Abstract
Amyloid precursor protein is linked with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The Australian cowplant Gymnema sylvestre is known in Indian and Chinese medicine. Therefore, it is of interest to screen the Amyloid precursor protein with compounds from the Australian cowplant. We report five compounds (Gymnemasaponin 5, Gymnemasin D, Gymnemoside A, Gymnemoside E, Gymnemoside F) derived from the Australian cowplant as the poteinal inhibitors of Amyloid precursor protein with optimal binding features for further consideration.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, Protein Network analysis, Gymnema sylvestre, Molecular docking
Background
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most frequent form of neurodegenerative disorder and the most prevalent cause of dementia commonly affecting the elderly people. It is well known that AD has complex various pathogenic factors, for example genetic factor, environmental factor, immunological factor, head injuries, depression, or hypertension [1- 5]. Among these factors, genetic factors are probable to attribute about 70% to the danger for AD [6]. As well, genetic analyses have confirmed that, personality differences of AD could be resulted from many genes and their variants, which apply a variety of biological functions in coordination to improve the risk of the disease [7,8,9]. Except for spot out the mechanisms drawn in in the AD pathogenesis, wide-ranging analyses of possible candidate genes could propose novel possible strategies to predictive or diagnostic test for AD. Hence in the present study we aimed to construct the current experimentally supported network of direct human protein interactions, explore it for potential target proteins for AD. Gymnema sylvestre is (commonly named as Gurmar, family: Asclepiadaceae) is one of the well known plant used in diabetic conditions and is officially mentioned in Indian Pharmacopoeia [10]. This plant has been proved for its various medicinal properties like anticancer, antimicrobial, antiarthritic [11]. Therefore, it is of interest to screen the Amyloid precursor protein with compounds from the Australian cow plant.
Materials and Methods:
Protein network constructions and hub identification:
Alzheimer's disease related protein network was constructed in cytoscape software [12]. Hub proteins were selected using the cytohubba plugin software [13].
Ligand Preparation:
Known compounds from Gymnema sylvestre was collected from literature. The corresponding data was downloaded from pubchem database in SDF and converted to the PDB format using Online Smiles Translator. Energy minimizations of ligands were done using ChemBio 3D Ultra 12.0.
Target protein:
High Resolution crystallographic structure of Amyloid beta protein (PDB ID: 1AAP) was downloaded from the RCSB PDB database [14].
Molecular Docking analysis:
The PatchDock server [15,16] was used for the docking of Known compounds from Gymnema sylvestre was collected from literature with the Amyloid beta protein (PDB ID: 1AAP).
Results and discussion:
In the present study Hub protein identification was performed using cytohubba. Cytohubba results were calculated based on Maximal Clique Centrality algorithm. Ten proteins were identified as most interactive proteins in the network. Among ten, the top most protein with Rank 1 was Amyloid precursor protein (Figure 1). It is an integral membrane protein expressed in many tissues and concentrated in the synapses of neurons. This Amyloid precursor protein is considered as a potential target for Alzheimer's disease. Hence in the present study it was taken as target protein for molecular docking studies. Compounds from Gymnema sylvestre was used for docking studies with Amyloid precursor protein and the interaction were analyzed. In the molecular docking paradigm, the ligand with more negative binding energy is considered more successful and more potent than to the one with less or positive binding energy. In the present study, results from PatchDock analysis revealed that the binding affinity of selected natural compounds gives significant result. For this study we took 26 phytocompounds from Gymnema sylvestre. Based on the results of docking studies best five were shown in Table 1. The atomic contact energy (ACE) value of selected 5 compounds range from -638.16 to -236.92 Kcal/mol. Thus from the calculated ACE values it can be inferred that these compounds showed the favorable binding energy with Amyloid precursor protein. This ligplot analysis shows the hydrogen bonding and the length of their interaction with the key residues of the Amyloid precursor protein in the active site pocket. Among the residues which play a vital role in the mechanisms of action we found that the ALA 9, THR11, TYR22, THR26 are the main interacting amino acids residues (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
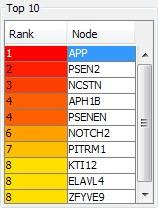
Hub proteins Identified from Cytohubba.
Table 1. Molecular docking results obtained through Patch dock server.
| S. No | Compound name | Score(kca l/mol) | ACE | Hond interaction | H bond length | No of non-bonded interaction |
| 1 | Gymnemasaponin 5 | 5398 | -408.46 | THR 26 OG1-O | 2.51 | 144 |
| TYR 22 OH-O | 2.29 | |||||
| 2 | Gymnemasin D | 3790 | -236.92 | ALA 9 N-O | 3.04 | 156 |
| THR 26 N-O | 2.83 | |||||
| THR 26 OG1-O | 2.69 | |||||
| 3 | Gymnemoside A | 4668 | -311.8 | ALA 9 N-O | 2.69 | 142 |
| THR 26 OG1-O | 1.92 | |||||
| THR 26 N-O | 2.83 | |||||
| 4 | Gymnemoside E | 5850 | -358.55 | ALA 9 N-O | 2.74 | 147 |
| THR 26 OG1-O | 3.01 | |||||
| THR 11 OG1-O | 2.72 | |||||
| TYR 22 OH-O | 2.65 | |||||
| THR 26 OG1-O | 3.18 | |||||
| 5 | Gymnemoside F | 5384 | -638.16 | THR 26 OG1-O | 2.09 | 263 |
| THR 11 N-O | 3.13 | |||||
| THR 11 OG1-O | 2.19 |
Figure 2.
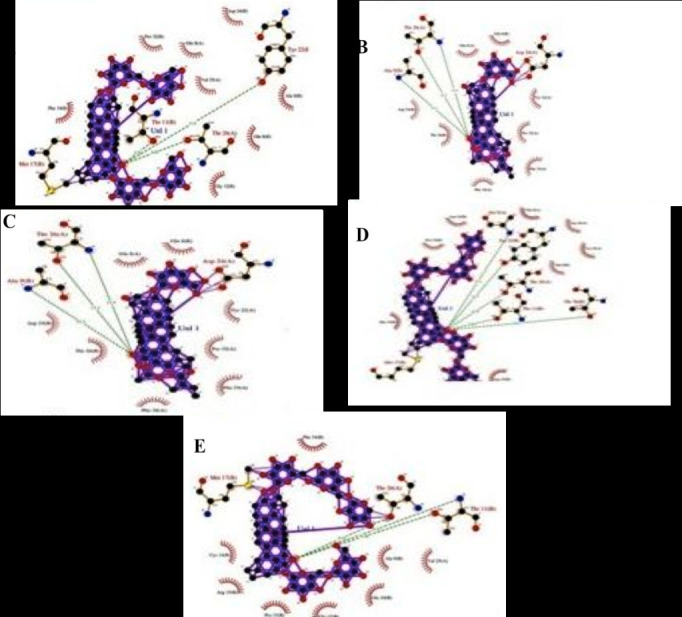
Ligplot analysis of docked amyloid precursor protein in complex with (A) Gymnemasaponin 5; (B) Gymnemasin D; (C) Gymnemoside A; (D) Gymnemoside E; (E) Gymnemoside F.
Conclusions:
We report five compounds (Gymnemasaponin 5, Gymnemasin D, Gymnemoside A, Gymnemoside E, Gymnemoside F) derived from the Australian cowplant as poteinal inhibitors of the Amyloid precursor protein with optimal binding features for further consideration.
Edited by P Kangueane
Citation: Selvaraj et al. Bioinformation 16(7):561-566 (2020)
References
- 1.Jayaraman A, et al. Curr Diabetes Rep. . 2014;14:476. doi: 10.1007/s11892-014-0476-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yan T, et al. Hereditas. . 2019;156:25. doi: 10.1186/s41065-019-0101-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rivera DS, et al. Biol Res. . 2016;49:10. doi: 10.1186/s40659-016-0074-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vijayan M, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. . 2016;54:427. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tolppanen AM, et al. Alzheimers Dement. . 2017;13:1371. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Girard H Potvin, et al. Neurobiol Aging. . 2018;64:157. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hokama M, et al. Cereb Cortex. . 2014;24:2476. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Naughton BJ, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. . 2015;43:93. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stopa EG, et al. Fluids Barriers of the CNS. . 2018;15:18. doi: 10.1186/s12987-018-0120-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grover JK, et al. J Ethnopharmacol. . 2002;81:81. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(02)00059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Khan F, et al. Front Pharmacol. . 2019;10:1223. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Su G, et al. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. . 2014;47:1. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0813s47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chin CH, et al. BMC Syst Biol. . 2014;4:S11. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bernstein FC, et al. Arch Biochem Biophys . 1978;185:584. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schneidman-Duhovny D, et al. Proteins. . 2003;52:107. doi: 10.1002/prot.10397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schneidman-Duhovny D, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. . 2005;33:W363. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


