging with Alexa Fluor 488 fluorescence dye (Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) were diluted in 1:50 and incubated cells at room temperature for 30 min. After resuspension, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1 channel of Accuri™ C6) were performed to detect and analyze γH2AX intensity.
4.11. 8-OxodG Analysis
Oxidative DNA damage marker (8-oxodG) was detected using antibody-based flow cytometry with a slight modification [42]. Briefly, the cells were fixed by 75% ethanol overnight before antibody reaction. 8-OHdG antibody (E-8) FITC (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) was diluted in 1:10,000 with BTP buffer to incubate cell suspensions at 4 °C for 1 h. After resuspension, flow cytometer and its accessory software (FL1 channel of Accuri™ C6) were performed to detect and analyze 8-oxodG intensity.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
For multiple comparison, significance of the difference was examined by JMP 12 software with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey HSD Post Hoc Test. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).
5. Conclusions
The sensitization of UVC-induced inhibitory proliferation of oral cancer cells is reported here for the first time for sulfonyl chromen-4-ones (CHW09). We found that combined treatments of UVC/CHW09 improved the inhibitory proliferation ability than individual treatments. This combined treatment of UVC/CHW09 shows enhanced ROS generation, MMP depletion, Mito mass production, apoptosis, and DNA damages. These results support the concept that oxidative stress modulating treatments may be a useful strategy for the inhibitory proliferation of cancer cells. Therefore, the combined treatment of UVC/CHW09 is paving the way for a new inhibitory proliferation technology for oral cancer cells.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/17/6443/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-Y.T. and H.-W.C.; Data curation, S.-C.W.; Formal analysis, S.-C.W.; Methodology, Y.-Y.W., L.-C.L., M.-Y.C., S.-S.F.Y.; Supervision, J.-Y.T. and H.-W.C.; Writing—original draft, S.-C.W. and H.-W.C.; Writing—review & editing, J.-Y.T. and H.-W.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partly supported by funds of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 108-2320-B-037-015-MY3 and MOST 108-2314-B-037-020), the National Sun Yat-sen University-KMU Joint Research Project (#NSYSUKMU 109-I002), the Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (KMUH108-8R67), the Kaohsiung Medical University Research Center (KMU-TC108A04), and the Health and welfare surcharge of tobacco products, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan, Republic of China (MOHW109-TDU-B-212-134016). The authors thank our colleague Dr. Hans-Uwe Dahms for editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
No competing interests are reported.
References
- 1.Lin A. radiation therapy for oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018;62:99–109. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2017.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hartner L. Chemotherapy for oral cancer. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018;62:87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2017.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wang S.-C., Ji H.-X., Hsiao C.-L., Wang T.-C., Syu Y.-R., Miao C.-E., Hou L.-L., Lin S.-S., Chang W.-S., Tsai C.-W. Protective effects of pyridoxamine against UVC-induced programmed cell death in HaCaT cells. Vivo. 2015;29:379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee Y.-S., Doonan B.B., Wu J.M., Hsieh T.-C. Combined metformin and resveratrol confers protection against UVC-induced DNA damage in A549 lung cancer cells via modulation of cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair. Oncol. Rep. 2016;35:3735–3741. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kawaguchi J., Adachi S., Yasuda I., Yamauchi T., Nakashima M., Ohno T., Shimizu M., Yoshioka T., Itani M., Kozawa O., et al. Cisplatin and ultra-violet-C synergistically down-regulate receptor tyrosine kinases in human colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Cancer. 2012;11:45. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chang H.-W., Tang J.-Y., Yen C.-Y., Chang H.-S., Huang H.-W., Chung Y.-A., Chen I.-S., Huang M.-Y. Synergistic anti-oral cancer effects of UVC and methanolic extracts of Cryptocarya concinna roots via apoptosis, oxidative stress and DNA damage. Int. J. Radiat. Boil. 2016;92:1–10. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2016.1145753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tang J.-Y., Wu C.-Y., Shu C.-W., Wang S.-C., Chang M.-Y., Chang H.-W. A novel sulfonyl chromen-4-ones (CHW09) preferentially kills oral cancer cells showing apoptosis, oxidative stress, and DNA damage. Environ. Toxicol. 2018;33:1195–1203. doi: 10.1002/tox.22625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tang J.-Y., Shu C.-W., Wang C.-L., Wang S.-C., Chang M.-Y., Lin L.-C., Chang H.-W. Sulfonyl chromen-4-ones (CHW09) shows an additive effect to inhibit cell growth of X-ray irradiated oral cancer cells, involving apoptosis and ROS generation. Int. J. Radiat. Boil. 2019;95:1226–1235. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1625490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chan W.-H., Yu J.-S. Inhibition of UV irradiation-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic biochemical changes in human epidermal carcinoma A431 cells by genistein. J. Cell. Biochem. 2000;78:73–84. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(20000701)78:1<73::AID-JCB7>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wlodkowic D., Skommer J., Darzynkiewicz Z. Flow cytometry-based apoptosis detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009;559:19–32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-017-5_2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.De Jager T.L., Cockrell A.E., Du Plessis S.S. Ultraviolet light induced generation of reactive oxygen species. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017;996:15–23. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-56017-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wei Y.-H., Lee C.-F., Lee5 H.-C., Ma Y.-S., Wang C.-W., Lu C.-Y., Pang C.-Y. Increases of mitochondrial mass and mitochondrial genome in association with enhanced oxidative stress in human cells harboring 4977 BP-deleted mitochondrial DNA. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001;928:97–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb05640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kryston T.B., Georgiev A.B., Pissis P., Georgakilas A.G. Role of oxidative stress and DNA damage in human carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2011;711:193–201. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Y., Liu H.-R., Cheng M., Xia P., Qian K., Wu P.-C., Lai C.-Y., Xia Y., Yang Z.-Y., Morris-Natschke S.L., et al. Antitumor agents 292. Design, synthesis and pharmacological study of S- and O-substituted 7-mercapto- or hydroxy-coumarins and chromones as potent cytotoxic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012;49:74–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.12.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Apostolova N., Gomez-Sucerquia L., Moran A., Alvarez A., Blas-Garcia A., Esplugues J. Enhanced oxidative stress and increased mitochondrial mass during Efavirenz-induced apoptosis in human hepatic cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010;160:2069–2084. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00866.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Trachootham D., Alexandre J., Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009;8:579–591. doi: 10.1038/nrd2803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huang M.L.-H., Chiang S., Kalinowski D.S., Bae D.-H., Sahni S., Richardson D.R. The role of the antioxidant response in mitochondrial dysfunction in degenerative diseases: Cross-Talk between antioxidant defense, autophagy, and apoptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019;2019:26. doi: 10.1155/2019/6392763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tang J.-Y., Ou-Yang F., Hou M.-F., Huang H.-W., Wang H.-R., Li K.-T., Fayyaz S., Shu C.-W., Chang H.-W., Farooqi A.A. Oxidative stress-modulating drugs have preferential anticancer effects involving the regulation of apoptosis, DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy, metabolism, and migration. Semin. Cancer Boil. 2019;58:109–117. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Salehi F., Behboudi H., Kavoosi G., Ardestani S.K. Oxidative DNA damage induced by ROS-modulating agents with the ability to target DNA: A comparison of the biological characteristics of citrus pectin and apple pectin. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:13902. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32308-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hanasoge S., Ljungman M. H2AX phosphorylation after UV irradiation is triggered by DNA repair intermediates and is mediated by the ATR kinase. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:2298–2304. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wakasugi M., Sasaki T., Matsumoto M., Nagaoka M., Inoue K., Inobe M., Horibata K., Tanaka K., Matsunaga T. Nucleotide excision repair-dependent DNA double-strand break formation and ATM signaling activation in mammalian quiescent cells. J. Boil. Chem. 2014;289:28730–28737. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Evans M., Cooke M.S., Podmore I.D., Zheng Q., Herbert K.E., Lunec J. Discrepancies in the measurement of UVC-induced 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine: Implications for the analysis of oxidative DNA damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999;259:374–378. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McAdam E., Brem R., Karran P. Oxidative stress-induced protein damage inhibits DNA repair and determines mutation risk and therapeutic efficacy. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016;14:612–622. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Van Houten B., Santa-Gonzalez G.A., Camargo M. DNA repair after oxidative stress: Current challenges. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017;7:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2017.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Davies M.J. Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem. J. 2016;473:805–825. doi: 10.1042/BJ20151227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Janion K., Szczepańska E., Nowakowska-Zajdel E., Walkiewicz K., Strzelczyk J. Lipid peroxidation and total oxidant/antioxidant status in colorectal cancer patients. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34:239–244. doi: 10.23812/19-386-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Farooqi A.A., Li K.-T., Fayyaz S., Chang Y.-T., Ismail M., Liaw C.-C., Yuan S.-S.F., Tang J.-Y., Chang H.-W. Anticancer drugs for the modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress. Tumor Boil. 2015;36:5743–5752. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3797-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Matés J.M., Segura J.A., Alonso F.J., Márquez J.D. Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012;86:1649–1665. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0906-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yeh C.-C., Yang J.-I., Lee J.-C., Tseng C.-N., Chan Y.-C., Hseu Y.-C., Tang J.-Y., Chuang L.-Y., Huang H.-W., Chang F.-R., et al. Anti-proliferative effect of methanolic extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata on oral cancer cells involves apoptosis, DNA damage, and oxidative stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012;12:142. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yen C.-Y., Chiu C.-C., Haung R.-W., Yeh C.-C., Huang K.-J., Chang K.-F., Hseu Y.-C., Chang F.-R., Chang H.-W., Wu Y.-C. Antiproliferative effects of goniothalamin on Ca9-22 oral cancer cells through apoptosis, DNA damage and ROS induction. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012;747:253–258. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chiu C.C., Haung J.W., Chang F.R., Huang K.J., Huang H.M., Huang H.W., Chou C.K., Wu Y.C., Chang H.W. Golden berry-derived 4beta-hydroxywithanolide E for selectively killing oral cancer cells by generating ROS, DNA damage, and apoptotic pathways. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e64739. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hiyama H., Reeves S.A. Role for cyclin D1 in UVC-induced and p53-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6:565–569. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yen Y.-H., Farooqi A.A., Li K.-T., Butt G., Tang J.-Y., Wu C.-Y., Cheng Y.-B., Hou M.-F., Chang H.-W. Methanolic extracts of Solieria robusta inhibits proliferation of oral cancer Ca9-22 cells via apoptosis and oxidative stress. Molecules. 2014;19:18721–18732. doi: 10.3390/molecules191118721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang H.-R., Tang J.-Y., Wang Y.-Y., Farooqi A.A., Yen C.-Y., Yuan S.-S.F., Huang H.-W., Chang H.-W. Manoalide preferentially provides antiproliferation of oral cancer cells by oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis and DNA damage. Cancers. 2019;11:1303. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen C.-Y., Yen C.-Y., Wang H.-R., Yang H.-P., Tang J.-Y., Huang H.-W., Hsu S.-H., Chang H.-W. Tenuifolide B from Cinnamomum tenuifolium stem selectively inhibits proliferation of oral cancer cells via apoptosis, ROS generation, mitochondrial depolarization, and DNA damage. Toxins. 2016;8:319. doi: 10.3390/toxins8110319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chang H.W., Lai Y.C., Cheng C.Y., Ho J.L., Ding S.T., Liu Y.C. UV inducibility of rat proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene promoter. J. Cell Biochem. 1999;73:423–432. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19990601)73:3<423::AID-JCB13>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vignon C., Debeissat C., Georget M.-T., Bouscary D., Gyan E., Rosset P., Herault O. Flow cytometric quantification of all phases of the cell cycle and apoptosis in a two-color fluorescence plot. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e68425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chang H.-W., Li R.-N., Wang H.-R., Liu J.-R., Tang J.-Y., Huang H.-W., Chan Y.-H., Yen C.-Y. Withaferin a induces oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis and DNA damage in oral cancer cells. Front. Physiol. 2017;8:634. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yeh C.-C., Tseng C.-N., Yang J.-I., Huang H.-W., Fang Y., Tang J.-Y., Chang F.-R., Chang H.-W. Antiproliferation and induction of apoptosis in Ca9-22 oral cancer cells by ethanolic extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Molecules. 2012;17:10916–10927. doi: 10.3390/molecules170910916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shih H.-C., El-Shazly M., Juan Y.-S., Chang C.-Y., Su J.-H., Chen Y.-C., Shih S.-P., Chen H.-M., Wu Y.-C., Lu M.-C. Cracking the cytotoxicity code: Apoptotic induction of 10-Acetylirciformonin B is mediated through ROS generation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Mar. Drugs. 2014;12:3072–3090. doi: 10.3390/md12053072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tang J., Peng S., Cheng Y., Wang C., Farooqi A.A., Yu T., Hou M.-F., Wang S., Yen C., Chan L., et al. Ethyl acetate extract of Nepenthes adrianii x clipeata induces antiproliferation, apoptosis, and DNA damage against oral cancer cells through oxidative stress. Environ. Toxicol. 2019;34:891–901. doi: 10.1002/tox.22748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tang J.Y., Huang H.W., Wang H.R., Chan Y.C., Haung J.W., Shu C.W., Wu Y.C., Chang H.W. 4beta-hydroxywithanolide E selectively induces oxidative DNA damage for selective killing of oral cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2018;33:295–304. doi: 10.1002/tox.22516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.