Correction to: Genetics in Medicine 21:2019; 10.1038/s41436-019-0554-6, published online 11 June 2019
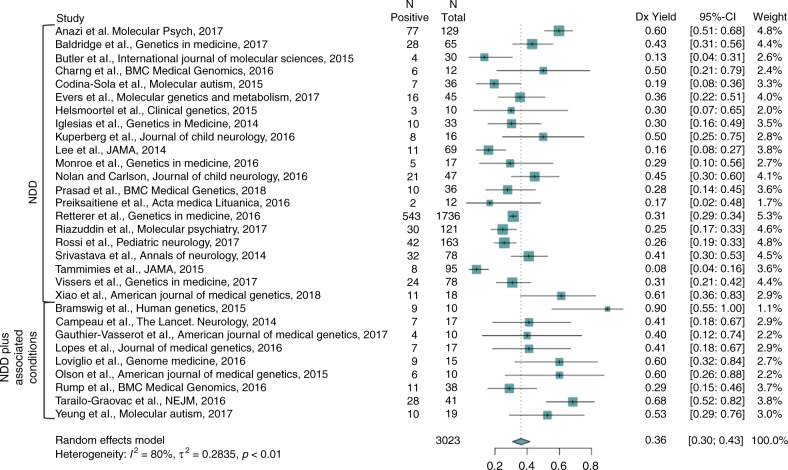
In our meta-analysis, we utilized incorrect numbers of individuals for one publication (Retterer et al. 2016) due to the fact the numbers for ASD and ID groups were not independent representations. We have updated our analysis using corrected numbers based on correspondence with the first author of this paper (diagnostic yield for NDD = 543/1736 as opposed to 570/2063). The updated analysis leads to the same (rounded) weighted diagnostic yield and confidence intervals (CI) as the initial publication (36% [30–43%]). The updated analysis results in the following updated values in Fig. 2: Retterer study values: N positive = 543, N total = 1736, study weight = 5.3% and meta-analysis statistics: I2 = 80%, τ2 = 0.2835, p < 0.01.
Fig. 2
The study is also included in two subanalyses reported in the Results. The isolated NDD subcategory (n = 21 articles), updated analysis leads to same (rounded) weighted diagnostic yield and confidence intervals as published (31% [25–38%]). For the subanalysis of mix of ID and/or ASD, the initial yield was 37% (CI: 29–46%). Following updated analysis, the yield of this subset is 39% (CI: 29–50%).
The PDF and HTML versions of the Article have been modified accordingly.