Abstract
Urochloa (syn.—Brachiaria s.s.) is one of the most important tropical forages that transformed livestock industries in Australia and South America. Farmers in Africa are increasingly interested in growing Urochloa to support the burgeoning livestock business, but the lack of cultivars adapted to African environments has been a major challenge. Therefore, this study examines genetic diversity of Tanzanian Urochloa accessions to provide essential information for establishing a Urochloa breeding program in Africa. A total of 36 historical Urochloa accessions initially collected from Tanzania in 1985 were analyzed for genetic variation using 24 SSR markers along with six South American commercial cultivars. These markers detected 407 alleles in the 36 Tanzania accessions and 6 commercial cultivars. Markers were highly informative with an average polymorphic information content of 0.79. The analysis of molecular variance revealed high genetic variation within individual accessions in a species (92%), fixation index of 0.05 and gene flow estimate of 4.77 showed a low genetic differentiation and a high level of gene flow among populations. An unweighted neighbor-joining tree grouped the 36 accessions and six commercial cultivars into three main clusters. The clustering of test accessions did not follow geographical origin. Similarly, population structure analysis grouped the 42 tested genotypes into three major gene pools. The results showed the Urochloa brizantha (A. Rich.) Stapf population has the highest genetic diversity (I = 0.94) with high utility in the Urochloa breeding and conservation program. As the Urochloa accessions analyzed in this study represented only 3 of 31 regions of Tanzania, further collection and characterization of materials from wider geographical areas are necessary to comprehend the whole Urochloa diversity in Tanzania.
Keywords: Apomixis, Brachiaria, Carbon sequestration, Polyploid, Principal coordinate analysis, Private alleles
Introduction
Urochloa (syn.—Brachiaria s.s.) that consists of about 100 species is among the most widely cultivated tropical forage grass in South America, Australia and East Asia and has been recognized for high yield, nutritional content and wider adaptability to diverse ecological niches (Miles et al. 1996). Urochloa is a tropical warm season forage native to Africa and was first introduced to Australia in about 1800 (Barnard 1969) and subsequently into tropical South America during the mid-nineteenth century (Parsons 1972). Urochloa is resistant to drought, insect pests and diseases and competes effectively with other plant species and quickly covers the ground (Stomayor-Rios et al. 1960). Urochloa produces a yearly dry forage yield of 5–36 t/ha depending on soil fertility, soil moisture content and fertilizer application (Bogdan 1977). The forage is palatable and highly nutritious contributing to a significant increase in livestock milk and meat production. Moreover, Urochloa sequesters carbon, enhances N use efficiency through a biological nitrification inhibition process and subsequently reduces greenhouse gas emission and groundwater pollution (Subbarao et al. 2009; Danilo et al. 2014; Arango et al. 2014).
Low livestock productivity is a common feature across sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) contributed largely by shortage of quality feed particularly during the dry seasons. Though not a tradition, farmers have started growing improved forages to support the emerging livestock sector in the region. Recently, Urochloa has emerged as one of the important forage options among smallholder farmers of Africa (Ghimire et al. 2015). However, the wider adoption of Urochloa grass in Africa is constrained by unavailability of seeds, lack of improved agronomic practices and nonexistence of a variety suitable for wide-ranging environments. The varieties currently introduced to Africa were developed in Australia and tropical America from the African germplasm. The commercial cultivation of these varieties developed elsewhere can lead to an elevated risk of pests and diseases, and of poor adaptation to other biotic and abiotic stresses. Therefore, the need for Africa-based Urochloa breeding program accommodating natural genetic diversity in the region has been recently realized with the aim to develop varieties suitable to different production environments.
The characterization of genetic diversity of a population is necessary for better use of genetic resources in breeding and biodiversity conservation programs. Therefore, knowledge of genetic diversity of the available germplasm is essential in selecting materials for cultivation or parents for cultivar development. The genetic diversity can be assessed using different tools including DNA markers (Kapila et al. 2008). Molecular markers are valuable tools for characterization and evaluation of genetic diversity within and between species and populations. Different molecular markers such as random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR), simple sequence repeats (SSR) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) have been used to assess the genetic diversity in plant species (Balasaravanan et al. 2003; Khan et al. 2005; Terzopoulos et al. 2005) of which the simple sequence repeats (SSR) are preferred due to ease of application, high reproducibility, rapid analysis, low cost, easy scoring patterns and higher allelic diversity (Chen et al. 1997). The SSR markers are codominant markers that can detect both homozygote and heterozygote individuals and are distributed throughout the genome (McCouch et al. 1997). Knowing the degree of genetic differences among Urochloa genotypes is useful to organize a working collection and to select genotypes for crossing and conservation (Mendes-Bonato et al. 2006). Despite the importance of Urochloa, limited information is available on biology and genetic diversity of the genus, which has severely constrained the breeding and conservation efforts. Therefore, this study was conducted to assess the genetic diversity and population structure of Tanzanian Urochloa accessions from the historical collection maintained at the Field Genebank of the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), Ethiopia. The result of this study would be highly useful in a Urochloa improvement and conservation program.
Materials and methods
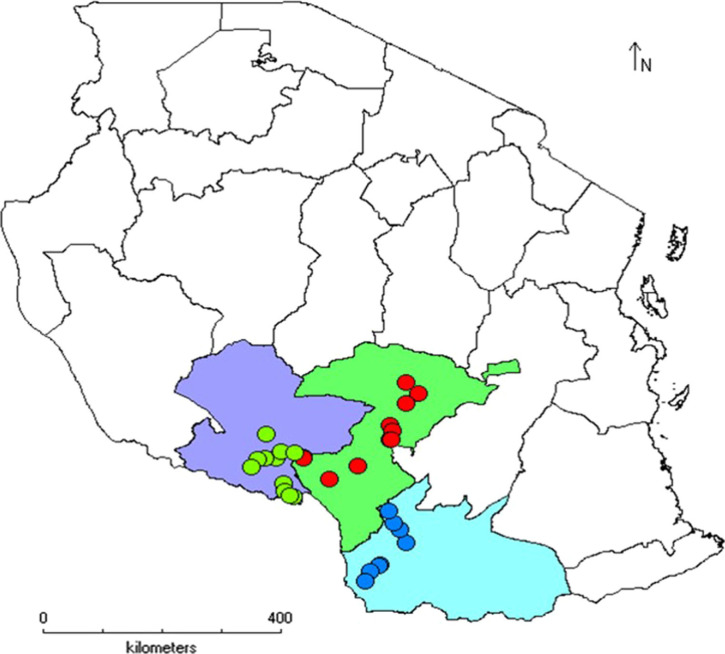
Source of plant materials – A total of 36 Urochloa accessions originally collected from Tanzania and six commercial cultivars (Basilisk, Humidicola, Llanero, MG4, Mulato II and Piata) were included in this study (Table 1). The Genbank accessions were collected from natural populations from the Iringa, Mbeya and Ruvuma regions of Tanzania (Fig. 1) during 1985 and since then maintained in ILRI’s Forage Field Genebank at Zwai, Ethiopia. Fresh young leaf samples were collected, dried in silica gel and transported to the Biosciences eastern and central Africa—International Livestock Research Institute (BecA-ILRI) Hub, Nairobi, Kenya, for subsequent analysis. Leaf samples of six commercial cultivars were collected from pasture evaluation plots at ILRI Headquarters, Nairobi, Kenya.
Table 1.
Details of Urochloa accessions and commercial cultivars used in the study
| S. no | Accession | Other ID # | Species | Variety | Origin | Region | Latitude | Longitude | Collection year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ILCA-814 | CIAT 26386 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.89 | 33.98 | 1985 |
| 2 | ILCA-726 | CIAT 26370 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 7.9501 | 35.56 | 1985 |
| 3 | ILCA-731 | CIAT 26371 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.3298 | 35.3104 | 1985 |
| 4 | ILCA-869 | CIAT 26397 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.5 | 33.4 | 1985 |
| 5 | ILCA-717 | CIAT 26407 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 7.78 | 35.75 | 1985 |
| 6 | ILCA-10871 | – | U. decumbens | Basilisk | Uganda | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 7 | ILCA-12470 | – | U. humidicola | Llanero | Zambia | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 8 | ILCA-828 | CIAT 26389 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.92 | 33.39 | 1985 |
| 9 | ILCA-821 | CIAT 26388 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.82 | 33.84 | 1985 |
| 10 | ILCA-849 | CIAT 26393 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 9.35 | 33.67 | 1985 |
| 11 | – | CIAT 16125 | U. brizantha | Piata | – | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 12 | ILCA-758 | – | U. jubata | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 10.77 | 35.13 | 1985 |
| 13 | ILCA-767 | CIAT 26380 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 10.3718 | 35.5573 | 1985 |
| 14 | ILCA-781 | CIAT 26381 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 10.0266 | 35.3737 | 1985 |
| 15 | ILCA-785 | CIAT 26384 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 9.28 | 34.38 | 1985 |
| 16 | ILCA-732 | CIAT 26434 | U. ruziziensis | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.3298 | 35.3104 | 1985 |
| 17 | ILCA-829 | CIAT 26423 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.93 | 33.27 | 1985 |
| 18 | ILCA-728 | CIAT 26411 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 7.9501 | 35.56 | 1985 |
| 19 | ILCA-727 | CIAT 26438 | U. bovonei | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 7.9501 | 35.56 | 1985 |
| 20 | ILCA-735 | CIAT 26414 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.5853 | 35.3122 | 1985 |
| 21 | ILCA-822 | CIAT 26422 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.82 | 33.84 | 1985 |
| 22 | ILCA-853 | CIAT 26427 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 9.48 | 33.7 | 1985 |
| 23 | ILCA-864 | CIAT 26430 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 9.55 | 33.76 | 1985 |
| 24 | ILCA-832 | CIAT 26424 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 9.0549 | 33.1715 | 1985 |
| 25 | ILCA-857 | CIAT 26428 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 9.57 | 33.83 | 1985 |
| 26 | – | CIAT 36087 | U. hybrid | Mulato-II | Colombia | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 27 | ILCA-810 | CIAT 26385 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.91 | 33.56 | 1985 |
| 28 | ILCA-756 | CIAT 26404 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 10.76 | 35.16 | 1985 |
| 29 | ILCA-769 | CIAT 26439 | U. bovonei | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 10.1543 | 35.4718 | 1985 |
| 30 | ILCA-815 | CIAT 26420 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.89 | 33.98 | 1985 |
| 31 | ILCA-734 | CIAT 26413 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.4303 | 35.3511 | 1985 |
| 32 | ILCA-819 | CIAT 26421 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.91 | 33.98 | 1985 |
| 33 | ILCA-782 | CIAT 26382 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 9.82 | 35.3 | 1985 |
| 34 | ILCA-760 | CIAT 26378 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 10.88 | 35.01 | 1985 |
| 35 | ILCA-744 | CIAT 26416 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 9.0392 | 34.8211 | 1985 |
| 36 | ILCA-736 | CIAT 26415 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 8.5798 | 35.324 | 1985 |
| 37 | ILCA-863 | CIAT 26396 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 9.55 | 33.76 | 1985 |
| 38 | ILCA-718 | CIAT 26408 | U. humidicola | NA | Tanzania | Iringa | – 7.6006 | 35.5495 | 1985 |
| 39 | ILCA-761 | CIAT 26379 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Ruvuma | – 11.04 | 34.92 | 1985 |
| 40 | – | CIAT 26646 | U. brizantha | MG4 | Trinidad | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 41 | ILCA-812 | CIAT 26405 | U. brizantha | NA | Tanzania | Mbeya | – 8.8 | 33.64 | 1985 |
| 42 | – | CIAT 679 | U. humidicola | Humidicola | South Africa | NA | NA | NA | NA |
NA not available
Fig. 1.
Map of Tanzania showing the origin of Urochloa accessions. Purple, blue and green colors in map represent Mbeya, Iringa and Ruvuma regions, respectively. (Color figure online)
Genomic DNA extraction – Genomic DNA was extracted from dried leaves using Zymo extraction kit (Zymo Research, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The quality, quantity and integrity of DNA were estimated using the NanoDrop 1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and visualized in 1% agarose gel (w/v) stained with 0.25X GelRed under ultraviolet light (UVP BioImaging Systems, Upland, CA). The DNA was adjusted to the final concentration of 20 ng/μl and stored at – 20 °C until further use.
PCR amplification and capillary electrophoresis – A total of 24 SSR markers initially developed for U. ruziziensis Germain & Evrard with the proven transferability to other Urochloa species were used in the study (Silva et al. 2013; Table 2). Primers were optimized for appropriate annealing temperature using gradient PCR. Thereafter, multiplex PCR was used to amplify genomic DNA using AccuPower® PCR PreMix without dye (Bioneer, Republic of Korea). PCR amplification was performed in a final reaction volume of 10 μl containing 40 ng genomic DNA, 0.09 μM of each forward and reverse primer (labeled with different fluorescent dyes: 6-FAM, VIC, NED and PET), 0.5 μM MgCl2 and 7.2 μl sterile water. The PCR amplifications were performed in a GeneAmp PCR System 9700 thermocycler (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) using the following PCR cycling conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 58/59 °C for 1 min, extension at 72 °C for 2 min and final extension at 72 °C for 20 min and hold at 15 °C. The amplicons were separated in 2% agarose gel stained with 0.25 × GelRed and run for 45 min at 100 V. A cocktail (LH) of 15 μl GeneScanTM500LIZ size standard (Applied Biosystems, USA) and 1 ml Hi-Di-formamide was prepared for capillary electrophoresis. Multiplexed PCR product (1.5 μl) was mixed with 9 μl of LH, denatured at 95 °C for 3 min and snap-chilled on ice for 5 min. The samples were then subjected to capillary electrophoresis at the Segolip Unit of BecA-ILRI HuU.
Table 2.
SSR markers used for the genetic diversity study of Tanzania Urochloa accessions and commercial varieties (adapted from Silva et al. 2013)
| Marker | Forward primer sequence | Reverse primer sequence | Annealing temperature (°C) | Expected product size range (bp) | Repeat motif |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br0012 | ACTCAAACAATCTCCAACACG | CCCCACAAATGGTGAATGTAAC | 59 | 144–196 | (AT)8 |
| Br0028 | CATGGACAAGGAGAAGATTGA | TGGGAGTTAACATTAGTGTTTTT | 58 | 111–197 | (TA)8 |
| Br0029 | TTTGTGCCAAAGTCCAAATAG | TATTCCAGCTTCTTCTGCCTA | 59 | 132–178 | (AG)14 |
| Br0031 | CCCCCATTTAACACCATAGTT | GCTCAAAATGCAATGTACGTG | 59 | 139–179 | (AT)9 |
| Br0067 | TTAGATTCCTCAGGACATTGG | TCCTATATGCCGTCGTACTCA | 59 | 130–171 | (AT)9 |
| Br0076 | CCTAGAATGCGGAAGTAGTGA | TTACGTGTTCCTCGACTCAAC | 59 | 120–262 | (AT)7 |
| Br0087 | TTCCCCCACTACTCATCTCA | AACAGCACACCGTAGCAAGT | 58 | 229–261 | (GA)9 |
| Br0092 | TTGATCAGTGGGAGGTAGGA | TGAAACTTGTCCCTTTTTCG | 59 | 200–295 | (AT)6 |
| Br0100 | CCATCTGCAATTATTCAGGAAA | GTTCTTGGTGCTTGACCATT | 58 | 229–286 | (AT)11 |
| Br0115 | AATTCATGATCGGAGCACAT | TGAACAATGGCTTTGAATGA | 59 | 231–315 | (AT)6 |
| Br0117 | AGCTAAGGGGCTACTGTTGG | CGCGATCTCCAAAATGTAAT | 59 | 233–345 | (TA)5 |
| Br0118 | AGGAGGTCCAAATCACCAAT | CGTCAGCAATTCGTACCAC | 59 | 237–321 | (CT)11 |
| Br0156 | CATTGCTCCTCTCGCACTAT | CTGCAGTTAGCAGGTTGGTT | 58 | 223–279 | (CA)6 |
| Br0130 | TCCTTTCATGAACCCCTGTA | CATCGCACGCTTATATGACA | 58 | 199–299 | (CT)14 |
| Br0149 | GCAAGACCGCTGTTAGAGAA | CTAACATGGACACCGCTCTT | 58 | 231–299 | (AT)11 |
| Br0152 | ATGCTGCACTTACTGGTTCA | GGCTATCAATTCGAAGACCA | 58 | 233–301 | (TC)11 |
| Br0214 | GCCATGATGTTTCATTGGTT | TTTTGCACCTTTCATTGCTT | 59 | 231–286 | (AC)7 |
| Br0203 | CGCTTGAGAAGCTAGCAAGT | TAGCCTTTTGCATGGGTTAG | 58 | 208–310 | (GA)8 |
| Br0212 | ACTCATTTTCACACGCACAA | CGAAGAATTGCAGCAGAAGT | 58 | 248–330 | (CA)5 |
| Br0213 | TGAAGCCCTTTCTAAATGATG | GAACTAGGAAGCCATGGACA | 58 | 212–337 | (CA)7 |
| Br0122 | TCTGGTGTCTCTTTGCTCCT | TCCATGGTACCTGAATGACA | 58 | 241–358 | (AT)8 |
| Br0235 | CACACTCACACACGGAGAGA | CATCCAGAGCCTGATGAAGT | 59 | 239–330 | (TC)9 |
| Br3002 | GCTGGAATCAGAATCGATGA | GAACTGCAGTGGCTGATCTT | 59 | 143–187 | (AAT)7 |
| Br3009 | AGACTCTGTGCGGGAAATTA | ACTTCGCTTGTCCTACTTGG | 58 | 116–199 | (AAT)10 |
Data analysis – Forty-two Urochloa genotypes consisting five species: U. bovonei (Chiov.) Robyns, U. brizantha (A. Rich.) Stapf, U. jubata (Fig. & De Not.) Stapf, U. humidicola (Rendle) Schweick, U. ruziziensis Germain & Evrard and six Urochloa cultivars were grouped into six populations for the genetic diversity study. The descriptive statistics for SSR markers were computed with PowerMarker v.3.25 software (http://www.powermarker.net). The population diversity description, principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) and analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) were performed using GenAlEx v6.41 (Peakall and Smouse 2006). The neighbor-joining method (NJ) was used to generate the dendrogram using Darwin v.6.0.010 (Perrier and Jacquemoud-Collet 2006). One thousand bootstrap replicates were used to determine branch support in the consensus tree. Structure v.2.3.4 (Pritchard et al. 2000) was used to infer the population structure and ancestry of samples based on Bayesian statistics. The parameter set for this analysis used the admixture model, and batch runs with correlated and independent allele frequencies among inferred populations were tested with burn-in and run length of 50,000 and 100,000, respectively. All other parameters were set to default values. A batch job with values of K ranging from 1 to 10 was set up, with ten independent runs for each successive K. This procedure clusters individuals into populations and estimates the proportion of membership in each population for every individual. The K value was determined by the log probability of data [(Ln P(D)] based on the rate of change in Ln P(D) between successive K. The optimum K value was predicted following the simulation method (Evanno et al. 2005) using the web-based software Structure Harvester v.0.6.92 (Earl and Von Holdt 2012).
Results
SSR polymorphism and genetic diversity – A total of 407 alleles ranging in size from 111 to 345 bp were detected (Tables 2, 3). The number of alleles scored per locus varied from 5 (Br0067) to 40 (Br0028) with an average of 16.96 alleles across all loci. The PIC value varied from 0.64 (Br0213) to 0.95 (Br0235) with an average of 0.79 per locus (Table 3).
Table 3.
Diversity indices for 24 microsatellite markers
| SSR locus | NA | NDA | I | HO | HE | PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br0012 | 9 | 9 | 0.86 | 0.50 | 0.35 | 0.85 |
| Br0029 | 11 | 10 | 0.73 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.71 |
| Br0031 | 9 | 9 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.66 |
| Br0067 | 5 | 5 | 0.84 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.82 |
| Br0076 | 9 | 9 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.80 |
| Br0087 | 22 | 16 | 0.75 | 0.43 | 0.31 | 0.74 |
| Br0092 | 7 | 7 | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 0.74 |
| Br0115 | 16 | 12 | 0.95 | 0.66 | 0.44 | 0.95 |
| Br0117 | 8 | 8 | 0.74 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.73 |
| Br0118 | 12 | 11 | 0.70 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.68 |
| Br0212 | 17 | 13 | 0.95 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.95 |
| Br0214 | 16 | 12 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.66 | 0.92 |
| Br0235 | 31 | 23 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.55 | 0.95 |
| Br3002 | 11 | 9 | 0.87 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 0.86 |
| Br0028 | 40 | 19 | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.78 |
| Br0100 | 13 | 13 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.72 |
| Br0122 | 10 | 9 | 0.78 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.76 |
| Br0130 | 18 | 11 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.47 | 0.75 |
| Br0149 | 13 | 12 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.66 |
| Br0152 | 29 | 19 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.43 | 0.73 |
| Br0156 | 38 | 22 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.85 |
| Br0203 | 22 | 15 | 0.80 | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.79 |
| Br0213 | 6 | 6 | 0.66 | 0.50 | 0.32 | 0.64 |
| Br3009 | 35 | 23 | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.49 | 0.80 |
| Mean | 16.96 ± 10.43 | 12.74 ± 5.32 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 0.56 ± 0.15 | 0.38 ± 0.12 | 0.79 ± 0.09 |
NA number of alleles, NDA number of different alleles, I Shannon index, HO observed heterozygosity, HE expected heterozygosity
Population genetic diversity – The genetic diversity indices for Urochloa populations are summarized in Table 4. The average number of effective alleles (NE), number of private alleles (NP) and percentage of polymorphic loci (%PL) across all loci ranged from 0.34–2.74, 0.08–1.53 and 17.19–68.75%, respectively, in the studied populations. The observed heterozygosity (HO) was in the range of 0.17–0.69, with a mean of 0.49. The high-level diversity was observed in U. brizantha population (I = 0.94) and a low-level diversity in U. bovonei population (I = 0.12). The observed heterozygosity was higher than expected for all populations.
Table 4.
Summary of population genetic diversity indices averaged over 24 SSR markers
| Population | N | NA | NE | NP | I | HO | HE | %PL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U. brizantha | 17 | 3.50 | 2.74 | 1.53 | 0.94 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 68.75 |
| U. humidicola | 15 | 2.70 | 2.37 | 1.03 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 0.40 | 57.81 |
| U. bovonei | 2 | 0.94 | 0.69 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 31.25 |
| U. ruziziensis | 1 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 17.19 |
| U. jubata | 1 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 29.67 |
| Urochloa Cultivars | 6 | 1.61 | 1.48 | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.46 | 0.30 | 46.88 |
| Mean | 8.4 | 1.89 | 1.64 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.31 | 41.93 |
| SE (±) | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 7.90 |
N number of accessions, NA number of alleles, NE number of effectives alleles, I information index, HO observed heterozygosity, HE expected heterozygosity, NP number of private alleles, %PL percentage of polymorphic loci
Genetic distance – The pairwise genetic distance and population matrix of Nei unbiased genetic identity were presented in Table 5. Among four populations analyzed (excluding U. ruziziensis and U. jubata), U. bovonei and commercial cultivar populations were distantly related (3.186), whereas U. brizantha and U. humidicola populations were the most closely related (1.639). Similarly, genetic identity was the highest between U. brizantha and U. humidicola populations (0.194) and the lowest between U. bovonei and commercial cultivar populations (0.041).
Table 5.
Pair-wise genetic distance based on shared allele (below diagonal) and genetic identity among Urochloa populations (above diagonal)
| Population | U. brizantha | U. humidicola | U. bovonei | Cultivars |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U. brizantha | – | 0.194 | 0.048 | 0.097 |
| U. humidicola | 1.639 | – | 0.055 | 0.067 |
| U. bovonei | 3.044 | 2.893 | – | 0.041 |
| Cultivars | 2.333 | 2.709 | 3.186 | – |
Analysis of molecular variance – Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) of 42 Urochloa genotypes showed that only 3% of the total variation in the population was due to differences among individual accessions. Differences within individual accessions in a population contributed 94% of total variation, and 5% was due to the differences among the Urochloa populations (Table 6). There was a low genetic differentiation in the total populations (FST- = 0.05) as evidenced by high level of gene flow estimate (Nm = 4.77).
Table 6.
Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) of populations of Urochloa accessions and cultivars based on 24 SSR loci
| Source | Degree of freedom | Sum of squared | Mean of squared | Estimated variance | Variation (%) | P values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among populations | 4 | 96.841 | 24.210 | 0.712 | 5 | 0.001 |
| Among individuals | 37 | 517.754 | 13.993 | 0.407 | 3 | 0.084 |
| Within individuals | 42 | 553.500 | 13.179 | 13.179 | 92 | 0.001 |
| Total | 83 | 1168.095 | 14.298 | 100 | ||
| FST = 0.05; Nm = 4.77 |
FST Fixation index, Nm Number of migration per generation
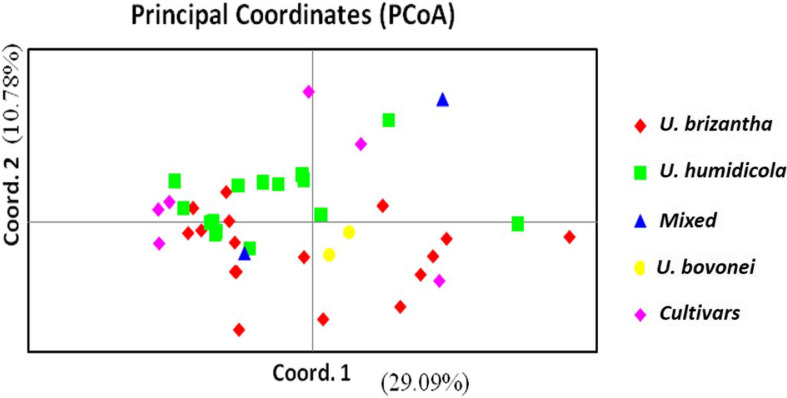
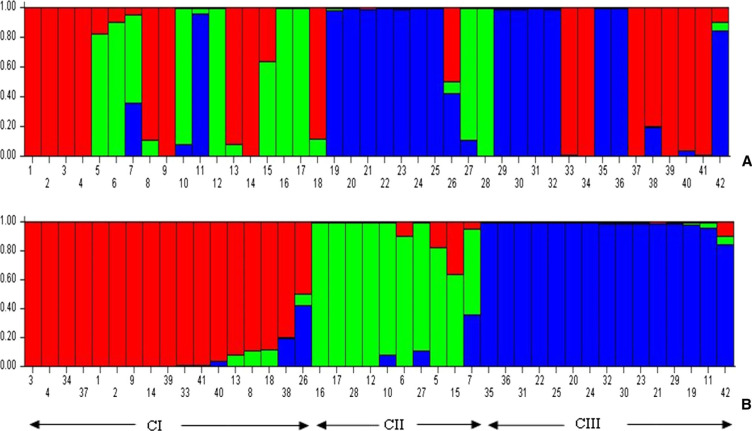
Population structure – The principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) bi-plot showed no distinct clustering pattern for 42 Urochloa genotypes studied (Fig. 2). The variations explained by axes 1 and 2 were 26.09 and 10.78%, respectively. An unweighted neighbor-joining dendrogram depicting genetic relationships among the Urochloa accessions and commercial cultivars showed three major clusters (Fig. 3). Of the 42 individuals including the commercial cultivars, 19, 18 and 5 individuals were grouped together in cluster I, II and III, respectively. Most of the accessions from U. brizantha and one commercial cultivar (MG4) grouped in cluster I, whereas most of accessions from U. humidicola, two accessions of U. bovonei and two commercial cultivars (Humidicola and Piata) grouped in cluster II. Three commercial cultivars (Basilisk, Llanero and Mulato II) and one available accession U. ruziziensis formed the cluster III. Overall topology of the dendrogram indicated the presence of three lineages in the Urochloa populations studied. A similar pattern was observed on Bayesian model-based clustering algorithm implemented in STRUCTURE software. The method of Evanno et al. (2005), implemented in STRUCTURE, predicted K = 3 to be the most likely number of clusters (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2.
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) bi-plot showing the clustering of 36 Urochloa accessions from Tanzania and six commercial cultivars. Percentages of variation explained by the first two axes (1, 2) are 26.09 and 10.78%, respectively. (Color figure online)
Fig. 3.
An unweighted neighbor-joining tree of 42 Urochloa genotypes (36 Tanzanian accessions and six commercial cultivars) using the simple matching similarity coefficient based on 24 microsatellite markers. The populations are color-coded as shown in the tree. (Color figure online)
Fig. 4.
a Analysis performed in STRUCTURE 2.2.3 using admixture model with correlated allele frequencies. The clustering profile obtained for K = 3 is displayed as indicated by different colors. b Each of the 42 individuals is represented by a single column broken into colored segments with lengths proportional to each of the K inferred gene pools. Three major clusters of individuals were identified and are indicated by red, green and blue colors (CI = 17, CII = 10 and CIII = 15), and bars with two colors represent individuals that share allelic pools. Membership coefficients (y-axis) are indicated, which were used to allocate individuals into clusters. (Color figure online)
Discussion
Genetic diversity assessment is an essential component of any Urochloa breeding and conservation program. Microsatellites are among the most widely used DNA markers for many purposes such as diversity, genome mapping and variety identification (da Silva 2005). These markers have been used to study genetic diversity in different plant species (Singh et al. 2004; Joshi and Behera 2006). In this study, the extent and pattern of genetic variation among 36 Tanzanian Urochloa accessions were evaluated and their genetic relationships with six Urochloa cultivars were examined using 24 SSR markers. The SSR markers used in the study were subsets of previously published markers (Silva et al. 2013) with high polymorphic information content (PIC) values, elevated allele detection profile and proven transferability to multiple Urochloa species.
The average number of alleles (16.96) detected in this study was higher than that reported by Jungmann et al. (2010), Bianca et al. (2011), Silva et al. (2013) and Pessoa-Filho et al. (2015), who reported average numbers of alleles of 7.33, 4.22, 12.3 and 9 using 172 U. brizantha, 11 U. ruziziensis, 63 African Ruzigrass and 58 U. humidicola accessions with 15, 30, 15 and 27 SSR markers, respectively. The mean PIC value for SSR markers was high (0.79) compared to previous studies (Sousa et al. 2010; Bianca et al. 2011; Silva et al. 2013) showing high discriminating ability of these markers among tested genotypes. The detection of more alleles and high PIC values in this study could have been attributed to high diversity in Tanzanian Urochloa accessions, use of primers with high allele detection ability, high PIC values and proven transferability to multiple Urochloa species or a combination thereof. The high number of alleles detected in this study signifies high genetic variations among test Urochloa accessions in consistent with high genetic diversity index (0.67–0.95) (Table 3). The result is not surprising as Tanzania is within the region that represents a center of diversity for Urochloa species. Moreover, these 36 Tanzanian Urochloa accessions represent five distinct species (Table 1).
All the diversity indices are measured in this study, including the numbers of private alleles were high for U. brizantha population, whereas U. bovonei and U. ruziziensis populations had lower values (Table 4). As the number of different alleles and the number of private alleles depend heavily on sample size (Szpiech et al. 2008), a high number of accessions in U. brizantha population might have largely contributed to such results. Despite similar sample size of U. jubata and U. ruziziensis, the U. jubata accession had a slightly higher number of private alleles and a higher percentage of polymorphic loci, signifying that factors other than sample size also contribute to diversity indices. The observed heterozygosity was higher than expected heterozygosity for all studied Urochloa populations suggesting presence of many equally frequent alleles and the high genetic variability in the populations indicating high value of these genetic resources in Urochloa improvement and conservation program. Mixing of two previously isolated Urochloa populations could be another possibility for higher observed heterozygosity than expected.
Genetic distance is the measure of the allelic substitutions per locus that have occurred during the separate evolution of two populations or species (Woldesenbet et al. 2015). The Nei unbiased genetic distance between U. brizantha and U. humidicola was smaller, while larger genetic distance was observed between U. bovonei and the commercial cultivars. The genetic closeness of two populations could be due to interspecific hybridization that has occurred throughout their evolution, which favors allele sharing (Cidade et al. 2013). The large genetic distance observed between U. bovonei and commercial cultivars could be attributed by lack of genetic similarity as five commercial cultivars used in this species are from three species (U. brizantha, U. decumbens Stapf and U. humidicola), while commercial cultivar, Mulato II, is a product of three-way cross of U. brizantha, U. decumbens and U. ruziziensis. Two species, i.e., U. jubata and U. ruziziensis, were not included in this analysis due to insufficient sample size.
The AMOVA test showed major and significant (92%; P = 0.001) contribution of within-individual difference to a total variation, whereas among-individual and among-population differences contributed 3 and 5%, respectively. The high level of genetic variation within species observed in our study was similar to that reported for Ruzigrass (Pessoa-Filho et al. 2015). These results are also in agreement with other studies (Bianca et al. 2011; Garcia et al. 2013; Teixeira et al. 2014). The high level of genetic variation within individual in a population could be attributed to genetic drift, mutation and environment conditions (Young et al. 2000). As the Urochloa population/species in this study are composed of genotypes originating from different locations with different geographical and environment conditions, a high within-population difference was expected. There was a low genetic variation among Urochloa accessions in consistent with the high genetic indices as evidenced by relatively low fixation index (FST = 0.05) among populations and high number of migration (Nm = 4.7) per generation (Slatkin 1981; Caccone 1985; Walples 1987). A low genetic differentiation among Urochloa populations was anticipated because of apomictic mode of reproduction, polyploidy-triggered meiotic anomalies obstructing sexual reproduction and dispersion of plant propagules by migratory herbivores and birds. Of five Urochloa species analyzed in this study, four (U. brizantha, U. humidicola, U. bovonei and U. jubata) are polyploid (Boldrini et al. 2009; Bianca et al. 2011) and U. ruziziensis is diploid with sexual mode of reproduction (Pessoa-Filho et al. 2015). Polyploid plants can effectively colonize and occupy different habitats favoring no genetic differentiation among Urochloa populations (De Wet 1980). This has also been observed in other apomictic polyploid forages such as Paspalum notatum Fluegge (Cidade et al. 2013).
In PCoA, no distinct clusters were observed; however, STRUCTURE and the unweighted neighbor-joining algorithm analyses consistently revealed three major clusters (Figs. 3, 4). Cluster I was mainly composed of U. brizantha accessions (15 out of 17), while most U. humidicola accessions (12 out of 15) were found in cluster II and 3 of 6 commercial cultivars were found in cluster III. Two accessions of U. bovonei and one of U. jubata were found in cluster II, but in different sub clusters. Although U. ruziziensis was found in cluster III, it is a bit far from the rest of accessions (Fig. 3). This is as expected because it is only one accession included in this study with diploid genome and sexual mode of reproduction. The accessions included in the study grouped together irrespective of their geographical origin indicating accessions from different geographical regions share the allelic pool (Sousa et al. 2010). However, a little admixture of accessions from different allelic pools was observed in all clusters showing possible interspecific hybridization that might have occurred during the evolution favoring allele sharing, or could be due to the error while assigning species. This study revealed a high genetic diversity in Tanzanian Urochloa accessions compared to six commercial Urochloa cultivars. The SSR markers used in this study were highly informative to assess genetic diversity in Urochloa species. The Urochloa accessions did not cluster according to the geographical regions but clustered by their genetic background. The accessions belonging to U. brizantha were more diverse than those from other four species and commercial cultivars, which can be tapped and used in conservation and breeding programs, especially in developing improved Urochloa varieties and hybrids that can produce high biomass and withstand well to biotic and abiotic environmental conditions. The cultivars and sexual diploid U. ruziziensis from cluster III can be used in future crosses with other accessions from cluster I and II depending on their ploidy to obtain heterosis in the progeny. As the Urochloa accessions analyzed in this study represent only 3 of 31 regions of Tanzania, collecting Urochloa germplasm from a wider geographical area is necessary to catalog the genetic variation of Urochloa in the country.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the BecA-ILRI Hub through the Africa Biosciences Challenge Fund (ABCF) Program. The ABCF Program is funded by the Australian Department for Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT) through the BecA-CSIRO partnership; the Syngenta Foundation for Sustainable Agriculture (SFSA); the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF); the UK Department for International Development (DFID); and the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida). The support of Asheber Tegegn in collecting experimental materials from Field Genebank of ILRI, Ethiopia, and Segolip Unit in genotyping is duly acknowledged.
Authors’ contributions
SOK, SRG, AD, AM, JH designed the study; SOK, CKM, MK conducted lab experiments; SOK, MK, SRG analysed the data; SOK, SRG wrote the manuscript, and AD, AM, JH reviewed the manuscript. SRG supervised the research project.
Data accessibility
Data are available from the Dryad Digital Depository (Kuwi, Kyalo, Mutai, Mwilawa, Hanson, Djikeng and Ghimire, 2018): DOI: https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.42075m1.
References
- Arango J, Moreta D, Núñez J, Hartmann K, Domínguez M, Ishitani M, Miles J, Subbarao G, Peters M, Rao I (2014) Developing methods to evaluate phenotypic variability in biological nitrification inhibition (BNI) capacity of Brachiaria grasses. Trop Grassl 2:6–8. 10.17138/TGFT(2)6-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Balasaravanan T, Pius PK, Raj Kumar R, Muraleedharan N, Shasany AK (2003) Genetic diversity among south Indian tea germplasm (Camellia sinensis, C. assamica and C. assamica spp. lasiocalyx) using AFLP markers. Plant Sci 165:365–372 [Google Scholar]
- Barnard C. (1969) Herbage plant species. Australian Herbage Plant Registration Authority, CSIRO, Canberra, p 154 [Google Scholar]
- Bianca VBZ, Jungmann L, Francisco PM, Zucchi MI, do Valle CB, de Souza AP (2011) Genetic diversity and population structure of the Brachiaria brizantha germplasm. Trop Plant Biol 4:157–169 [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan A. (1977) Tropical pastures and fodder plants. Longman, London [Google Scholar]
- Boldrini KR, Micheletti PL, Gallo PH, Mendes-Bonato AB, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB (2009) Origin of a polyploid accession of Brachiaria humidicola (Poaceae: Panicoideae: Paniceae). Genet Mol Res 8:888–895 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccone C. (1985) Gene flow in cave arthropods: a qualitative and quantitative approach. Evolution 39:1223–1235 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, McCouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:553–567 [Google Scholar]
- Cidade FW, Vigna BB, de Souza FH, Valls JFM, Dall’Agnol M, Zucchi MI, Souza AP (2013) Genetic variation in polyploid forage grass: assessing the molecular genetic variability in the Paspalum genus. BMC Genet 14:50 10.1186/1471-2156-14-50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva JA. (2005) Molecular markers for phylogeny, breeding and ecology in agriculture In: Thangadurai D, Pullaiah T, Tripathy L (eds) Genetic resources and biotechnology. Regency, New Delhi, pp 221–256 [Google Scholar]
- Danilo EM, Jacobo A, Mauricio S, Daniel V, Alvaro R, Manabu I, Aracely C, John M, Michael P, Joe T, Subbarao GV, Idupulapati M (2014) Biological nitrification inhibition (BNI) in Brachiaria pastures: a novel strategy to improve eco-efficiency of croplivestock systems and to mitigate climate change. Trop Grassl 2:88–91 [Google Scholar]
- De Wet JMJ. (1980) Origins of polyploids In: Lewis WH. (ed) Polyploidy: biological relevance, 1st edn. Plenum, New York [Google Scholar]
- Earl DA, Von Holdt BM (2012) Structure harvester: a website and program for visualizing structure output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Res 4:359–361. 10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. 10.1111/j.1365-294x.2005.02553x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M, Vigna BBZ, Sousa ACB, Jungmann L, Fernanda W, Toledo-silva G, Souza AP (2013) Molecular genetic variability, population structure and mating system in tropical forages. Trop Grassl Forrajes Trop 1:25–30 [Google Scholar]
- Ghimire S, Njarui D, Mutimura M, Cardoso J, Johnson L, Gichangi E, Teasdale S, Odokonyero K, Caradus J, Rao I, Djikeng A (2015) Climate-smart Brachiaria for improving livestock production in East Africa: emerging opportunities In: Vijaya D, Srivastava M, Gupta C, Malaviya D, Roy M, Mahanta S, Singh J, Maity A, Ghos P (eds) Sustainable use of grassland resources for forage production, biodiversity and environmental protection. Proceedings of the 23rd international grassland congress, New Delhi, India, November 20–24, pp 361–370 [Google Scholar]
- Joshi RK, Behera L (2006) Identification and differentiation of indigenous non-Basmati aromatic rice genotypes of India using microsatellite markers. Afr J Biotechnol 6(4):348–354 [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann L, Vigna BBZ, Boldrini KR, Sousa ACB, do Valle CB, Resende R, de Souza P (2010) Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of the tropical pasture grass Brachiaria humidicola based on microsatellites, cytogenetics, morphological traits, and geographical origin. Genome 53:698–709. 10.1139/g10-055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapila RK, Yadav RS, Plaha P, Rai KN (2008) Genetic diversity among pearl millet maintainers using microsatellite markers. Plant Breed 127:33–37 [Google Scholar]
- Khan IA, Awan FS, Ahmad A, Fu YB (2005) Genetic diversity of Pakistan wheat germplasm as revealed by RAPD markers. Genet Res Crop Evol 52:239–244 [Google Scholar]
- McCouch SR, Chen X, Panaud O, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, Huang N, Ishii T, Blair M (1997) Microsatellite mapping and applications of SSLP’s in rice genetics and breeding. Plant Mol Biol 35:89–99 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes-Bonato AB, Risso-Pascotto C, Pagliarini MS, do Valle CB (2006) Chromosome number and meiotic behavior in Brachiaria jubata (Gramineae). J Genet 85(1):83–87. 10.1007/BF02728976 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles JW, Maass BL, do Valle CB, Kumble V (1996) Brachiaria: biology, agronomy and improvement. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuaria (EMBRAPA), Campo Grande, p 288 [Google Scholar]
- Parson JJ. (1972) Spread of African grasses to the American tropics. J Range Manag 25:12–17 [Google Scholar]
- Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel, Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol 6:288–295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software: dissimilarity analysis and representation for Windows (version 6.0.010). http:darwin.cirad.fr/darwin. Cited 05 April 2016
- Pessoa-Filho M, Azevedo ALS, Sobrinho FS, Gouvea EG, Martins AM, Ferreira ME (2015) Genetic diversity and structure of Ruzigrass germplasm collected in Africa and Brazil. Crop Sci 55:2736 10.2135/cropsci2015.02.0096 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P, Alexandre MM, Ediene GG, Marco PF, Márcio EF (2013) Development and validation of microsatellite markers for Brachiaria ruziziensis obtained by partial genome assembly of Illumina single-end reads. BMC Genom 14:17 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2164/14/17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh RK, Sharma RK, Singh AK, Singh VP, Singh NK, Tiwari SP, Mohapatra T (2004) Suitability of mapped sequence tagged microsatellite site markers for establishing distinctness, uniformity and stability in aromatic rice. Euphytica 135(2):135–143 [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin M. (1981) Estimating levels of gene flow in natural populations. Genetics 99:323–335 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sousa ACB, Carvalho MA, Ramos AKB, Sforça DA, Campos T, Jungmann L, Zucchi MI, Jan L, Souza AP (2010) Development and characterization of microsatellite loci for Calopogonium mucunoides Desv. molecular ecology resources primer dev consortium. Mol Ecol Res 10:576–579 [Google Scholar]
- Stomayor-Rios A, Ve’lez-Forturia J, Sierra-Biacera A (1960) Description and cytology of a form of Signal grass behavior compared to Guinea grass (Panicum maximum IACIC). J Agric Univ P R 44:208–220 [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao GV, Nakahara K, Hurtado MP, Ono H, Moreta DE, Salcedo AF, Yoshihashi AT, Ishikawa T, Ishitani M, Ohnishi-Kameyama M, Yoshida M, Rondon M, Rao IM, Lascano CE, Berry WL, Ito O (2009) Evidence for biological nitrification inhibition in Brachiaria pastures. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 106:17302–17307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpiech ZA, Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA (2008) ADZE: a rarefaction approach for counting alleles private to combinations of populations. Bioinformatics 24:2498–2504 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira H, Rodríguez-Echeverría S, Nabais C (2014) Genetic diversity and differentiation of Juniperus thurifera in Spain and Morocco as determined by SSR. PLoS ONE 9:e88996 10.1371/journal.pone.0088996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzopoulos PJ, Kolano B, Bebeli PJ, Kaltsikes PJ, Metzidakis I (2005) Identification of Olea europaea L. cultivars using intersimple sequence repeat markers. Sci Hortic 105(1):45–51 [Google Scholar]
- Walples RS. (1987) A multispecies approach to the analysis of gene flow in marine shore fishes. Evolution 41:385–400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldesenbet DT, Tesfaye K, Bekele E (2015) Genetic diversity of Sesame germplasm collection (Sesamum indicum L.): implication for conservation, improvement and use. Int J Biotechnol Mol Biol Res 6:7–18. 10.5897/IJBMBR2014.0219 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Young A, Boshier D, Boyle T (2000) Forest conservation genetics: principles and practice. CSIRO, Collingwood [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the Dryad Digital Depository (Kuwi, Kyalo, Mutai, Mwilawa, Hanson, Djikeng and Ghimire, 2018): DOI: https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.42075m1.