Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases account for the number one cause of deaths in the world. Part of the reason for such grim statistics is our limited understanding of the underlying mechanisms causing these devastating pathologies, which is made difficult by the invasiveness of the procedures associated with their diagnosis (e.g., inserting catheters into the coronal artery to measure blood flow to the heart). Likewise, it is also difficult to design and test assistive devices without implanting them in vivo. However, with the recent advancements made in biomedical scanning technologies and computer simulations, image-based modeling (IBM) has arisen as the next logical step in the evolution of non-invasive patient-specific cardiovascular medicine. Yet, due to its novelty, it is still relatively unknown outside of the niche field. Therefore, the goal of this manuscript is to review the current state-of-the-art and the limitations of the methods used in this area of research, as well as their applications to personalized cardiovascular investigations and treatments. Specifically, the modeling of three different physics – electrophysiology, biomechanics and hemodynamics – used in the cardiovascular IBM is discussed in the context of the physiology that each one of them describes and the mechanisms of the underlying cardiac diseases that they can provide insight into. Only the “bare-bones” of the modeling approaches are discussed in order to make this introductory material more accessible to an outside observer. Additionally, the imaging methods, the aspects of the unique cardiac anatomy derived from them, and their relation to the modeling algorithms are reviewed. Finally, conclusions are drawn about the future evolution of these methods and their potential toward revolutionizing the non-invasive diagnosis, virtual design of treatments/assistive devices, and increasing our understanding of these lethal cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: image-based modeling, personalized cardiovascular medicine, cardio electromechanics, hemodynamics, thrombogenesis, simulation, biomechanics, heart
Introduction: Image-Based Modeling of the Heart
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S., with one person dying from it every 37 s, or about 647,000 each year (i.e., 1 in every 4 deaths), and amounting to a $219 billion per year burden to the public health system (CDC, 2019). Understanding it is very difficult, because it is a complex interaction of biomechanics, electrophysiology and non-Newtonian hemodynamics. This is further complicated by the interaction with external medical devices (pacemakers, pumps, etc.) that are commonly implanted in order to assist a failing or dysfunctional heart. Moreover, the heart’s properties (e.g., shape, structure, stiffness, electrical conductivity) that play an important role in determining its pumping ability are patient specific. Finally, it is difficult to extract information about the physiological processes occurring in living hearts, due to its constant motion, and the fact that invasive probing can be life threatening. For these reasons, Image-Based Modeling (IBM) – a patient-specific experimentally constrained computational approach – is a lucrative way for gaining novel insight into the cardiovascular diseases and their treatments.
An illustrative example of the IBM’s usefulness is HeartFlow Inc. – a company located in California, United States with about 300 employees and backed by $467 million capital investment (Craft, 2019). Their application is the diagnosis of Coronary artery disease (CAD) – an impairment of blood flow in the arteries that supply the heart, due to cholesterol plaque buildup. The disease is one of the most misdiagnosed: a recent study, which included data from more than 1,100 U.S. hospitals, found that over half of the more than 385,000 patients with suspected CAD underwent an invasive coronary angiography (ICA) only to find out that they did not have the disease (Patel et al., 2014). This is bad because ICA is an invasive technique that in itself could lead to mortality, because it uses catheters inserted into the femoral (groin) or radial (wrist) arteries to measure pressure difference across a coronary artery stenosis in order to check the likelihood of a blockage’s presence.
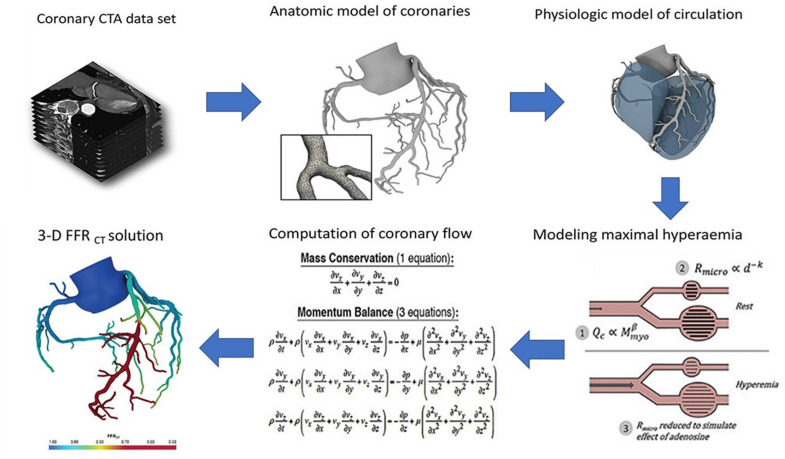
Conversely, HeartFlow calculates pressure differences virtually by simulating the blood flow through the patients’ own arteries, the structure of which is derived from a three-dimensional (3D) computerized tomography (CT) scan. This information is then used to calculate the fractional flow reserve (FFR), which is a statistic used to assess the hemodynamic significance of the stenosis by determining the ratio of the pressures before and after the narrowing. Therefore, this technology effectively serves as a non-invasive alternative to the ICA (Figure 1) (HeartFlow, 2019).
FIGURE 1.
Process flow diagram outlining the image-based computational pipeline of the HeartFlow’s approach to calculating the fractional flow reserve computerized tomography (FFRCT). (Reproduced with permission from Nick Curzen, Professor of Interventional Cardiology/Consultant Cardiologist, University Hospital Southampton).
The HeartFlow’s method has been evaluated in four large prospective clinical trials, enrolling a total of more than 1,100 patients at major medical centers worldwide. It received the European Economic Area CE mark in 2011 and U.S. FDA clearance in August 2019 (i.e., it is currently commercially available in the U.S.) (FDA, 2019). To date, clinicians have used the HeartFlow approach for over 30,000 patients in the diagnosis of heart disease (Kim, 2019). Therefore, it serves as the most mature IBM application in the context of cardiovascular disease. Yet, it is also one of the simplest in that it does not include the heart itself, and the blood assumed a homogeneous (i.e., no cells) fluid. At the same time, more advanced models are coming online as well. Yet, they are relatively unknown outside of this niche field.
Although many excellent reviews already exist in the image-based heart-modeling area, most of them are focused on just one or two specific aspects: for example, image acquisition and processing (Weese et al., 2013; Lamata et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015; Watson et al., 2018), hemodynamic flow simulations (Tang et al., 2010; Mittal et al., 2016; Quarteroni et al., 2017; Zhong et al., 2018); electrical conduction and stimulation modeling (Trayanova, 2011, 2012; Tobon-Gomez et al., 2013; Lopez-Perez et al., 2015; Rodriguez et al., 2015; Beheshti et al., 2016; Gray and Pathmanathan, 2018; Ni et al., 2018); tissue mechanics computations (Trayanova, 2011, 2012; Sun et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015; Chabiniok et al., 2016; Niederer et al., 2019a,b), ventricular thrombosis (Mittal et al., 2016) and the use of models in diagnostic procedures (Tang et al., 2010; Trayanova, 2012). Whereas, the goal of this manuscript is to provide a brief introductory overview of the entire cardiovascular IBM for a non-expert audience, in order to increase the broader exposure of this exciting topic and its numerous potential applications: CAD, Arrhythmias, Heart Failure (HF), Left-Ventricular Assist Devices (LVAD) and Pathogenic Thrombosis/Embolism.
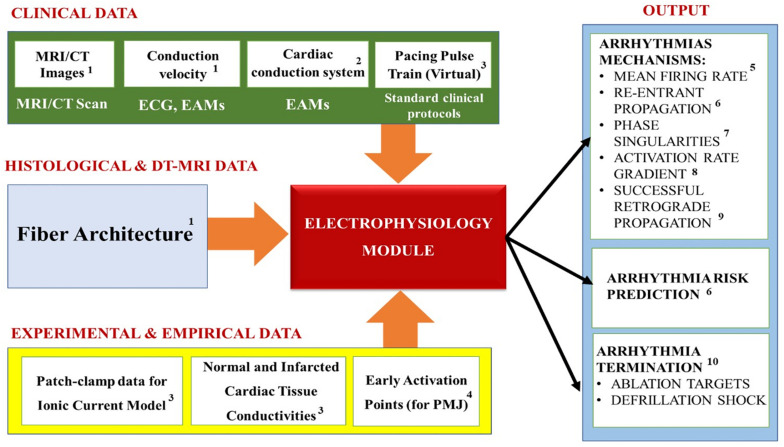
To that end, this review is organized as follows: Section “Methods: Literature Search” describes our literature search methods; Section “Background: Cardio Electromechanics and Hemodynamics” provides a brief background of the relevant cardiovascular physiology that explains how the tissue electromechanics and blood biology are interrelated in vivo; Section “Geometry Module” reviews how the model geometry is obtained using imaging, in order to establish a connection with the individual’s unique anatomy; Sections “Electrophysiology Module,” “Biomechanics Module,” “Simplified Hemodynamics Module,” and “Hemodynamics with Thrombogenesis Module” illustrate the mathematical formulation of the simulation modules used by these models, such as electrophysiology, biomechanics, simplified hemodynamics with and without thrombogenesis, respectively. Finally, Section “Summary and Conclusion” presents our summary and conclusions regarding the inputs and outputs of all cardiac modules as well as the directions that the field of personalized cardiovascular IBM is expected to go into.
Methods: Literature Search
In order to provide a “big picture” snapshot overview of the image-based cardiovascular modeling and its potential penetration into the clinical sector, we gathered works from the recent (i.e., approximately the last 5 years) proceedings of the following meetings: Interagency Modeling and Analysis Group Consortium Meetings, National Institute for Mathematical and Biological Synthesis workshops, Personalized Medicine Coalition resources, International Workshop on Cancer Systems Biology meetings and conferences, Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, Biomedical Engineering Society, American Institute of Chemical Engineers. Additionally, we performed manual searches with key words and terms including “image-based modeling of the heart,” “patient-specific cardiovascular modeling,” “cardio electrophysiology/biomechanics/electromechanics/hemodynamics image-based modeling” or “ventricular thrombosis modeling,” etc. for both research and review articles on databases, such as PubMed central, Web of Science, Research Gate, and Google Scholar. Additionally, we relied on the corresponding author’s own decade and a half long experience of working on biomedical image-based simulations. The obtained publication database was then screened by running citation reports to identify groups of researchers (typically led by a senior professor, who is joined by collaborators, postdocs, and students) that have established a track-record of being active within the various sub-areas of the cardiovascular modeling fields. Furthermore, to avoid bias (and to keep the work manageable) we tried to limit the literature sampling to just one most relevant publication from each of the groups. However, this was not always possible, because some of the researchers dominate their respective niches; and have published more than one article critical to our review.
Background: Cardio Electromechanics and Hemodynamics
Macroscopic Overview of How the Three Physics Are Coupled With Each Other
Before going into the details of the computational models, it is first important to understand the three types of coupled physics occurring in the heart: electrical signal conduction, biomechanics of the contraction and hemodynamics (which could also include clot formation and embolism).
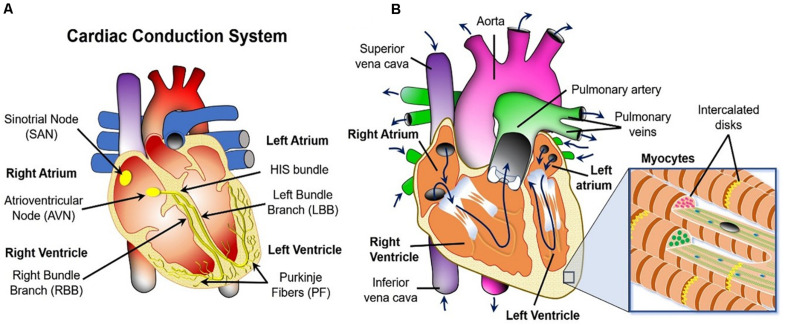
Figure 2A illustrates the cardiac conduction system (CCS) – a heterogeneous complex 3D network of highly specialized conductive cells (SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers) that transfer signals through the heart and cause it to contract. The electrical activity is initiated at the sinoatrial node (i.e., the natural pacemaker of the heart) where voltage signals called “action potentials” are produced periodically. Next the signals travel to the AV node, through the Bundle of HIS, down its branches and through the Purkinje Fibers. Ultimately, they are propagated to the myocardium (i.e., the muscular tissue of the heart) through discrete sites called Purkinje-Myocyte Junctions (not shown), causing the left and the right ventricles to contract independently of each other. This creates a double pumping action of the blood (see Figure 2B).
FIGURE 2.
Macroscopic overview of the three physics occurring in the heart. (A) Cardiac conduction system schematic. (B) Blood flow path (navy blue arrows) and the fibrous structure defining the biomechanics of the heart wall (inset).
Specifically, oxygen-poor blood returns from the body to the right side of the heart (i.e., atrium and ventricle), which then sends it to the lungs for re-oxygenation. Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs then enters the left side of the heart and is pumped through the aorta back to the body. The blood can also carry thrombi (or their embolized pieces) from other parts of the body, and/or the clots could be generated within the heart itself via activation of platelets (blood cells responsible for clot formation) and the coagulation cascade (a series of biochemical reactions that results in the formation of a polymer mesh that facilitates the structural integrity of the clot). The presence of these objects in the cardiovascular system can interfere with the mechanical action of the heart by creating rigid obstructions. Furthermore, the blood clots can also get stuck in the cardio-vasculature and block the delivery of metabolites to the heart tissue. This leads to necrosis of the latter, commonly referred to as an ischemia or a heart attack.
Structural Importance of the Myocardium
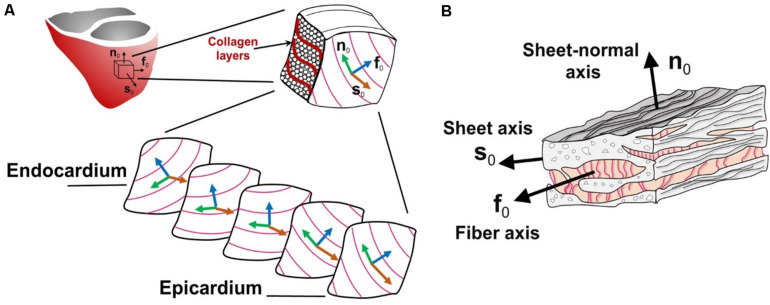
The organization of the cardiomyocyte fibers in the heart’s walls is thought to be critical to both the conductive and to the mechanical properties of the organ. Specifically, the contractile myocytes cells that cause the heart ventricles to beat are arranged in fibers (see inset of Figure 2B). These fibers make up the walls of the heart, which are lined with collagen and elastin extracellular matrix on the inside (i.e., endocardium) and the outside (i.e., epicardium). Their thickness varies both spatially and temporarily throughout the cardiac cycle.
If one were to take a representative sample from the left ventricle (which pumps the most blood) as in Figure 3A, it would be possible to see that the 3D layered organization of the myocytes changes throughout the wall thickness from the epicardium to the endocardium. In fact, Figure 3A shows that the muscle fiber direction rotates from +50° to +70° (sub-epicardial region) to nearly 0° in the mid-wall region to −50° to −70° (sub-endocardial region) with respect to the circumferential direction of the left ventricle (Holzapfel and Ogden, 2009). Finally, Figure 3B show that the myocyte fibers (or myofibrils) are arranged into composite layers (or sheets), which are interconnected by collagen fibers. Therefore, for IBM to be physiologically representative, it must account for how this intricate structure affects the complex physics that occur in the heart.
FIGURE 3.
Schematic diagram of the heart tissue microstructure. (A) The transmural configuration of the muscle fibers and laminar sheets. (B) The layered organization of myocytes and the collagen fibers between the sheets. f0, fiber axis; s0, sheet axis and n0, sheet-normal axis. (Adopted with permission from Holzapfel and Ogden, 2009).
Geometry Module
The most common ways for obtaining a realistic macroscopic morphology of the heart and its surrounding blood vessels are computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the typical MRI/CT machines provide relatively coarse resolution datasets of the personalized cardiac geometry, with large gaps between slices (Schulte et al., 2001; Frangi et al., 2002; Appleton et al., 2005). This necessitates the use of interpolation procedures. Hence, the microscopic details (e.g., blood vessels, trabeculations, the Purkinje Fibers, the location and activity of the PMJs, the orientations of the myofibril sheets, etc.) are harder to resolve due to their small size. Yet, they strongly determine the electrophysiological and biomechanical properties of cardiac tissue (Watson et al., 2018). Consequently, there are three main methods for accounting for these fine details:
Rule-Based Heuristics
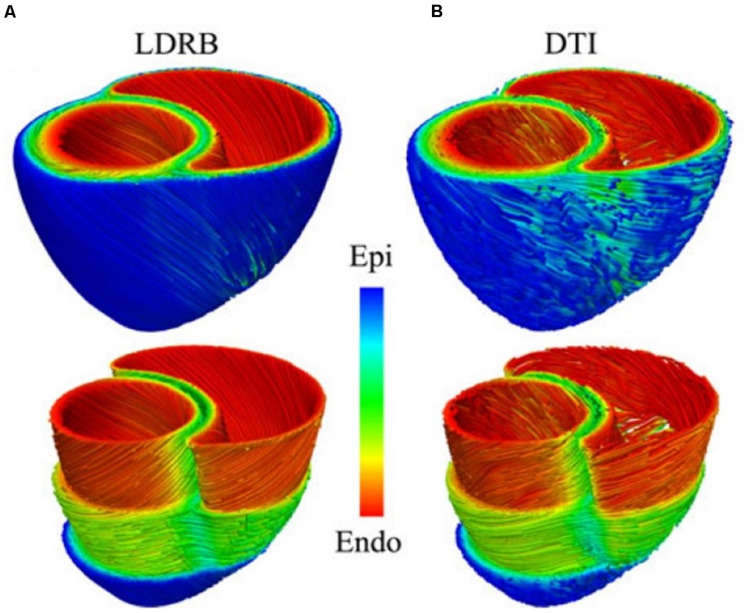
The most rudimentary approach is to generate these features mathematically, based on observed trends (see Figure 4A) (Streeter Daniel et al., 1969). Briefly, the longitudinal fiber direction is assumed to rotate clockwise from the endocardium to the epicardium. Specifically, it is made parallel to the long axis of the papillary muscles, trabeculae at these regions and parallel to the endocardial and epicardial surfaces at the ventricular walls. Lastly, the fiber orientation in the septum is assumed to be running along the ventricular walls (Bayer et al., 2012). A popular way to personalize the algorithm to a patient specific structure of the heart is to use the minimal distance between the imaged endocardial and the epicardial surfaces to approximate orientation of the fibers. More stable and advanced rule based approaches, such as the Laplace-Dirichlet method also exist (Bayer et al., 2012). However, the heuristics are not guaranteed to be physiologically accurate, nor are they fully patient specific. Yet they remain the most common approach due to their low cost and ease of implementation, as well as due to the difficulty of imaging the microstructural details in a beating heart in vivo. And, as Figure 4 shows, they yield results that are comparable with the best of the imaging techniques (which typically require for the heart to be explanted and fixed in order to acquire such fine details).
FIGURE 4.
Comparison between (A) rule-based method and (B) DTI-based estimation of the myocardial fiber orientation for a 3D model of canine ventricles. (Reproduced with permission from Bayer et al., 2012).
Histology/Optical Microscopy
The fiber orientation can also be approximated from histology of explanted hearts (Vetter and McCulloch, 1998; Deng et al., 2012), where the tissue is sliced into very thin 2D sections and dyed using special agents that highlight the features of interest. Although it is possible to create a 3D reconstruction based on the 2D slices using this approach, manual sectioning of the tissue may result in uneven slice thicknesses and feature distortion (Burton et al., 2006). Additionally, confocal microscopy has been used to image the fine structure of the myocardium (Hooks et al., 2002, 2006). However, the light penetration depth into the sample is typically limited to ∼100 mm. Hence, imaging a whole heart using this technique is also impractical. Therefore, both histology and confocal are typically used to provide localized information on explanted samples only. However, this information is useful for validating the rule-based methods, the in vivo imaging, and the modeling results.
Diffusion-Tensor MRI, Micro-CT With Contrast and 3D Ultrasound Backscatter Tensor Imaging
Additional detail can be obtained from MRI images using a Gadolinium contrast agent (Bishop et al., 2010) and a special technique called Diffusion Tensor imaging (DTI) (see Figure 4B). The latter maps the diffusion of water molecules in the biological tissues, which is not free, but reflects the interactions with obstacles like macromolecules, fibers and membranes. For the cardiac DTI, it is well known that the direction of the primary eigenvector corresponding to each voxel of the received images matches the longitudinal axis of cardiac myocytes (Scollan et al., 1998; Holmes et al., 2000). This information can then be mapped onto the volumetric mesh of a 3D cardiac macro-geometry to include the microscopic fiber orientation (Plank et al., 2009; Vadakkumpadan et al., 2010). Likewise, micro-computed tomography (mCT) with iodine staining has also recently been used to assess the myocyte fiber orientation in the heart tissue (Aslanidi et al., 2013). However, both techniques are too slow to capture a beating heart in 3D without motion artifacts. Luckily, advanced ultrasound-based imaging techniques are coming online, which can map the myocardial fibers orientation and its dynamics with a temporal resolution of 10 ms during a single cardiac cycle, non-invasively and in-vivo in entire volumes (Papadacci et al., 2017). However, given the novelty, complexity and cost of these techniques, they are not yet widely available to the majority of the cardiovascular IBM researchers.
Imaging-to-Modeling Pipeline
Perhaps the most difficult aspect of the in vivo scanning of live hearts is the need to perform significant image alignment using “registration” techniques. Furthermore, once the images are aligned, they must be “segmented” to identify the various tissue types and structural features of interest within the data. The segmentation can be either based on contrast dyes and/or on morphological feature detection (both manual and automated). The images can also be enhanced using digital post-processing, such as deconvolution (i.e., minimizing noise caused by objects outside of the imaging plane) and structure tensor analysis (e.g., enhancing visibility of the structural features for the fiber orientation detection) (Burton et al., 2006; Zhao et al., 2013). Numerical interpolation and machine learning techniques can further enhance the apparent resolution of the images digitally. Finally, the cardiovascular geometry must be “meshed” (i.e., broken up into pieces) to discretize the objects obtained from the images as a set of finite elements for numerical analysis. The latter is a simulation necessity that enables solving systems of complex (e.g., partial differential) equations by recasting them as algebraic approximations of the true solution. The trade-off for the simplified math is that the solution accuracy must be increased by making the mesh finer. This grows the number of equations that must be solved simultaneously, and thus the computational resource and time requirements. Overall, the imaging pipeline procedures are often very complicated and necessitate manual labor. This is both cumbersome (e.g., due to the large size of the high-resolution images) and subjective (e.g., due to the lack of contrast agents which necessitate user input). Therefore, there is an on-going effort to automate the imaging-to-modeling pipeline (Bishop et al., 2010).
Electrophysiology Module
The simplest types of the heart models tend to be focused on cardiac arrhythmias. This is an “umbrella” term for irregularities in the conduction or pacing of the electrical signals that control the heartbeat rhythm. Given that some arrhythmias can lead to mortality, it is important to understand the underlying electrophysiological mechanisms of these disorders. Yet, electrocardiograms of the heart provide only limited information, which often fails to predict lethal outcomes (Goldberger et al., 2011). Therefore, computational modeling offers a better alternative for studying these diseases.
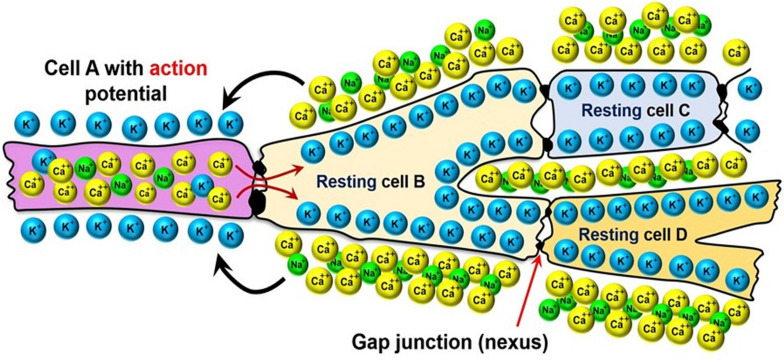
Most arrhythmia models focus on the electrophysiology of the heart, while assuming that it is isolated from the biomechanics of the contractions that lead to the pumping of the blood. As mentioned in Section “Methods: Literature Search,” the contraction of cardiomyocytes is initiated by electrical impulses called “action potentials,” which travel through the cardiac conduction system (see Figure 2A) into the myocardium. This electrical potential travels from one cell to another in the form of ions that pass through gap junctions between the cardiomyocytes (see Figure 5).
FIGURE 5.
Electrical coupling of the neighboring cardiomyocytes via the gap-junctions between their membranes.
The cardiomyocytes are polarized, meaning that there is an electrical potential across the cell membrane: in the resting state the cells are more negative on the inside and positive on the outside, while the charge polarity is temporarily reversed as the action potential passes through them. This reversal occurs via the transport of Ca++ and Na+ ions from the outside of the cells to their inside, and K+ ions in the reverse direction (see Figure 5). The internalization of the Ca++ ion is especially important to the contraction of the cardiomyocytes, because it triggers a sub-cellular signaling cascade that generates tension inside of the cells. Therefore, the electrophysiology models simulate the propagation of the ionic currents through the myocardium.
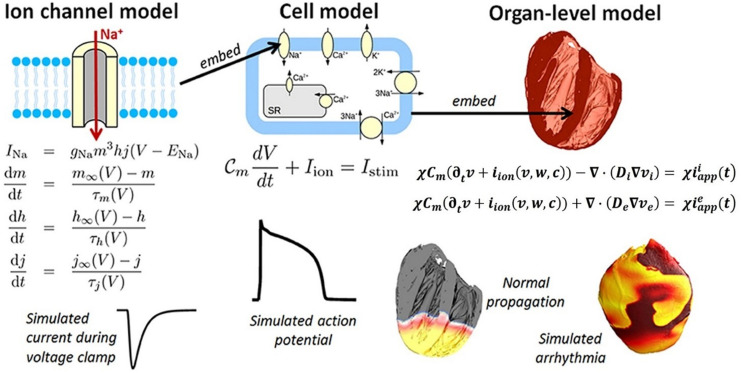
However, given that there are many cells in the heart, and each one of them has the ionic channels and transmembrane potentials, the problem is an inherently multiscale one (see Figure 6). On the subcellular scale (see Figure 6-LEFT), differential equations are used to model the transport of ionic species based on the Hodgkin–Huxley formulation (originally developed for the propagation of action potentials in neurons) (Hodgkin and Huxley, 1952). The subcellular models are then combined into cell scale models that can account for up to dozens of different ionic species and signaling intra-cellular cascades (see Figure 6, CENTER). Among these, the leading model is currently considered to be by O’Hara et al. (2011), which is based on experimental data from >150 undiseased human hearts. Finally, the individual ion currents are used to calculate the overall transmembrane potential, and its transport across the myocardium is treated as a diffusion across a homogenous medium (i.e., no discrete cells are considered by these models).
FIGURE 6.
Components of a multiscale cardiac electrophysiology model. (Left) Equations and sample output for a Hodgkin-Huxley formulation of the rapid sodium current through an ion channel. Multiple such sub-cellular models can be used to define a cell model. (Center) Schematic of sub-cellular processes included in a hypothetical cell model, together with the differential equation governing the transmembrane voltage, and sample output. Cell models differ in their formulation of the ionic current iion and can be made up of dozens of ordinary differential equations. (Right) Cell models can be incorporated into the bidomain equations and solved on a computational mesh of the heart (top right: high-resolution rabbit biventricular mesh of Bishop et al., 2010), to simulate normal or arrhythmic cardiac activity (bottom right). (Adopted with permission from Pathmanathan and Gray, 2018).
There are two types of formulations for the organ-level diffusion (which is related to the ionic conductivity) of the action potential across the myocardium: (1) the bidomain formulation, which considers different diffusivities inside and outside of the cell (Quarteroni et al., 2017) (see Figure 6, RIGHT):
| (1) |
The bidomain formulation is used for simulating the action potential propagation throughout the myocardium in the intra- and the extra- domains separately. The myocardium is assumed to be a continuum in which the potential is considered to vary along the longitudinal direction of the conducting cells, while it is constant in the transversal (or radial) directions (Quarteroni et al., 2017). In this formulation, vi, ve and ‘v’ are intracellular, extracellular and transmembrane potentials, respectively; and stand for applied stimuli on the intra- and extracellular spaces, respectively; iion are the ionic currents following a Hodgkin–Huxley-type description for different ionic species (Hodgkin and Huxley, 1952); w are gating variables taking values in [0,1] that regulate the transmembrane currents and have a mutual relation with the intracellular concentrations c of different ionic species (which also vary depending on the values of transmembrane potentials v) (Quarteroni et al., 2017); Cm is the membrane capacitance; ‘χ’ is the ratio of membrane area per tissue volume; Di and De are the conductivity tensors of the intra- and extracellular media, respectively.
and (2) the monodomain formulation, which simplifies the problem by considering only the transmembrane potential (Quarteroni et al., 2017):
| (2) |
In this formulation, the cardiac tissue is also assumed to be a continuum, but the current conservation is written in terms of the transmembrane potential v only (i.e., not considering the intra- and extracellular potentials) (Quarteroni et al., 2017). Instead, the intracellular and extracellular diffusivities are assumed to be proportional to each other, and therefore can be represented by a single variable. Herein, D0 is the conductivity tensor in a fixed reference state, J is the determinant of the deformation gradient tensor, which represents the volume change of a deformable object. The trade-off for the simplicity is that the monodomain model is unable to describe cardiomyocyte repolarization patterns. For this reason, the bidomain model is more widely used (Bishop and Plank, 2011).
Module Personalization
Table 1 summarizes the most common electrophysiology module personalization approaches encountered in the recent IBM works, while Figure 7 maps the relationships between the module’s inputs, outputs and applications. In this, and in the subsequent modules, the heart’s macroscopic anatomy can be personalized for a specific patient by acquiring its geometry from the in vivo imaging (see “Geometry Module” section). Furthermore, pathological tissue remodeling (e.g., locations and extension of infarct scars, diffuse fibrosis, etc.) can be accounted for via the imaging as well (Vadakkumpadan et al., 2009; Mewton et al., 2011; Dass et al., 2012; Ashikaga et al., 2013; Arevalo et al., 2016; Trayanova et al., 2017). However, there are two important types of microscopic structural information that cannot be completely personalized yet: the myocardial fiber orientation and the CCS.
TABLE 1.
A recent literature survey of how the Electrophysiology Module is typically personalized using image-based information.
| Imaging method | Personalized information from imaging | Mapping of the personalized information from imaging to the module’s inputs | Citation |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the conduction velocity (CV) in human cardiac tissue. | Ashikaga et al., 2013 |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Arevalo et al., 2016 |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Trayanova et al., 2017 |
| CT | Geometry | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivities were adjusted to fit local activation times, which were obtained using electro-anatomical maps (EAMs). | Cardenes et al., 2014 |
| CT and MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivities were adjusted to fit patient-specific electrical activation using EAMs. | Palamara et al., 2014 |
| MRI | Geometry | Geometry was personalized; tissue conductivities were adjusted to fit patient-specific electrical activation and ECG; and ionic currents were also personalized (via blood electrolyte concentrations measurement). | Krueger et al., 2013a |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized; tissue conductivities were adjusted to fit a human cardiac tissue model; and ionic currents were personalized via blood electrolyte concentrations measurements. | Krueger et al., 2013b |
| Cardiac delayed enhancement-MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions, papillary muscles and main endocardial trabeculations | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Lopez-Perez et al., 2019 |
| MRI | Geometry | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivities were adjusted to match clinically measured propagation times of the patient using EAMs. | Sermesant et al., 2008 |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Bruegmann et al., 2016 |
| Cine MRI (with torso geometries) | Geometry with orientation and position of heart | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match patient-specific ECG data. | Kayvanpour et al., 2015 |
| MRI (with torso geometries) | Geometry with orientation and position of heart | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Mincholé et al., 2019 |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Deng et al., 2016 |
| MRI | Geometry with infarcted regions | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match the CV in human cardiac tissue. | Prakosa et al., 2018 |
| Late gadolinium enhancement MRI | Detailed geometry, including the atrial structure, mitral and tricuspid valves, coronary sinus, pulmonary veins, superior and inferior vena cava. | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were adjusted to match patient-specific activation mapping data using EAMs. | Roney et al., 2018 |
| Cardiac magnetic resonance procedure | Detailed geometry, including the atrial structure, aortic arch, caval veins, torso surface, trabeculated myocardium between the wall and the intracavitary blood. | Geometry was personalized and tissue conductivity values were tuned to match patient-specific activation mapping using EAMs and ECG data. | Potse et al., 2014 |
FIGURE 7.
Summary of the Electrophysiology module’s inputs, outputs and applications. Superscripts in the figure correspond to the following references: 1Cardenes et al., 2014; Kayvanpour et al., 2015; Lopez-Perez et al., 2015; 2Cardenes et al., 2014; Palamara et al., 2014; 3Arevalo et al., 2016; Trayanova et al., 2017; 4Lopez-Perez et al., 2015; 5Behradfar et al., 2014; 6Arevalo et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2016; Trayanova and Chang, 2016; Prakosa et al., 2018; 7Boyle et al., 2016; Roney et al., 2018; 8Smith et al., 2011; Boyle et al., 2013; Potse et al., 2014; 9Trayanova, 2011; Behradfar et al., 2014; 10Arevalo et al., 2016; Trayanova et al., 2017; Deng et al., 2019.
Both are, unfortunately, still too difficult to image in a moving heart in vivo. Thus, typically an approximated personalization is performed to include these microscopic features using the rule-based algorithms (see “Geometry Module” section). Additional CCS approximation methods are based on: early activation points obtained from the literature (Durrer et al., 1970); manual delineation of CCS on the endocardial surfaces (Romero et al., 2010); ex vivo data obtained by means of histological studies of animal hearts (Sebastian et al., 2013); from in vivo electro-anatomical maps (EAMs) (Cardenes et al., 2014; Palamara et al., 2014). The EAMs data can provide the location of some of the PMJs, and can also be used to reconstruct patient-specific electrical activation patterns (Cardenes et al., 2014; Palamara et al., 2014).
Likewise, the conductivity values of different tissue zones (normal and abnormal/damaged) are typically too difficult to measure in living human patients, and are thus initialized based on accepted literature values: 2–3 m/s in the His-Purkinje system and 0.3–0.4 m/s in the conductive myocardial cells (Ideker et al., 2009). They are then either further adjusted to match the human myocardium conduction velocity (CV) (i.e., speed at which action potentials are distributed throughout the tissue) measured using explanted hearts (Arevalo et al., 2016; Trayanova et al., 2017; Lopez-Perez et al., 2019), or are tuned to fit patient-specific electrical activation patterns obtained from electrocardiograms (ECG), body surface potential maps (BSPM) or EAM (Sermesant et al., 2008; Lopez-Perez et al., 2015).
Unfortunately, at the cellular level, the patient-specific transmembrane current dynamics (i.e., iion) cannot yet be measured; and hence, the existing mathematical models are not personalized at such detail. Similarly, the electrical heterogeneity between the different regions (e.g., transmural heterogeneity in the ventricular walls), the electrical remodeling and the effects due to an individual’s genetic mutations on the cardiac electrophysiology cannot yet be accounted for (Lopez-Perez et al., 2015). However, a cellular level electrophysiology model that best matches the patient’s pathology can instead be chosen from either existing literature datasets that are representative of a patient-group (Krueger et al., 2013a,b) or from patch-clamp studies of cells harvested from pathologic zones of the patient (Cabo and Boyden, 2003; Decker and Rudy, 2010). Additionally, the extracellular ion concentrations can be estimated and set into a model from personalized measurements of blood electrolyte concentrations (Krueger et al., 2013a,b).
Module Outputs and Applications
Overall, the electrophysiology modeling studies the normal conduction in the heart, as well as the pathological mechanisms that arise and cause cardiac arrhythmias. It is typically used to calculate physiological parameters (see Figure 7) like: the Mean firing rate (i.e., the number of spikes during a cardiac cycle divided by cycle duration, spike/s) (Behradfar et al., 2014); Re-entrant arrhythmias propagation (Arevalo et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2016; Trayanova and Chang, 2016; Prakosa et al., 2018) (i.e., a propagation of an impulse that fails to die out after normal activation of the heart and continues to re-excite it after the refractory period has ended, Antzelevitch, 2001); Phase singularities (Boyle et al., 2016; Pathmanathan and Gray, 2018; Roney et al., 2018) which represent the sites in which the activation state cannot be determined, because the particular location is surrounded by activation states ranging from fully activated to fully recovered (Valderrabano et al., 2003); Activation rate gradient which quantifies how fast the transmembrane voltage Vm changes in different cardiac regions (Smith et al., 2011; Boyle et al., 2013; Potse et al., 2014); Successful retrograde propagation which measures whether conduction at a terminal Purkinje node is successful or refractory (Trayanova, 2011; Behradfar et al., 2014); and the organization of electrical wavelets as they propagate through the myocardium (Starobin et al., 1996; Keldermann et al., 2009; Trayanova, 2014). In our experience, the majority of the electrophysiological modeling is used for elucidating the mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmia, especially for “reentrant propagation of complex waves” (e.g., effects of cardiac microstructure, spiral wave breakup, early afterdepolarizations, scroll-wave filaments, action potential duration, electrical alternans, etc.) (Trayanova, 2011); as well as for prediction of arrhythmia risks in specific patients. Furthermore, these models are also used to examine the mechanisms of defibrillation shock in the heart for terminating arrhythmia, as well as for increasing the understanding of ablation targets in the arrhythmia treatments (Trayanova et al., 2017).
Module Personalization Example
The following is a discussion of a representative example of the personalized electrophysiology modeling applied to an arrythmia risk assessment in post-infarcted hearts. Specifically, personalized 3D computer models of the post-infarction hearts was constructed based on clinical MRI of specific patients. First, an individualized geometric model of the postinfarction ventricles was reconstructed from late-gadolinium-enhanced-MRI (Arevalo et al., 2016), with representations of both the scar and the infarcted border zones. Due to the difficulty imaging the myocardial fiber orientation from a moving heart in vivo, an approximated personalization was performed using a rule-based algorithm (Bayer et al., 2012). Region-specific cell and tissue electrical properties were then assigned to the electrophysiological model based on literature data. After that, a virtual multi-site delivery of electrical stimuli from various bi-ventricular locations was conducted, in order to computationally determine all the ventricular tachycardia reentrant pathways that the infarct-remodeled ventricular substrate can sustain. This methodology was then validated in an arrhythmia risk prediction clinical study including 41 patients and significantly surpassed several existing clinical metrics in predicting upcoming arrhythmic events (Arevalo et al., 2016).
Biomechanics Module
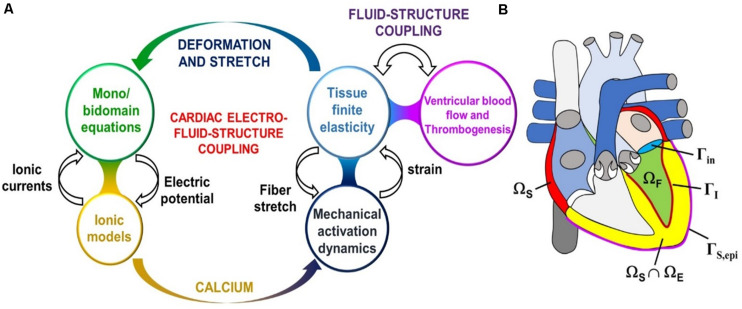
The next level of complexity are the models of myocardial abnormalities/heart failure (HF) and the blood pumping assist devices such as the Left-Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD). Since these models are interested in how the presence of abnormalities or assist devices affects the blood circulation, they must account for the contraction solid mechanics and the blood hemodynamics. However, if they are not interested in clot formation, the models are simplified by homogenizing the blood flow. Therefore, they are not as complicated as the ones that do account for the thrombosis. Yet, they are still complex, because they include solving multiple different types of coupled physics (see Figure 8, LEFT) applied in different parts of the heart (see Figure 8, RIGHT).
FIGURE 8.
(A) Sketch of the cardiac electro-fluid–structure coupling. (B) The three computational domains (fluid domain ΩF, solid mechanics domain ΩS, electrophysiology domain ΩE) considered in the cardiac multiphysics problem. In this example the electrophysiology physics are only considered in the ventricles, whereas the solid mechanics physics applies to the atria also. Additionally pictured are the fluid–structure interface ΓI inside the left ventricle, the epicardial surface ΓS,epi, and the mitral valve inlet surface Γin. Lastly, the domains ΩE and ΩS overlap within the ventricular part of the heart. (Adopted with permission from Quarteroni et al., 2017).
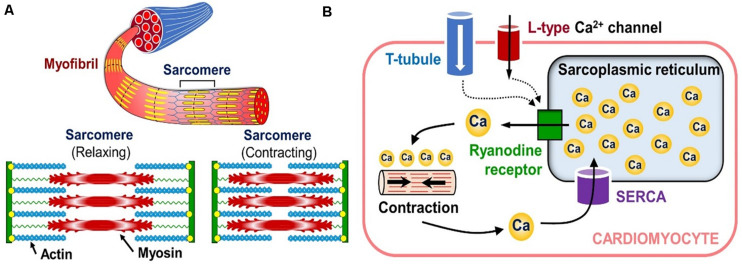
Since the electrophysiology in these models is treated similarly to the arrhythmia models, the cardio biomechanics framework will be discussed next. Central to this physics type is the fact that the myocytes in the heart contain rod-like structures called myofibrils, which are composed of repeating contractile units called “sarcomeres” (see Figure 9, LEFT). Each sarcomere contains thin and thick filaments, made from actin and myosin proteins, respectively.
FIGURE 9.
Sub-cellular tension generation mechanisms. (A) Organization of the cardiac muscle cell’s contraction mechanism (bottom inset shows the contraction-relaxation cycle of a single sarcomere). (B) Diagram showing how calcium release from internal cytosol storage causes cardiomyocyte contraction in response to the “outside-to-inside” calcium signaling.
After depolarization, calcium enters the cardio-myocytes through the ion channels in their membrane, and triggers the release of cytosolic calcium stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (a storage compartment) of the cells through a cascade of intra-cellular signaling (see Figure 9, RIGHT). This release of the internal calcium leads to the binding of myosin heads to the actin filaments in the sarcomeres, which in turn causes the filaments to slide against each other and contract the entire cell (see bottom inset in Figure 9, LEFT). This process is called the “crossbridge mechanism” and it corresponds to the active tension in the biomechanical calculations of the heart.
The kinetics of this process have been modeled using Monte Carlo (Walcott and Sun, 2009) and partial differential equations (Huxley, 1957). However, both approaches are too computationally expensive to be calculated at the organ level. Consequently, the latter model has been simplified by considering a single cross bridge representative of the whole distribution (i.e., mean field theory) (Negroni and Lascano, 2008; Rice et al., 2008; Washio et al., 2012) or by averaging the distributions over a single cell (Bestel et al., 2001). Simpler yet is the assumption that the active contraction of the individual cells depends on the intracellular ionic concentrations and the local deformation gradient (Quarteroni et al., 2017). Ultimately, the microscopic sarcomere sliding velocity is related to the macroscopic strain along the myocardial fibers via a constitutive relationship (i.e., microscopic rate-of-strain depends on the macroscopic strain), such as the Hill-Maxwell rheological model which is a modification from Hill’s force-velocity relation (Sainte-Marie et al., 2006). Herein, a specific choice of the attachment and detachment rates was modified so that they were not only dependent upon the sarcomere strain, but also on the strain rate.
The active contraction can be expressed by the following active stress formulation from Rossi et al. (2014):
| (3) |
And the active strain formulation can be derived from Quarteroni et al. (2017):
| (4) |
Where, WA is the active component of the free energy, FA is the active deformation, ‘c’ is the intracellular calcium concentration, I4,f is the local deformation gradient invariant in the myofiber direction, and are elastic invariants (described in more details in Rossi et al., 2014). The incorporation of the microscopic active tension, , at the tissue level is a key aspect in the multi-scale framework of the cardiac function (Quarteroni et al., 2017) and can be derived by:
| (5) |
where RF−L(I4,f) is a function that represents the force–length relationship of the cardiac cells (defined in Ruiz-Baier et al., 2014) which depends on I4,f; f (c) specifies the amount of force generated by the cross-bridges in response to intracellular calcium release; and α is a positive parameter. Thus, the represents the active tension generated within the sarcomeres, which then drives the macroscopic muscular contractions.
In addition to the active tension generated by the cross-bridge mechanism, the solid mechanics calculations must also account for the passive stiffness of the myocardium (e.g., when it is expanded by the blood flow entering the heart). This is modeled by assuming that the myocardium is an isotropic linear elastic tissue. The general formulation of passive stress (i.e., Cauchy stress) can be expressed by Avazmohammadi et al. (2019):
| (6) |
Where, the second Piola–Kirchhoff stress tensor ‘S’ can be described in terms of the stored energy density function ‘W’ through: S = 2∂W/∂C, and ‘W’ can be derived based on Holzapfel–Ogden constitutive law which is divided into three parts - the isotropic isochoric part, the isotropic volumetric part, and the orthotropic part:
| (7) |
where
| (8) |
and the material parameters a, af, as, afs, b, bf, bs, bfs are experimentally fitted (Quarteroni et al., 2017). The parameter ‘κ’ is the bulk modulus that “penalizes” local volume changes to enforce the incompressibility of the tissue.
Furthermore, since stretching a cell changes the distance between the gap junctions and their neighbors, this leads to changes in the ion channels, and consequently, in the conductivity of the action potential from cell to cell. This electromechanics coupling is typically included by modifying the conductivity tensor in the original equation of the electrophysiological propagation (see Equation 2). Specifically, the fixed reference state conductivity tensor ‘D0’ is replaced with the spatial configuration conductivity tensor ‘D’. Furthermore, an explicit dependence on the solid deformation tensor ‘F’ is included into the conductivity tensor in order to account for the geometric feedback, due to deformation of the tissue structure (Quarteroni et al., 2017):
| (9) |
Moreover, an additional inward ionic current, induced by the stretch-activated channels, also contributes to the depolarization. This is commonly modeled as follows:
| (10) |
Where, ‘E’ and ‘g’ are the reversal potential and the maximal conductance of the channels.
Lastly, in vivo the heart is immersed in a pericardial fluid; and it is also loosely supported by a flexible double-layered pericardium membrane. Therefore, spring-like external support enforced by Robin-type boundary conditions (Moireau et al., 2012) are typically tuned to mimic the global motion of the modeled heart. An explicit solution of the pericardium–heart contact problem has been proposed as well (Fritz et al., 2014).
Module Personalization
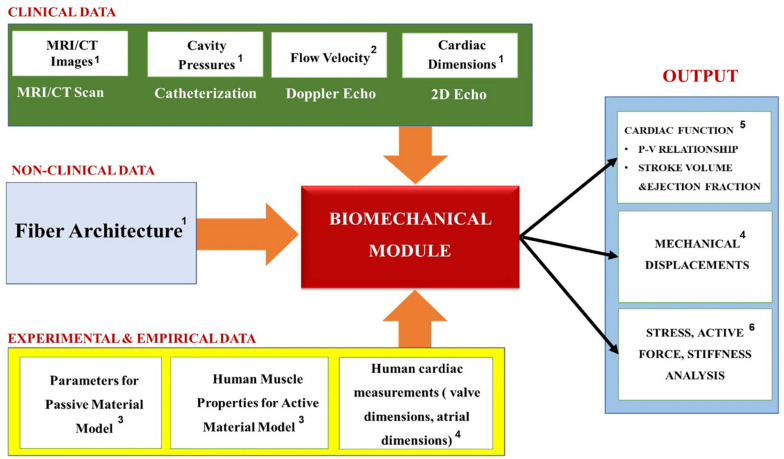
Table 2 summarizes the most common biomechanics module personalization approaches encountered in the recent IBM publications, while Figure 10 the relationships between the module’s inputs, outputs and applications. Before personalizing the modeling of the passive (i.e., resting) properties of the myocardium, the parameters of the Holzapfel and Ogden model (see Equations 7 and 8) are typically initialized using experimental data from biaxial (Krishnamurthy et al., 2013) and shear tests (Dokos et al., 2002; Sommer et al., 2015) of explanted myocardial tissue. The passive mechanics parameters are then further optimized to match the patient-specific end-diastolic pressure and volume (EDPV) relations (Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Meoli et al., 2015; Finsberg et al., 2018; Palit et al., 2018). The EDPV relation is a graphical representation of the pressure-volume loop related to the passive filling of the left ventricle during diastole (i.e., relaxation), and is a measure of the passive ventricle stiffness. The chamber volume of the left ventricle at the end of the diastole is defined as the end-diastolic volume (EDV), which is used to estimate the preloading volume of the heart and indicate the stiffness of the ventricle.
TABLE 2.
A recent literature survey of how the Biomechanics module is typically personalized using image-based information.
| Imaging method | Personalized Information from Imaging | Mapping of the Personalized Information from the Imaging to the Module’s Inputs | Citation |
| CT combined transthoracic 2D; and continuous-wave Doppler echocardiography | Geometry with Infarcted regions, ventricular dimensions including early diastolic volume, EDV, ESV and blood flow velocities | Geometry was personalized; passive mechanics parameters were fitted to match the previous experimental results on cardiac tissues and match patient-specific EDPV relations; active mechanics parameters were adjusted to match the patient-specific measured peak left ventricular pressures and ESV. | Krishnamurthy et al., 2013 |
| DT-MRI from explanted heart | Fiber direction | ||
| Cine cardiac MRI | Geometry with ventricular dimensions and ejection fraction (EF). | Geometry was personalized; passive mechanics parameters were fitted to match the previous experimental results and match the previous results of EDPV relations (due to the unavailability of subject-specific ventricular pressures that require invasive measurements). | Palit et al., 2018 |
| Cine cardiac MRI | Geometry with ventricular dimensions and regional strain-time | Geometry was personalized; passive mechanics parameters were fitted to match patient-specific EDPV relations; active mechanics parameters were adjusted to match the patient-specific end-systolic state. | Finsberg et al., 2018 |
| MRI flow tracing and echocardiographic Doppler velocity tracings | Geometry with ventricular dimensions and blood flow velocities. | Geometry was personalized; passive mechanics parameters were fitted to match the previous experimental results on cardiac tissues and match patient-specific EDPV relations; active mechanics parameters were adjusted to match the patient-specific measured peak left ventricular pressures. | Meoli et al., 2015 |
| MRI | Geometry with ventricular dimensions | Geometry was personalized; passive parameters were tuned so that the resultant EDV matched the corresponding MRI-measured cavity volume; active parameters were adjusted so that the resultant ESV matched the corresponding MRI-measured cavity volume. | Lee et al., 2013 |
| Cine MRI and Echocardiography | Geometry with ventricular dimensions and EF | Geometry was personalized; passive and active parameters were determined by minimizing the sum of the squared differences between computed and measured EF, stroke volume, EDV, ESV, end-diastolic pressure and end-systolic pressure. | Kayvanpour et al., 2015 |
| Cine MRI | Geometry with ventricular volume waveforms | Geometry was personalized; biomechanics parameters were tuned along with hemodynamics parameters; passive parameters were adjusted to match the measured EDPV; active parameters were adjusted to match patient-specific volume and pressure waveforms. | Shavik et al., 2020 |
| Phase-contrast MRI | Luminal area waveforms |
FIGURE 10.
Summary of the Biomechanics module’s inputs, outputs and applications. Superscripts in the figure correspond to the following references: 1Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Meoli et al., 2015; Finsberg et al., 2018; 2Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Meoli et al., 2015; 3Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Kayvanpour et al., 2015; Meoli et al., 2015; Finsberg et al., 2018; Palit et al., 2018; Shavik et al., 2020; 4Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; 5Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Palit et al., 2018; 6Lee et al., 2013; Meoli et al., 2015; Finsberg et al., 2018.
The active contraction modeling, on the other hand, is coupled with the cardiac hemodynamics, so it is important to link it with the patient-specific hemodynamic metrics corresponding with the end-systolic condition. For example, the pumping ability of the heart is represented by the end-systolic pressure (ESP) and the end-systolic volume (ESV), which are the peak values of pressure and ventricular volume at the end of systole (i.e., contraction), respectively. The active contraction is also associated with ejection fraction (EF), which is defined as a measurement of the percentage of blood leaving out of the left ventricle with each contraction. Therefore, the optimization procedure is performed to find the patient-specific parameters that best replicate the clinical hemodynamics of the patient in terms of the mean, maximum and minimum values of the pressures, flows and the cardiac volumes (such as the clinically recorded values of the ESP, ESV, and EF).
Module Outputs and Applications
Overall, the biomechanics models tend to perform stress analysis, which is used to evaluate the effects that a defective myocardium structure has on the heart function, and design new therapies and treatment devices for reducing the abnormal stress (Guccione et al., 2003; Wall et al., 2006; Lee et al., 2013; Finsberg et al., 2018) (see Figure 10). Additionally, they calculate the stiffness of the heart, which strongly corresponds to its ability to function normally and can be used as an indicator for HF (e.g., heart attacks caused by a diastolic dysfunction that occurs when the ventricle becomes too stiff or weak to pump blood effectively). Ultimately, however, since the goal of these models is to obtain the relationship between the biomechanics of the myocardium tissue and the blood pumping ability of the heart, they also include a simplified (i.e., no discrete blood cells) hemodynamics module, which is discussed in the next section.
Module Personalization Example
The following is a discussion of a representative example of the personalized Biomechanics module applied to five HF failure patients from San Diego Veteran’s Affairs Medical Center. Specifically, personalized 3D models of ventricular biomechanics in their failing hearts were derived from cardiac CT imaging. The human fiber orientation was modeled using DT-MRI data from an isolated (i.e., fixed) human organ-donor heart, and then transposed to the specific patient’s geometric model. The biomechanics model was then developed for optimizing the passive material properties to match previous experimental results on cardiac tissues and patient-specific end-diastolic pressure and volume relations. The material properties of the active contraction were also optimized to match patient-specific measured peak left ventricular pressures and end-systolic volumes. These components were then integrated to generate a multi-scale computational approach for the patient-specific hearts. The simulation results in the patients demonstrated good agreement with their measured echocardiographic and cardiac output parameters, such as EF and peak cavity pressures. This model was developed for stress analysis in HF patients and could be further developed with the goal of predicting treatments for heart disease under different interventions.
Simplified Hemodynamics Module
In the cardiovascular models where clot formation is not considered, the blood flow is simulated using the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. This means they do not account for discrete cells floating in the plasma. Instead the blood is treated as a homogeneous weakly non-Newtonian fluid (Shibeshi and Collins, 2005), which flows mostly in the laminar regime [though the strong vortices can create transition to turbulence with Reynolds numbers in the 1500–2500 range (Quarteroni et al., 2017)]. The fluid-structure interaction between the blood and the myocardium walls is typically modeled explicitly using moving mesh approaches: for example, Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (Cheng et al., 2005; Chnafa et al., 2014; Su et al., 2014), immersed boundary (Kohl et al., 2001; Vigmond et al., 2008) and level-set based methods (Mihalef et al., 2011). The heart valves, on the other hand, are commonly approximated using the Bernoulli equation for orifice flow (Flachskampf et al., 1990; Vandervoort Pieter et al., 1995; Donati et al., 2017).
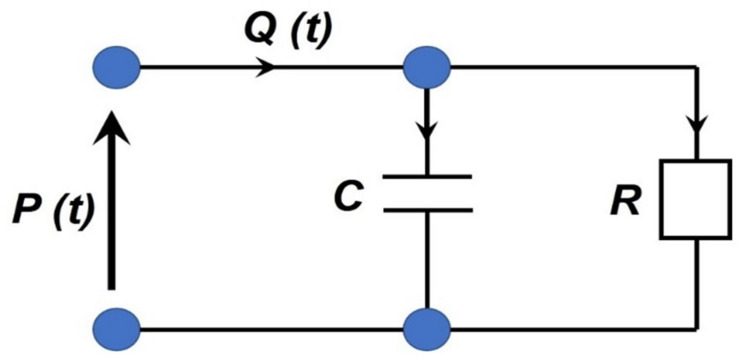
Additionally, the myocardium hemodynamics are typically coupled to the rest of the body’s circulation via the Windkessel circuit model, which mimics the arterial blood pressure’s waveform. This is a relatively simple method used to obtain the relationship between the blood flow and the pressure in a modeled segment through the resistive ‘R’ and the capacitance ‘C’ properties of the arterial vasculature (see Figure 11) (Wall et al., 2006). Specifically, the heart and the systemic arterial system are treated as a closed hydraulic circuit, which, contains a pump connected to a chamber partially filled with a liquid. As it is pumped, the latter compresses the air pocket in the chamber, which in turn pushes the liquid back out (i.e., creating a back-and-forth cycle). Consequently, the arterial compliance, the peripheral resistance, and the inertia are modeled as a capacitor, a resistor, and an inductor, respectively. In this model, the physiological variables such as pressure ‘P’ and flow ‘Q’ only vary as a function of time ‘t’ (Morris et al., 2016). The relationship between the flow rate Q(t) and the pressure P(t) can be expressed by:
FIGURE 11.
Two-element Windkessel circuit analogy illustrated.
| (11) |
It essentially states that the volumetric flowrate must equal to the sum of the volume stored in the capacitive element and the volumetric outflow through the resistive element. During the diastole there is no blood inflow (Q = 0), so the Windkessel equation can be solved for the P(t):
| (12) |
where td is the time of the start of the diastole and P(td) is the blood pressure at that time. Due to its simplicity, the Windkessel equation is frequently used to approximate various components and boundary conditions in the cardiovascular system (Morris et al., 2016). However, this model is only a rough approximation of the arterial circulation. To that end, the next section covers the approaches to more detailed hemodynamic formulations.
Hemodynamics With Thrombogenesis Module
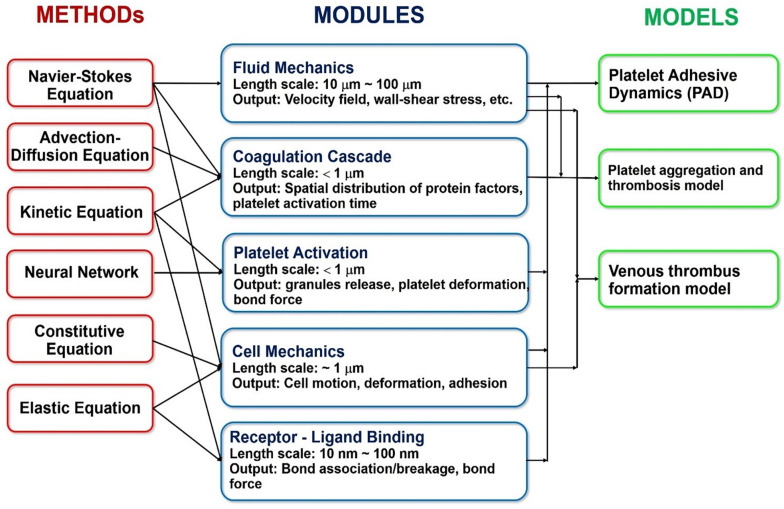
The last class of the cardiovascular models is the one in which the hydrodynamics of the discrete blood cells, and the biochemistry associated with their physiological activity, are of interest. For example, such simulations could be focused on studying pathological clot formation inside of the heart (Choi et al., 2015; Mittal et al., 2016; Seo et al., 2016; Harfi et al., 2017), or embolism into it from other parts of the body. Therefore, these types of models must simulate the blood as a suspension of deformable cells (e.g., platelets and/or red blood cells), whose fate is intertwined with the mechanical motion of the myocardium (and by association with the electrophysiology of the heart). This is typically done using Stokesian Dynamics methods, Dissipative Particle Dynamics, Completed Double Layer Boundary Integration Equation Method and Lattice Boltzmann Method (Wang and King, 2012). These are mesoscopic off- and on- lattice frameworks that calculate trajectories of the cells under the influence of hydrodynamic and Brownian forces; while the deformation of the structure is typically simulated using continuum-based models that treat the cell membrane and intracellular fluids as homogeneous materials: some popular approaches are the Boundary Integral Method, the Immersed Boundary Method, and the Fictitious Domain Method (Li et al., 2017).
To make matters even more complicated, the mechanism of the blood clot formation strongly depends on the following three processes: Receptor-Ligand Binding, Platelet Activation and the Coagulation Cascade. Specifically, the initiation of thrombus development starts with tethering of circulating platelets onto the exposed subendothelial layer where a blood vessel is injured. This process involves bonding between the various receptors on the platelet surfaces to the extravascular proteins, such as the von Willebrand Factor. It is typically modeled using a Monte Carlo approach called Adhesive Dynamics, while the rate of the receptor-ligand bond formation and breakage are determined by the Bell Model that calculates the probability of dissociation events occurring over a specific timespan.
Once the platelets have been recruited to the injury site, they undergo a metamorphosis that is generally described as “activation.” During this process, the membrane receptors transmit signals to the inside of the cells, which results in the dumping of chemical agonists stored in the internal vesicles called lysosomes and granules (e.g., dense and alpha). The release of these molecules then activates other neighboring platelets, which ultimately leads them to becoming “stickier” and compacting into the blood clot’s body. Unfortunately, the bottom-up description of the process contains numerous unknowns (Dolan and Diamond, 2014). For this reason, it has been instead described via a top-down Neural Network approach, which was trained on patient-specific experimental data (Flamm et al., 2012).
Lastly, the coagulation cascade is a system of coupled biochemical reactions with two different initiation pathways, which both ultimately lead to the polymerization of soluble fibrinogen (a blood plasma protein) into an insoluble fibrin mesh that holds the clot together. The kinetic portion of the cascade involves 34 differential equations, with 42 rate constants, that cumulatively account for 27 independent equilibrium expressions and fates of 34 chemical species (Hockin et al., 2002). Additionally, the mass transport of these species must be tracked under the flow conditions experienced in the cardiovascular system (which involves Knudsen diffusion within the porous clot). Figure 12 summarizes the coupling of the various hemodynamics submodules, as well as the methods used to solve them.
FIGURE 12.
Overview of the specific methods, modules and models commonly used in the state-of-the-art multiscale platelet hemodynamics and thrombus development studies. (Adopted with permission from Wang and King, 2012).
Module Personalization
Table 3 summarizes the most common hemodynamics module personalization approaches encountered in the recent IBM works, while Figure 13 maps the relationships between the module’s inputs, outputs and applications. Similarly to the previous modules, the macroscopic geometry of the heart, and that of the surrounding blood vessels, is commonly obtained for use in the Hemodynamics modules via the in vivo imaging techniques (such as MRI and CT). Additionally, for the body’s circulation, the parameters values for the Windkessel model (i.e. ‘R’ and ‘C’ elements) are typically chosen to match the patient specific cardiac output, flow waveforms and pressure pulses (Kim et al., 2009, 2010; Kung et al., 2014) obtained via contrast-enhanced CT scans, Doppler ultrasound scanning and invasive blood pressure measurements (IBPM). Particularly, the Doppler ultrasonography allows the measurement of the cardiac output and heart rate; and the IBPM allows to measure the systolic and diastolic pressures (Bonfanti et al., 2019). Specifically, they are first chosen based on literature data (Segers et al., 2002; Kim et al., 2009) and are then iterated until the calculated flow parameters match the subject’s unique physiological profile (Kim et al., 2009).
TABLE 3.
A recent literature survey of how the Hemodynamics modules are typically personalized using image-based information.
| Imaging method | Personalized Information from Imaging | Mapping of the Personalized Information from the Imaging to the Module’s Inputs | Citation |
| CT | Coronary arteries geometry | Geometry was personalized; parameter values for coronary model were obtained from literature; parameter values of lumped heart model (for the inlet) and Windkessel models (for the outlet) were adjusted to match subject-specific cardiac output and pulse pressure. | Kim et al., 2010 |
| MRI | Coronary arteries geometry | Geometry was personalized; parameter values of lumped heart model (for the inlet) and Windkessel models (for the outlet) were adjusted to match subject-specific flow distribution and measured brachial artery pulse pressure. | Kim et al., 2009 |
| CT angiogram | Right coronary artery with aneurysmal region | Geometry was personalized; Windkessel model’ parameters were adjusted to match subject-specific flow distribution and pressure at outlet boundary of the coronary artery. | Kung et al., 2014 |
| Phase contrast MRI | 3-component flow velocity at two slice locations in the coronary aneurysm geometry | ||
| Contrast-enhanced CT | Aortic dissection geometry | Geometry was personalized; inlet flowrate was obtained by adjusting a typical ascending aorta blood flow waveform to match the patient-specific hemodynamic data including cardiac output, heat-rate and systolic-to-diastolic duration ratio; for the outlet, Windkessel models parameters were adjusted to achieve patient-specific physiological flow distribution at each outlet, and to obtain the measured systolic and diastolic pressures at the inlet. | Bonfanti et al., 2019 |
| Doppler ultrasonography | Cardiac output and heart rate | ||
| CT angiogram | Coronary arteries geometry | Geometry was personalized; parameter values of lumped heart model (for the inlet) and Windkessel models (for the outlet) were adjusted to match subject-specific flow distribution and measured aortic pressure. | Grande Gutierrez et al., 2017 |
| 4D cardiac CT images and echocardiogram | Whole-heart geometry with kinematics of left ventricle lumen: heart rate, EDV, ESV, EF, stroke volume. | Geometry was personalized; the immersed boundary-based method is used to match the patient-specific kinematics of the left ventricular lumen including heart rate, EDV, ESV, EF and stroke volume. | Harfi et al., 2017 |
FIGURE 13.
Summary of the Hemodynamics modules’ inputs, outputs and applications. Superscripts in the figure correspond to the following references: 1Kim et al., 2009, 2010; Kung et al., 2014; Bonfanti et al., 2019; 2Tang et al., 2010; Choi et al., 2015; 3Kung et al., 2014; Grande Gutierrez et al., 2017; 4Kim et al., 2010; Bonfanti et al., 2019; 5Seo et al., 2016; Harfi et al., 2017; 6Koo et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2014; Min et al., 2015.
Unfortunately, due to the enormous complexities and computational costs of the heart modeling, oversimplifications are common in the personalization of the blood properties within the Hemodynamics modules. Given that it is typically assumed to be a Newtonian (or weakly non-Newtonian) fluid, it effectively does not contain discrete blood cells, such as the platelets or the erythrocytes. This, in turn, means that only simple flow properties, like fluid viscosity can be personalized to the subject. Consequently, the patient-specific biology of these cells (e.g., thrombotic propensity, sickle cell anemia, etc.) are omitted. Yet, in the non-cardio blood modeling, attempts at personalizing such functionality and disorders have been made: for example, the application of the Neural Networks trained on the patient-specific experimental data in order to phenotype the platelet activation (Flamm et al., 2012). However, we could not find an example of such an extensive blood personalization in the cardiovascular modeling literature.
Module Outputs and Applications
Figure 13 summarizes the inputs, outputs and applications of the cardiac hemodynamics module. Overall, the models that use the simplified hemodynamics formulation tend to calculate the blood flow parameters, like the pressure-volume relationship of the cardiac cycle. These, in turn, help to elucidate quantities that are key to understanding the heart dysfunctions: such as the end-diastolic and the end-systolic pressure volume relationships. Additionally, Fractional Flow Reserve, which is defined as the pressure difference across a coronary artery stenosis (e.g., a narrowing due to atherosclerosis), can be calculated to determine the likelihood that the latter would impede oxygen delivery to the heart and lead to a myocardial ischemia. Furthermore, the biomechanical models measure “compliance,” which is the ability of the blood vessel walls to stretch in order to accommodate an increasing amount of blood; and “resistance” (defined as the ratio of the pressure drop and the flow change across the segment) that the blood flow experiences due to viscous stresses and constrictions by the blood vessels. Most importantly, the biomechanics-hemodynamics modeling can be used to predict the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) - a main indicator of HF, which is expressed as a percentage of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. Lastly, such models can be used to investigate the effects of the blood pumping assist devices (e.g., LVAD) on the cardiac function, which may otherwise be too difficult or costly to study experimentally.
Conversely, the models that use the thrombogenesis hemodynamics module tend to try to assess the propensity of clot formation at (or near) the heart, based on parameters that are related to platelet activation: such as the Wall Shear Rate; the blood Residence Time Near a Damaged Tissue; the Ejection Fraction (i.e., the percentage of the blood leaving the left ventricle each time it contracts); Washout Ratio (i.e., the ratio of delayed ejection volume to the total ventricular blood at the beginning of the cycle). Additionally, some of these models simulate how drugs and clot breakup devices (e.g., Vena cava filters) help to protect the heart from pathogenic events. Overall, this is the most computationally expensive model type, due to the complexity of the thrombogenesis/embolism processes (which are themselves still being actively investigated) (Wang and King, 2012).
Module Personalization Example
The following is a discussion of a representative example of the personalized hemodynamics modeling applied to predicting the thrombosis risk in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) (Grande Gutierrez et al., 2019). Thrombosis is a major complication associated with coronary artery aneurysms (CAAs) resulting from the KD. In this research, the aneurysm hemodynamics were investigated for thrombotic risk stratification in ten KD patients, and were compared to the standard clinical guidelines for anticoagulation therapy. The patient-specific models were generated from MRI data by performing an angiography of: the heart, the main coronary arteries (right, left main, left anterior descending and circumflex), and the aorta and its arch branches (the brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery). This was done via the injection of gadolinium-based contrast with a cardiac and respiratory-gated 3D TrueFISP sequence. Computational hemodynamic simulations were then performed in the reconstructed anatomical model using SimVascular software (Grande Gutierrez et al., 2019). The pulsatile flow, deformable arterial walls and Windkessel parameters were tuned to match the patient-specific arterial pressure and cardiac output. Local hemodynamics variables were derived from the simulation results, including the time-averaged wall shear stress, low wall shear stress exposure and blood residence time. These variables were then used to develop a framework for predicting the thrombosis risk. Although platelet activation and aggregation are typically associated with regions of higher fluid shear (Casa et al., 2015) and longer blood stagnation (Hathcock James, 2006), this study showed that a combination of low shear stress coupled with a high residence time correlated to thrombus formation in the KD CAAs patients. Furthermore, it was shown that the prediction of the thrombotic risk using the hemodynamic variables was validated with a higher sensitivity and specificity in comparison with the standard clinical metrics. In conclusion, this type of personalized computational modeling can be used to provide a non-invasive thrombotic risk stratification that is more accurate than the current clinical approaches. This, in turn, can assist the long-term medical management of the KD patients with the CAAs.
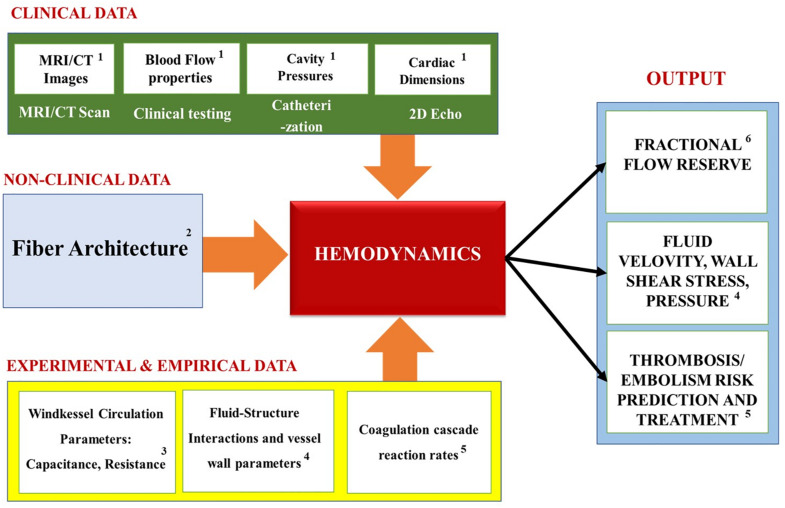
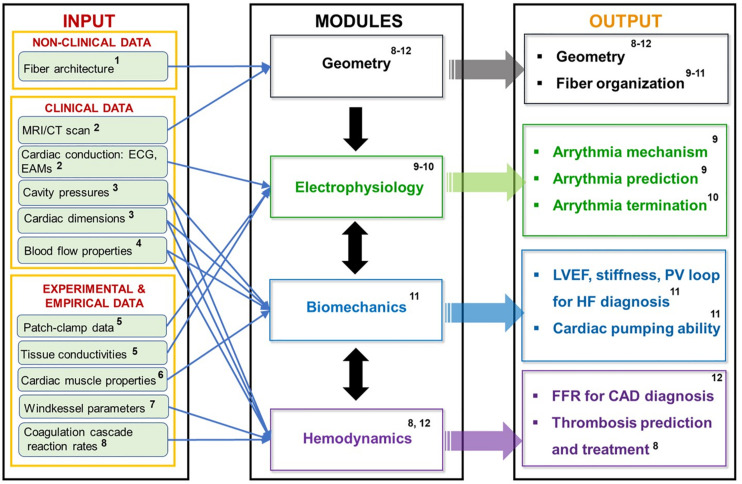
Summary and Conclusion
Most of the published cardiovascular modeling reviews are typically oriented at an expert audience, which makes it difficult for the outsiders to understand the full medical potential of these methods. One of the barriers to penetrating the field is that these works tend to focus on just one or two specific aspects of the simulation approach at a time: such as imaging (Weese et al., 2013; Lamata et al., 2014; Watson et al., 2018), electrophysiology (Lopez-Perez et al., 2015; Rodriguez et al., 2015; Beheshti et al., 2016; Gray and Pathmanathan, 2018; Ni et al., 2018), biomechanics (Wang et al., 2015; Chabiniok et al., 2016), hemodynamics (Zhong et al., 2018), electro-biomechanical coupling (Trayanova, 2011, 2012; Tobon-Gomez et al., 2013; Niederer et al., 2019b), biomechanics-hemodynamics coupling (Tang et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2014), etc. In contrast, our manuscript provides a “big picture” overview of the components that these models are built from; their mechanisms, inputs, outputs and connecting pipelines; the underlying physiological processes that they represent; their image-based personalization to the individual patient’s unique anatomy; and their applications to the different cardiovascular disease understanding and treatments.
As a part of our review, it was found that although this type of modeling holds a tremendous potential for revolutionizing personalized cardiovascular medicine, it is still in its infancy (with HeartFlow being the only commercially available product). Furthermore, due to the slow speed of high-resolution imaging, most of the IBM in academia still rely on scans of dead hearts (as opposed to beating ones). This, however, is expected to change, as the imaging speeds of mCT and MRI are increased. As far as the physics being modeled, the modules, their inputs and outputs are summarized in Figure 14. The simplest application of the cardiovascular IBM is to the study of arrythmias, which simulates the propagation of electrical impulses through the myocardium, while ignoring the biomechanics and hemodynamics. At the subcellular level, these models calculate transfer of ions across the cell membrane channels, while at the macro level the transfer of potential between the cells is modeled as a diffusive process. Conduction irregularities, ablation targets, and effects of defibrillation are just some of the outputs provided by the electrophysiological models.
FIGURE 14.
Summary of cardiovascular IBM’s modules and their respective inputs and outputs with corresponding references: 1Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Lopez-Perez et al., 2015; 2Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Cardenes et al., 2014; Kayvanpour et al., 2015; Lopez-Perez et al., 2015; 3Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Grande Gutierrez et al., 2017; Finsberg et al., 2018; 4Meoli et al., 2015; Bonfanti et al., 2019; 5Arevalo et al., 2016; Trayanova et al., 2017; Lopez-Perez et al., 2019; 6Krishnamurthy et al., 2013; Finsberg et al., 2018; Palit et al., 2018; 7Kung et al., 2014; Grande Gutierrez et al., 2017; Bonfanti et al., 2019; 8Choi et al., 2015; Seo et al., 2016; Harfi et al., 2017; 9Arevalo et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2016; Trayanova and Chang, 2016; Prakosa et al., 2018; 10Arevalo et al., 2016; Trayanova et al., 2017; Deng et al., 2019; 11Voorhees and Han, 2015; Walmsley et al., 2017; Lee et al., 2018; 12Koo et al., 2011; Min et al., 2012, 2015; Zhang et al., 2014; Min et al., 2015.
The more complex models account for the biomechanical processes occurring in the myocardium. These models are focused on how abnormalities in the tissue morphology and stiffness affect the pumping efficiency of the heart. At the subcellular level, they simulate how the electrically driven calcium signaling governs the crossbridge mechanism of the active tension generation via the actin-myosin interactions in the cells’ sarcomeres. Additionally, the solid mechanics calculation also involves the passive stress of the myocardium, which represents the stress-strain relationship of the cardiac fibers without the electrical stimulation. The resulting tissue deformation is then backwards-coupled to the electrophysiology, since the stretching of the cells can change the gap junction distance to their neighbors (which results in changes to the ionic conductivity).
Lastly, these models are coupled to the hemodynamics calculations via fluid-structure interactions. If only the blood flow without the clot formation is of interest, then the structure of the fluid is approximated to be homogeneous and Newtonian; while the rest of the body’s circulation is introduced as an oscillating pressure boundary condition that is assumed to behave like a simple RC circuit. This type of model can provide insight into HF due to deformities and obstructions, as well as allow for virtual design and testing of assisted pumping devices. On the other hand, if clotting information is necessary, the blood must be treated as a suspension of deformable particles, with receptor ligand interactions, intra-cellular signaling, and coupled biochemical reactions representing the coagulation cascade. Although a lot more involved, this type of model can be useful for antithrombotic drug development and design of clot breakup devices (e.g., Vena cava filters) meant to protect the heart. However, for simplicity most cardiovascular IBM do not account for the hydrodynamics and biomechanics of the individual blood cells. Likewise, the coagulation cascade and the platelet activation, both of which are central to thrombogenesis, are oversimplified relative to the state-of-the-art within the non-cardiovascular blood modeling field.
Overall, the cardiovascular IBM is expected to become more mainstream as the computational and imaging technologies advance. This could potentially revolutionize how cardiovascular medicine is done in the future. Yet, significant improvements are still required to personalize the models more. For example, a common limitation across all of the modules is that the myocardium (e.g., conductivity and tissue stiffness) and the blood (e.g., hematocrit, coagulation cascade and platelet activation kinetics and deficiencies) properties that they use are typically estimated based on empirical measurements performed ex vivo and using samples that are not derived from the same individual (or even from the same species for that matter). Therefore, better imaging methods need to be developed, such that these properties could be estimated by scanning the individual patient. Furthermore, a finer image resolution is needed to capture the individualized variations in the conductive and contractile fibers, and their junctions. Likewise, the computational methods need to improve their modeling of the intra-cellular processes (e.g., the crossbridge mechanism) for the cardiovascular IBM to become more physiologically representative and adopted by the mainstream clinical market. However, given the fast pace of the technological progress, the near future impact of the IBM on the cardiovascular medicine is imminent.
Author Contributions
TN and OK devised the manuscript, performed review of literature, and wrote the manuscript. RV provided the feedback and edits on all aspects of the manuscript. All the authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the copyright owners who allowed us to use their images in this manuscript. Additionally, Ms. Anh (Anne) Tong is graciously thanked for her useful discussions.
Glossary
Action Potential
A brief reversal (i.e., “depolarization” increase from a negative resting state followed by “repolarization” down to the original levels) in the voltage polarity of cardiomyocytes, which is generated by ion (e.g., Ca++, Na+, and K+) exchange across specialized channels in the cell membrane. The propagation of this electrical impulse through the heart tissue occurs via currents of the Ca++ and K+ ions moving through the gap junctions from the activated cells to their resting neighbors. This leads to the eventual contraction of the cardiac fibers along the conduction pathway.
Activation Rate Gradient
An arrythmia measure indicating a difference in the speed with which cardiomyocytes in the epicardial and in the endocardial tissues activate (i.e., depolarize/repolarize) in response to applied external stimuli (e.g., electrodes, needles, heat, blocking ion channels via medications, etc.) during Ventricular Fibrillation studies.
Bidomain Formulation
A mathematical framework that is used in Electrophysiology modeling to simulate the propagation of the Action Potential (see definition) through the myocardium. As opposed to the Monodomain Formulation (see definition), it considers both the intra- and the extra- cellular domains of the ion exchange across the cardiomyocyte membrane separately.
Cauchy–Green (Left and Right) Tensors
Rotation-independent measures of the material (e.g., myocardium tissue) deformation, in a spatial reference and in the object’s coordinate systems, respectively. They are often used when describing the passive properties of hyperelastic materials, such as the diastolic cardiac dysfunction.
Conductivity Tensor
A mathematical quantity that describes the electrical conductivity of the myocardium. This property is highly dependent on the orientation of the fibers that the conductive heart cells are arranged into within the tissue. For this reason, the effective conductivity of the myocardium differs, depending on the direction of the current flow. Therefore, the tensor encompasses 9 total conductivity values: three of them represent directions along each of the principle axes, while the other six express the correlation of the conductivity between each pair of the principal directions.
Deformation Gradient Tensor
A mathematical quantity that describes a shape change (e.g., stretch), as well as overall rotation, relative to an initial state of a material (e.g., cardiac fiber structure). It holds information about the difference in the current locations of neighboring cardiomyocytes and is unity when they are displaced equally (i.e., for no deformation).
Diffusion Tensor
A mathematical quantity calculated in magnetic resonance imaging to visualize structural arrangements (e.g., fibers, sheets) of the cardiomyocytes within the myocardium. It is based on at least 6 unique (plus one baseline) measurements of how the diffusion of water molecules is restricted or biased in different directions by the structural obstructions that they encounter during their motion in the tissues of the hearts. Therefore, the tensor encompasses three main elements that represent diffusion coefficients along each of the principal axes, while the off-diagonal terms reflect the correlation of random motions between each pair of principal directions.
Determinant of the Deformation Gradient Tensor
A scalar value corresponding to the ratio of the deformed to the undeformed volume, which is computed from the elements of the Deformation Gradient Tensor (see definition) in order to quantify the amount of transformation occurring in the cardiac geometry.
Invariant
A property of a mathematical quantity which remains unchanged after an application of an operation or a transformation. For example, when calculating strain and stress of the cardiac fibers it is important that the resulting principal values remain the same, regardless of the coordinate system chosen for their calculation or measurement.
Membrane Capacitance
A constant that describes the relationship between the voltage across the membrane of a cell and the ionic charge that builds up on its interior and exterior surfaces. In cardiomyocytes it effectively determines how quickly the Action Potential (see definition) can travel through the myocardium. It is therefore useful for both modeling and understanding their excitability and pathological conditions.
Monodomain Formulation
A mathematical framework that is used in Electrophysiology modeling to simulate the propagation of the Action Potential through the myocardium. As opposed to the Bidomain Formulation (see definition), it does not consider both the intra- and the extra- cellular domains of the ion exchange across the cardiomyocyte membrane. Instead, the framework is expressed in terms of a transmembrane potential, which assumes that the intracellular and extracellular ion diffusivities are proportional to each other.
Neural Network
A set of artificial intelligence algorithms, modeled loosely after how the human brain learns, that are designed to recognize patterns within complex datasets. In cardiovascular modeling specifically, they are used to represent processes that are too difficult to describe mathematically using first-principle methods: for example, platelet “activation” – a cascade of cell membrane surface receptor activation, intracellular signaling, dumping of granules, etc. – in the context of thrombosis.
Stored (a.k.a., Strain) Energy Density Function
Energy per unit volume of a material temporarily deformed by an applied force, like a coiled spring or a stretched elastic band. This quantity is commonly used to formulate constitutive force-deformation relationships that characterize the spatial and temporal variations in the orthotropic (i.e., different in the axial, radial, and circumferential directions) properties of the myocardium. It is largely dominated by the structural arrangements of the myocardial fibers in the heart tissue.
Footnotes
Funding. The study was financially supported by the New Jersey Health Foundation Grant #PC101-17 and the Gustavus and Louise Pfeiffer Research Foundation’s Major Investment Grant.
References
- Antzelevitch C. (2001). Basic mechanisms of reentrant arrhythmias. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 16 1–7. 10.1097/00001573-200101000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleton B., Qing W., Crozier S., Feng L., Wilson S., Ling X., et al. (2005). “An electrical heart model incorporating real geometry and motion,” in Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Shanghai, 345–348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo H. J., Vadakkumpadan F., Guallar E., Jebb A., Malamas P., Wu K. C., et al. (2016). Arrhythmia risk stratification of patients after myocardial infarction using personalized heart models. Nat. Commun. 7:11437. 10.1038/ncomms11437 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashikaga H., Arevalo H., Vadakkumpadan F., Blake R. C., Bayer J. D., Nazarian S., et al. (2013). Feasibility of image-based simulation to estimate ablation target in human ventricular arrhythmia. Heart Rhythm 10 1109–1116. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.04.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslanidi O. V., Nikolaidou T., Zhao J., Smaill B. H., Gilbert S. H., Holden A. V., et al. (2013). Application of micro-computed tomography with iodine staining to cardiac imaging, segmentation, and computational model development. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32 8–17. 10.1109/TMI.2012.2209183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avazmohammadi R., Soares J. S., Li D. S., Raut S. S., Gorman R. C., Sacks M. S. (2019). A contemporary look at biomechanical models of myocardium. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 21 417–442. 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-062117-121129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer J. D., Blake R. C., Plank G., Trayanova N. A. (2012). A novel rule-based algorithm for assigning myocardial fiber orientation to computational heart models. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40 2243–2254. 10.1007/s10439-012-0593-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beheshti M., Umapathy K., Krishnan S. (2016). Electrophysiological cardiac modeling: a review. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 44 99–122. 10.1615/CritRevBiomedEng.2016016454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behradfar E., Nygren A., Vigmond E. J. (2014). The role of Purkinje-myocardial coupling during ventricular arrhythmia: a modeling study. PLoS One 9:e88000. 10.1371/journal.pone.0088000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestel J., Clément F., Sorine M. (2001). “A biomechanical model of muscle contraction,” in Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2001, eds Niessen W. J., Viergever M. A. (Berlin: Springer; ), 1159–1161. 10.1007/3-540-45468-3_143 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop M. J., Plank G. (2011). Bidomain ECG simulations using an augmented monodomain model for the cardiac source. Proc. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58 2297–2307. 10.1109/TBME.2011.2148718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop M. J., Plank G., Burton R. A., Schneider J. E., Gavaghan D. J., Grau V., et al. (2010). Development of an anatomically detailed MRI-derived rabbit ventricular model and assessment of its impact on simulations of electrophysiological function. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 298 H699–H718. 10.1152/ajpheart.00606.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfanti M., Franzetti G., Maritati G., Homer-Vanniasinkam S., Balabani S., Díaz-Zuccarini V. (2019). Patient-specific haemodynamic simulations of complex aortic dissections informed by commonly available clinical datasets. Med. Eng. Phys. 71 45–55. 10.1016/j.medengphy.2019.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. M., Masse S., Nanthakumar K., Vigmond E. J. (2013). Transmural IK(ATP) heterogeneity as a determinant of activation rate gradient during early ventricular fibrillation: mechanistic insights from rabbit ventricular models. Heart Rhythm 10 1710–1717. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.08.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. M., Zahid S., Trayanova N. A. (2016). Towards personalized computational modelling of the fibrotic substrate for atrial arrhythmia. Europace 18 (Suppl. 4), iv136–iv145. 10.1093/europace/euw358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruegmann T., Boyle P. M., Vogt C. C., Karathanos T. V., Arevalo H. J., Fleischmann B. K., et al. (2016). Optogenetic defibrillation terminates ventricular arrhythmia in mouse hearts and human simulations. J. Clin. Invest. 126 3894–3904. 10.1172/JCI88950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton R. A., Plank G., Schneider J. E., Grau V., Ahammer H., Keeling S. L., et al. (2006). Three-dimensional models of individual cardiac histoanatomy: tools and challenges. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1080 301–319. 10.1196/annals.1380.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabo C., Boyden P. A. (2003). Electrical remodeling of the epicardial border zone in the canine infarcted heart: a computational analysis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 284 H372–H384. 10.1152/ajpheart.00512.2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenes R., Sebastian R., Berruezo A., Camara O. (2014). “Inverse estimation of ventricular Purkinje tree pathways from sequences of depolarization,” in Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Computing in Cardiology, Cambridge, MA, 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Casa L. D. C., Deaton D. H., Ku D. N. (2015). Role of high shear rate in thrombosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 61 1068–1080. 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.12.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CDC (2019). Heart Disease Facts [Online]. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/facts.htm (accessed on 26 December 2019) [Google Scholar]
- Chabiniok R., Wang V. Y., Hadjicharalambous M., Asner L., Lee J., Sermesant M., et al. (2016). Multiphysics and multiscale modelling, data–model fusion and integration of organ physiology in the clinic: ventricular cardiac mechanics. Interf. Focus 6:20150083. 10.1098/rsfs.2015.0083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Oertel H., Schenkel T. (2005). Fluid-structure coupled CFD simulation of the left ventricular flow during filling phase. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33 567–576. 10.1007/s10439-005-4388-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chnafa C., Mendez S., Nicoud F. (2014). Image-based large-eddy simulation in a realistic left heart. Comput. Fluids 94 173–187. 10.1016/j.compfluid.2014.01.030 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. J., Constantino J., Vedula V., Trayanova N., Mittal R. (2015). A new MRI-based model of heart function with coupled hemodynamics and application to normal and diseased canine left ventricles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 3:140. 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft (2019). HeartFlow [Online]. Available online at: https://craft.co/heartflow (accessed on 26 December 2019). [Google Scholar]
- Dass S., Suttie J. J., Piechnik S. K., Ferreira V. M., Holloway C. J., Banerjee R., et al. (2012). Myocardial tissue characterization using magnetic resonance noncontrast t1 mapping in hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 5 726–733. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.976738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K. F., Rudy Y. (2010). Ionic mechanisms of electrophysiological heterogeneity and conduction block in the infarct border zone. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 299 H1588–H1597. 10.1152/ajpheart.00362.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng D., Arevalo H. J., Prakosa A., Callans D. J., Trayanova N. A. (2016). A feasibility study of arrhythmia risk prediction in patients with myocardial infarction and preserved ejection fraction. Europace 18 (Suppl. 4), iv60–iv66. 10.1093/europace/euw351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng D., Jiao P., Ye X., Xia L. (2012). An image-based model of the whole human heart with detailed anatomical structure and fiber orientation. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2012:891070. 10.1155/2012/891070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng D., Prakosa A., Shade J., Nikolov P., Trayanova N. A. (2019). Sensitivity of ablation targets prediction to electrophysiological parameter variability in image-based computational models of ventricular tachycardia in post-infarction patients. Front. Physiol. 10:628. 10.3389/fphys.2019.00628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokos S., Smaill B. H., Young A. A., LeGrice I. J. (2002). Shear properties of passive ventricular myocardium. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 283 H2650–H2659. 10.1152/ajpheart.00111.2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan A. T., Diamond S. L. (2014). Systems modeling of Ca(2+) homeostasis and mobilization in platelets mediated by IP3 and store-operated Ca(2+) entry. Biophys. J. 106 2049–2060. 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.03.028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donati F., Myerson S., Bissell M. M., Smith N. P., Neubauer S., Monaghan M. J., et al. (2017). Beyond Bernoulli: improving the accuracy and precision of noninvasive estimation of peak pressure drops. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 10:e005207. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.005207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrer D., Van Dam R. T. H., Freud G. E., Janse M. J., Meijler F. L., Arzbaecher R. C. (1970). Total excitation of the isolated human heart. Circulation 41 899–912. 10.1161/01.CIR.41.6.899 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FDA (2019). 510(k) Premarket Notification. Silver Spring, MD: FDA. [Google Scholar]
- Finsberg H., Xi C., Tan J. L., Zhong L., Genet M., Sundnes J., et al. (2018). Efficient estimation of personalized biventricular mechanical function employing gradient-based optimization. Int. J. Numer. Method Biomed. Eng. 34:e2982. 10.1002/cnm.2982 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flachskampf F. A., Weyman A. E., Guerrero J. L., Thomas J. D. (1990). Influence of orifice geometry and flow rate on effective valve area: an in vitro study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 15 1173–1180. 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90260-V [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamm M. H., Colace T. V., Chatterjee M. S., Jing H., Zhou S., Jaeger D., et al. (2012). Multiscale prediction of patient-specific platelet function under flow. Blood 120 190–198. 10.1182/blood-2011-10-388140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangi A. F., Rueckert D., Schnabel J. A., Niessen W. J. (2002). Automatic construction of multiple-object three-dimensional statistical shape models: application to cardiac modeling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 21 1151–1166. 10.1109/TMI.2002.804426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz T., Wieners C., Seemann G., Steen H., Dossel O. (2014). Simulation of the contraction of the ventricles in a human heart model including atria and pericardium. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 13 627–641. 10.1007/s10237-013-0523-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger J. J., Buxton A. E., Cain M., Costantini O., Exner D. V., Knight B. P., et al. (2011). Risk stratification for arrhythmic sudden cardiac death: identifying the roadblocks. Circulation 123 2423–2430. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.959734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grande Gutierrez N., Kahn A., Burns J. C., Marsden A. L. (2017). Computational blood flow simulations in Kawasaki disease patients: insight into coronary artery aneurysm hemodynamics. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2017:e201729. 10.21542/gcsp.2017.29 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grande Gutierrez N., Mathew M., McCrindle B. W., Tran J. S., Kahn A. M., Burns J. C., et al. (2019). Hemodynamic variables in aneurysms are associated with thrombotic risk in children with Kawasaki disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 281 15–21. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.01.092 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. A., Pathmanathan P. (2018). Patient-specific cardiovascular computational modeling: diversity of personalization and challenges. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 11 80–88. 10.1007/s12265-018-9792-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guccione J. M., Salahieh A., Moonly S. M., Kortsmit J., Wallace A. W., Ratcliffe M. B. (2003). Myosplint decreases wall stress without depressing function in the failing heart: a finite element model study. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 76 1171–1180. 10.1016/s0003-4975(03)00731-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfi T. T., Seo J. H., Yasir H. S., Welsh N., Mayer S. A., Abraham T. P., et al. (2017). The E-wave propagation index (EPI): a novel echocardiographic parameter for prediction of left ventricular thrombus. Derivation from computational fluid dynamic modeling and validation on human subjects. Int. J. Cardiol. 227 662–667. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.10.079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathcock James J. (2006). Flow effects on coagulation and thrombosis. Arterioscl. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26 1729–1737. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000229658.76797.30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HeartFlow (2019). Transforming the Diagnosis and Management of Coronary Artery Disease Worldwide. Available online at: https://www.heartflow.com/ (accessed on 13 December 2019) [Google Scholar]
- Hockin M. F., Jones K. C., Everse S. J., Mann K. G. (2002). A model for the stoichiometric regulation of blood coagulation. J. Biol. Chem. 277 18322–18333. 10.1074/jbc.M201173200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Huxley A. F. (1952). A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117 500–544. 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. A., Scollan D. F., Winslow R. L. (2000). Direct histological validation of diffusion tensor MRI in formaldehyde-fixed myocardium. Magn. Reson. Med. 44 157–161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzapfel G. A., Ogden R. W. (2009). Constitutive modelling of passive myocardium: a structurally based framework for material characterization. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 367 3445–3475. 10.1098/rsta.2009.0091 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks D. A., Tomlinson K. A., Marsden S. G., LeGrice I. J., Smaill B. H., Pullan A. J., et al. (2002). Cardiac microstructure: implications for electrical propagation and defibrillation in the heart. Circ. Res. 91 331–338. 10.1161/01.res.0000031957.70034.89 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks D. A., Trew M. L., Smaill B. H., Pullan A. J. (2006). Do intramural virtual electrodes facilitate successful defibrillation? Model-based analysis of experimental evidence. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 17 305–311. 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2006.00360.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F. (1957). 6 - Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 7 255–318. 10.1016/S0096-4174(18)30128-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ideker R. E., Kong W., Pogwizd S. (2009). Purkinje fibers and arrhythmias. Pac. Clin. Electrophysiol. PACE 32 283–285. 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.02232.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayvanpour E., Mansi T., Sedaghat-Hamedani F., Amr A., Neumann D., Georgescu B., et al. (2015). Towards personalized cardiology: multi-scale modeling of the failing heart. PLoS One 10:e0134869. 10.1371/journal.pone.0134869 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keldermann R. H., ten Tusscher K. H. W. J., Nash M. P., Bradley C. P., Hren R., Taggart P., et al. (2009). A computational study of mother rotor VF in the human ventricles. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 296 H370–H379. 10.1152/ajpheart.00952.2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. J., Vignon-Clementel I. E., Coogan J. S., Figueroa C. A., Jansen K. E., Taylor C. A. (2010). Patient-specific modeling of blood flow and pressure in human coronary arteries. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38 3195–3209. 10.1007/s10439-010-0083-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. J., Vignon-Clementel I. E., Figueroa C. A., LaDisa J. F., Jansen K. E., Feinstein J. A., et al. (2009). On coupling a lumped parameter heart model and a three-dimensional finite element aorta model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37 2153–2169. 10.1007/s10439-009-9760-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. (2019). Fast Company Names HeartFlow One of the World’s Most Innovative Companies [Online]. Available online at: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20190220005218/en/Fast-Company-Names-HeartFlow-World’s-Innovative-Companies/ (accessed on 13 December 2019) [Google Scholar]
- Kohl P., Noble D., Hunter P. J., Kovács S. J., McQueen D. M., Peskin C. S. (2001). Modelling cardiac fluid dynamics and diastolic function. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 359 1299–1314. 10.1098/rsta.2001.0832 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Koo B. K., Erglis A., Doh J. H., Daniels D. V., Jegere S., Kim H. S., et al. (2011). Diagnosis of ischemia-causing coronary stenoses by noninvasive fractional flow reserve computed from coronary computed tomographic angiograms. Results from the prospective multicenter DISCOVER-FLOW (Diagnosis of Ischemia-Causing Stenoses Obtained Via Noninvasive Fractional Flow Reserve) study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58 1989–1997. 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy A., Villongco C. T., Chuang J., Frank L. R., Nigam V., Belezzuoli E., et al. (2013). Patient-specific models of cardiac biomechanics. J. Comput. Phys. 244 4–21. 10.1016/j.jcp.2012.09.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger M. W., Schulze W. H., Rhode K. S., Razavi R., Seemann G., Dossel O. (2013a). Towards personalized clinical in-silico modeling of atrial anatomy and electrophysiology. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51 1251–1260. 10.1007/s11517-012-0970-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger M. W., Seemann G., Rhode K., Keller D. U. J., Schilling C., Arujuna A., et al. (2013b). Personalization of atrial anatomy and electrophysiology as a basis for clinical modeling of radio-frequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32 73–84. 10.1109/TMI.2012.2201948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung E., Kahn A. M., Burns J. C., Marsden A. (2014). In vitro validation of patient-specific hemodynamic simulations in coronary aneurysms caused by Kawasaki disease. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 5 189–201. 10.1007/s13239-014-0184-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamata P., Casero R., Carapella V., Niederer S. A., Bishop M. J., Schneider J. E., et al. (2014). Images as drivers of progress in cardiac computational modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 115 198–212. 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.08.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. W. C., Costa C. M., Strocchi M., Rinaldi C. A., Niederer S. A. (2018). Computational modeling for cardiac resynchronization therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 11 92–108. 10.1007/s12265-017-9779-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. C., Wall S. T., Klepach D., Ge L., Zhang Z., Lee R. J., et al. (2013). Algisyl-LVR with coronary artery bypass grafting reduces left ventricular wall stress and improves function in the failing human heart. Int. J. Cardiol. 168 2022–2028. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.01.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Li H., Chang H. Y., Lykotrafitis G., Em Karniadakis G. (2017). Computational biomechanics of human red blood cells in hematological disorders. J. Biomech. Eng. 139 0210081–02100813. 10.1115/1.4035120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Perez A., Sebastian R., Ferrero J. M. (2015). Three-dimensional cardiac computational modelling: methods, features and applications. BioMed. Eng. Online 14:35. 10.1186/s12938-015-0033-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Perez A., Sebastian R., Izquierdo M., Ruiz R., Bishop M., Ferrero J. M. (2019). Personalized cardiac computational models: from clinical data to simulation of infarct-related ventricular tachycardia. Front. Physiol. 10:580. 10.3389/fphys.2019.00580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meoli A., Cutri E., Krishnamurthy A., Dubini G., Migliavacca F., Hsia T. Y., et al. (2015). A multiscale model for the study of cardiac biomechanics in single-ventricle surgeries: a clinical case. Interface Focus 5:20140079. 10.1098/rsfs.2014.0079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mewton N., Liu C. Y., Croisille P., Bluemke D., Lima J. A. (2011). Assessment of myocardial fibrosis with cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 57 891–903. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihalef V., Ionasec R. I., Sharma P., Georgescu B., Voigt I., Suehling M., et al. (2011). Patient-specific modelling of whole heart anatomy, dynamics and haemodynamics from four-dimensional cardiac CT images. Interface Focus 1 286–296. 10.1098/rsfs.2010.0036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min J. K., Koo B. K., Erglis A., Doh J. H., Daniels D. V., Jegere S., et al. (2012). Usefulness of noninvasive fractional flow reserve computed from coronary computed tomographic angiograms for intermediate stenoses confirmed by quantitative coronary angiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 110 971–976. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.05.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min J. K., Taylor C. A., Achenbach S., Koo B. K., Leipsic J., Norgaard B. L., et al. (2015). Noninvasive fractional flow reserve derived from coronary CT angiography: clinical data and scientific principles. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 8 1209–1222. 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.08.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincholé A., Zacur E., Ariga R., Grau V., Rodriguez B. (2019). MRI-based computational torso/biventricular multiscale models to investigate the impact of anatomical variability on the ECG QRS complex. Front. Physiol. 10:1103. 10.3389/fphys.2019.01103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R., Seo J. H., Vedula V., Choi Y. J., Liu H., Huang H. H., et al. (2016). Computational modeling of cardiac hemodynamics: current status and future outlook. J. Comput. Phys. 305 1065–1082. 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.11.022 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Moireau P., Xiao N., Astorino M., Figueroa C. A., Chapelle D., Taylor C. A., et al. (2012). External tissue support and fluid-structure simulation in blood flows. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 11 1–18. 10.1007/s10237-011-0289-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. D., Narracott A., von Tengg-Kobligk H., Silva Soto D. A., Hsiao S., Lungu A., et al. (2016). Computational fluid dynamics modelling in cardiovascular medicine. Heart 102 18–28. 10.1136/heartjnl-2015-308044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negroni J. A., Lascano E. C. (2008). Simulation of steady state and transient cardiac muscle response experiments with a Huxley-based contraction model. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 45 300–312. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.04.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni H., Morotti S., Grandi E. (2018). A heart for diversity: simulating variability in cardiac arrhythmia research. Front. Physiol. 9:958. 10.3389/fphys.2018.00958 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederer S. A., Campbell K. S., Campbell S. G. (2019a). A short history of the development of mathematical models of cardiac mechanics. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 127 11–19. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.11.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederer S. A., Lumens J., Trayanova N. A. (2019b). Computational models in cardiology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 16 100–111. 10.1038/s41569-018-0104-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara T., Virag L., Varro A., Rudy Y. (2011). Simulation of the undiseased human cardiac ventricular action potential: model formulation and experimental validation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 7:e1002061. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palamara S., Vergara C., Catanzariti D., Faggiano E., Pangrazzi C., Centonze M., et al. (2014). Computational generation of the Purkinje network driven by clinical measurements: the case of pathological propagations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 30 1558–1577. 10.1002/cnm.2689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palit A., Bhudia S. K., Arvanitis T. N., Turley G. A., Williams M. A. (2018). In vivo estimation of passive biomechanical properties of human myocardium. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 56 1615–1631. 10.1007/s11517-017-1768-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadacci C., Finel V., Provost J., Villemain O., Bruneval P., Gennisson J.-L., et al. (2017). Imaging the dynamics of cardiac fiber orientation in vivo using 3D ultrasound backscatter tensor imaging. Sci. Rep. 7:830. 10.1038/s41598-017-00946-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. R., Dai D., Hernandez A. F., Douglas P. S., Messenger J., Garratt K. N., et al. (2014). Prevalence and predictors of nonobstructive coronary artery disease identified with coronary angiography in contemporary clinical practice. Am. Heart J. 167 846–852e842. 10.1016/j.ahj.2014.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathmanathan P., Gray R. A. (2018). Validation and trustworthiness of multiscale models of cardiac electrophysiology. Front. Physiol. 9:106. 10.3389/fphys.2018.00106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plank G., Burton R. A. B., Hales P., Bishop M., Mansoori T., Bernabeu M. O., et al. (2009). Generation of histo-anatomically representative models of the individual heart: tools and application. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 367 2257–2292. 10.1098/rsta.2009.0056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potse M., Krause D., Kroon W., Murzilli R., Muzzarelli S., Regoli F., et al. (2014). Patient-specific modelling of cardiac electrophysiology in heart-failure patients. Europace 16 (Suppl. 4), iv56–iv61. 10.1093/europace/euu257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakosa A., Arevalo H. J., Deng D., Boyle P. M., Nikolov P. P., Ashikaga H., et al. (2018). Personalized virtual-heart technology for guiding the ablation of infarct-related ventricular tachycardia. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2 732–740. 10.1038/s41551-018-0282-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarteroni A., Lassila T., Rossi S., Ruiz-Baier R. (2017). Integrated heart—coupling multiscale and multiphysics models for the simulation of the cardiac function. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 314 345–407. 10.1016/j.cma.2016.05.031 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J. J., Wang F., Bers D. M., de Tombe P. P. (2008). Approximate model of cooperative activation and crossbridge cycling in cardiac muscle using ordinary differential equations. Biophys. J. 95 2368–2390. 10.1529/biophysj.107.119487 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez B., Carusi A., Abi-Gerges N., Ariga R., Britton O., Bub G., et al. (2015). Human-based approaches to pharmacology and cardiology: an interdisciplinary and intersectorial workshop. EP Europace 18 1287–1298. 10.1093/europace/euv320 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero D., Sebastian R., Bijnens B. H., Zimmerman V., Boyle P. M., Vigmond E. J., et al. (2010). Effects of the purkinje system and cardiac geometry on biventricular pacing: a model study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38 1388–1398. 10.1007/s10439-010-9926-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roney C. H., Williams S. E., Cochet H., Mukherjee R. K., O’Neill L., Sim I., et al. (2018). Patient-specific simulations predict efficacy of ablation of interatrial connections for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation. Europace 20 (Suppl. 3), iii55–iii68. 10.1093/europace/euy232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi S., Lassila T., Ruiz-Baier R., Sequeira A., Quarteroni A. (2014). Thermodynamically consistent orthotropic activation model capturing ventricular systolic wall thickening in cardiac electromechanics. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 48 129–142. 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2013.10.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Baier R., Gizzi A., Rossi S., Cherubini C., Laadhari A., Filippi S., et al. (2014). Mathematical modelling of active contraction in isolated cardiomyocytes. Math. Med. Biol. 31 259–283. 10.1093/imammb/dqt009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainte-Marie J., Chapelle D., Cimrman R., Sorine M. (2006). Modeling and estimation of the cardiac electromechanical activity. Comput. Struct. 84 1743–1759. 10.1016/j.compstruc.2006.05.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte R. F., Sands G. B., Sachse F. B., Dössel O., Pullan A. J. (2001). Creation of a human heart, model and its customisation using ultrasound images. Biomed. Eng. 46 26–28. 10.1515/bmte.2001.46.s2.26 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Scollan D. F., Holmes A., Winslow R., Forder J. (1998). Histological validation of myocardial microstructure obtained from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 275 H2308–H2318. 10.1152/ajpheart.1998.275.6.H2308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian R., Zimmerman V., Romero D., Sanchez-Quintana D., Frangi A. F. (2013). Characterization and modeling of the peripheral cardiac conduction system. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32 45–55. 10.1109/TMI.2012.2221474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers P., Stergiopulos N., Westerhof N. (2002). Relation of effective arterial elastance to arterial system properties. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 282 H1041–H1046. 10.1152/ajpheart.00764.2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo J. H., Abd T., George R. T., Mittal R. (2016). A coupled chemo-fluidic computational model for thrombogenesis in infarcted left ventricles. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 310 H1567–H1582. 10.1152/ajpheart.00855.2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sermesant M., Peyrat J.-M., Chinchapatnam P., Billet F., Mansi T., Rhode K., et al. (2008). Toward patient-specific myocardial models of the heart. Heart Fail. Clin. 4 289–301. 10.1016/j.hfc.2008.02.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shavik S. M., Tossas-Betancourt C., Figueroa C. A., Baek S., Lee L. C. (2020). Multiscale modeling framework of ventricular-arterial bi-directional interactions in the cardiopulmonary circulation. Front. Physiol. 11:2. 10.3389/fphys.2020.00002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibeshi S. S., Collins W. E. (2005). The rheology of blood flow in a branched arterial system. Applied 15 398–405. 10.1901/jaba.2005.15-398 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N., de Vecchi A., McCormick M., Nordsletten D., Camara O., Frangi A. F., et al. (2011). euHeart: personalized and integrated cardiac care using patient-specific cardiovascular modelling. Interface Focus 1 349–364. 10.1098/rsfs.2010.0048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer G., Schriefl A. J., Andrä M., Sacherer M., Viertler C., Wolinski H., et al. (2015). Biomechanical properties and microstructure of human ventricular myocardium. Acta Biomater. 24 172–192. 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.06.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starobin J. M., Zilberter Y. I., Rusnak E. M., Starmer C. F. (1996). Wavelet formation in excitable cardiac tissue: the role of wavefront-obstacle interactions in initiating high-frequency fibrillatory-like arrhythmias. Biophys. J. 70 581–594. 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79624-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter Daniel D., Spotnitz Henry M., Patel Dali P., Ross J., Sonnenblick Edmund H. (1969). Fiber orientation in the canine left ventricle during diastole and systole. Circ. Res. 24 339–347. 10.1161/01.RES.24.3.339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su B., Zhong L., Wang X. K., Zhang J. M., Tan R. S., Allen J. C., et al. (2014). Numerical simulation of patient-specific left ventricular model with both mitral and aortic valves by FSI approach. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 113 474–482. 10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun W., Martin C., Pham T. (2014). Computational modeling of cardiac valve function and intervention. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 16 53–76. 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071813-104517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang D., Yang C., Geva T., Del Nido P. J. (2010). Image-based patient-specific ventricle models with fluid-structure interaction for cardiac function assessment and surgical design optimization. Prog. Pediatr. Cardiol. 30 51–62. 10.1016/j.ppedcard.2010.09.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobon-Gomez C., Duchateau N., Sebastian R., Marchesseau S., Camara O., Donal E., et al. (2013). Understanding the mechanisms amenable to CRT response: from pre-operative multimodal image data to patient-specific computational models. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51 1235–1250. 10.1007/s11517-013-1044-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayanova N. A. (2011). Whole-heart modeling: applications to cardiac electrophysiology and electromechanics. Circ. Res. 108 113–128. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayanova N. A. (2012). Computational cardiology: the heart of the matter. ISRN Cardiol. 2012:269680. 10.5402/2012/269680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayanova N. A. (2014). Mathematical approaches to understanding and imaging atrial fibrillation: significance for mechanisms and management. Circ. Res. 114 1516–1531. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayanova N. A., Chang K. C. (2016). How computer simulations of the human heart can improve anti-arrhythmia therapy. J. Physiol. 594 2483–2502. 10.1113/JP270532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayanova N. A., Pashakhanloo F., Wu K. C., Halperin H. R. (2017). Imaging-based simulations for predicting sudden death and guiding ventricular tachycardia ablation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 10:e004743. 10.1161/CIRCEP.117.004743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadakkumpadan F., Arevalo H., Prassl A. J., Chen J., Kickinger F., Kohl P., et al. (2010). Image-based models of cardiac structure in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2 489–506. 10.1002/wsbm.76 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadakkumpadan F., Rantner L. J., Tice B., Boyle P., Prassl A. J., Vigmond E., et al. (2009). Image-based models of cardiac structure with applications in arrhythmia and defibrillation studies. J. Electrocardiol. 42:e00151-10. 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2008.12.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valderrabano M., Chen P. S., Lin S. F. (2003). Spatial distribution of phase singularities in ventricular fibrillation. Circulation 108 354–359. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000080322.67408.B4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandervoort Pieter M., Greenberg Neil L., Pu M., Powell Kimerly A., Cosgrove Delos M., Thomas James D. (1995). Pressure recovery in bileaflet heart valve prostheses. Circulation 92 3464–3472. 10.1161/01.CIR.92.12.3464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter F. J., McCulloch A. D. (1998). Three-dimensional analysis of regional cardiac function: a model of rabbit ventricular anatomy. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 69 157–183. 10.1016/S0079-6107(98)00006-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigmond E. J., Clements C., McQueen D. M., Peskin C. S. (2008). Effect of bundle branch block on cardiac output: a whole heart simulation study. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 97 520–542. 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2008.02.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees A. P., Han H.-C. (2015). Biomechanics of cardiac function. Comprehens. Physiol. 5 1623–1644. 10.1002/cphy.c140070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walcott S., Sun S. X. (2009). Hysteresis in cross-bridge models of muscle. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11 4871–4881. 10.1039/B900551J [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall S. T., Walker J. C., Healy K. E., Ratcliffe M. B., Guccione J. M. (2006). Theoretical impact of the injection of material into the myocardium: a finite element model simulation. Circulation 114 2627–2635. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.657270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley J., van Everdingen W., Cramer M. J., Prinzen F. W., Delhaas T., Lumens J. (2017). Combining computer modelling and cardiac imaging to understand right ventricular pump function. Cardiovasc. Res. 113 1486–1498. 10.1093/cvr/cvx154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang V. Y., Nielsen P. M. F., Nash M. P. (2015). Image-based predictive modeling of heart mechanics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 17 351–383. 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071114-040609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., King M. R. (2012). Multiscale modeling of platelet adhesion and thrombus growth. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40 2345–2354. 10.1007/s10439-012-0558-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washio T., Okada J. I., Sugiura S., Hisada T. (2012). Approximation for cooperative interactions of a spatially-detailed cardiac sarcomere model. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 5 113–126. 10.1007/s12195-011-0219-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. R., Dormer J. D., Fei B. (2018). Imaging technologies for cardiac fiber and heart failure: a review. Heart Fail. Rev. 23 273–289. 10.1007/s10741-018-9684-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weese J., Groth A., Nickisch H., Barschdorf H., Weber F. M., Velut J., et al. (2013). Generating anatomical models of the heart and the aorta from medical images for personalized physiological simulations. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51 1209–1219. 10.1007/s11517-012-1027-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. M., Zhong L., Luo T., Huo Y., Tan S. Y., Wong A. S., et al. (2014). Numerical simulation and clinical implications of stenosis in coronary blood flow. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014:514729. 10.1155/2014/514729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Butters T. D., Zhang H., LeGrice I. J., Sands G. B., Smaill B. H. (2013). Image-based model of atrial anatomy and electrical activation: a computational platform for investigating atrial arrhythmia. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32 18–27. 10.1109/TMI.2012.2227776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong L., Zhang J.-M., Su B., Tan R. S., Allen J. C., Kassab G. S. (2018). Application of patient-specific computational fluid dynamics in coronary and intra-cardiac flow simulations: challenges and opportunities. Front. Physiol. 9:742. 10.3389/fphys.2018.00742 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]