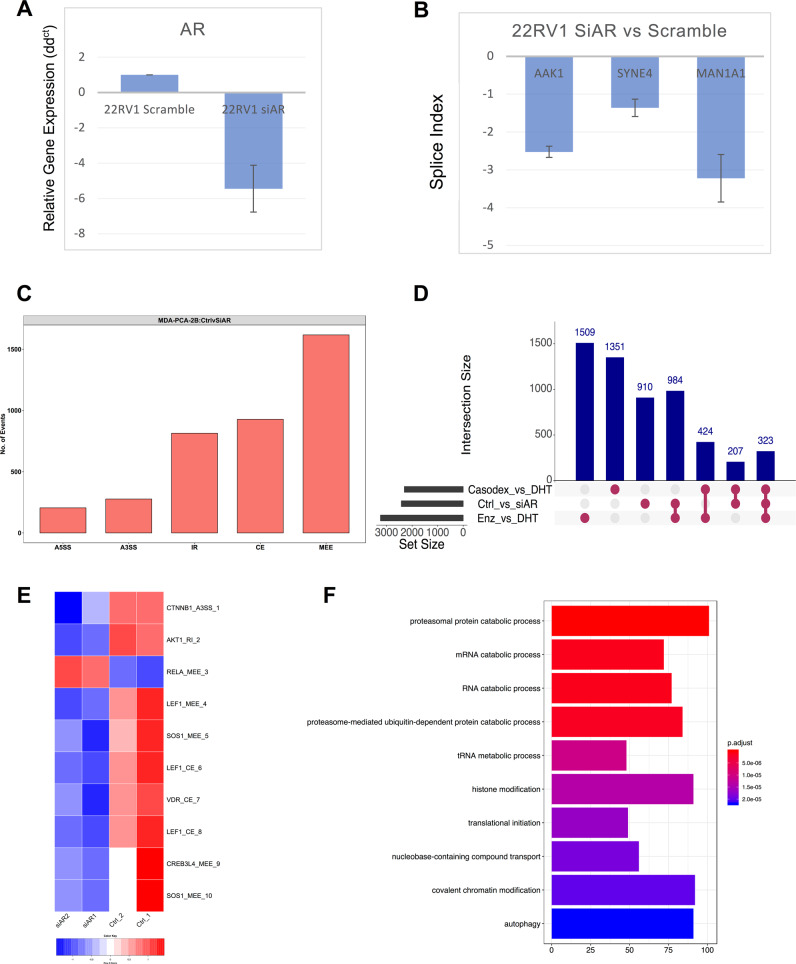
Fig. 3. Direct genomic inhibition of androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells induces alternative splicing.
Bar graph comparing expression of AR in 22RV1 treated with scramble siRNA or siRNA against AR. b Bar graph showing expression of AAK1, SYNE4, and MAN1A1 in LNCaP cells treated with siRNA against AR in comparison to scramble siRNA. c Bar graph showing total number of rMATS predicted splicing events in MDA-PCa-2b cells treated with siRNA against AR or scrambled control. d Upset plot comparing the genes predicted to undergo alternative splicing by rMATS or HTA-2.0 analysis in prostate cancer cells treated with casodex or enzalutamide in comparison to DHT or siRNA against AR in comparison to scrambled siRNA. e The heatmap comparing PSI for prostate cancer genes across MDA-PCa-2b cells treated with scrambled or siRNA against AR. f Bar graph revealing the GO pathway enriched for genes under undergoing ASE modulated by genomic inhibition of AR in MDA-PCa-2b.