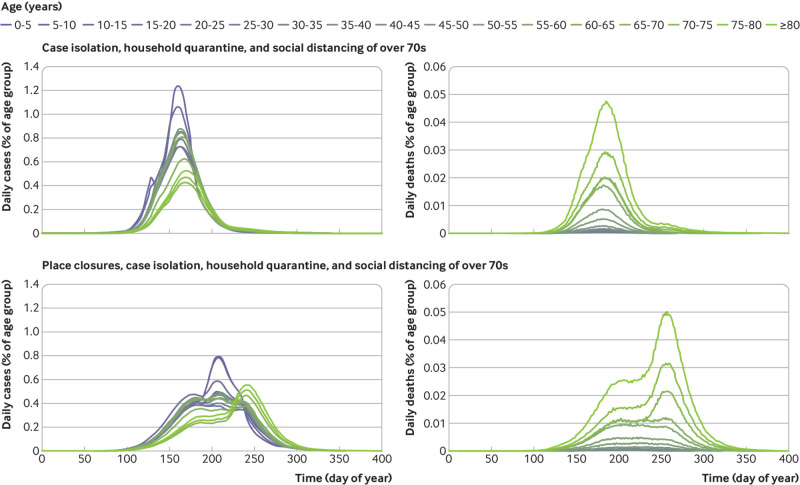
Fig 2.
Simulated values for daily numbers of people with coronavirus disease 2019 and deaths related to two scenarios. Interventions are triggered by reaching 100 cumulative intensive care unit cases. After the trigger, all the interventions are in place for 91 days: the general social distancing runs to day 194 and the enhanced social distancing for over 70s runs for an extra 30 days. Results are broken down into age categories, with social distancing of over 70s interventions affecting the three oldest groups. In the case isolation, household quarantine, and social distancing of over 70s scenario, a single peak of cases is seen, with greatest infection in the younger age groups but most deaths in the older age groups. In the place closures, case isolation, household quarantine, and social distancing of over 70s scenario, three peaks occur in the plot of daily cases, with the first peak appearing at a similar time to the other scenario, but with reduced severity. The second peak seems to be a response to the ending of place closure and mostly affects the younger age groups; therefore has little impact on the total number of deaths. The third peak triggered by relaxing social distancing of over 70s affects the older age groups, leading to a substantial increase in the total number of deaths