To the Editor: Collision tumors are rare neoplasms comprising two cell populations that develop in juxtaposition to one another with minimal to no areas of intermingling.[1] The most common sites at which collision tumors occur have been reported to include the lungs, cranium, rectum, liver, uterus, bladder, and testis.[2,3] However, the biologic behavior of esophageal collision tumors remains largely unknown, with only a small number of studies originating from case reports having been published. This study reports five cases of esophageal collision tumors to provide evidence-based recommendations for the care of future patients.
We retrospectively reviewed five patients who underwent surgery at the Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences between January 2000 and December 2018 and were diagnosed with esophageal collision tumors based on a histopathologic examination. The clinicopathologic characteristics and prognoses of these patients with esophageal collision tumors are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinicopathologic characteristics of five cases of esophageal collision tumor.
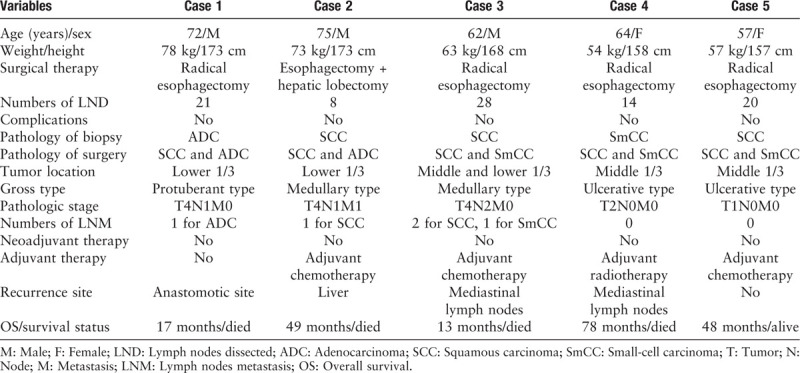
Case 1: A 72-year-old man presented at our department with epigastric pain and dysphagia for 3 months. Based on a provisional diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, the patient underwent an open trans-thoracic partial esophagogastrectomy with standard lymphadenectomy. Histologically, the tumor consisted of a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma that abutted a moderately differentiated squamous-cell carcinoma in a colliding manner. The patient did not receive adjuvant therapy. After 4 months of follow-up, he had a relapse of dysphagia and died of tumor recurrence at 17 months after the initial diagnosis.
Case 2: A 75-year-old man was admitted to our hospital for a focal liver lesion found during a routine physical examination. Enhanced computed tomography demonstrated thickening and an enhanced lesion in the cardiac wall as well as some swelling in a pericardial lymph node. The patient underwent proximal sub-total gastrectomy plus left hepatic lobectomy. Pathologic examination demonstrated an infiltrative malignant neoplasm comprising basal-like squamous-cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. There was no intermingling or transitional area between the two types. A metastatic adenocarcinoma of the left lobe of the liver was confirmed. Regarding liver metastasis, the patient received adjuvant therapy. However, the patient died of tumor recurrence at 4 years and 1 month after the initial diagnosis.
Case 3: A 62-year-old man who had experienced dysphagia for 3 months was admitted. Esophagogastrostomy with standard lymphadenectomy was performed. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated an infiltrative malignant neoplasm comprising moderately differentiated squamous-cell carcinoma and small-cell carcinoma. There was no merging of the tissue components of these tumors at the tumor cell interface. Given that the pathologic diagnosis was collision tumor as well as the advanced stage, the patient received three courses of adjuvant chemotherapy. There was no sign of recurrence until 6 months of follow-up. However, the patient died of tumor metastasis 13 months after the initial diagnosis.
Case 4: A 64-year-old woman was hospitalized with a 2-month history of a choking feeling accompanied by sub-sternal chest pain. The patient then underwent a radical esophagectomy with intra-thoracic esophagogastric anastomosis. The resected tumor comprised squamous-cell carcinoma and small-cell carcinoma on microscopic examination [Supplementary Figure 1A and 1B]. Immunostaining of the tumor cells demonstrated that the squamous component was strongly and extensively stained with cytokeratin 34βE12 (CK34βE12) [Supplementary Figure 1C] and p63. Additionally, the small cell component was positive for staining with synaptophysin [Supplementary Figure 1D], chromogranin A, cluster of differentiation 56 (CD56), and thyroid transcription factor 1. Two months after the operation, a computed tomography showed enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, suggesting metastasis; therefore, she received adjuvant radiotherapy. However, the patient died of tumor recurrence at 6 years and 6 months after the initial diagnosis.
Case 5: A 57-year-old woman complained of belching for one year and chest pain after swallowing for approximately 1 month. The patient underwent a minimally invasive McKeown esophagectomy together with extensive mediastinal and abdominal lymphadenectomy. Pathologic examination and immunohistochemistry confirmed that small-cell carcinoma and squamous-cell carcinoma tissues were collided at the middle of the esophagus. Immunostaining of the tumor cells demonstrated that the squamous component was strongly and extensively stained with CK34βE12 and p16. Additionally, the small cell component was positively stained with synaptophysin, chromogranin A, and CD56. The patient received four continuous courses of chemotherapy. She has showed no evidence of recurrence or metastasis 4 years after surgery and is currently living a normal life.
Collision tumors are not always easy to identify and should be distinguished from composite tumors or primary synchronous carcinomas. Nakata et al[4] proposed that collision tumors are dual-origin tumors that grow in proximity until they become juxtaposed, unlike composite tumors, which feature two divergent lineages that originate from the same neoplastic clonal proliferation. Obtaining a correct diagnosis of such conditions is important because individualized therapy and surveillance usually depend on the diagnosis. However, collision tumors are difficult to diagnose pre-operatively based on endoscopic biopsy and rely on observation of the sampled site of the collision tumor. Hence, it is important to obtain multiple tumor biopsy sites to improve the efficacy of pre-operative diagnosis. If immunohistochemistry remains inconclusive, molecular genetic analysis may be an important supplementary method for the diagnosis of collision tumors.[5] However, the etiology and oncogenic mechanisms of collision tumors remain unclear.
To date, surgery remains the first-line treatment for these patients. In general, these tumors are aggressive entities. Most of them have an unfavorable prognosis that is dependent on the tumor stage at diagnosis and the components involved in the collision tumor. Consequently, patients need to be closely followed after surgery, but little evidence is available to suggest the appropriate adjuvant therapy or interval for follow-up. Future studies that explore the pathogenesis and optimal management of this type of tumor are urgently needed.
In conclusion, esophageal collision tumors are clinically difficult to distinguish from non-collision tumors. Moreover, pre-operative diagnosis is rare, given that they present no special clinical or biologic features. Our report offers thorough insights into the clinicopathologic characteristics and biologic behavior of esophageal collision tumors and highlights the existence of rare collision tumors, which should receive more attention.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms in which the patient/family members of the patients provided their consent for the clinical information to be reported in the journal. They understand that the patient's name and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, although anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC1303201).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
How to cite this article: Zhang GC, Wang BZ, Wang LY, Wang YL, Guo W, Sun N, Gao SG, Xue Q, He J. Collision tumor of the esophagus: a report of five cases. Chin Med J 2020;133:2386–2388. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000982
References
- 1.Majmudar B, Dillard R, Susann PW. Collision carcinoma of the gastric cardia. Hum Pathol 1978; 9:471–473. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Syed S, Karambizi DI, Baker A, Groh DM, Toms SA. A comparative report on intracranial tumor-to-tumor metastasis and collision tumors. World Neurosurg 2018; 116:454–463. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schizas D, Katsaros I, Michalinos A, Damaskos C, Garmpis N, Ntomi V, et al. Collision tumors of the gastrointestinal tract: a systematic review of the literature. Anticancer Res 2018; 38:6047–6057. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nakata S, Nagata Y, Sugaya M, Yasuda M, Yamashita T, Takenoyama M, et al. Primary pulmonary collision cancer consisting of large cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg 2005; 80:340–342. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2003.12.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Terada T, Maruo H. Esophageal combined carcinomas: Immunohoistochemical and molecular genetic studies. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18:1545–1551. doi: 10.3748/wjg. v18.i13.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


