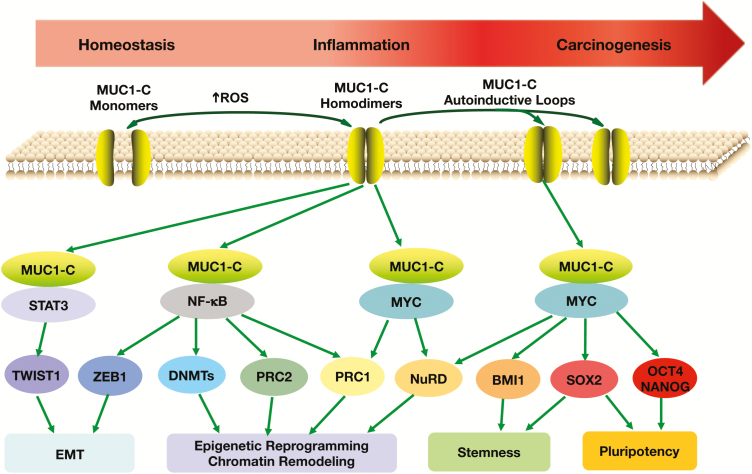
Figure 4.
MUC1-C promotes progression of inflammation and carcinogenesis by integrating EMT, epigenetic reprogramming and stemness. MUC1-C activates the IKK→NF-κB→p65 and JAK1→STAT3 pathways, which are linked to inflammatory responses and are aberrantly activated in cancer cells. The MUC1 gene is also activated by NF-κB→p65 and STAT3, resulting in the formation of auto-inductive circuits that can drive sustained signaling of these pathways in settings of chronic inflammatory responses. MUC1-C/STAT3 complexes activate TWIST1 and the EMT program (44). MUC1-C/NF-κB→p65 complexes induce (i) ZEB1 and EMT, (ii) DNMT1/3b and DNA methylation of TSGs and (iii) EZH2/PRC2 and epigenetic reprogramming (36). Binding of the MUC1-C CQC motif to the MYC HLH-LZ contributes to activation of MYC target genes, including those encoding components of the NuRD and BMI1/PRC1 complexes (18,36). MUC1-C/MYC complexes have also been linked to activation of SOX2, OCT4 and NANOG pluripotency factors (41,47). Prolonged auto-induction of MUC1-C in settings of chronic inflammation drives EMT, epigenetic reprogramming, chromatin remodeling, stemness and pluripotency that promote carcinogenesis (41).