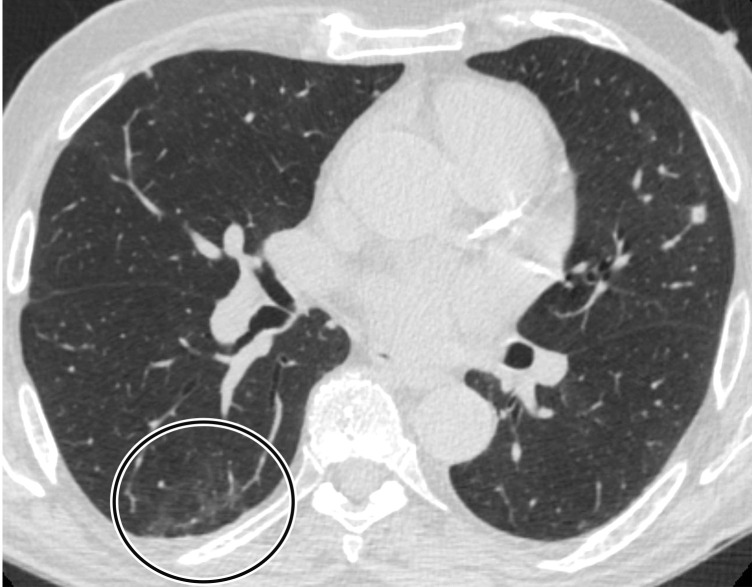
Figure 8c.
Reverse halo sign in a 76-year-old man with COVID-19 and a history of pancreatic cancer. (a, b) Axial (a) and coronal (b) contrast-enhanced CT images show a nodular opacity (black arrow) in the right lower lobe, with central GGOs and peripheral solid consolidation, consistent with a reverse halo sign. Note the subtle bilateral peripheral GGOs (white arrows). (c) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image obtained 3 weeks after diagnosis shows subsequent resolution of the reverse halo sign, with vague residual opacity (circle).