Abstract
Abstract
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare and progressive cystic lung disease with limited therapeutic options. We retrospectively analyzed the effects of a comprehensive 4-week inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) program in 58 patients with advanced LAM (FEV1: 45 ± 34%predicted, 6-min walk distance (6MWD): 338 ± 167 m). Exercise performance (6MWD: + 49 ± 50 m; p < 0.001) and quality of life (SF-36 physical component: + 2.4 ± 7.8 points; p = 0.049 and mental component: + 5.2 ± 12.1 points; p < 0.001) increased significantly after PR comparable to an COPD cohort. There were no clinical parameters that predicted changes in outcomes following PR. PR seems to be an effective therapeutic option even in patients with advanced LAM.
Trial registration
Clinical-Trials registration number: NCT04184193; date of registration: December 3, 2019.
Keywords: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, LAM, Pulmonary rehabilitation, Exercise, Quality of life, Therapy
Introduction
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a very rare, systemic neoplastic disease associated with progressive cystic lung destruction mostly affecting young women (prevalence: 3.4 to 7.8 per million women) [1]. LAM results in airflow limitation, hyperinflation, and reduced diffusion capacity which in turn leads to dyspnea and impaired exercise performance, physical activity, and quality of life [2, 3]. Available drugs (mTOR-inhibitor) may slow down lung destruction, however, the disease remains incurable and lung transplantation is often the only therapeutic option [1, 4]. Similar to other chronic lung diseases pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) might improve LAM patients´ symptoms and limitations [5]. Since LAM is a rare disease data collection is difficult and therefore, we performed a retrospective analysis of LAM patients that were referred to PR.
Methods
Data for this analysis were consecutively collected between July 2000 and November 2019 during a 4-week inpatient PR program at the Schoen Klinik Berchtesgadener Land (Schoenau, Germany). Patients performed a comprehensive multimodal, multidisciplinary PR program with contents specialized for patients with chronic respiratory diseases. The program was provided on 5 to 6 days per week and consisted of daily exercise training sessions (including endurance and strength training for 60 min) following recommendations for exercise training in COPD [6]. Patients participated also in structured general education sessions (e.g. disease management or oxygen therapy) and respiratory physiotherapy – smoking cessation, nutritional and psychological counseling were provided on a case by case basis.
This retrospective analysis was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Philipps-University Marburg (ID EK_MR_26_11_2019_koczulla) and is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04184193).
Statistical analyses
The primary outcomes were changes in 6-min walk distance (6MWD) [7] and quality of life (short-form 36 question health survey [SF-36]). Results were provided by mean values +/− standard deviation. For comparing pre to post PR, a two-tailed Wilcoxonrank sum test (W-test) was applied. The Mann-Whitney U-test(U-test) was used to compare the two groups at the beginning and the delta values (pre to post PR) with a significance level of p < 0.05. A logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the relationship between various baseline characteristics on changes in 6MWD and the physical (PCS) and mental health component score (MCS) of the SF-36. Also odds ratios of each parameter were calculated. Therefore, patients were classified into a group of poor and good responders for 6MWD (cut-off: Δ30m) and SF-36 (cut-offs: ΔPCS: 2.7; ΔMCS: 4.0). For group comparison, a 1:1-matching from an own retrospective COPD cohort (n = 708) was performed using FEV1 +/− 5%. Five LAM patients could not be assigned to an COPD patient. Therefore, a matching partner was assigned manually so that the mean values of FEV1% predicted did not differ significantly.
All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 23 (IBM, Inc., USA).
Results
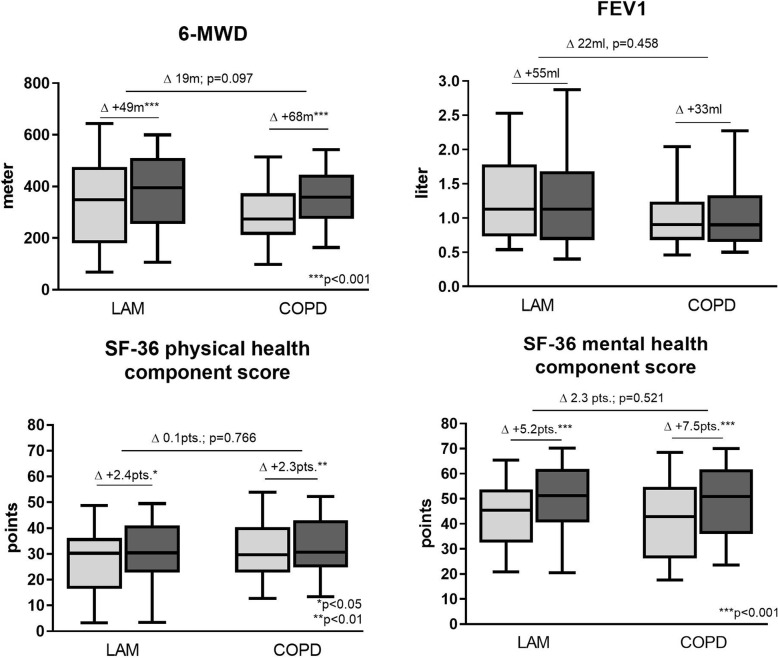
A total of n = 85 female patients with LAM performed PR during the observational period. However, n = 27 patients were excluded from the analysis due to following reasons: n = 21 (78%) performed repeated PR, n = 3 (11%) had missing data, and n = 3 (11%) were referred to another hospital due to acute clinical problems or worsening. The remaining 58 LAM patients showed a severely impaired lung function and exercise performance (Table 1). Eighteen patients (31%) received an mTOR inhibitor therapy with doses of 1.9 ± 0.5 mg. Following PR, 6MWD increased significantly by 49 ± 50 m (Fig. 1) exceeding the minimal important difference of 30 m [8]. Also quality of life (SF-36) improved significantly following PR (Fig. 1). These benefits were similar to the improvements in the COPD cohort. Results of the logistic regression analysis showed that none of the included variables (anthropometrics, lung function, mTOR inhibitor therapy, 6MWD or SF-36) was a significant predictor related to the improvements in 6MWD or quality of life. No exercise-related serious adverse events were recorded.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of LAM patients and a COPD comparison cohort (data are presented as mean ± SD and [median])
| LAM | COPD | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 58 | 58 | – |
| Female sex, n | 58 (100%) | 58 (100%) | – |
| Age, ys | 48.2 ± 10.3 [48.4] | 59.9 ± 11.6 [59.4] | < 0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.9 ± 5.9 [21.6] | 24.60 ± 7.19 [22.4] | 0.071 |
| Smoking status, never/former/current/unknown | 35/17/2/4 | 7/45/6/0 | < 0.001 |
| FEV1, l | 1.32 ± 0.74 [1.13] | 1.00 ± 0.45 [0.91] | 0.043 |
| FEV1, %predicted | 45.8 ± 24 [42.8] | 45.4 ± 21.7 [41.5] | 0.965 |
| IVC, l | 2.5 ± 1.0 [2.3] | 1.9 ± 0.7 [1.9] | 0.003 |
| IVC, %predicted | 72.1 ± 24.9 [74.4] | 51.2 ± 15.9 [53.4] | 0.001 |
| DLCO, %pred. | 40.7 ± 17.8 [37.2] | 44.3 ± 17.1 [43.4] | 0.481 |
| PaO2, mmHg | 65.7 ± 12.1 [63.9] | 59.0 ± 10.4 [59.5] | < 0.001 |
| PaCO2, mmHg | 35.3 ± 5.2 [34.1] | 41.0 ± 8.8 [38.4] | < 0.001 |
| CRP, mg/l | 3.2 ± 4.0 [2.0] | 12.5 ± 28.0 [4.2] | < 0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dl | 0.76 ± 0.24 [0.74] | 0.82 ± 0.23 [0.80] | 0.028 |
| Long-term oxygen therapy, n | 36 (62%) | 41 (71%) | 0.326 |
| Oxygen supplementation at rest, lpm | 1.4 ± 1.5 [1] | 1.2 ± 1.1 [1.5] | 0.766 |
| Oxygen supplementation during exercise, lpm | 2.4 ± 1.9 [2] | 1.8 ± 1.4 [2.0] | 0.085 |
| 6MWD, m | 338 ± 167 [330] | 287 ± 121 [275] | 0.097 |
| 6MWD, %predicted | 47.7 ± 22.7 [48.3] | 47.1 ± 20.2 [42.1] | 0.850 |
| SpO2 nadir during 6MWD | 79.4 ± 6.8 [84] | 84.9 ± 7.9 [87] | < 0.001 |
| Listed for lung transplantation, n | 28 (48%) | 23 (40%) | 0.350 |
| SF-36 physical health component score | 26.9 ± 12.8 [30.2] | 30.8 ± 11.7 [29.6] | 0.139 |
| SF-36 mental health component score | 44.0 ± 13.5 [45.4] | 41.2 ± 16.3 [42.8] | 0.359 |
Abbreviations: BMI Body mass index, FEV1 Forced expiratory volume in 1 s, IVC Inspiratory vital capacity, DLCO Diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide, PaO2 Partial pressure of oxygen, CRP C-reactive protein, 6MWD 6-min walk distance
Fig. 1.
Outcome measures before (light grey boxplots) and after (dark grey boxplots) a 4-week pulmonary rehabilitation program (PR) in 58 LAM and 58 COPD patients for changes in 6-min walk distance (6MWD), forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) and quality of life (SF-36 questionnaire)
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge this is the largest cohort of LAM patients, who were systemically analyzed before and after a comprehensive PR. To date, there is only one randomized, controlled trial available that investigated the effects of PR in 37 LAM patients [9]. In line with our results Araujo et al. found also significant improvements in exercise performance and quality of life. However, LAM patients that were included in that study had a much milder disease compared to patients in our study (FEV1: 72% and 6MWD: 517 m). Therefore, our study adds new evidence that PR is a beneficial treatment option even in patients with advanced LAM including patients listed for lung transplantation. Furthermore, we found that PR benefits were similar to the ones of a COPD cohort with similar disease severity. Until now, the best evidence for PR benefits is available for COPD patients [5]. In contrast, current LAM treatment guidelines either don’t mention PR as a treatment option [1] or state that PR may be offered to patients with LAM who are limited by dyspnoea (evidence level: expert opinion) [10]. The current ATS/ERS statement on PR lists LAM as a condition that may be appropriate for referral to PR. But this recommendation based only on extrapolating PR benefits from other chronic respiratory diseases and not on data [5].
PR had to be stopped in three patients (n = 1 pneumothorax, n = 1 acute worsening of dyspnea, and n = 1 pleural effusion) who needed to be transferred to an acute hospital. We interpret these events to be part of the natural course of the disease rather than to be related to any intervention during PR. In general, PR and in particular exercise training were regarded as feasible and safe in patients with advanced LAM.
Our study has some limitations. First, the COPD comparison group was significantly older, since not sufficient young COPD patients with severe airflow limitation were available. Second, data was collected using a retrospective study design over an observational period of two decades which is a rather long period given the fact that LAM is an orphan disease and medical treatment with mTOR inhibitors might have induced a bias during the last decade of our data collection. However, we could not identify any variability of PR effects over time.
Conclusion
This study investigated the effects of PR in LAM. We found significant and clinically relevant improvements in exercise performance and quality of life following PR. Based on our systematic analyses of available data we recommend PR as a treatment option also for patients with LAM - a rare disease without many therapeutic options.
Acknowledgements
We thank Clancy Dennis for the linguistic review of this manuscript.
Authors’ contributions
RG drafted the manuscript. CN performed statistical analyses. All authors shared scientific discussion. All authors review and approved the final manuscript and take responsibility for the integrity of the data.
Funding
None.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This retrospective analysis was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Philipps-University Marburg (ID EK_MR_26_11_2019_koczulla) and is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04184193).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.McCormack FX, Gupta N, Finlay GR, Young LR, Taveira-DaSilva AM, Glasgow CG, et al. Official American thoracic society/Japanese respiratory society clinical practice guidelines: lymphangioleiomyomatosis diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194:748–761. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201607-1384ST. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bahmer T, Watz H, Waschki B, Gramm M, Magnussen H, Rabe KF, et al. Reduced physical activity in lymphangioleiomyomatosis compared with COPD and healthy controls: disease-specific impact and clinical correlates. Thorax. 2016;71:662–663. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baldi BG, Albuquerque AL, Pimenta SP, Salge JM, Kairalla RA, Carvalho CR. Exercise performance and dynamic hyperinflation in lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:341–348. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201203-0372OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johnson J, Johnson SR. Cross-sectional study of reversible airway obstruction in LAM: better evidence is needed for bronchodilator and inhaled steroid use. Thorax. 2019;74:999–1002. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spruit MA, Singh SJ, Garvey C, ZuWallack R, Nici L, Rochester C, et al. An official American thoracic society/European respiratory society statement: key concepts and advances in pulmonary rehabilitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:e13–e64. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201309-1634ST. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gloeckl R, Marinov B, Pitta F. Practical recommendations for exercise training in patients with COPD. Eur Respir Rev. 2013;22:178–186. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00000513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Holland AE, Spruit MA, Troosters T, Puhan MA, Pepin V, Saey D, et al. An official European respiratory society/American thoracic society technical standard: field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur Respir J. 2014;44:1428–1446. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00150314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Singh SJ, Puhan MA, Andrianopoulos V, Hernandes NA, Mitchell KE, Hill CJ, et al. An official systematic review of the European respiratory society/American thoracic society: measurement properties of field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur Respir J. 2014;44:1447–1478. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00150414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Araujo MS, Baldi BG, Freitas CS, Albuquerque AL, Marques da Silva CC, Kairalla RA, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: a controlled clinical trial. Eur Respir J. 2016;47:1452–1460. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01683-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johnson SR, Cordier JF, Lazor R, Cottin V, Costabel U, Harari S, et al. European respiratory society guidelines for the diagnosis and management of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Eur Respir J. 2010;35:14–26. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00076209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.