Abstract
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) is an essential electron donor in all organisms, and provides the reducing power for anabolic reactions and redox balance. NADPH homeostasis is regulated by varied signaling pathways and several metabolic enzymes that undergo adaptive alteration in cancer cells. The metabolic reprogramming of NADPH renders cancer cells both highly dependent on this metabolic network for antioxidant capacity and more susceptible to oxidative stress. Modulating the unique NADPH homeostasis of cancer cells might be an effective strategy to eliminate these cells. In this review, we summarize the current existing literatures on NADPH homeostasis, including its biological functions, regulatory mechanisms and the corresponding therapeutic interventions in human cancers, providing insights into therapeutic implications of targeting NADPH metabolism and the associated mechanism for cancer therapy.
Subject terms: Cancer metabolism, Drug development
Background
In cancer cells, the appropriate levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential for signal transduction and cellular processes.1,2 However, the overproduction of ROS can induce cytotoxicity and lead to DNA damage and cell apoptosis.3 To prevent excessive oxidative stress and maintain favorable redox homeostasis, tumor cells have evolved a complex antioxidant defense system that strategically adjusts multiple antioxidant enzymes such as catalase, glutathione reductase, and antioxidant molecules. The latter are dependent on the generation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), which is used to maintain reduced glutathione (GSH) and thioredoxin (TRX).4–6 NADPH is also well known as an essential electron donor and an indispensable cofactor that is used for transferring and reserving reduction potential for numerous anabolic reactions.7
NADP(H) is predominantly bound to intracellular proteins with different affinities.8 The intracellular content of NADP(H) differs markedly among tissues and cell types. For instance, the total NADP(H) is about 420 nmol/g wet weight in rat liver and 59% of total NADP(H) is found in mitochondria, and 30 nmol/g wet weight in skeletal muscle,5,8 and the NADPH concentration in the cytosol is 3.1 ± 0.3 and 37 ± 2 µM in the mitochondrial matrix in HeLa cells.9 In addition, the redox potentials of the mitochondrial and cytosolic NADP(H) systems are the same around—400 mV in the liver.8
A growing body of evidence has shown that regeneration and maintenance of the cellular NADP(H) content is strongly implicated in a variety of pathological conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, aging,4,5 especially in tumorigenesis and cancer progression.10 Compared with non-tumor cells, tumor cells usually maintain high levels of NADPH, not only to power redox defense but also to use for biosynthetic reactions to sustain their rapid growth.5,11 This realization has prompted molecular studies of NADPH metabolism and its exploitation for the development of anticancer agents. Recent advances have revealed that therapeutic modulation based on NADPH metabolism has been widely viewed as a novel and effective anticancer strategy.
In this review, we summarize the current existing literatures on NADPH metabolism, including its biological functions, regulatory mechanisms, and the corresponding therapeutic interventions directly or indirectly targeting NADPH metabolism in cancer.
NADPH-dependent biological functions in cancer
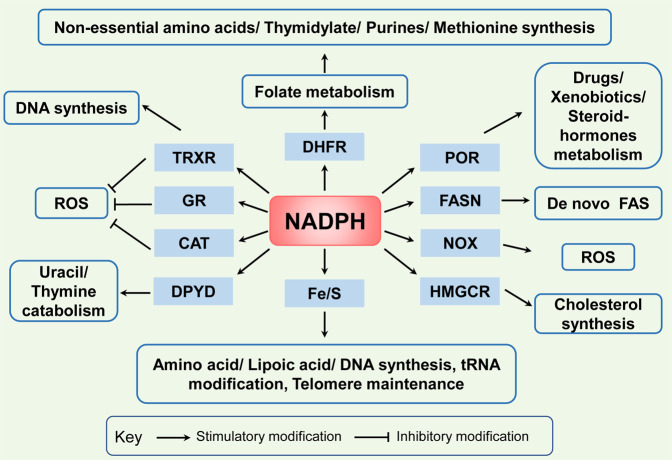
Both NAD(H) and NADP(H) are cofactors that are used for transferring and reserving reduction potential.7,9 Although the structures are closely related, NAD(H) and NADP(H) are recognized by unique compartmentalized enzymes and exert different functions. NAD(H) is mainly involved in catabolic reactions,5,12,13 whereas NADP(H) is primarily involved in cellular antioxidative effects and anabolic reactions as shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
NADPH-dependent biological functions in cancer. There are three principal ways in which NADPH is used. First, NADPH is an essential cofactor of glutathione reductase (GR) and TRXR in GSH and TRX-peroxiredoxin (PRX) system, respectively, and reactivates catalase (CAT) to deactivate ROS for antioxidation; Second, NADPH is a crucial electron source for DHFR, Fe/S, POR, FANS, HMGCR, DPYD contributing to several reductive synthesis reactions, such as FAS, non-essential amino acids, nucleotides, and steroids synthesis; Third, NADPH is a substrate for NOXs to generate ROS
Antioxidative effects
In cancer cells, overcoming oxidative stress is a critical step for tumor progression. NADPH plays a key role in cellular antioxidation systems by providing reducing equivalents to generate reduced forms of antioxidant molecules, which are highly corrected with cancer cell biological behaviors.14 On the one hand, GSH reductase converts GSSG to GSH using NADPH as an important cofactor, then GSH acts as a cosubstrate for GSH peroxidase (GPX) that reduces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and other peroxides to H2O or alcohol to deactivate ROS.15,16 On the other hand, TRX reductase (TRXR) utilizes NADPH as an electron donor to maintain the reduced form of TRX, which contributes to scavenge H2O2 and reduce ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) for DNA synthesis.17,18 In addition, in some cell types, NADPH binds to the important H2O2-disposing enzyme: catalase, and reactivates it when it has been inactivated by H2O2.19
Reductive synthesis
NADPH is also a crucial electron source for several reductive synthesis reactions, including fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotides, and steroids synthesis to sustain rapid tumor cell growth.20 Primarily, NADPH provides reducing equivalents for fatty acid synthase (FASN), the main rate-limiting enzyme, to synthesize fatty acids with acetyl-CoA serving as a primer and malonyl-CoA as a two-carbon donor,21,22 and provides the needed electrons for iron–sulfur (Fe/S) protein assembly that participate in non-essential amino acid biosynthesis and lipoic acid synthesis, tRNA modification, DNA replication and repair, and telomere maintenance.23 NADPH is also needed for dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) enzyme to catalyze the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate (THF) in folate metabolism, which is required for de novo biosynthesis of thymidylate, purines, methionine, and some amino acids.24 Besides, NADPH acts as the reducing reagent for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), the rate-limiting enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, which leads to the synthesis of cholesterol and nonsterol isoprenoids.25 NADPH also acts as a cosubstrate for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD), which catalyzes the reduction of uracil and thymine to 5,6-dihydrouracil and 5,6-dihydrothymine, respectively.26 In addition, the activity of the cytochrome P450 reductase (POR) also requires NADPH, which has a major role in the metabolism of drugs, xenobiotics, and steroid hormones.27
Free radical generation
In addition, NADPH is also responsible for the generation of free radicals by NADPH oxidases (NOX) as a substrate. NOXs (NOX1–5 and dual oxidases (DUOX) 1 and 2) catalyze the superoxide anions or H2O2 from NADPH and oxygen.28–30 NOX-mediated ROS broadly and specifically regulate various redox-sensitive signaling pathways involved in cancer progression via stimulating oncogenes, such as Src and Ras, and inactivating tumor suppressor proteins, such as TP53 and PTEN.31
Molecular mechanisms of NADPH homeostasis in cancer
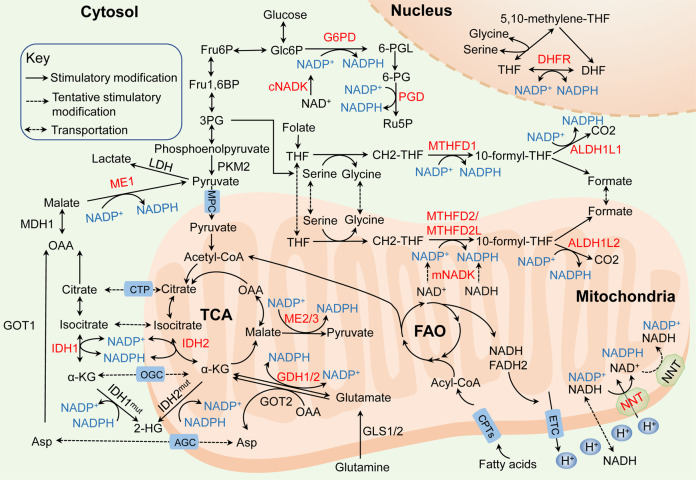
Understanding NADPH production and consumption routes is essential to a global understanding of cancer metabolism. As shown in Fig. 2, the NADPH homeostasis is mainly regulated by several metabolic pathways and enzymes including NAD kinase (NADK), the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), the folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism, malic enzymes (ME), the nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT), cytosolic or mitochondrial NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH1 and IDH2), the glutamine metabolism, and the fatty acid oxidation (FAO). However, for the general NADPH generation in cells, the relative contribution of these pathways and enzymes to NADPH production remains elusive. Recent study show that cellular NADPH could be largely generated by PPP, the folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism and ME in cancer and proliferation cells.32,33 Also, mounting evidence suggests that these different processes and enzymes have functional connections for NADPH homeostasis in cancer. For instance, FAO accelerates the TCA cycle to produce citrate, which is exported to the cytosol to engage in NADPH production through ME1 and IDH1.34 Here we review current knowledge of the underlying mechanisms of NADPH homeostasis following its de novo synthesis, relative contribution of related enzymes and pathways in cancer.
Fig. 2.
Molecular mechanisms of NADPH homeostasis in cancer. The principal generation of NADPH (blue) with dysregulated pathways and enzymes (red) in cancer: (i) NADKs catalyze the phosphorylation of NAD(H) to form NADP(H) via the de novo synthesis (cNADK in the cytosol and mNADK in mitochondria). (ii) the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) utilizes G6PD and PGD to maintain the cytosolic NADPH. (iii) the folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism reduces NADP+ to NADPH by MTHFD1/ALDH1L1 in the cytosol, MTHFD2/MTHFD2L/ALDH1L2 in mitochondria and DHFR in the nucleus. (iv) IDH1 located in the cytosol and IDH2 located in mitochondria generate NADPH, but mutant IDHs consume NADPH. (v) ME1 located in the cytosol and ME2/3 located in mitochondria convert NADP+ into NADPH; (vi) the glutamine metabolism generates NADPH by GDH1/2 directly in mitochondria and generates aspartate that is transported into the cytosol for NADPH production depending on ME1. (vii) NNT catalyzes the transfer of hydride ions from NADH to NADP+ and produces NADPH to maintain the mitochondrial NADPH and the reverse-mode NNT that consumes NADPH may exist in cancer cells. (viii) The CPT1/2-mediated FAO generates acetyl CoA that enters the TCA cycle and contributes to NADPH production depending on IDHs and MEs. MPC mitochondirial pyruvate carrier, CTP citrate transport protein, OGC α-ketoglutarate-malate carrier, AGC aspartate–glutamate carrier
NAD kinase
NADPH de novo synthesis is catalyzed by NADKs, which catalyze the phosphorylation of NAD+ to form NADP+. Subsequently, the dehydrogenases/reductases in various metabolic pathways convert NADP+ into NADPH.10,12 NADKs are found in almost all human organs except skeletal muscle, and localized in both cytosol and mitochondria. Compared to cytosolic NADK (cNADK), mitochondrial NADK (mNADK) has a distinctive feature that it can directly phosphorylate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) to generate NADPH to alleviate oxidative stress in mitochondria.35
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database indicates both cNADK overexpression and the presence of several cNADK mutants in multiple tumor types.10 Notably, a novel cNADK mutant, NADK-I90F, is found in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cancer (PDAC) patients. CNADK-I90F has a lower Km and higher Vmax for NAD+ compared to wild-type cNADK, which indicates increased enzyme activity. Consistently, compared with cNADK wild-type cells, cells expressing cNADK-I90F have elevated NADPH levels and reduced ROS levels.36,37 In addition, in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and colon cancer, silencing cNADK with shRNA impairs the pool of NADPH and suppresses cancer cell growth.38 In terms of NADKs activities, cNADK phosphorylated at S44, S46, and S48, which may be mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)–Akt signaling, has enhanced activity in breast cancer and lung cancer cells, thereby increasing NADPH production.39 Based on its recent discovery, the relevant role of mNADK in human cancers still need to be clarified, but the wild-type and mutant cNADK are potential clinical targets for cancer therapy.
Pentose phosphate pathway
The PPP diverges at the first step of glycolysis, which serves as the largest contributor of cytosolic NADPH and NADPH generation undergoes three irreversible reactions in the PPP oxidative branch.40–42 Studies have proved that NADPH production is dramatically increased by enhancing the flux of glucose into the PPP oxidative branch in various cancers.43,44 Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) that exists as either an active dimer or an inactive monomer dehydrogenates G6P to yield 6-phosphogluconolactone (6-PGL) and NADPH in the first reaction. Then, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (PGD) that often functions as a homodimer catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of 6-phosphogluconate (6-PG) to synthesize ribulose-5-phosphate (Ru5P) and a second NADPH in the third reaction.45,46
Increasingly, more studies have shown that G6PD activity is increased in several types of cancers, including bladder, breast, prostate, gastric cancers compared with normal tissues, and the high expression of G6PD predicts poor clinical outcome in various cancer patients and plays critical roles in tumorigenesis and chemoresistance.47,48 PGD is also hyperactive and plays a fundamental role in tumor growth.49,50 G6PD or PGD depletion significantly decrease NADPH levels and enhance chemotherapeutic drugs-induced cell apoptosis by redox modulation.51,52 For what concerns activity regulation, NADP+ is required for G6PD enzymatic activity, whereas NADPH negatively regulates its activity. Hence, tumor cells with higher NADPH consumption exhibit higher levels of active G6PD.45 Interestingly, a study also shows that NADPH level is not changed by silencing PGD expression, which is possible that a temporally increased NADP+/NADPH ratio compensatory increased G6PD activity, thus generating NADPH.45
The NADPH homeostasis is also regulated by the rate-limiting enzyme activity affected by the posttranslational modification. Studies indicate that the glycosylation, SIRT5-mediated deglutarylation and SIRT2-mediated deacetylation all enhance G6PD activity and maintain cellular NADPH homeostasis.53–55 Both the phosphorylation of PGD at Y481 upon EGFR activation and acetylation of PGD at K76 and K294 by acetyltransferases enhance its activation for producing NADPH in cancer cells.56,57 Conversely, protein kinase A (PKA) inhibits G6PD activity by directly phosphorylating it on serine and threonine residues.58 Additionally, G6PD activity can be regulated by several signaling pathways in tumors, such as the PI3K/AKT, Ras, Src, Nrf2, mTORC1, PETEN, ATM, and TP53 pathways, in a direct or indirect manner (reviewed in refs. 45,47). For instance, the PTEN protein and cytosolic TP53 bind to G6PD to prevent the assembly of G6PD monomers into active dimers and thus decease the PPP flux.59,60
Folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism
Folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism has been long recognized and attributed to its function of producing one-carbon units for nucleic acid and methionine synthesis, another crucial function of this pathway is generating reducing power NADPH.61,62 Serine and glycine are the major carbon sources of this pathway. The activation of serine biosynthesis pathway enhances NADPH generation in cancer cells.63 Conversely, eliminating serine from the medium decreases the NADPH/NADP+ ratio and impairs cancer cell growth.64 Methylene tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenases (MTHFD1 in cytosol and MTHFD2 or MTHFD2L in mitochondria) catalyze the oxidation of 5,10-methylene-THF (CH2-THF) to form 10-formyl-THF, and 10-formyl-THF dehydrogenases (ALDH1L1 in cytosol and ALDH1L2 in mitochondria) catalyze the oxidization of 10-formyl-THF to generate CO2 with concomitant NADPH production. In the nucleus, the THF carrier is oxidized to DHF in an NADPH-generating reaction with electrons used to reduce one-carbon units to the methyl level.65–67
MTHFD2 is postulated to be the “main switch” that produces additional one-carbon units in mitochondria to enable rapid growth.63 The expression of MTHFD2 is closely related to the response of the folate antagonist methotrexate (MTX) and the thymidylate synthase inhibitor pemetrexed.68,69 Both MTHFD2 and MTHFD1 are markedly elevated and correlated with poor survival across human cancers.70–72 Moreover, study indicates that combining serum AFP with MTHFD1 enhances the prognostic prediction accuracy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).73 Quantitative flux analysis reveals depletion of either MTHFD2 or MTHFD1 results in decreased cellular NADPH/NADP+ and GSH/GSSG ratios and increased cell sensitivity to oxidative stress.32 Suppression of MTHFD2 disturbs redox homeostasis, accelerates cell death in both colorectal cancer (CRC),74,75 and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).64 MTHFD2 is also critical for cancer stem-like properties and chemoresistance, suggesting that disturbing NAPDH homeostasis may prevent recurrence and eradicate tumors.76 And, MTHFD1 depletion reduces both the frequencies of circulating melanoma cells in the blood and metastatic disease burden in mice bearing melanoma,77 suggesting that NAPDH homeostasis represents therapeutic targets to impede distant metastasis. However, the association between MTHFD2L, which can use either NAD+ or NADP+ for dehydrogenase activity, and tumors remains to be investigated.
Cytosolic ALDH1L1 mainly regulates reduced folate pools and purine biosynthesis, while mitochondrial ALDH1L2 produces NADPH in response to oxidative stress.78 Although ALDH1L1 is overexpressed in NSCLC and GC cancer,79,80 ALDH1L1 is reported profoundly downregulated or silenced in cancers, rendering it a candidate tumor suppressor.81,82 Nevertheless, ALDH1L2 is highly expressed and presents as an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in melanoma, PDAC, and CRC.77,78,83 Depletion of ALDH1L2 markedly decreases the NADPH/NADP+ and GSH/GSSG ratios, reduces the circulating tumor cells in blood and alleviates the metastatic burden.77,83,84 In addition, the expression of ALDH1L2 is upregulated by some certain drugs, such as thapsigargin and tunicamycin, endoplasmic reticulum stress inducers in immortalized human B cells,85 mitotane, an adjuvant monotherapy used for treating adrenocortical carcinoma,86 and the indomethacin, an anti-inflammatory agent in breast cancer cells.87 Thus, further exploration of the association between the effects of these drugs on the ALDH1L2 expression and the cellular response to redox stress is needed.
Malic enzymes
ME participate in reactions that link the components of catabolic metabolism in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle via the oxidative decarboxylation of malate to pyruvate, thereby inducing the anabolic metabolism with concomitant NADPH production.32,88 A quantitative flux analysis showed that the direct contribution of ME to NADPH generation was estimated to equal the contribution of the PPP.89 ME family consists of three isoforms: ME1 is located in the cytosol and ME2, ME3 are located in mitochondria. ME1 and ME3 require NADP+ and ME2 utilizes either NAD+ or NADP+ for their catalytic activities, thus NADPH can be produced by ME both directly and indirectly through the activity of the NNT that catalyzes the transfer of hydride ions from NADH to NADP+ and produces NADPH in mitochondria.90 However, ME1 and ME2 seem to be the main isoforms because ME3 is hardly negligibly detected in many assessed mammalian cells.91
The overexpression of ME1 is significantly associated with a poor prognosis for people with cancer, including those with gastric cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, etc.92–95 Silencing ME1 markedly reduces NADPH and increases ROS levels, ultimately induces cell apoptosis under oxidative stress, such as glucose starvation or anoikis.96,97 Moreover, the ME1 protein is hypophosphorylated at S336 and hyperacetylated at K337 by PGAM family member 5 and acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, respectively, resulting in ME1 translocation from mitochondria to the cytosol, dimerization and activation, thus strongly promoting NADPH generation and tumorigenesis.98 ME1 expression is also regulated by well-known tumor suppressors or oncogenes such as TP53 or KRAS.91,99 Intriguingly, there is a direct crosstalk between ME1 and PPP components, and ME1 increases the ability of PGD to bind to 6-PG, enhancing NADPH generation.100
ME2 is also overexpressed in several cancers according to recent investigations, and is closely associated with cancer growth, metastasis, and poor outcomes.101,102 ME2 depletion, accompanied by an increased NADP+/NADPH ratio and ROS levels, impacts PI3K/AKT signaling and enhances the sensitivity of erythroleukemia and NSCLC cells to cisplatin.103,104 Besides, ME2 ablation results in elevated cellular ROS levels, which activates the AMPK pathway and then stimulates TP53 to attenuate melanoma cell proliferation.105,106 ME2 is frequently hemizygously codeleted along with tumor suppressor SMAD4 in human solid tumors including gastric cancer and PDAC.107,108 In ME2-unexpressed gastric cancer cells, its isoenzyme ME1 is upregulated to replenish intracellular NADPH and promotes cell survival under glucose starvation and anoikis.107 ME3 is in lower enzymatic activity than do ME2 in mitochondria. However, in ME2 homozygously deleted PDAC cell lines, its isoenzyme ME3 plays the compensatory roles for intracellular NADPH homeostasis.108,109 These findings provide a prime ‘collateral lethality’ therapeutic strategy for the treatment of a substantial fraction of GC or PDAC patients.
Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase
NNT is an integral mitochondrial inner membrane protein in eukaryotes that catalyzes the transfer of hydride ions from NADH to NADP+ and produces NADPH utilizing the proton motive force generated by the electron transport chain (ETC).110 The process is essential for maintaining the mitochondrial NADPH and NADH pools. NNT activity contributes to 45% of the total NADPH in mitochondrial pool, indicating a significant role of NNT for NADPH pool maintenance,111 and NADPH obtained by NNT is also used for the reductive carboxylation of α-KG to isocitrate mediated by IDH2.112 In contrast to this prevailing view, a fascinating work illustrates that the NNT reverses the direction upon NADPH consumption to support NADH and ATP productions under a pathological workload, at the cost of NADPH-linked antioxidative capacity. The models unexpectedly show that lacking a functional NNT presents with less oxidative damage to the heart compared to mice with active NNT.113 This finding provides potentially fresh insights into pathology and metabolic regulation, but more study about the NNT reversal process in cancer is urgently needed.
In cancer cells, NNT activity is stimulated by hyperpolarized mitochondria. Further, the NADH from increased glycolysis in the cytosol can be transferred to mitochondria to drive NADH-dependent NNT.89 Additionally, NNT is overexpressed in gastric cancer cell, which is associated with lower overall survival and disease-free survival. NNT knockdown shows limited ability to maintain NADPH levels and reduces tumorigenicity under oxidative stress conditions, such as that induced by anoikis, glucose deprivation in vitro, or impairs peritoneal dissemination and lung metastasis in vivo.114 Similar effects are observed in liver cancer,115 pheochromocytoma116 and NSCLC,111 and NNT is likely to be activated by NADPH consumption, such as in IDH-mutant cells.117 Additionally, considered as a key antioxidative enzyme, NNT is critical for inducing macrophage inflammatory responses118 and preventing ROS-induced cytotoxicity in T cells exposed to asbestos that can cause a reduction in antitumor immunity.119 To date, NNT appears to play a key role in tumorigenesis and modification of NNT may regulate immune effects of anti-tumor. Unfortunately, pharmacological inhibitors specific for NNT have not been reported and need to be developed.
Isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDH)
IDH also facilitates the generation of NADPH from NADP+ by catalyzing the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) for TCA cycle.120 There are three subtypes of IDH: IDH1 is located within the cytosol and peroxisomes, and IDH2/3 are primarily found in mitochondria. IDH1/2 use NADP+ as a cofactor and conduct a reversible reaction, while IDH3 uses NAD+ as a cofactor and conducts irreversible conversion.121,122
Multiple lines of evidences have revealed that IDH1 is overexpressed in numerous cancers and is closely correlated with poor prognoses of patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC),123 PDAC,124 or one of several hematological malignancies.125 Notably, ELISA demonstrate that IDH1 level is also significantly elevated in the plasma of NSCLC patients, suggesting that it can be used as a potential plasma biomarker.126 The upregulation of IDH1 may represent a common metabolic adaptation for diminishing oxidative stress and supporting macromolecular synthesis, consequently promoting tumor growth and therapy resistance.125 Furthermore, IDH1 silencing results in decreased NADPH and α-KG levels, with the increased ROS levels, leading to cancer cell apoptosis in NSCLC.123 Besides, oxidative stress conditions also increase the innately high IDH1 expression, and IDH1 silencing significantly enhances cell sensitivity to cancer chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and photodynamic therapy by reducing NADPH.124,127,128 In addition, IDH1 is hyperacetylated in CRC cells and is significantly correlated with distant metastasis and poor survival. SIRT2-dependent IDH1 deacetylation at K224 impairs its enzymatic activity and represses its malignant behaviors in CRC.129 Specially, studies also found that IDH1 is significantly downregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) compared with normal kidney cells, suggesting that IDH1 may function as a candidate tumor suppressor for ccRCC.130,131
Most studies indicate that IDH2 is also significantly upregulated in ESCC,132 ovarian cancer,133 lung cancer and other types of cancer,134 playing a pro-oncogenic role. Overexpression of IDH2 decreases ROS levels and increases cancer cell growth.121 IDH2 depletion decreases the expression of HIF1α and leads to the attenuation of tumor growth in lung cancer.134 However, because of heterogeneity among cancer cells, other studies have shown that IDH2 expression is decreased in metastatic HCC and gastric cancer tissues compared with paired normal tissues.135,136 The underlying mechanism is that these cells lacking IDH2 show enhanced invasive behavior due to the increase in matrix metalloproteases, which depend on the NF-κB pathway. In addition, NAD+ production by the NNT enhance SIRT3-mediated deacetylation and loss of NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT3 increases the acetylation of IDH2 at K413 and decreases its enzymatic activity by reducing dimerization, thus regulates mitochondrial redox status and promotes cell tumorigenesis in luminal B breast cancer,137 and B cell malignancies.138 SIRT5-mediated IDH2 desuccinylation also regulates cellular NADPH homeostasis and redox potential.54
The contribution of IDH to NADPH generation in cancer remains controversial. IDH1 and IDH2 also catalyze the reductive carboxylation and support tumor cells growth with defective mitochondria. Studies show that IDH1/2 syntheses isocitrate/citrate from α-KG with NADPH consumption, then the isocitrate/citrate import into the mitochondria and contribute to suppress mitochondrial ROS.139,140 In addition, recently, IDH1 and IDH2 gene mutations have been prevalent in several diverse malignancies, including glioma, AML, angioimmunoblastic lymphomas, chondrosarcoma, and melanomas.141,142 Recurrent somatic mutation of residues are mainly located at enzymatic active sites that bind to isocitrate, typically at R132 including R132H, R132L, R132S, R132C, and R132G in IDH1, and R140Q or R172K in IDH2.143,144 The mutated IDH1 and IDH2 proteins are endowed with a novel ability to catalyze the reduction of α-KG to generate a rare metabolite, 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), while consuming NADPH.145 Further, the relevance of these mutations and their roles in carcinogenesis and possible therapeutic implications have been extensively reviewed elsewhere.141,146,147
Glutamine metabolism
Glutamine metabolism is a major cellular carbon source for the TCA cycle, a nitrogen donor for nucleotide, amino acid, and lipid biosynthesis, it is also critical for maintaining NADPH levels.148,149 Proliferating cancer cells exhibit aerobic glycolysis, leading to a shift in glucose carbon away from the TCA cycle, which results in the increased use of glutamine to fuel anabolic processes to support rapid cell growth with increased NADPH and ammonia generation. Glutaminolysis is the mitochondrial pathway by which glutamine is first deaminated to glutamate by glutaminases (GLS1/2). Then, either NADPH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenases (GDH) or other transaminases, including glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 2 (GOT2) and glutamate pyruvate transaminase 2 (GPT2), convert glutamate into a-KG to meet the need for corresponding amino acids.89
Conventionally, GDH (coded by the GLUD gene) is the more predominant enzymes vital for the reactions needed to replenish the TCA cycle and yield NADPH than GOT2 and GPT2, which consists of ubiquitously expressed GDH1 and GDH2 mainly existing in neuronal and testicular tissue and having lower activity than GDH1.150 GDH1 is highly expressed in most tumor samples and correlated with tumor progression stage, including breast cancer and lung cancer cells.151,152 GDH1 depletion results in imbalanced redox homeostasis and cell cytotoxicity and attenuates cancer cell proliferation, which as well as the results in erythroleukemia cells, while it negligibly affects normal cell proliferation.151 Additionally, enhanced GDH1 activity has also been reported to be a possible prognostic marker and an indicator of metastasis in patients with CRC or gastric cancer.153,154 Under conditions of insufficient glycolysis caused by glucose deprivation, 2-deoxyglucose treatment or Akt signaling inhibition, glutamine-addicted cells are more sensitive to GDH1 deficiency.155 Furthermore, GDH-derived NADPH is consumed to support the reductive carboxylation of α-KG by IDH2, and the compensatory increase in the expression of GDH1 or GDH2 promote the growth of IDH-mutant glioma cells.156 Besides, with the consumption of extracellular glutamine, GDH can also catalyze ammonia derived from glutaminolysis and α-KG to support the synthesis of glutamate and downstream metabolites by reductive amination in a NADPH consumption manner to meet the cancer cells growth.148,157,158
Specifically, some cancer cells, such as PDAC and CRC cells, depend on a noncanonical glutamine metabolism pathway in the cytosol under the regulation of oncogenic KRAS activation. Glutamine-derived aspartate induced by GOT2 is transported into the cytosol and converted by GOT1 to oxaloacetate, then converted by malate dehydrogenase (MDH1) into malate and subsequently oxidized into pyruvate by ME1 to create NADPH.159,160 GHD1 shRNA has no effect on PDAC cells growth, while knocking down GOT2 elevates ROS levels and leads to cell senescence.161 Further, cytosolic GOT1 inhibition decreases oxaloacetate levels and reduces the cellular NADPH/NADP+ and GSH/GSSG ratios.159 Consistent with these findings, the addition of exogenous malate protects cells from excessive ROS accumulation in MDH1-knockdown cells.162 Consequently, targeting the glutamine metabolism pathway, which is essential for cancer cells but dispensable for normal cells, may lead to novel therapeutic approaches to treat refractory tumors.
Fatty acid oxidation
In addition, FAO pathway is also key for providing NADPH indirectly, which is indispensable in many cancers especially under metabolic stress. FAO generates NADH, FADH2, and acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) in each round,163 and NADH and FADH2 enter the ETC while the acetyl CoA enters the TCA cycle to produce citrate, which is exported to the cytosol to engage in NADPH production through ME1 and IDH1.34 FAO and FAS are both essential for tumor progression and support each other. Acetyl CoA and NADPH accumulated from FAO metabolism in the cytosol are needed to initiate FAS.164 The carnitine palmitoyl transferases (CPT), the rate-limiting enzymes in the FAO pathway, transport long-chain acyl-CoA from the cytosol to mitochondria.165 CPT-mediated FAO activation is reported to play key roles in maintaining NADPH homeostasis and promoting cell metastasis and chemoresistance in gastrointestinal cancer166,167 and melanoma.168 Recent studies also show that knocking down PPAR coactivator 1α (PGC1α), an important transcriptional coactivator regulating CPT1A and CPT1B, obviously decreases the ratio of NADPH/NADP+ and ATP levels, impairing radiation resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells.169 What’s more, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) also regulates the function of FAO in maintaining NADPH homeostasis and promotes tumor cell survival under oxidative stress or metabolic stress.170–173
Therapeutic implications for targeting NADPH metabolism
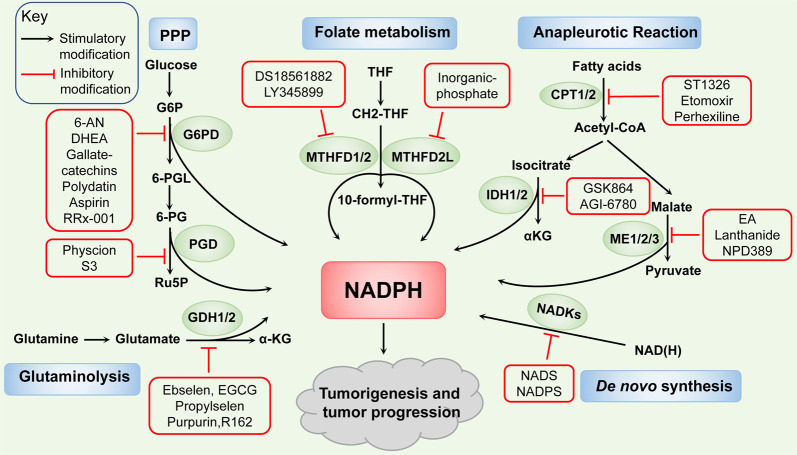
Compared with their normal counterparts, many types of cancer cell have increased oxidative stress and the upregulation of antioxidant capacity. With the metabolic reprogramming of NADPH, cancer cells increase the demand of NADPH for antioxidative effects and anabolic reactions. The specific vulnerability of tumor cells leveraging the aberrant NADPH-synthesis pathways can be exploited to induce cell death under various cellular stresses. Manipulating ROS levels by redox modulation is a way to selectively kill cancer cells without causing significant toxicity to normal cells. This strategy is the basis for many anticancer therapeutics, including chemotherapeutics, radiotherapies, and most small-molecule inhibitor-based therapies, which impair tumor metabolism and induce excessive ROS accumulation, inducing cell toxicity and death.11,174 As illustrated in Fig. 3, the inhibitors targeting NADPH-synthesis enzymes are being extensively developed. The specific target, anti-tumor effect, and clinical progress of these inhibitors targeting NADPH metabolism are also summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
Fig. 3.
Therapeutic implications for targeting NADPH metabolism. Many inhibitors targeting NADPH-synthesis enzymes have been discovered to impair NADPH pool, thus attenuate tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Such as NADS, NADPS of NADKs. 6-AN, DHEA, gallate-catechins, polydatin, aspirin, RRx-001 of G6PD. Physcion, S3 of PGD. DS18561882, LY345899 of MTHFD1/2. Inorganic phosphate of MTHFD2L. GSK864 of IDH1 and AGI-6780 of IDH2. Lanthanide of ME1 and EA, NPD389 of ME2. ST1326, Etomoxir of CPT1, and perhexiline of CPT2. Ebselen, EGCG, propylselen of GDH1/2 and purpurin, R162 of GDH1
Table 1.
The pre-clinical studies with inhibitors targeting NADPH metabolism in cancer
| Target | Compound | Cancer | Concentration range | IC50 for tumor cell | IC50 for normal cell | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADK | Thionicotinamide | Colorectal cancer | 10–100 μM | ~75 μM (c85, 96 h) | LD50 > 800 mg/kg | 38 |
| G6PD | DHEA | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 5–100 μM | ~75 μM (HEP-G2, 72 h) | Not available | 183 |
| 6-AN | Bladder cancer | 5–10 μM | ~16 μM (TCCSUP, 24 h) | Not available | 179 | |
| Polydatin | Breast cancer | 10–70 μM | 17 µM (MCF7, 48 h) | LD50 > 200 mg/kg | 181 | |
| Aspirin | Breast cancer | 0.25–2.5 mM | 0.69 mM (SKBR3, 48 h) | 0.5 mM (WI 38,48 h) | 182; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22, 3168–3171 (2012) | |
| RRx-001 | Colorectal cancer | 5–100 μM | ~50 μM (CaCo2, 72 h) | Not available | 183 | |
| 6PGD | Physcion | Leukemia | 10–40 μM | ~40 μM (K562, 48 h) | >100 μM (HDF, PIG1, 48 h) | Nat. Cell Biol. 17, 1484–1496 (2015) |
| MTHFDs | LY345899 | Colorectal cancer | 10 μM | ~12 μM (SW620, 72 h) | >200 μM (CCD-112, 72 h) | 74 |
| MTHFD2 | DS18561882 | Breast cancer | 140 nM | 140 nM (MDA-MB-231, 24 h) | Not available | 186 |
| GDHs | Propylselen | Lung cancer cells | 0–10 μM | 3.4 μM (A549, 48 h) | Not available | 187 |
| R162 | Non-small cell lung carcinoma | 20–40 μM | 10 μM (KG1a, 48 h) | >40 μM (MRC-5, HFF, 48 h) | 151 | |
| IDH1 | GSK864 | Glioma | 5–100 μM | 5 μM (LN382, 48 h) | Not available | 125 |
| IDH2 | AGI-6780 | Non-small cell lung carcinoma | 0–50 μM | ~5 μM (A549, 24 h) | >50 μM (MRC-5, 48 h) | 134 |
| ME1 | Piperazine-1-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione | Colorectal cancer | 50 μM | <50 μM (HCT116, 24 h) | >50 μM (IEC6, 24 h) | 90 |
| ME2 | Embonic acid | Non-small cell lung carcinoma | 1–10 μM | 1.4 μM (H1299, 48 h) | Not available | 189 |
| CPTs | Perhexiline | Colorectal cancer | 10–40 μM | <20 μM (HCT116, 24 h) | >20 μM (CCD841, 24 h) | 167 |
| CPT1 | Etomoxir | Prostate cancer | 50–200 μM | <75 μM (VCaP, 48 h) | >75 μM (BPH-1, 48 h) | Mol. Cancer Ther. 13, 2361–2371 (2014) |
| CPT1A | ST1326 | Burkitt’s lymphoma | 1–50 μM | 8.6 μM (Raji, 72 h) | 47 μM (GM130C, 72 h) | J. Natl Cancer Inst. 105, 489–498 (2013) |
IC50: Half-maximal inhibitory concentration, LD50: median lethal dose
Table 2.
The clinical trials with inhibitors targeting NADPH metabolism in cancer
| Target | Inhibitor | Tumor type | Phase | Clinical trial ID | Recruitment status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD | RRx-001 | Malignant solid tumor lymphoma | Phase 1 | NCT02518958 | Completed |
| RRx-001 | Lymphomas | Phase 1 | NCT01359982 | Completed | |
| RRx-001 | Small cell cancer | Phase 3 | NCT03699956 | Active, not recruiting | |
| RRx-001 | Colorectal neoplasms | Phase 2 | NCT02096354 | Active, not recruiting | |
| G6PD | DHEA | Breast cancer | Phase 3 | NCT01376349 | Completed |
| DHEA | Breast cancer | Phase 3 | NCT01376349 | Completed | |
| DHEA | Multiple myeloma and plasma cell neoplasm | Phase 3 | NCT00006219 | Completed | |
| G6PD, 6PGD, IDH, GDH | EGCG | Colon cancer | Early Phase 1 | NCT02891538 | Recruiting |
| EGCG | Breast neoplasms | Phase 2 | NCT02580279 | Enrolling by invitation | |
| EGCG | Lung neoplasms | Phase 2 | NCT02577393 | Enrolling by invitation | |
| GDH | Ebselen | Hearing loss/cancer | Phase 1 | NCT01452607 | Completed |
| Ebselen | Lung cancer head and neck cancer | Phase 2 | NCT01451853 | Unknown | |
| IDHs | AG-881 | Glioma with an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation | Phase 3 | NCT04164901 | Recruiting |
| BAY1436032 | Leukemia, myeloid, acute with IDH1 mutations | Phase 1 | NCT03127735 | Completed | |
| IDH1 | AG-120 (Tibsovo) | Advanced hematologic malignancies with an IDH1 mutation | Phase 1 | NCT02074839 | Approved |
| IDH305 | Advanced malignancies with IDH1 mutations | Phase 1 | NCT02381886 | Active, not recruiting | |
| FT-2102 | Tumors with IDH1 mutations including: glioma chondrosarcoma, hepatobiliary tumors | Phase 1/2 | NCT03684811 | Active, not recruiting | |
| IDH2 | AG-221 (Enasidenib) | Hematologic neoplasms with an IDH2 mutations | Phase 1/2 | NCT01915498 | Approved |
For de novo NADPH synthesis pathway, correlation studies have revealed that thionicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADS) and thionicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPS), converted from the pro-drug thionicotinamide (TN), act as inhibitors of NADKs through targeting the NAD-binding site of NADKs and decreasing the levels of NADPH.37 Combining TN with several chemotherapeutic drugs induces synergistic cell killing, indicating its efficacious antitumor effect in DLBCL and colon cancer.38 Further, reduced NADPH levels induced by NADPS results in accelerated degradation of DHFR and impairment of the folate cycle, which delays cancer cell growth.175
For the PPP enzymes, recent studies have discovered some inhibitors targeting on G6PD, such as NADP+ analogs, the competitive inhibitor 6-aminonicotinamide (6-AN), noncompetitive inhibitors epiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) which reduces the availability of NADPH and inhibits the cell growth.176 The combination of cisplatin and 6-AN optimizes the clinical dose and minimized the side effects.177–179 The new small molecule inhibitors are gradually being discovered, such as, gallated catechins (EGCG, GCG, ECG, CG), as the competitive inhibitors of NADP+, repress the activity of G6PD and suppress NADPH production.180 The natural molecule polydatin increases the NADP+/NADPH ratio and decreases the invasion of breast cancer cells by inhibiting G6PD activity.181 Further, the activity of G6PD is also repressed by aspirin casing acetylation of G6PD to decrease the activity of G6PD and the generation of NADPH, and by RRx-001, a novel clinical-stage chemosensitizer and radiosensitizer, which exerts antiproliferative effects in human tumor cells.182,183 Moreover, physcion and its derivative S3, novel small-molecule PGD inhibitors which fits in a pocket of PGD near the binding site of 6-PG to inhibit PGD enzyme activity and then decrease the NADPH level, exhibit excellent anticancer effects and sensitize leukemia cells to antimalarial agent dihydroartemisinin (DHA).184 For the folate metabolism pathway, the NADP+-dependent dehydrogenase activity of MTHFD2 and MTHFD2L can be inhibited by inorganic phosphate.185 Besides, other MTHFD2 inhibitors have been reported, including DS18561882 and LY345899 in a substrate-based manner, and treatments based on them decrease cellular NADPH/NADP+ ratio, increase cellular ROS levels, and impair tumorigenesis and metastasis.74,186 For the glutamine metabolism pathway, ebselen, epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG), and propylselen are reported to bind to GDH-active sites to abolish NADP+ binding and impair in cancer cell functions.187 A study also shows that purpurin and its analog, R162, acting as mixed model inhibitors of GDH1, inhibit GDH1 activity, elevate ROS levels and thus attenuate cancer cell proliferation.151
For the NADPH-synthesis enzymes involved in anapleurotic reactions, including IDH1/2, ME1/2/3, and CPT1/2, the targeting inhibitors are also being extensively developed. Study shows that treatment with GSK864 as IDH1 inhibitor binding an allosteric site on IDH1 reduces the NADPH/NADP+ ratio and prolongs the survival of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) PDXs model.125 AGI-6780 treatment, binding with IDH2 or mutant IDH2 in an allosteric manner at the dimer interface, reduce the IDH2 activity and lead to the repression of cell growth in lung cancer.134 Mutant IDH-targeted therapy and a number of important recent pre-clinical and clinical studies in IDH-mutant solid tumors have been extensively reviewed elsewhere,147 and listed in Table 2. Furthermore, NPD389 binding to ME2 in fast-binding mode impairs its activity,188 and embonic acid (EA) induces the cellular senescence of H1299 cancer cells through its noncompetitive inhibitory activity against ME2.189 Further, ME1 treated with the inhibitor (piperazine-1-pyrrolidine-2,5-dione) has little effect on normal rat intestinal epithelial cells but strongly suppresses human CRC cell growth by targeting ME1 NADP+-binding site and reducing the NADPH level.90 Lanthanide treatment represses cell proliferation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by inhibiting ME1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.93 In addition, CPTs are also considered to be targeted. Glioma cells with FAO inhibited by etomoxir, a CPT1 inhibitor, exhibits a profound decrease in NADPH levels, reduced GSH content and elevation of intracellular ROS levels. Besides, CPT1A-suppression or etomoxir treatment fails to maintain redox homeostasis in detached CRC cells and induces sensitivity to glucose deprivation in PDAC cells.166,190 Further, in gastrointestinal cancer cells, genetic inhibition or pharmacological treatment of CPT2 with perhexiline disrupts NADPH and promotes cell apoptosis after oxaliplatin treatment. Combining perhexiline with oxaliplatin leads to a significant suppression of cancer progression.167 Other inhibitors of CPTs are also discovered, such as Ro25-0187, ST1326 which are expected to be used for cancer treatment.191
Conclusions
In summary, the essential role of NADPH homeostasis has been increasingly recognized in cancer development and progression through cellular antioxidative effects and anabolic reactions. Pharmacological restriction of cellular NADPH availability by targeting its synthesis pathways to impair NADPH homeostasis is currently recognized as a crucial and potential strategy for cancer treatment.
However, there is an interdependent relationship in which the NADPH pool is simultaneously supported and used by various pathways in cells. For example, pyruvate kinase muscle isoform 2 (PKM2) inactivation can both attenuate the glucose flux to PPP and enhance folate metabolism to mediate NADPH generation.32,43 Moreover, because of the heterogeneous nature of tumors, there are considerable variations in NADPH-related processes in different tumors, for example, the main pathways of glutamine metabolism in the context of PDAC are different from the previous prevailing view as informed by studies of other cancers,159,192 indicating the need for careful analyses of individual characteristics among cancers for establishing individualized precision therapy. Moreover, the special functions of these metabolic enzymes are not fully understood in cancer. For instance, the reverse-mode NNT that consumes NADPH to support NADH and ATP productions in contrast to the conventional view has not been reported with respect to cancer.113 Besides, because of the high plasticity of the metabolic network and metabolite exchange among cancer and stromal cells, a compensatory response can be readily induced to produce limiting metabolites.193 In addition, the relative contribution of these pathways and enzymes to NADPH production can be variable in different cell types and under different conditions. Hence, additional studies are needed to evaluate the entire NADPH metabolome, identify the important interrelationships and determine the main pathway to select more suitable targets. Also, the effects of NADPH metabolism on immune cells in the tumor microenvironment are needed to explore for exploiting novel anticancer opportunities.
As the NADPH metabolism are shared in normal and cancer cells, selectively targeting NADPH synthesis under special circumstances without affecting normal cells is difficult. Therefore, one of the greatest challenges to target cancer metabolism is the induction of toxic effects on noncancerous cells. Further, many reported small-molecule inhibitors target several metabolic enzymes with similar structures, for example, EGCG targets both NADPH-dependent FASN and NADP+-dependent GDH.21,187 The functions can be also markedly different among the isoforms of these enzymes. For instance, cytosolic ALDH1L1 mainly regulates reduced synthesis, while mitochondrial ALDH1L2 produces NADPH to attenuate oxidative stress.78 IDH1/2 use NADP+ as a cofactor while IDH3 needs NAD+121. The development of highly selective or isoform-specific inhibitors will reduce side effects and is an important goal for the near future. Most compounds specifically targeting cancer NADPH metabolism are in preclinical studies, thus there are still challenges to address before these compounds enter the clinic. Collectively, to better understand the therapeutic potential of NADPH metabolism, more preclinical and clinical studies should be implemented to address these difficulties, and combined approaches with immunotherapy and/or chemotherapeutics should be pursued as the best strategies because of their synergistic effects.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1313304, 2018YFC1313300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81930065, 81871951), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2019A1515010233, 2018B030306049), Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (201806010002), and CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2019-I2M-5-036).
Author contributions
Conceptualization, R.-H.X. and H.-Q.J.; Writing-review and editing, J.-F.L., T.T., H.-Q.J., and D.X.; Supervision, R.-H.X. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally: Huai-Qiang Ju, Jin-Fei Lin
References
- 1.Chiarugi A, Dolle C, Felici R, Ziegler M. The NAD metabolome-a key determinant of cancer cell biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012;12:741–752. doi: 10.1038/nrc3340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen Z, Tian R, She Z, Cai J, Li H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020;152:116–141. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nogueira V, Hay N. Molecular pathways: reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and implications for cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013;19:4309–4314. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ying W. NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: regulation and biological consequences. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008;10:179–206. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xiao W, Wang RS, Handy DE, Loscalzo J. NAD(H) and NADP(H) redox couples and cellular energy metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018;28:251–272. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Xu D, et al. The protein kinase activity of fructokinase A specifies the antioxidant responses of tumor cells by phosphorylating p62. Sci. Adv. 2019;5:eaav4570. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cao X, Wu L, Zhang J, Dolg M. Density functional studies of coenzyme NADPH and its oxidized form NADP(+): structures, UV–Vis spectra, and the oxidation mechanism of NADPH. J. Comput. Chem. 2020;41:305–316. doi: 10.1002/jcc.26103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Houtkooper R, Cantó C, Wanders R, Auwerx J. The secret life of NAD+: an old metabolite controlling new metabolic signaling pathways. Endocr. Rev. 2010;31:194–223. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tao R, et al. Genetically encoded fluorescent sensors reveal dynamic regulation of NADPH metabolism. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:720–728. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pramono AA, Rather GM, Herman H, Lestari K, Bertino JR. NAD- and NADPH-contributing enzymes as therapeutic targets in cancer: an overview. Biomolecules. 2020;10:358. doi: 10.3390/biom10030358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324:1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.1160809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Katsyuba E, Romani M, Hofer D, Auwerx J. NAD+ homeostasis in health and disease. Nat. Metab. 2020;2:9–31. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0161-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ju HQ, et al. Regulation of the Nampt-mediated NAD salvage pathway and its therapeutic implications in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016;379:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Murphy MP. Mitochondrial thiols in antioxidant protection and redox signaling: distinct roles for glutathionylation and other thiol modifications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012;16:476–495. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moreno-Sanchez R, Gallardo-Perez JC, Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Saavedra E, Marin-Hernandez A. Control of the NADPH supply for oxidative stress handling in cancer cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017;112:149–161. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Corso CR, Acco A. Glutathione system in animal model of solid tumors: From regulation to therapeutic target. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2018;128:43–57. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Palde PB, Carroll KS. A universal entropy-driven mechanism for thioredoxin-target recognition. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:7960–7965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504376112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.J Z, et al. Small molecule inhibitors of mammalian thioredoxin reductase as potential anticancer agents: an update. Med. Res. Rev. 2019;39:5–39. doi: 10.1002/med.21507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kirkman HN, Gaetani GF. Catalase: a tetrameric enzyme with four tightly bound molecules of NADPH. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1984;81:4343–4347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.J L, H Y, BL S. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:225–245. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lupu R, Menendez JA. Pharmacological inhibitors of fatty acid synthase (FASN)-catalyzed endogenous fatty acid biogenesis: a new family of anti-cancer agents? Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2006;7:483–493. doi: 10.2174/138920106779116928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Buckley D, et al. Fatty acid synthase—modern tumor cell biology insights into a classical oncology target. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017;177:23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Stehling O, Lill R. The role of mitochondria in cellular iron-sulfur protein biogenesis: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013;5:a011312. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a011312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.MV R, et al. DHFR inhibitors: reading the past for discovering novel anticancer agents. Molecules. 2019;24:1140. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Luo J, Yang H, Song B. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:225–245. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.van Gennip A, van Lenthe H, Abeling N, Bakker H, van Kuilenburg A. Combined deficiencies of NADPH- and NADH-dependent dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenases, a new finding in a family with thymine-uraciluria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1995;18:185–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00711762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pandey AV, Fluck CE. NADPH P450 oxidoreductase: structure, function, and pathology of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013;138:229–254. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lambeth JD, Kawahara T, Diebold B. Regulation of Nox and Duox enzymatic activity and expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007;43:319–331. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.HQ J, et al. Mutant Kras- and p16-regulated NOX4 activation overcomes metabolic checkpoints in development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:14437. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ju HQ, et al. Mechanisms of overcoming intrinsic resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the redox modulation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015;14:788–798. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Block K, Gorin Y. Aiding and abetting roles of NOX oxidases in cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012;12:627–637. doi: 10.1038/nrc3339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fan J, et al. Quantitative flux analysis reveals folate-dependent NADPH production. Nature. 2014;510:298–302. doi: 10.1038/nature13236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liu L, et al. Malic enzyme tracers reveal hypoxia-induced switch in adipocyte NADPH pathway usage. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016;12:345–352. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Qu Q, Zeng F, Liu X, Wang QJ, Deng F. Fatty acid oxidation and carnitine palmitoyltransferase I: emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2226. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ohashi K, Kawai S, Murata K. Identification and characterization of a human mitochondrial NAD kinase. Nat. Commun. 2012;3:1248. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tsang YH, et al. Functional annotation of rare gene aberration drivers of pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:10500. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tedeschi PM, et al. NAD+ kinase as a therapeutic target in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:5189–5195. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tedeschi PM, et al. Suppression of cytosolic NADPH pool by thionicotinamide increases oxidative stress and synergizes with chemotherapy. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015;88:720–727. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.096727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hoxhaj G, et al. Direct stimulation of NADP synthesis through Akt-mediated phosphorylation of NAD kinase. Science. 2019;363:1088–1092. doi: 10.1126/science.aau3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sun L, Suo C, Li ST, Zhang H, Gao P. Metabolic reprogramming for cancer cells and their microenvironment: beyond the Warburg effect. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2018;1870:51–66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen L, et al. NADPH production by the oxidative pentose-phosphate pathway supports folate metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2019;1:404–415. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0043-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jiang P, Du W, Wu M. Regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway in cancer. Protein Cell. 2014;5:592–602. doi: 10.1007/s13238-014-0082-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Anastasiou D, et al. Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 by reactive oxygen species contributes to cellular antioxidant responses. Science. 2011;334:1278–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.1211485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yi W, et al. Phosphofructokinase 1 glycosylation regulates cell growth and metabolism. Science. 2012;337:975–980. doi: 10.1126/science.1222278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Patra KC, Hay N. The pentose phosphate pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014;39:347–354. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Du W, et al. TAp73 enhances the pentose phosphate pathway and supports cell proliferation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013;15:991–1000. doi: 10.1038/ncb2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yang HC, et al. The redox role of G6PD in cell growth, cell death, and cancer. Cells. 2019;8:1055. doi: 10.3390/cells8091055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jiang P, Du W, Yang X. A critical role of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in TAp73-mediated cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 2013;12:3720–3726. doi: 10.4161/cc.27267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bhanot H, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia cells require 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase for cell growth and NADPH-dependent metabolic reprogramming. Oncotarget. 2017;8:67639–67650. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sarfraz I, et al. 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase fuels multiple aspects of cancer cells: from cancer initiation to metastasis and chemoresistance. BioFactors. 2020;46:550–562. doi: 10.1002/biof.1624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ju HQ, et al. Disrupting G6PD-mediated redox homeostasis enhances chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36:6282–6292. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ma L, Cheng Q. Inhibiting 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase reverses doxorubicin resistance in anaplastic thyroid cancer via inhibiting NADPH-dependent metabolic reprogramming. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018;498:912–917. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rao X, et al. O-GlcNAcylation of G6PD promotes the pentose phosphate pathway and tumor growth. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:8468. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhou L, et al. SIRT5 promotes IDH2 desuccinylation and G6PD deglutarylation to enhance cellular antioxidant defense. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:811–822. doi: 10.15252/embr.201541643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Xu SN, Wang TS, Li X, Wang YP. SIRT2 activates G6PD to enhance NADPH production and promote leukaemia cell proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:32734. doi: 10.1038/srep32734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Liu R, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation activates 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase and promotes tumor growth and radiation resistance. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:991. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08921-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shan C, et al. Lysine acetylation activates 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase to promote tumor growth. Mol. Cell. 2014;55:552–565. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Xu Y, Osborne BW, Stanton RC. Diabetes causes inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase via activation of PKA, which contributes to oxidative stress in rat kidney cortex. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2005;289:F1040–F1047. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00076.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hong X, et al. PTEN antagonises Tcl1/hnRNPK-mediated G6PD pre-mRNA splicing which contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis. Gut. 2014;63:1635–1647. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jiang P, et al. p53 regulates biosynthesis through direct inactivation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011;13:310–316. doi: 10.1038/ncb2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ducker GS, Rabinowitz JD. One-carbon metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2017;25:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yang M, Vousden KH. Serine and one-carbon metabolism in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2016;16:650–662. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ben-Sahra I, Hoxhaj G, Ricoult SJH, Asara JM, Manning BD. mTORC1 induces purine synthesis through control of the mitochondrial tetrahydrofolate cycle. Science (New York, NY) 2016;351:728–733. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pikman Y, et al. Targeting MTHFD2 in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2016;213:1285–1306. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pietzke M, Meiser J, Vazquez A. Formate metabolism in health and disease. Mol. Metab. 2020;33:23–37. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.05.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Newman AC, Maddocks ODK. One-carbon metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 2017;116:1499–1504. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ducker GS, et al. Reversal of cytosolic one-carbon flux compensates for loss of the mitochondrial folate pathway. Cell Metab. 2016;23:1140–1153. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Moran DM, et al. KRAS mutation status is associated with enhanced dependency on folate metabolism pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014;13:1611–1624. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tedeschi PM, Vazquez A, Kerrigan JE, Bertino JR. Mitochondrial methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (MTHFD2) overexpression is associated with tumor cell proliferation and is a novel target for drug development. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015;13:1361–1366. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nilsson R, et al. Metabolic enzyme expression highlights a key role for MTHFD2 and the mitochondrial folate pathway in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:3128. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Liu F, et al. Increased MTHFD2 expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:8685–8690. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lin H, et al. MTHFD2 overexpression predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma and is associated with cell proliferation and vimentin-modulated migration and invasion. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018;51:991–1000. doi: 10.1159/000495402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Yu H, et al. Overexpression of MTHFD1 in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts poorer survival and recurrence. Future Oncol. 2019;15:1771–1780. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ju HQ, et al. Modulation of redox homeostasis by inhibition of mthfd2 in colorectal cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111:584–596. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djy160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Wei Y, et al. The effect of MTHFD2 on the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cell lines. OncoTargets Ther. 2019;12:6361–6370. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S210800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nishimura T, et al. Cancer stem-like properties and gefitinib resistance are dependent on purine synthetic metabolism mediated by the mitochondrial enzyme MTHFD2. Oncogene. 2019;38:2464–2481. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0589-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Piskounova E, et al. Oxidative stress inhibits distant metastasis by human melanoma cells. Nature. 2015;527:186–191. doi: 10.1038/nature15726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Krupenko SA, Krupenko NI. ALDH1L1 and ALDH1L2 folate regulatory enzymes in cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018;1032:127–143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-98788-0_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Li K, et al. The prognostic roles of ALDH1 isoenzymes in gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2016;9:3405–3414. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S102314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lee S, et al. KRAS The combination of loss of ALDH1L1 function and phenformin treatment decreases tumor growth in-driven lung cancer. Cancers. 2020;12:1382. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Krupenko SA, Horita DA. The role of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the function of candidate tumor suppressor ALDH1L1. Front. Genet. 2019;10:1013. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Krupenko SA, Krupenko NI. Loss of ALDH1L1 folate enzyme confers a selective metabolic advantage for tumor progression. Chem.–Biol. Interact. 2019;302:149–155. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Noguchi K, et al. The mitochondrial one-carbon metabolic pathway is associated with patient survival in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018;16:1827–1834. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Miyo M, et al. The importance of mitochondrial folate enzymes in human colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017;37:417–425. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Dombroski BA, et al. Gene expression and genetic variation in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in human cells. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010;86:719–729. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zsippai A, et al. Effects of mitotane on gene expression in the adrenocortical cell line NCI-H295R: a microarray study. Pharmacogenomics. 2012;13:1351–1361. doi: 10.2217/pgs.12.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ackerstaff E, Gimi B, Artemov D, Bhujwalla ZM. Anti-inflammatory agent indomethacin reduces invasion and alters metabolism in a human breast cancer cell line. Neoplasia. 2007;9:222–235. doi: 10.1593/neo.06673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Loeber G, Dworkin MB, Infante A, Ahorn H. Characterization of cytosolic malic enzyme in human tumor cells. FEBS Lett. 1994;344:181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ciccarese F, Ciminale V. Escaping death: mitochondrial redox homeostasis in cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2017;7:117. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Fernandes L, et al. Malic enzyme 1 (ME1) is pro-oncogenic in Apc mice. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:14268. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32532-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Jiang P, Du W, Mancuso A, Wellen KE, Yang X. Reciprocal regulation of p53 and malic enzymes modulates metabolism and senescence. Nature. 2013;493:689–693. doi: 10.1038/nature11776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Shi Y, et al. Malic enzyme 1 (ME1) is a potential oncogene in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor survival of gastric cancer patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2019;12:5589–5599. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S203228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Nakashima C, et al. Expression of cytosolic malic enzyme (ME1) is associated with disease progression in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:2036–2045. doi: 10.1111/cas.13594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Liao R, et al. ME1 promotes basal-like breast cancer progression and associates with poor prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:16743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35106-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Chakrabarti G. Mutant KRAS associated malic enzyme 1 expression is a predictive marker for radiation therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2015;10:145. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0457-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Murai S, et al. Inhibition of malic enzyme 1 disrupts cellular metabolism and leads to vulnerability in cancer cells in glucose-restricted conditions. Oncogenesis. 2017;6:e329. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2017.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Zheng FJ, et al. Repressing malic enzyme 1 redirects glucose metabolism, unbalances the redox state, and attenuates migratory and invasive abilities in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Chin. J. Cancer. 2012;31:519–531. doi: 10.5732/cjc.012.10088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Zhu Y, et al. Dynamic regulation of ME1 phosphorylation and acetylation affects lipid metabolism and colorectal tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell. 2020;77:138–149.e135. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Shen H, et al. MicroRNA-30a attenuates mutant KRAS-driven colorectal tumorigenesis via direct suppression of ME1. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24:1253–1262. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Yao P, et al. Evidence for a direct cross-talk between malic enzyme and the pentose phosphate pathway via structural interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2017;292:17113–17120. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.810309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Cheng CP, et al. The mechanisms of malic enzyme 2 in the tumorigenesis of human gliomas. Oncotarget. 2016;7:41460–41472. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Woo SH, et al. Down-regulation of malic enzyme 1 and 2: Sensitizing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to therapy-induced senescence. Head Neck. 2016;38:E934–E940. doi: 10.1002/hed.24129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ren JG, Seth P, Everett P, Clish CB, Sukhatme VP. Induction of erythroid differentiation in human erythroleukemia cells by depletion of malic enzyme 2. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e12520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Ren JG, et al. Knockdown of malic enzyme 2 suppresses lung tumor growth, induces differentiation and impacts PI3K/AKT signaling. Sci. Rep. 2014;4:5414. doi: 10.1038/srep05414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Chang YL, et al. Human mitochondrial NAD(P)(+)-dependent malic enzyme participates in cutaneous melanoma progression and invasion. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015;135:807–815. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Zheng B, Fisher DE. Metabolic vulnerability in melanoma: a ME2 (me too) story. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015;135:657–659. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Lu YX, et al. ME1 regulates NADPH homeostasis to promote gastric cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018;78:1972–1985. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Dey P, et al. Genomic deletion of malic enzyme 2 confers collateral lethality in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2017;542:119–123. doi: 10.1038/nature21052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Zhang Q, Li J, Tan XP, Zhao Q. Effects of ME3 on the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Neoplasma. 2019;66:896–907. doi: 10.4149/neo_2019_190119N59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Murphy MP. Redox modulation by reversal of the mitochondrial nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase. Cell Metab. 2015;22:363–365. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Ward NP, Kang YP, Falzone A, Boyle TA, DeNicola GM. Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase regulates mitochondrial metabolism in NSCLC through maintenance of Fe–S protein function. J. Exp. Med. 2020;217:e20191689. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Hoek J, Rydström J. Physiological roles of nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase. Biochem. J. 1988;254:1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2540001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Nickel AG, et al. Reversal of mitochondrial transhydrogenase causes oxidative stress in heart failure. Cell Metab. 2015;22:472–484. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Li S, et al. Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase-mediated redox homeostasis promotes tumor growth and metastasis in gastric cancer. Redox Biol. 2018;18:246–255. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Ho HY, Lin YT, Lin G, Wu PR, Cheng ML. Nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) deficiency dysregulates mitochondrial retrograde signaling and impedes proliferation. Redox Biol. 2017;12:916–928. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.04.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Meimaridou E, et al. Mutations in NNT encoding nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase cause familial glucocorticoid deficiency. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:740–742. doi: 10.1038/ng.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Gameiro PA, Laviolette LA, Kelleher JK, Iliopoulos O, Stephanopoulos G. Cofactor balance by nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) coordinates reductive carboxylation and glucose catabolism in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:12967–12977. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.396796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.McCambridge G, et al. Saturated fatty acid activates T cell inflammation through a nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT)-dependent mechanism. Biomolecules. 2019;9:79. doi: 10.3390/biom9020079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Yamamoto S, et al. Enhanced expression of nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) and its role in a human T cell line continuously exposed to asbestos. Environ. Int. 2020;138:105654. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.M Gagné L, Boulay K, Topisirovic I, Huot M-E, Mallette FA. Oncogenic activities of IDH1/2 mutations: from epigenetics to cellular signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2017;27:738–752. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Bergaggio E, Piva R. Wild-type IDH enzymes as actionable targets for cancer therapy. Cancers. 2019;11:563. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Al-Khallaf H. Isocitrate dehydrogenases in physiology and cancer: biochemical and molecular insight. Cell Biosci. 2017;7:37. doi: 10.1186/s13578-017-0165-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Tan F, et al. Identification of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer by proteomic analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012;11:M111.008821. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.008821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Zarei M, et al. Posttranscriptional upregulation of IDH1 by HuR establishes a powerful survival phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4460–4471. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Calvert AE, et al. Cancer-associated IDH1 promotes growth and resistance to targeted therapies in the absence of mutation. Cell Rep. 2017;19:1858–1873. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Sun N, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 is a novel plasma biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013;19:5136–5145. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kim SY, et al. Regulation of singlet oxygen-induced apoptosis by cytosolic NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007;302:27–34. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Wahl DR, et al. Glioblastoma therapy can be augmented by targeting IDH1-mediated NADPH biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 2017;77:960–970. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Wang B, et al. SIRT2-dependent IDH1 deacetylation inhibits colorectal cancer and liver metastases. EMBO Rep. 2020;21:e48183. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Laba P, Wang J, Zhang J. Low level of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 predicts unfavorable postoperative outcomes in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:852. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4747-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Chen K, et al. Loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is linked to gene body hypermethylation in kidney cancer. Cell Res. 2016;26:103–118. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Chen X, et al. The clinical significance of isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017;7:700–714. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Wang LN, et al. Quantitative proteome analysis of ovarian cancer tissues using a iTRAQ approach. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012;113:3762–3772. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Li J, et al. Wild-type IDH2 promotes the Warburg effect and tumor growth through HIF1alpha in lung cancer. Theranostics. 2018;8:4050–4061. doi: 10.7150/thno.21524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Tian GY, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 suppresses the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via matrix metalloproteinase 9. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015;37:2405–2414. doi: 10.1159/000438593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Wu D. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion via matrix metalloproteinase 7. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:5225–5230. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Zou X, et al. SIRT3-mediated dimerization of IDH2 directs cancer cell metabolism and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3990–3999. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Yu W, et al. Loss of SIRT3 provides growth advantage for B cell malignancies. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291:3268–3279. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.702076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Jiang L, et al. Reductive carboxylation supports redox homeostasis during anchorage-independent growth. Nature. 2016;532:255–258. doi: 10.1038/nature17393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Mullen A, et al. Reductive carboxylation supports growth in tumour cells with defective mitochondria. Nature. 2011;481:385–388. doi: 10.1038/nature10642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Molenaar RJ, Maciejewski JP, Wilmink JW, van Noorden CJF. Wild-type and mutated IDH1/2 enzymes and therapy responses. Oncogene. 2018;37:1949–1960. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0077-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Yu D, et al. Triptolide suppresses IDH1-mutated malignancy via Nrf2-driven glutathione metabolism. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:9964–9972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913633117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Clark O, Yen K, Mellinghoff IK. Molecular pathways: isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:1837–1842. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Xiang S, Gu H, Jin L, Thorne RF, Zhang XD, Wu M. LncRNA IDH1-AS1 links the functions of c-Myc and HIF1α via IDH1 to regulate the Warburg effect. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:E1465–E1474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711257115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Wang YP, Lei QY. Metabolic recoding of epigenetics in cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018;38:25. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0302-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Tommasini-Ghelfi S, Murnan K, Kouri FM, Mahajan AS, May JL, Stegh AH. Cancer-associated mutation and beyond: the emerging biology of isocitrate dehydrogenases in human disease. Sci. Adv. 2019;5:eaaw4543. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw4543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Waitkus MS, Diplas BH, Yan H. Biological role and therapeutic potential of IDH mutations in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:186–195. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Takeuchi Y, Nakayama Y, Fukusaki E, Irino Y. Glutamate production from ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase 2 activity supports cancer cell proliferation under glutamine depletion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018;495:761–767. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Cai WF, et al. Glutaminase GLS1 senses glutamine availability in a non-enzymatic manner triggering mitochondrial fusion. Cell Res. 2018;28:865–867. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0057-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Smith HQ, Li C, Stanley CA, Smith TJ. Glutamate dehydrogenase, a complex enzyme at a crucial metabolic branch point. Neurochem. Res. 2019;44:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2428-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Jin L, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 signals through antioxidant glutathione peroxidase 1 to regulate redox homeostasis and tumor growth. Cancer Cell. 2015;27:257–270. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Craze ML, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase (GLUD1) expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019;174:79–91. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-5060-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Liu G, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase is a novel prognostic marker and predicts metastases in colorectal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2015;13:144. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0500-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Wu YJ, et al. Glutamate dehydrogenase inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancer through the Notch signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark.: Sect. A Dis. Mark. 2019;26:303–312. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Yang C, et al. Glioblastoma cells require glutamate dehydrogenase to survive impairments of glucose metabolism or Akt signaling. Cancer Res. 2009;69:7986–7993. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Chen R, et al. Hominoid-specific enzyme GLUD2 promotes growth of IDH1R132H glioma. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:14217–14222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409653111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Spinelli J, et al. Metabolic recycling of ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase supports breast cancer biomass. Science. 2017;358:941–946. doi: 10.1126/science.aam9305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Moreno-Sánchez R, et al. Physiological role of glutamate dehydrogenase in cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2020;10:429. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Son J, et al. Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature. 2013;496:101–105. doi: 10.1038/nature12040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Hong C, Zheng J, Li X. Inhibition of GOT1 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017;79:835–840. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Yang S, et al. Mitochondrial glutamine metabolism via GOT2 supports pancreatic cancer growth through senescence inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:55. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0089-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Wang Y-P, et al. Arginine methylation of MDH1 by CARM1 inhibits glutamine metabolism and suppresses pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cell. 2016;64:673–687. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Xiong J. Fatty acid oxidation in cell fate determination. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018;43:854–857. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Carracedo A, Cantley LC, Pandolfi PP. Cancer metabolism: fatty acid oxidation in the limelight. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2013;13:227–232. doi: 10.1038/nrc3483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Kuo CY, Ann DK. When fats commit crimes: fatty acid metabolism, cancer stemness and therapeutic resistance. Cancer Commun. 2018;38:47. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0317-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Wang Y-N, et al. CPT1A-mediated fatty acid oxidation promotes colorectal cancer cell metastasis by inhibiting anoikis. Oncogene. 2018;37:6025–6040. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0384-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Wang Y, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid catabolism augments the efficacy of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. 2020;473:74–89. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.12.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Li XX, et al. Nuclear receptor Nur77 facilitates melanoma cell survival under metabolic stress by protecting fatty acid oxidation. Mol. Cell. 2018;69:480–492.e487. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Du Q, et al. PGC1α/CEBPB/CPT1A axis promotes radiation resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through activating fatty acid oxidation. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:2050–2062. doi: 10.1111/cas.14011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Jeon SM, Chandel NS, Hay N. AMPK regulates NADPH homeostasis to promote tumour cell survival during energy stress. Nature. 2012;485:661–665. doi: 10.1038/nature11066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Mihaylova MM, Shaw RJ. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011;13:1016–1023. doi: 10.1038/ncb2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wang MD, et al. HBx regulates fatty acid oxidation to promote hepatocellular carcinoma survival during metabolic stress. Oncotarget. 2016;7:6711–6726. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Li Q, et al. CircACC1 regulates assembly and activation of AMPK complex under metabolic stress. Cell Metab. 2019;30:157–173.e157. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Trachootham D, Khoonin W. Disrupting redox stabilizer: a novel therapeutic strategy for colorectal cancer. Cancer Commun. 2019;39:9. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0355-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Hsieh YC, et al. Enhanced degradation of dihydrofolate reductase through inhibition of NAD kinase by nicotinamide analogs. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013;83:339–353. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.080218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Di Monaco M, et al. Role of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase inhibition in the antiproliferative effects of dehydroepiandrosterone on human breast cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer. 1997;75:589–592. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Riganti C, Gazzano E, Polimeni M, Aldieri E, Ghigo D. The pentose phosphate pathway: an antioxidant defense and a crossroad in tumor cell fate. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012;53:421–436. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Roshanzadeh A, et al. Real-time monitoring of NADPH levels in living mammalian cells using fluorescence-enhancing protein bound to NADPHs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019;146:111753. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Chen X, et al. Modulation of G6PD affects bladder cancer via ROS accumulation and the AKT pathway in vitro. Int. J. Oncol. 2018;53:1703–1712. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Shin E, et al. Catechin gallates are NADP+-competitive inhibitors of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and other enzymes that employ NADP+ as a coenzyme. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008;16:3580–3586. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Mele L, et al. A new inhibitor of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase blocks pentose phosphate pathway and suppresses malignant proliferation and metastasis in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:572. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0635-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Ai G, et al. Aspirin inhibits glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in HCT 116 cells through acetylation: Identification of aspirin-acetylated sites. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016;14:1726–1732. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Oronsky B, Scicinski J, Reid T, Oronsky A, Cabrales P. RRx-001, a novel clinical-stage chemosensitizer, radiosensitizer, and immunosensitizer, inhibits glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in human tumor cells. Discov. Med. 2016;21:251–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Elf S, et al. Targeting 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in the oxidative PPP sensitizes leukemia cells to antimalarial agent dihydroartemisinin. Oncogene. 2017;36:254–262. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Shin M, Bryant JD, Momb J, Appling DR. Mitochondrial MTHFD2L is a dual redox cofactor-specific methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase expressed in both adult and embryonic tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2014;289:15507–15517. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Kawai J, et al. Discovery of a potent, selective, and orally available MTHFD2 inhibitor (DS18561882) with in vivo antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem. 2019;62:10204–10220. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Hou W, et al. Propylselen inhibits cancer cell growth by targeting glutamate dehydrogenase at the NADP(+) binding site. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019;509:262–267. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Wen Y, et al. Discovery of a novel inhibitor of NAD(P)(+)-dependent malic enzyme (ME2) by high-throughput screening. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014;35:674–684. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Hsieh JY, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor suppresses the tumor-associated mitochondrial NAD(P)+-dependent malic enzyme (ME2) and induces cellular senescence. Oncotarget. 2015;6:20084–20098. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Luo J, Hong Y, Tao X, Wei X, Zhang L, Li Q. An indispensable role of CPT-1a to survive cancer cells during energy stress through rewiring cancer metabolism. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:15795–15804. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5382-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Schlaepfer I, Joshi M. CPT1A-mediated fat oxidation, mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Endocrinology. 2020;161:bqz046. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqz046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Tian Y, et al. Systematic analyses of glutamine and glutamate metabolisms across different cancer types. Chin. J. Cancer. 2017;36:88. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0255-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Schulze A, Harris AL. How cancer metabolism is tuned for proliferation and vulnerable to disruption. Nature. 2012;491:364–373. doi: 10.1038/nature11706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]