Table 1.
Isotopically labeled methyl residue precursors for NOESY experiments.
| Site of 13CH3 | Precursor Name | Precursor Structure | 1L single density growth | Additional Supplements | Notes/Potential issues | Suppliers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-δ1 | α-Keto-butyrate | 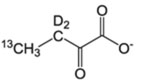 |
60 mg/L | – | Incompatible with A labeling. | CIL, Isotec, NMR-Bio | [1] |
| 2-(S)-Hydroxy-2-ethyl-3-keto-butyrate | 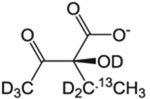 |
60 mg/L | – | Compatible with A labeling | NMR-Bio | [45] | |
| M-ε | l-Methionine |  |
250 mg/L | – | – | CIL, Isotec, NMR-Bio | [72] |
| L-δ/V-γ racemic pro-R pro-S | α-Keto-isovalerate | 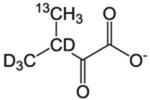 |
120 mg/L | – | – | CIL, Isotec, NMR-Bio | [4] |
| L-δ1, δ2/V-γ1, γ2 | α-Keto-isovalerate | 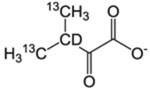 |
120 mg/L | – | This labeling scheme works best to establish intra-residue resonance pairings for L and V, less so for long range NOEs | Isotec | [2] |
| V-γ | α-Keto-isovalerate | Either of the above two precursors | 120 mg/L | 10% deuterated Bioexpress or Isogro | Addition of Bioexpress/Isogro has been observed to decrease I-δ1 and T-γ2 incorporation. Use to distinguish L/V resonances If also labeling I-δ1, add α-acetolactate 1 h before induction and α-ketobutyrate 20 min before induction | CIL, Isotec, or NMR-BioCIL, Isotec for supplement NMR-Bio | [52] |
| L-δ/V-γ pro-S | 2-(S)-Aceto-lactate |  |
300 mg/L | – | [50] | ||
| A-β | l-Alanine | 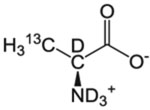 |
600 mg/L | 200 mg/L deuterated α-ketoisovalerate, 60 mg/L deuterated isoleucine (unless labeling L/V or I) | Scrambling to I-γ2 makes this label incompatible with α-ketobutyrate I labeling for NOE studies. 2-(S)-hydroxy-2-ethyl-3-ketobutyrate must be used instead for this scenario | CIL, Isotec, NMR-Bio | [45,49] |
| T-γ2 | l-Threonine | 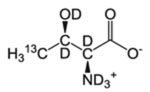 |
50 mg/L | 60 mg/L deuterated α-ketobutyrate (unless also labeling I-δ1) and 100mg/L deuterated Gly | – | CIL, Isotec, NMR-Bio | [46] |
