Abstract
Background
Virtual reality (VR) is the use of computer technology to create an interactive three-dimensional (3D) world, which gives users a sense of spatial presence. In nursing education, VR has been used to help optimize teaching and learning processes.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of VR in nursing education in the areas of knowledge, skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time.
Methods
We conducted a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of VR in nursing education based on the Cochrane methodology. An electronic literature search using the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), up to December 2019 was conducted to identify studies that reported the effectiveness of VR on knowledge, skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time. The study selection and data extraction were carried out by two independent reviewers. The methodological quality of the selected studies was determined using the Cochrane criteria for risk-of-bias assessment.
Results
A total of 12 studies, including 821 participants, were selected for the final analysis. We found that VR was more effective than the control conditions in improving knowledge (standard mean difference [SMD]=0.58, 95% CI 0.41-0.75, P<.001, I2=47%). However, there was no difference between VR and the control conditions in skills (SMD=0.01, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.26, P=.93, I2=37%), satisfaction (SMD=0.01, 95% CI –0.79 to 0.80, P=.99, I2=86%), confidence (SMD=0.00, 95% CI –0.28 to 0.27, P=.99, I2=0%), and performance time (SMD=–0.55, 95% CI –2.04 to 0.94, P=.47, I2=97%).
Conclusions
The results of this study suggest that VR can effectively improve knowledge in nursing education, but it was not more effective than other education methods in areas of skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time. Further rigorous studies with a larger sample size are warranted to confirm these results.
Keywords: virtual reality, nursing education, meta-analysis
Introduction
With the rapid development of information technology and shortages of nurse workforce, a transformation of nursing education is needed to prepare nursing students for evolving and complex health care environments [1-3]. In US nursing schools, 75,029 qualified applicants for bachelor’s degrees and nursing postgraduate courses were rejected in 2018 due to an insufficient number of faculty, clinical sites, classroom space, clinical preceptors, and budget constraints [4].
The ultimate goal of nursing education is to promote the application of theoretical knowledge in clinical practice [5]. However, limited clinical practice time affects the opportunity for students of having clinical experience with real patients [6]. This lack of clinical practice, which prepares students for the real clinical environment, can contribute to nursing procedure errors that compromise the safety of patients [7]. Narrowing the gap between theory and practice during the educational process is necessary, but poses several challenges to nursing educators [8]. In this scenario, to guarantee the quality and safety of nursing education, educators have adopted various teaching strategies including simulation experience for students [9].
Simulation has been shown to be a valuable teaching-learning strategy to support the changing world of nursing education and to help optimize the teaching process [10-12]. As the National Council of State Boards of Nursing stated, simulation is a key component of nursing education [13]. The use of simulation as a nursing education tool is becoming increasingly common, providing students with realistic opportunities to practice skills learned in theory [14]. Through simulation, students have a variety of practical opportunities to repeat clinical scenarios and make immediate decisions and reflections [15].
With the development of simulation technology, the virtual world was discovered—initially used in military and medical science and later, in medical education [16,17]. Virtual reality (VR) is the use of computer technology to create an interactive three-dimensional (3D) world in which users have a sense of spatial presence [18]. It provides a first-person active learning experience through different degrees of immersion, or, in other words, the real perception of the digital world and the ability to interact with objects and/or perform a series of actions in this digital world [19,20]. VR is highly conducive to clinical and procedure-focused training by enabling simulation [21]. VR simulation refers to the use of a variety of immersive, highly visual, 3D characteristics to replicate real-life situations and health care procedures, incorporating physical or other interfaces such as a computer keyboard, a mouse, speech/voice recognition, motion sensors, or haptic devices [22]. Virtual simulation refers to the involvement of real people operating simulated systems via a computer screen (virtual, that is, as the situation is not physical or in real time), and may include surgical simulators used for on-screen procedural training, usually integrated with haptic devices to interact with the system [18]. In general, VR can make simulation become an effective supplemental tool for teaching [22,23].
As VR technology advances and becomes increasingly affordable, nursing education is being transformed [24]. VR has gained increasing attention in the field of nursing education and been used to teach many nursing concepts including leadership, communication, decision-making, critical thinking, inclusivity, health appraisal, and disaster triage [25,26]. The use of VR in simulations allows repetitive, hands-on training to develop cognitive and skill mastery among nursing students, which are usually defined as the measure of participants’ understanding of concepts and the ability of a participant to demonstrate a procedure or technique, respectively [8,27]. Additionally, VR simulations can give nursing students the opportunity to practice skills in a safe environment without risk to patients [28]. In a study, 98% of the participating students recommended virtual simulation for future use in nursing education [29].
Although the use of VR has many advantages, some researchers have reported that VR is not more effective than other traditional methods on some outcomes such as knowledge and performance scores [30,31]. There are still some inconsistencies on the effectiveness of VR among studies. Up to date, meta-analyses on the effectiveness of VR have been conducted in some areas of medicine and education [32,33]. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no meta-analysis evaluating the effectiveness of VR in nursing education. Only one article systematically reviewed and evaluated the effectiveness of VR without meta-analysis, focusing on the effectiveness of VR simulation compared to other simulated methods on clinical psychomotor skills for pre-registration nursing students [34]. Therefore, there is a need to determine the effectiveness of VR in nursing education. The aim of this study was to perform a meta-analysis of the effectiveness of VR use on knowledge (participants’ understanding of concepts), skills (ability of participants to demonstrate a procedure or technique), satisfaction (participants’ perception with VR learning intervention), confidence (self-confidence in learning content and process), and performance time (time taken on the test task) in nursing education.
Methods
This meta-analysis was conducted according to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses) guidelines [35].
Search Strategy
An electronic literature search was carried out in the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, and CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature) from their inception to December 2019. The search strategies used in PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library are listed in the Multimedia Appendix 1. Slightly modified search strategies were used in the other databases. Additionally, we manually examined reference lists of the selected articles to retrieve other relevant publications. Two investigators conducted searches independently, and EndNote software was used to import and manage selected documents.
Inclusion Criteria
This study included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or trials employing quasi-experimental randomized design, including those in the form of dissertations and conference papers, based on the PICO (Population–Intervention –Comparison–Outcome) method. In this study, the PICO elements were as follows:
Population: pre-/post-registration nursing students or nursing staff
Intervention: all kinds of VR education methods
Comparison: traditional education methods (including presentations, classes, written instructions, etc) and non-VR simulation methods (including high/low fidelity simulation, mannequin-based simulation, etc)
Outcomes: knowledge, skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time
Data Extraction
Two reviewers (FQC and YFL) independently extracted information based on preset standards, including authors, publication date, nation, sample size, participants type, research project, intervention regimens, and outcomes.
Risk-of-Bias Assessment
Two reviewers (FQC and YFL) assessed the studies’ quality independently by referring to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [36], which includes 7 domains corresponding to a specific type of bias: (1) random sequence generation (selection bias); (2) allocation concealment (selection bias); (3) blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias); (4) blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias); (5) incomplete outcome data (attrition bias); (6) selective reporting (reporting bias); and (7) other biases. A judgement of “low risk,” “high risk,” or “unclear risk” of bias was assigned to each domain. When disagreements between reviewers could not be resolved through discussion, two additional reviewers (ZLS and JFG) made the final decision.
Data Synthesis and Analysis
The meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.3 [37], a desktop version of Review Manager software used for Cochrane intervention and flexible reviews. For continuous data, we reported standard mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals. In each analysis, I2 was used to measure the statistical heterogeneity among studies. According to the values of P and I2, the fixed-effect model (P>.1, I2<50%) or random-effects model (0<P<.1, I2≥50%) were selected [38].
Results
Results of the Literature Search
A total of 2716 potential studies were identified from 5 databases (n=2712) and relevant references (n=4). After removing 1072 duplicates, the remaining articles were reviewed and those that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. A total of 1644 articles were screened by title and abstract, of which 1581 articles were excluded. A total of 63 full-text articles were downloaded and assessed, from which 51 were excluded. Finally, 12 studies, including 821 participants, were selected for this study. A flow chart of the study selection process is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
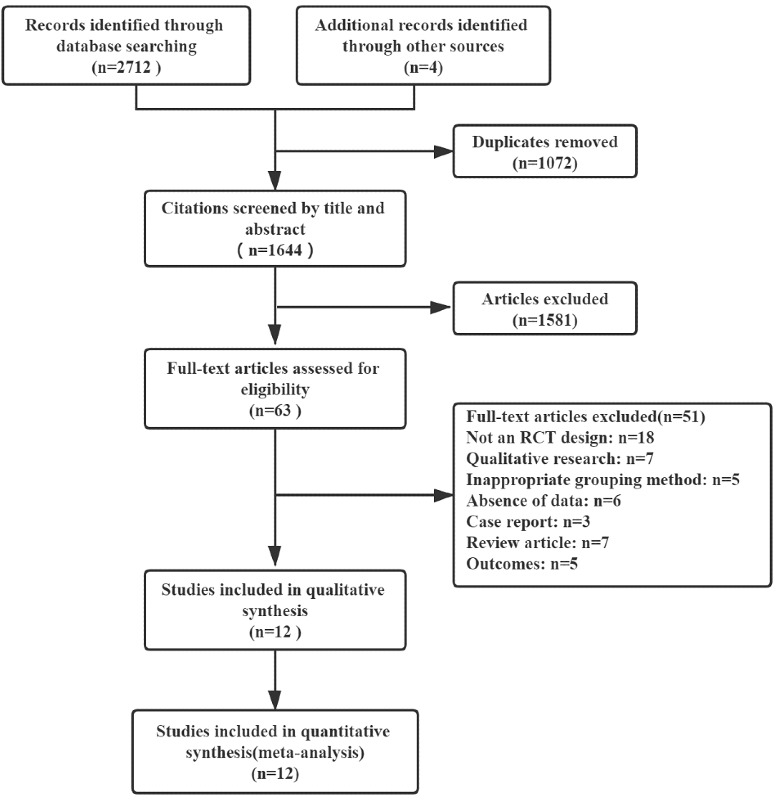
Flowchart of the study selection process. RCT: randomized controlled trial.
Study Characteristics
Studies included trials conducted in 7 countries: United States [31,39-42], Turkey [43], Canada [44], Korea [45], Singapore [46], Portugal [47], and China [48,49]. Two trials adopted a 3-arm group design [42,45], while 10 trials used a 2-arm group design. Sample sizes ranged from 20 to 172 participants. In all trials, participants were nursing students, except for one study in which participants were nursing staff [49]. Six of 12 trials compared VR education with traditional education [31,39,41,42,48,49], while the remaining trials compared VR education with other simulation types including fidelity manikin [44,47], mannequin-based simulation [40,45,46], and plastic model [43]. The characteristics of the participants, intervention details, and outcome measures are presented in Table 1. Supplementary information of intervention in experimental and control conditions is shown in Multimedia Appendix 2.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the 12 included studies.
| Author (year), country | Type of participant | Research project | Number of participants | Outcomes | ||
|
|
|
|
Total (number of groups) | Experimental group (VRa) | Control group (condition) |
|
| Bryant et al (2015) [31], USA | Nurse practitioner students | Advanced health assessment | 60 (2) | 22 | 38 (traditional education) | Satisfaction, confidence |
| Butt et al (2018) [39], USA | Junior level nursing students | Urinary catheterization | 20 (2) | 10 | 10 (traditional education) | Performance time |
| Cobbett and Snelgrove-Clarke (2016) [44], Canada |
Third-year nursing students | Maternal -newborn nursing | 56 (2) | 27 | 28 (non-VR simulation) | Self-confidence |
| Haerling (2018) [40], USA | Fifth- and sixth-quarter associate degree in nursing students | Nursing care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 28 (2) | 13 | 15 (non-VR simulation) | Knowledge assessment, performance scores, satisfaction, and self-confidence |
| Ismailoglu and Zaybak (2018) [43], Turkey |
Second-year nursing students |
Intravenous catheter insertion | 65 (2) | 33 | 32 (non-VR simulation) | Knowledge assessment, skill scores, self-confidence scores |
| Jung et al (2012) [45], Korea |
First-year nursing students |
Intravenous injection | 114 (3) | 38 | 38 (non-VR simulation) and 38 (VR plus non-VR simulation) | Procedure score, satisfaction, performance time |
| Leflore et al (2012) [41], USA |
Senior nursing students |
Care of pneumonia and cystic fibrosis exacerbation | 93 (2) | 46 | 47 (traditional education) | Knowledge assessment |
| Liaw et al (2014) [46], Singapore |
Senior nursing students |
Assessing and managing deterioration | 61 (2) | 31 | 30 (non-VR simulation) | Performance scores |
| Padilha et al (2019) [47], Portugal |
Second-year nursing students |
Respiratory process in relation to ineffective airway clearance and hypoxia | 42 (2) | 21 | 21 (non-VR simulation) | Knowledge assessment, satisfaction |
| Smith et al (2018) [42], USA |
Senior nursing students | Decontamination training | 172 (3) | 59 (immersive VR) 58 (desktop VR) |
55 (traditional education) | Knowledge assessment |
| Tsai et al (2008) [49], China |
Novice nurses | Port-A cath injection | 82 (2) | 42 | 40 (traditional education) | Knowledge assessment |
| Gu et al (2017) [48], China |
Second-year students | Course of fundamental of nursing | 28 (2) | 14 | 14 (traditional education) | Knowledge assessment |
aVR: virtual reality.
Risk of Bias
Based on the Cochrane criteria, a risk-of-bias assessment is presented in Figures 2 and 3. Four of 12 studies reported randomized methods in detail [41,43,46,47], while the remaining 8 trials did not provide the methods of sequence generation. None of the trials provided concealment methods, except for one that reported the use of anonymization [47]. In all trials, no blind method was used on participants due to the particularity of the intervention methods. Two trials reported employing blinding of assessors [39,43]. Additionally, 2 studies mentioned dropouts without detail on handling information [46,49].
Figure 2.
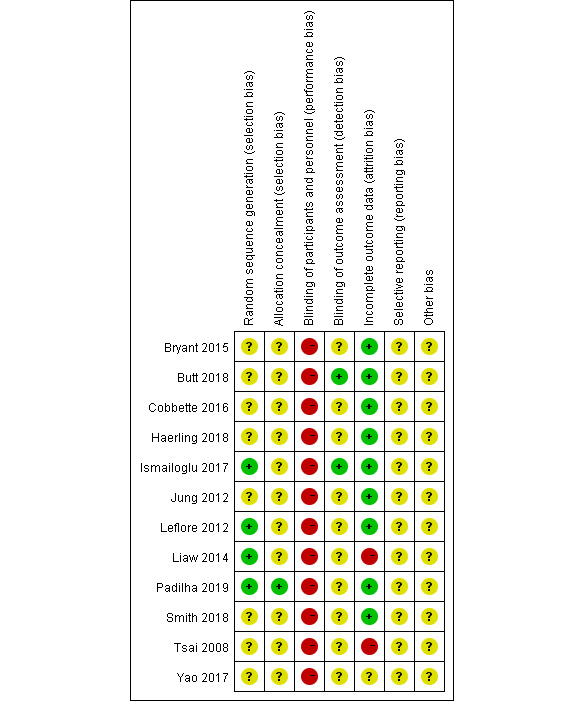
Risk of bias analysis of each included study.
Figure 3.
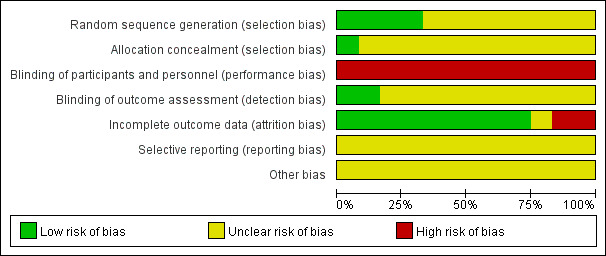
Overall risk of bias analysis of included studies.
Results of the Meta-analysis
Knowledge
A total of 7 studies reported knowledge scores as the outcome [40-43,47-49]. The results indicated that VR education can improve knowledge of participants more effectively than the control conditions (SMD=0.58, 95% CI 0.41-0.75, P<.001, I2=47%, Figure 4).
Figure 4.
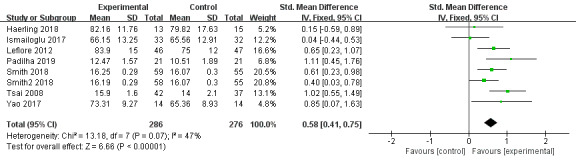
Forest plot of virtual reality on knowledge.
Skills
A total of 5 trials used skills as the outcome measure [40,42,43,45,46]. The results indicated that there was no significant difference between VR education and other education methods on skills enhancement (SMD=0.01, 95% CI –0.24 to 0.26), P=.93, I2=37%; Figure 5).
Figure 5.
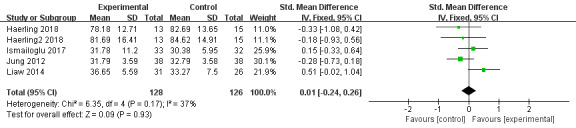
Forest plot of virtual reality on skills.
Satisfaction
A total of 4 articles reported participants’ satisfaction scores [31,40,45,47]. Participants in VR groups showed no difference when compared to control groups (SMD=0.01, 95% CI –0.79 to 0.80, P=.99, I2=86%). High heterogeneity was found. The leave-one-out method was used to carry out sensitivity analysis, and the random-effects model was adopted. One trial [47] caused significant heterogeneity, showing VR education is more satisfactory to participants than the control conditions (SMD=1.30, 95% CI 0.63-1.97, P=.001; Figure 6).
Figure 6.
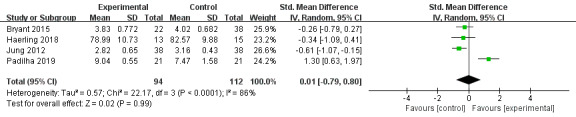
Forest plot of virtual reality on satisfaction.
Confidence
A total of 4 studies reported confidence results [31,40,43,44] and showed no statistical difference between VR education and other education methods (SMD=0.00, 95% CI –0.28 to 0.27, P=.99, I2=0%; Figure 7).
Figure 7.
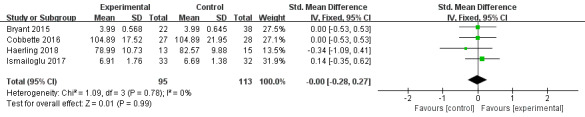
Forest plot of virtual reality on confidence.
Performance time
Performance time was employed as an outcome measure in 3 trials [39,42,45]. There was no significant difference between the experimental and control groups (SMD=–0.55, 95% CI –2.04 to 0.94, P=.47, I2=97%]. Heterogeneity in this outcome was high. Therefore, the random-effects model was used, and the sensitivity analysis was carried out by using the leave-one-out method. Nevertheless, heterogeneity remained significant even when removing one study at a time (Figure 8).
Figure 8.
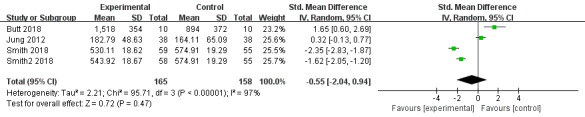
Forest plot of virtual reality on performance time.
Discussion
This meta-analysis assessed the effectiveness of VR simulation methods in nursing education. We found that VR education methods can improve the knowledge of nursing students. However, there was no difference between VR and other education methods on the outcomes of skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time.
A total of 12 trials with 821 participants were included in the meta-analysis. All studies used VR education as the interventions in experimental groups, and education methods in control groups including traditional education, high/low fidelity manikin, mannequin-based simulation, and plastic model. Among the 12 studies, 4 trials reported random sequence generation. Only 1 study described the allocation concealment; 2 studies reported the blindness of outcome assessment. In addition, blinded interventions of students and educators were not possible because of the particularity of the VR education method. In general, the overall risk of bias of the included studies was judged to be unclear due to lack of information.
Knowledge
For the outcome of knowledge, VR education showed more effectiveness on nursing education than traditional education or other simulation education methods. A qualitative study on VR use in nursing education also concluded that, through the concrete experience of the virtual patient simulation and the reflection tool, students could understand what they were taught and how to utilize the new knowledge [50]. Additionally, a previous study, which focused on virtual reality for health professions education, indicated that VR with higher interactivity showed more effectiveness for knowledge [21]. These studies support the fact that an interactive learning environment encourages students to establish connections between concepts [51]. Most of the studies included in our meta-analysis used interactive VR education methods, which could explain the results.
Skills
Our results found no significant difference between VR education and other education methods for the outcome of skills, which seems to be in line with a previous systematic review [34]. The review concluded that virtual reality groups performed comparably to simulation groups in skill performance scores and skill success rate [34]. In our study, all the included trials that reported skills employed other simulation education methods in control groups. Similarly, we concluded that VR was not more effective in improving skills than other simulation methods in nursing education. A possible reason for these results is that there is a gap between completing virtual cases and real practice. Nursing skills learned on a virtual platform may not be transferable to real situations effectively because of the immaturity of VR technology [48].
Satisfaction
There was no significant difference on participants’ satisfaction between VR education and education methods in control groups. High heterogeneity was found. Through sensitive analysis, we found that 1 of the 4 included studies showed that VR was more satisfactory [47]. In one trial conducted in 2012, some participants pointed out the immaturity of VR technology affecting users’ satisfaction [45]. In contrast, 2 studies in recent years showed no difference between the 2 groups [31,40]. Thus, we consider that participants’ satisfaction with VR education may vary according to technical conditions. Although in the 21st century nursing students had already shown high levels of usefulness, ease, and intention to use clinical VR simulation, VR is not widely used in nursing education [52]. With the progress of technology, VR can better satisfy the users. However, further research is needed to confirm our results.
Confidence
The results in confidence indicated no difference between experimental and control conditions. VR could not enhance the confidence of participants more effectively than control conditions, which was consistent with a previous study from Korea [53]. When VR was used for operation exercises, it was often necessary to use a mouse at the same time [53]. Thus, the operation method is more difficult in VR when compared with other simulations such as the manikin.
Performance Time
We also conducted a meta-analysis of performance time. The results suggested that VR was not more effective on reducing performance time than other educational methods. We found large heterogeneity among studies, even when a sensitivity analysis was conducted by using the leave-one-out method. The observed heterogeneity may be due to the different research designs of the selected studies, such as operation projects, VR devices, and education methods in control groups. One study on the effectiveness of VR endoscopy simulation training analyzed performance time with sufficient data and found no difference between VR and control groups; however, the quality of the evidence was very low [54]. In contrast, a study conducted in clinical medicine found that VR can help operators shorten performance time [55]. Therefore, more experiments are needed in the future to study the effectiveness of VR on performance time in nursing education.
Strengths and Limitations
Our study has the following strengths. First, our study is the first meta-analysis assessing the impact of VR on nursing education. Second, to assess the effectiveness of VR education, we evaluated 5 outcome measurements—knowledge, skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time—which can probably provide reference for nursing education.
There are also some limitations in our study. First, we only included articles published in English, which may affect the results of meta-analysis. Second, some of the included studies failed to provide the details of sequence generation, allocation concealment, and blinding methods. Third, we included 12 studies that have different interventions in control groups, which may cause significant heterogeneity among the studies.
Conclusions
This meta-analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of the use of VR on nursing education. We found that VR education methods can improve nursing students’ knowledge. However, for the outcomes of skills, satisfaction, confidence, and performance time, there seems to be no difference between VR and other education methods. In general, the use of VR should be considered to enhance knowledge and as a complement of other simulation strategies to improve the quality and safety of clinical practice. However, the heterogeneity and risk of bias among the included studies should be taken into consideration. Rigorously designed large-scale studies are required to further confirm the results in this review.
Acknowledgments
ZLS was supported by Key project of Jiangsu Province Education Science 13th Five-Year Plan 2016 projects (B-a/2016/01/18), Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine 2018 Flipped Classroom Course & Open Online Course - Health Assessment, and Opening project of innovative practical teaching team of Qing Lan Project in Jiangsu Province (NZYHLXPPQL2019-25).
Abbreviations
- CINAHL
cumulative index to nursing and allied health literature
- PICO
Population–Intervention–Comparison–Outcome
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses
- RCT
randomized controlled trials
- VR
virtual reality
Appendix
Search strategies of PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Library.
Supplementary information of intervention in experimental and control groups.
Footnotes
Authors' Contributions: FQC and YFL searched the medical database and collected and extracted the data. FQC, YFL, and JFG discussed and analyzed data together and wrote papers. ZLS, DWW, CL, and BC provided suggestions for writing preparation and process. The final version of the article was reviewed by all authors.
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Pepin J, Goudreau J, Lavoie P, Bélisle M, Blanchet Garneau A, Boyer L, Larue C, Lechasseur K. A nursing education research framework for transformative learning and interdependence of academia and practice. Nurse Educ Today. 2017 May;52:50–52. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2017.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nardi DA, Gyurko CC. The global nursing faculty shortage: status and solutions for change. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2013 Sep;45(3):317–26. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Juraschek SP, Zhang X, Ranganathan V, Lin VW. United States registered nurse workforce report card and shortage forecast. Am J Med Qual. 2019;34(5):473–81. doi: 10.1177/1062860619873217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fact sheet: Nursing faculty shortage. American Association of Colleges of Nursing. 2019. [2020-06-26]. https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/42/News/Factsheets/Faculty-Shortage-Factsheet.pdf.
- 5.Shin S, Park J, Kim J. Effectiveness of patient simulation in nursing education: meta-analysis. Nurse Educ Today. 2015 Jan;35(1):176–82. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2014.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yuan HB, Williams BA, Fang JB, Ye QH. A systematic review of selected evidence on improving knowledge and skills through high-fidelity simulation. Nurse Educ Today. 2012 Apr;32(3):294–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2011.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Uysal N. Improvement of nursing students' learning outcomes through scenario-based skills training. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2016 Aug 08;24:e2790. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.1310.2790. https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104-11692016000100358&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=en. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dubovi I, Levy ST, Dagan E. Now I know how! The learning process of medication administration among nursing students with non-immersive desktop virtual reality simulation. Comput Educ. 2017 Oct;113:16–27. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2017.05.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dalton L, Gee T, Levett-Jones T. Using clinical reasoning and simulation-based education to 'flip' the Enrolled Nurse curriculum. Aust J Adv Nurs. 2015;33(2):28–34. https://www.ajan.com.au/archive/Vol33/Issue2/4Dalton.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ricketts B. The role of simulation for learning within pre-registration nursing education - a literature review. Nurse Educ Today. 2011 Oct;31(7):650–4. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2010.10.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Robinson BK, Dearmon V. Evidence-based nursing education: effective use of instructional design and simulated learning environments to enhance knowledge transfer in undergraduate nursing students. J Prof Nurs. 2013;29(4):203–9. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2012.04.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cant RP, Cooper SJ. Use of simulation-based learning in undergraduate nurse education: An umbrella systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017 Feb;49:63–71. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alexander M, Durham CF, Hooper JI, Jeffries PR, Goldman N, Kardong-Edgren S, Kesten KS, Spector N, Tagliareni E, Radtke B, Tillman C. NCSBN Simulation Guidelines for Prelicensure Nursing Programs. Journal of Nursing Regulation. 2015 Oct;6(3):39–42. doi: 10.1016/s2155-8256(15)30783-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brewer E. Successful techniques for using human patient simulation in nursing education. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2011 Sep;43(3):311–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2011.01405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Flott EA, Linden L. The clinical learning environment in nursing education: a concept analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2016 Mar 09;72(3):501–13. doi: 10.1111/jan.12861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dev P, Youngblood P, Heinrichs WL, Kusumoto L. Virtual worlds and team training. Anesthesiol Clin. 2007 Jun;25(2):321–36. doi: 10.1016/j.anclin.2007.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rosen KR. The history of medical simulation. J Crit Care. 2008 Jun;23(2):157–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2007.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality . In: Healthcare Simulation Dictionary. Lopreiato L, editor. Rockville: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cao C, Cerfolio RJ. Virtual or augmented reality to enhance surgical education and surgical planning. Thorac Surg Clin. 2019 Aug;29(3):329–37. doi: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2019.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sherman WR, Craig AB. Understanding virtual reality—Interface, application, and design. Presence: Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2003 Aug;12(4):441–2. doi: 10.1162/105474603322391668. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kyaw BM, Saxena N, Posadzki P, Vseteckova J, Nikolaou CK, George PP, Divakar U, Masiello I, Kononowicz AA, Zary N, Tudor Car L. Virtual reality for health professions education: Systematic review and meta-analysis by the digital health education collaboration. J Med Internet Res. 2019 Jan 22;21(1):e12959. doi: 10.2196/12959. https://www.jmir.org/2019/1/e12959/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shin H, Rim D, Kim H, Park S, Shon S. Educational characteristics of virtual simulation in nursing: An integrative review. Clinical Simulation in Nursing. 2019 Dec;37:18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2019.08.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smith PC, Hamilton BK. The effects of virtual reality simulation as a teaching strategy for skills preparation in nursing students. Clinical Simulation in Nursing. 2015 Jan;11(1):52–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2014.10.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Foronda CL, Alfes CM, Dev P, Kleinheksel A, Nelson DA, OʼDonnell JM, Samosky JT. Virtually nursing: Emerging technologies in nursing education. Nurse Educ. 2017;42(1):14–7. doi: 10.1097/NNE.0000000000000295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fealy S, Jones D, Hutton A, Graham K, McNeill L, Sweet L, Hazelton M. The integration of immersive virtual reality in tertiary nursing and midwifery education: A scoping review. Nurse Educ Today. 2019 Aug;79:14–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2019.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wright RR, Tinnon EA, Newton RH. Evaluation of vSim for nursing in an adult health nursing course: A multisite pilot study. Comput Inform Nurs. 2018 Feb;36(2):84–9. doi: 10.1097/CIN.0000000000000388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Smith SJ, Farra S, Ulrich DL, Hodgson E, Nicely S, Matcham W. Learning and retention using virtual reality in a decontamination simulation. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2016;37(4):210–4. doi: 10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Weiner E, Gordon J, Rudy S, McNew R. Expanding virtual reality to teach ultrasound skills to nurse practitioner students. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2019 Aug 21;264:893–7. doi: 10.3233/SHTI190352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Foronda C, Gattamorta K, Snowden K, Bauman EB. Use of virtual clinical simulation to improve communication skills of baccalaureate nursing students: a pilot study. Nurse Educ Today. 2014 Jun;34(6):e53–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2013.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Farra SL, Smith S, Gillespie GL, Nicely S, Ulrich DL, Hodgson E, French D. Decontamination training: with and without virtual reality simulation. Adv Emerg Nurs J. 2015;37(2):125–33. doi: 10.1097/TME.0000000000000059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bryant R, Miller CL, Henderson D. Virtual clinical simulations in an online advanced health appraisal course. Clin Simul Nurs. 2015 Oct;11(10):437–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2015.08.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Neguț A, Matu S, Sava FA, David D. Virtual reality measures in neuropsychological assessment: a meta-analytic review. Clin Neuropsychol. 2016 Feb;30(2):165–84. doi: 10.1080/13854046.2016.1144793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Merchant Z, Goetz ET, Cifuentes L, Keeney-Kennicutt W, Davis TJ. Effectiveness of virtual reality-based instruction on students' learning outcomes in K-12 and higher education: A meta-analysis. Comput Educ. 2014 Jan;70:29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2013.07.033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rourke S. How does virtual reality simulation compare to simulated practice in the acquisition of clinical psychomotor skills for pre-registration student nurses? A systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020 Feb;102:103466. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.103466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009 Jul 21;339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. http://www.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=19622551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors . Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6. Cochrane; 2019. [2019-11-05]. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.RevMan 5. Cochrane training. [2020-06-26]. http://community.cochrane.org/tools/review-production-tools/revman-5.
- 38.Higgins J, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002 Jun 15;21(11):1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Butt AL, Kardong-Edgren S, Ellertson A. Using game-based virtual reality with haptics for skill acquisition. Clin Simul Nurs. 2018 Mar;16:25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2017.09.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Haerling KA. Cost-utility analysis of virtual and mannequin-based simulation. Simul Healthc. 2018 Feb;13(1):33–40. doi: 10.1097/SIH.0000000000000280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.LeFlore JL, Anderson M, Zielke MA, Nelson KA, Thomas PE, Hardee G, John LD. Can a virtual patient trainer teach student nurses how to save lives--teaching nursing students about pediatric respiratory diseases. Simul Healthc. 2012 Feb;7(1):10–7. doi: 10.1097/SIH.0b013e31823652de. doi: 10.1097/SIH.0b013e31823652de. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Smith SJ, Farra SL, Ulrich DL, Hodgson E, Nicely S, Mickle A. Effectiveness of two varying levels of virtual reality simulation. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2018;39(6):E10–E15. doi: 10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Günay İsmailoğlu Elif, Zaybak A. Comparison of the effectiveness of a virtual simulator with a plastic arm model in teaching intravenous catheter insertion skills. Comput Inform Nurs. 2018 Feb;36(2):98–105. doi: 10.1097/CIN.0000000000000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cobbett S, Snelgrove-Clarke E. Virtual versus face-to-face clinical simulation in relation to student knowledge, anxiety, and self-confidence in maternal-newborn nursing: A randomized controlled trial. Nurse Educ Today. 2016 Oct;45:179–84. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2016.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jung E, Park DK, Lee YH, Jo HS, Lim YS, Park RW. Evaluation of practical exercises using an intravenous simulator incorporating virtual reality and haptics device technologies. Nurse Educ Today. 2012 May;32(4):458–63. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2011.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liaw SY, Chan SW, Chen F, Hooi SC, Siau C. Comparison of virtual patient simulation with mannequin-based simulation for improving clinical performances in assessing and managing clinical deterioration: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2014 Sep 17;16(9):e214. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3322. https://www.jmir.org/2014/9/e214/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Padilha JM, Machado PP, Ribeiro A, Ramos J, Costa P. Clinical virtual simulation in nursing education: Randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2019 Mar 18;21(3):e11529. doi: 10.2196/11529. https://www.jmir.org/2019/3/e11529/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gu Y, Zou Z, Chen X. The effects of vSIM for nursing™ as a teaching strategy on fundamentals of nursing education in undergraduates. Clin Simul Nurs. 2017 Apr;13(4):194–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2017.01.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tsai S, Chai S, Hsieh L, Lin S, Taur F, Sung W, Doong J. The use of virtual reality computer simulation in learning Port-A cath injection. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2008 Mar;13(1):71–87. doi: 10.1007/s10459-006-9025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Forsberg E, Ziegert K, Hult H, Fors U. Assessing progression of clinical reasoning through virtual patients: An exploratory study. Nurse Educ Pract. 2016 Jan;16(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2015.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jeffries P. A framework for designing, implementing, and evaluating simulations used as teaching strategies in nursing. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2005;26(2):96–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Padilha JM, Machado PP, Ribeiro AL, Ramos JL. Clinical Virtual Simulation in Nursing Education. Clin Simul Nurs. 2018 Feb;15:13–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2017.09.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hwang J, Kim H. Comparison of training effectiveness for IV injections: Intravenous (IV) arm model versus computer simulator. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2014 Aug 31;21(3):302–10. doi: 10.7739/jkafn.2014.21.3.302. doi: 10.7739/jkafn.2014.21.3.302. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Khan R, Plahouras J, Johnston BC, Scaffidi MA, Grover SC, Walsh CM. Virtual reality simulation training for health professions trainees in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 17;8:CD008237. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008237.pub3. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/30117156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mishra S, Kurien A, Patel R, Patil P, Ganpule A, Muthu V, Sabnis RB, Desai M. Validation of virtual reality simulation for percutaneous renal access training. J Endourol. 2010 Apr;24(4):635–40. doi: 10.1089/end.2009.0166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Search strategies of PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Library.
Supplementary information of intervention in experimental and control groups.


