Fig. 1.
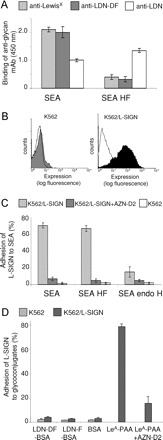
Binding of S. mansoni SEA by L-SIGN transfected cells. (A) ELISA was performed to characterize the glycan epitopes of SEA and defucosylated SEA (SEA HF). Similar amounts of SEA (5 μg/mL) were applied in each case. Using antibodies recognizing the fucose-containing glycan epitopes LeX and LDN-DF the efficacy of HF-treatment was determined. In parallel, an anti-LDN mAb was employed to evaluate the integrity of the remaining glycans. Data represent a typical result out of three experiments performed in duplicate, with error bars indicating standard deviation. (B) The expression of L-SIGN on transfected (K562/L-SIGN) and nontransfected K562 cells was determined by flow cytometry using the mAb AZN-D2 that recognizes L-SIGN. The isotype control is shown as lines. (C) Binding of L-SIGN to soluble egg antigen (SEA) of S. mansoni, defucosylated SEA (SEA HF) and endo H-treated SEA (SEA endo H) was determined by cell adhesion assays using K562/L-SIGN transfected cells in the absence (light grey bars) or presence (dark grey bars) of a blocking mAb to L-SIGN (AZN-D2). All results are representative of three independent experiments, performed in triplicate, with error bars indicating standard deviation. (D) Adhesion of K562/L-SIGN transfected cells to neoglycoconjugates carrying LDN-F (LDN-F-BSA) and LDN-DF (LDN-DF-BSA). The neoglycoconjugate LeA-PAA was used as a positive control. One representative experiment out of three is shown.
