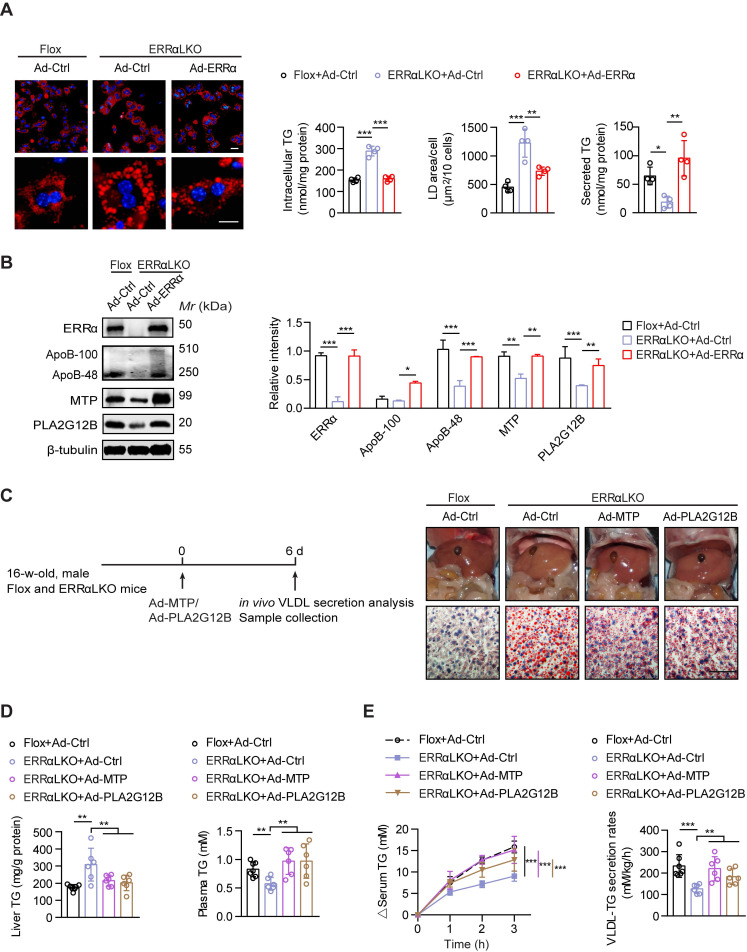
Figure 3.
Rescued hepatic VLDL-TG secretion in ERRαLKO mice are essential to preventing hepatosteatosis. (A) Representative fields of male Flox and ERRαLKO hepatocytes infected with adenovirus expressing ERRα (Ad-ERRα) or control adenovirus (Ad-Ctrl) for 36 h. Lipid droplets (LDs) were labeled with Nile Red (red). Scale bar, 20 µm. Intracellular TG contents, average LD area and secreted TG from Flox and ERRαLKO hepatocytes infected with Ad-ERRα or Ad-Ctrl (n = 4). (B) Levels of proteins in male Flox and ERRαLKO hepatocytes infected with Ad-ERRα or Ad-Ctrl (left panel). Densitometry analysis of the western blotting data normalized to the intensity of β-tubulin (right panel). (C and D) Schematic of the experimental procedure of Ad-MTP, Ad-PLA2G12B or Ad-Ctrl-injected male Flox and ERRαLKO mice (n = 6-7 mice per group). Representative images of liver tissue (top), sections stained with Oil Red O (bottom) (C), liver TG and plasma TG levels (D) from indicated mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Analysis of VLDL-TG secretion (left panel) and rates (right panel) in treated mice (n = 6-7 mice per group). Data presented as means ±SD. *P< 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc analysis (A-B) or two-tailed Student's t test (D-E).