ABSTRACT
The term small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) refers to all those RNAs that even without encoding for a protein, can play important functional roles. Transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA-derived fragments (tRFs and rRFs, respectively) are an emerging class of ncRNAs originally considered as simple degradation products, which though play important roles in stress responses, signalling, or gene expression. They control all levels of gene expression regulating transcription and translation and affecting RNA processing and maturation. They have been linked to pivotal cellular processes such as self-renewal, differentiation, and proliferation. For this reason, mis-regulation of this novel class of ncRNAs can lead to various pathological processes such as neurodegenerative and development diseases, metabolism and immune system disorders, and cancer. In this review, we summarise the classification, biogenesis, and functions of tRFs and rRFs with a special focus on their role in immunity and cancer.
KEYWORDS: Transfer RNA fragments, ribosomal RNA fragments, tRFs, rRFs, tRNA cleavage, stress-induced tRNA cleavage, translation initiation, immune system, cancer
Introduction
In the past decades, the existence of functional regulatory small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) has been revealed in different species. Recent transcriptome-wide studies and advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies have allowed to the discovery and sequence of the big plethora of these small ncRNAs. The term non-coding RNA refers to all the RNA molecules that do not encode for a protein, without however excluding that such RNAs do not contain information or play a specific function in a cell[1]. For instance, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are ncRNAs with an important role in protein synthesis since they specifically recognise messenger RNA (mRNA) codons and transfer their charged amino acid into the growing peptide during translation [2]. Since the discovery in 1993 of small ncRNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans [3], many classes of small ncRNAs with various regulatory functions have been identified in a multitude of organisms of the eukaryotic domain [4]. The most well known are the small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs) and piwi–interacting RNAs (piRNAs). In this category are also included tRNA-derived small RNA fragments that have been recently discovered. tRNA fragments were first detected in the urine of cancer patients [5]. Since then, they have been described in all domains of life including bacteria, archaea, and eukaryote and they are considered a new class of ncRNAs called tRNA-derived small RNAs [6–11].
Initially, they were thought to be non-specific degradation products due to a defect in processing, folding, and damaged functions of an RNA molecule. However, a growing body of evidence indicates that fragmentation could also represent a different way to generate truncated transcripts that will perform distinct functions compared to the original RNA molecules [12]. Considering their abundance inside the cell, the most common source for RNA fragments is represented by tRNAs and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs). Small ncRNA-derived RNA fragments are usually 15–40 nucleotides (nt) long and are generated by endonucleolytic cleavage of fully mature transcripts mediated by different endoribonucleases [13]. These small RNA fragments have been implicated in specific biological functions such as suppression of gene expression, translational regulation, viral infections, regulation of survival, epigenetic inheritance, stem cell biology, cancer development, immune signalling or neurodevelopment disorders [14–23].
Recent research has revealed that tRNAs and rRNAs undergo stress-induced cleavage to produce stable RNA products that induce transient translational arrest [15,16]. All the cells contain specific mechanisms to adapt and respond to stress conditions such as cell cycle arrest, translation repression, repair, and in extreme cases cell death. Indeed, an important component of the stress response involves the control of RNA metabolism. RNA surveillance mechanisms play a crucial role in the control of RNA expression, allowing for a rapid downregulation of specific RNA molecules or degradation of aberrant RNAs [24]. Recent findings have shown that a fraction of the small RNA fragment pool presents a characteristic size distribution and origin that is different from siRNAs and miRNAs. Despite this difference, some of them have been also found to associate with AGO family members suggesting a role in gene expression regulation similar to miRNAs [25]. Furthermore, the RNA fragments show a specific response to the loss of components of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, suggesting the presence of an interplay between RNA silencing and RNA processing [26].
In this review, we have analysed RNA fragments generated from tRNAs and rRNAs with a special insight regarding their classification, biogenesis, post-transcriptional modifications, their role in gene expression silencing and translation and their association with immune system and cancer development and progression.
tRNA fragments: classification and biogenesis
Types of tRNA fragments
tRNA-derived fragments are generally classified according to their length, tRNA domain of origin and their function (Table 1). All are present in tissues and cells of different organisms. The class of tRNA regulatory fragments or tRFs, usually 13–30 nt in length, have a 3′-hydroxyl group, are similar to miRNAs at the 5′-phosphate and are produced by endonucleolytic cleavage of mature tRNAs or during pre-tRNA processing. They are classified into three mayor subclasses: tRF-1, tRF-3, or tRF-5, depending on their origin (Fig. 1A). tRF-3 and tRF-5 are generated from mature tRNAs by endonucleolytic cleavage. tRF-5s, also known as 5ʹtRFs, derive from 5ʹ end cleavage of tRNAs near the D-loop. tRF-3s, or 3ʹtRFs, derive from the 3ʹ end cleavage in the TψC-loop [6]. As 5′ and 3′tRFs derive from mature tRNAs, they likewise lack introns, and in most cases contain the post-transcriptionally added 3′CCA sequence and may carry plenty of base modifications. In contrast to tRF-3 and tRF-5, tRF-1 are generated from pre-tRNA processing of the trailer sequences and contained a poly-U tail at the 3ʹ end [11]. For instance, the tRF-1 called tRF1001 is generated by cleavage at the 3ʹ end of the precursor of tRNA-Ser-TGA. Due to their origin, their number, compared to the abundance of the other two subclasses of tRFs, is extremely lower. The class or family of endogenous tRFs is more complex and derive from cleavage of internal domains of mature tRNAs, they are variable in length and domain origin and their production seem to be linked to disease states [27,28]. Finally, the most known class is represented by the so-called tRNA halves are 30–40 bases long. 5ʹtRNA halves start from the 5ʹ end of a mature tRNAs and end in the anticodon loop, whereas 3ʹ tRNA halves start from the anticodon loop and terminate at the 3ʹ end of a mature tRNA [29]. Thompson et al., using a model of oxidative stress, observed a stress response that was accompanied by tRNA cleavage at the anticodon loop and was conserved from yeasts to mammals [10]. For this reason, originally tRNA halves were called stress-induced tRNA fragments, tiRNAs or tsRNAs (Fig. 1A). Although tiRNAs are mainly found in cells undergoing stress, tRNA halves can be found under non-stress conditions [30–32].
Table 1.
Definition of several features of the most common tRNA-derived fragments.
| Name and type | Length (nt) | Domain of origin | Endonucleases | Known Biological Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRNA fragment 1 (tRF-1) | 13-30 | Generated from pre-tRNA processing of trailer sequence | RNase Z (ELAC2) |
|
| tRNA fragment 3 (tRF-3) | 13-30 | Generated from mature tRNA by endonucleolytic 3ʹ-end cleavage in the TΨC loop |
|
|
| tRNA fragment 5 (tRF-5) | 13-30 | Generated from mature tRNA by endonucleolytic 5ʹ-end cleavage close to the D loop |
|
|
| 3ʹ tRNA halves | 30-40 | Generated from mature tRNA by endonucleolytic cleavage in the anticodon loop. Start from the anticodon loop and terminate in the 3ʹ-end of mature tRNA | Angiogenin and Rny1 |
|
| 5ʹ tRNA halves | 30-40 | Generated from mature tRNA by endonucleolytic cleavage in the anticodon loop. Start from the 5ʹ-end and terminate in the anticodon loop of mature tRNA | Angiogenin and Rny1 |
|
Figure 1.
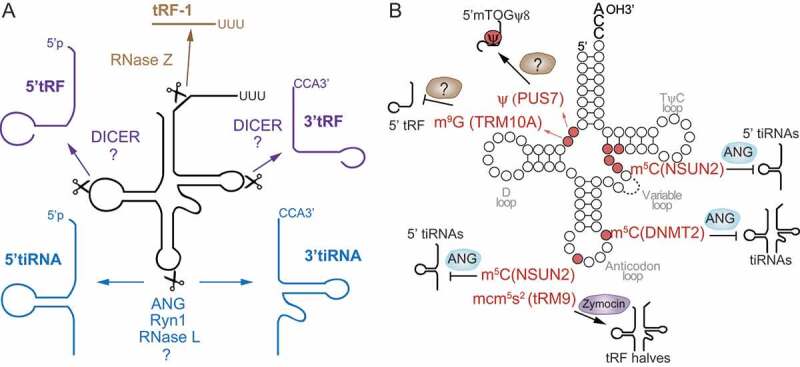
Biogenesis and diversity of transfer RNA-derived fragments (tRFs). A) Different types of tRFs are produced from pre-tRNAs or mature tRNAs. RNase Z removes the 3ʹ trailer of pre-tRNAs and produces tRF-1 (brown). Several tRFs are produced by endonucleolytic cleavage of the mature tRNAs. 3ʹtRF (or tRF-3s and 5ʹtRFs (or tRF-5s) (purple) are produced by DICER and other unknown endonucleases (?) cleaving at the D- and T-loop of mature tRNAs. 5ʹ and 3ʹtRNA halves or tiRNAs (light blue) are produced by endonucleolytic cleavage mediated by ANG and RNase L (in vertebrates), Ryn1 (yeast), and other unknown enzymes (?). B) The mature tRNA contains multiple modified nucleosides which regulate its cleavage into tRNA fragments. Modifications that affect tRNA cleavage are indicated in red as well as the modifying enzyme (in brackets) and the enzyme responsible for cleavage (when known) and the tRNA fragment that is produced by the modification (indicated by –>) or inhibited (indicated by –l).
Biogenesis
tRNA fragments were initially considered to be debris of the tRNA surveillance and clearance pathways that degrade tRNAs with altered structural and functional integrity [2]. However, we know now that the generation of each of these classes of tRFs is extremely regulated and mediated by specific endonucleases (Fig. 1A). Indeed, although tRNAs are one of the most abundant RNA species in the cell (~10% of total cellular RNA), only a small fraction of tRNAs is cleaved to produce tRFs [33]. Stress-induced cleavage at the anticodon loop of mature tRNAs to originate tRNA halves are produced by Angiogenin (ANG), an RNase Type A ribonuclease, in high eukaryotes, and Rny1, a member of the RNase T2 family, in yeast [15, 33]. ANG is induced by a large variety of stresses such as oxidative stress, UV irradiation, heat shock, or viral infection [15,30,31]. The primary targets of ANG in vivo in human HEK293T cells are exclusively tRNAs tRNA-Glu, tRNA-Gly, tRNA-Lys, tRNA-Val, tRNA-His, tRNA-Asp, and tRNA-SeC to produce tRNA halves and 5ʹtRFs that are 26–30 bases long [34]. Other endonucleases include endonucleases belonging to the RNase T2 family encoded by RNT2A, RNT2B and RNT2C genes in the protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila that are induced during amino acid starvation and contribute to the production of tRNA halves [7]. Ribonucleases of the RNase T2 family able to produce stress-induced tRNA fragments have not been found in mammals yet. Emerging data have also show that human cells may cleave tRNAs with RNase L in response to viral infections [35].
Concerning shorter tRFs, some studies have indicated that tRNAs show a secondary structure similar to a hairpin and this region is recognized and processed by DICER resulting in the generation of 5ʹtRFs and 3ʹtRFs [14,36–38]. Other reports have however indicated that biogenesis of most short tRFs is DICER independent [6,39], and mostly nothing is known concerning the identification of the endonucleases responsible for the cleavage in the D or TψC loops of mature tRNAs (Fig. 1A). Those contradicting facts may indicate that DICER is essential for the biogenesis of a particular signature of tRFs which is dependent on the cell type, tissue, organism, or condition, but it is not required for the vast number of tRFs. Several other enzymes have been implicated in the generation of tRFs in vertebrates. For instance, RNase Z (ELAC2) cuts off the 3ʹ trailer sequence from the tRNA precursors to produce mature 3ʹ ends and the trailer sequence being liberated gives rise to tRF-1 series [11,37].
Thus, tRNA fragmentation, by generating a wide variety of tRNA microspecies, amplifies the complexity of the small ncRNA repertoire for binding to regulatory factors that will trigger the activation of pathways to respond to specific signals.
RNA modifications in the regulation of tRNA cleavage
tRFs production is not random but cell type, tissue, condition, or disease associated. How endonucleases are activated and guided to the right tRNA domain or sequence motif is still beginning to be elucidated. tRNA base modifications seem to be some of the determinants of the biology associated with tRNA fragment biogenesis. Originally, it was thought that tRNA chemical modifications were a static process occurring on specific tRNA sites and tRNA modifications would contribute to secondary and tertiary structures preservation, thermodynamic stability, protection from degradation and rapid tRNA decay and translation control and fidelity (reviewed in [2]). However, recent evidences have shown that the population of covalent modifications dynamically fluctuate upon stress or along cell differentiation processes [40,41]. Some of these modifications have been shown to be inhibitory and protect from stress-induced endonucleolytic cleavage, and thus indicating that tRNA fragmentation is a stress-regulated process and is tuned by tRNA modifications (Fig. 1B).
Cytosine-5 methylation at position C38 at the anticodon loop of tRNAs was shown by Schaefer and Lyko to protect tRNAs from cleavage in Drosophila upon stress [8]. Deposition of 5-methylcytosine (m5C) at C38 is mediated by the methyltransferase DNMT2 and flies lacking Dnmt2 showed an accumulation of tRNA halves derived from the 5ʹ ends of DNMT2-tRNA targets [8]. While the fly ribonuclease responsible for the stress-induced cleavage of hypomethylated tRNAs was not found, Schaefer et al. showed that tRNAs lacking m5C38 were susceptible to be cleaved by the human recombinant ANG in vitro. These and other studies have suggested a role for tRNA modifications at the anticodon loop protecting from ANG-induced tRNA cleavage [42,43]. Later studies showed that lack of Dnmt2 in mice led too to 5ʹtRNA halves accumulation [44], however, mutant mice were not lethal. These studies suggested that tRNA fragmentation into tRNA halves is a well-monitored process activated during stress response and tRNA modifications play an important role impeding excessive loss of mature tRNAs, which would have lethal consequences.
Similar to DNMT2, the role of the cytosine-5 methyltransferase NSUN2 was later shown to be essential for tRNA halves biogenesis and stress responses. NSUN2 methylates cytosine residues mainly at the intersection of the variable loop and the T arm of most tRNAs [18] (Fig. 1B). In the absence of NSun2 in mice and humans, tRNAs are not methylated at the variable loop and are more vulnerable to be sliced by ANG, leading to the accumulation of 5′tiRNAs [18]. NSUN2-deficient human and mouse cells show reduced viability under stress conditions, which could be rescued upon treatment with ANG inhibitors [18,19]. In Blanco et al., the study suggested that while tRNA fragmentation is an essential event for the initial activation of the stress response, prolonged tRNA fragmentation and excessive accumulation of 5ʹtiRNAs were detrimental and cells would need to protect from it [18]. Indeed, NSUN2 expression was shown to decrease sharply right after cell exposure to stress, but the expression would recover hours later [18,45], suggesting that upon an initial period of decreased methylation activity, the subsequent increased expression of NSUN2 would fully methylate and protect tRNAs from ANG cleavage again. Deletion of Nsun2 in mice leads to neurodevelopment problems and microcephaly [18,46,47]. In humans too, inactivating mutations of NSUN2 lead to microcephaly and intellectual disability disorder [48]. These and other studies showed that lack of tRNA methylation, 5ʹtiRNAs and increased expression of ANG prompted cells into a state of stress hypersensitivity [15,18,19,30]. In sum, the studies indicated that the levels of cytosine-5 methylation of tRNAs fine-tune the production of a subtype of tRNA halves that regulate stress responses, suggesting that cells may vary the levels of tRNA methylation to survive. Indeed, in a recent study, Gkatza et al. showed that the levels of m5C changes site-specifically and dynamically in response to stress, which in turn influence tRF biogenesis [45].
Another tRNA modification protects tRNA from cleavage is 1-methylguanosie (m1G) at position G9 (Fig. 1B). This modification is catalysed by the tRNA methyltransferase TRMT10A [49]. TRMT10A deficiency leads to decreased of m1G deposition in tRNAs and to the accumulation of 22-nt long 5ʹtRFs derived from tRNA-Gln, suggesting that m1G9 protects tRNAs from endonucleolytic cleavage [49]. Both hypomethylated tRNAs in TRMT10A-deficient cells and transfection of cells with tRNA-Gln derived 5ʹtRFs increased β-cell apoptosis, leading to early-onset diabetes, microcephaly, and intellectual disability [49,50]. The enzymes generating tRNA fragments and the mechanism through which 5ʹtRFs trigger β-cell apoptosis remain to be elucidated.
There are, however, reports of tRNA modifications that are essential for endonucleolytic cleavage of tRNAs and tRFs biogenesis as is the case of wobble uridine (U34) modification catalysed by tRM9 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae [51] (Fig. 1B). Zymocin (γ-subunit) of the dairy yeast Kluyveromyces lactis induces cleavage in the anticodon loop of S. cerevisiae tRNA-Lys and tRNA-Gln that carry a 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine (mcm5s2U) residue at position 34 [52], and the lack of mcm5s2U reduces Zymocin cleavage efficiency. In a recent report, Guzzi et al. observed that Pseudouridine Synthase 7 (PUS7)-mediated pseudouridylation was a critical regulator of the biogenesis of tRFs in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) [17]. They found that Pseudouridine (ψ) at the eighth position of tRNAs regulated the production of 18-nt long tRNA fragments containing a 5ʹ terminal oligoguanine (mTOGs). They could show that mTOGs were enriched in hESCs and PUS7 deletion led to a significant depletion of mTOGs (Fig. 1B).
All these findings highlight the importance of tRNA modifications at any particular site in modulating the biogenesis of subsets of specific families of tRFs. Given the diversity of tRNA modifications within a tRNA and that any particular site can range from being unmodified to almost fully modified, modifications thus introduce an infinitive complexity that in different contexts may affect tRFs generation and function differently.
tRNA fragments’ molecular activity
It is now widely accepted that tRNA-derived small ncRNAs harbour biological activity and are not random fragmentation products due to increased cell death or stress. Since 2009 from their discovery, stress-induced tRNA fragments have been well characterized for having a conserved potent biological activity, which is repression of global protein synthesis and stress granule (SG) formation during stress [10,15,30,31]. Several other biological activities have been described for tRNA fragments. For instance, tRF-3 fragments can load into AGO complexes and have been involved in gene silencing, but also in retrotransposon silencing, ribosome biogenesis, and protein translation inhibition [14–17,22,23,25]. Other tRFs series have been shown to interact and participate in silencing activities.
Role of tRNA fragments in gene expression silencing
The discovery of stable tRFs-AGO complexes led to the hypothesis that tRFs could work as miRNA inhibiting gene expression. Initially, it was found that tRF-5s were only poorly associated with AGO complexes [36], while tRF-1s were found to be preferentially associated with AGO3 and AGO4 in human cell lines [37]. In addition, Haussecker et al. also observed that while target inhibition by tRF-1-s was not sequence-dependent, they found an miRNA-like target inhibition for tRF-5s and tRF-3s. Similarly, Kumar et al. found too that tRF-3s and −5s, but not tRF-1s, were associated with the four human AGO proteins [6].
However only recently, mRNA targets for tRF-AGO complexes have been identified. In Maute et al. a tRF-3 derived from tRNA-Gly (called CU1276) was shown to bind to AGO and repress Replication Protein A1 (RPA1), a gene implicated in DNA replication and repair [14]. In addition, they showed that a tRF-3 fragment shared structural and functional characteristics with miRNAs, including a DICER-dependent biogenesis. This was the first evidence that a tRF can play the role of a miRNA in mammals. Other sub-class of tRF-3s have been shown to repress mRNAs in an AGO-dependent manner with sequence complementarity to the 3ʹ untranslated region (UTR) [25].
tRF-5 fragments have been associated with post-transcriptional RNA silencing too. 12-nt long tRFs (5ʹtRFs and middle-derived tsRNAs) which are abundant in Drosophila were shown to repress the expression of specific targets in an RNAi-like manner [53]. In Luo S. et al. it was also shown that tRFs inhibit the translational efficiency of specific mRNAs by conserved antisense pairing. tRF-mediated target silencing was further found to be dependent on AGO2, however, unlike miRNAs, tRF-5s were able to bind equally effective all over the mRNA [53]. Another miRNA gene targeting function was also observed in virus-infected human cells, where tRF-5s would suppress antiviral target genes by sequence-specific binding to the 3′ UTR of viral mRNAs [54].
In sum, since AGO proteins are effector molecules of the RNA silencing complex, their association with tRFs suggests that tRFs are able to enter the RNAi pathway to regulate gene expression (Fig. 2A). However, while some reports have demonstrated tRFs target complementary-dependent gene silencing, a general understanding of AGO-dependent tRFs-targeting is still lacking.
Figure 2.
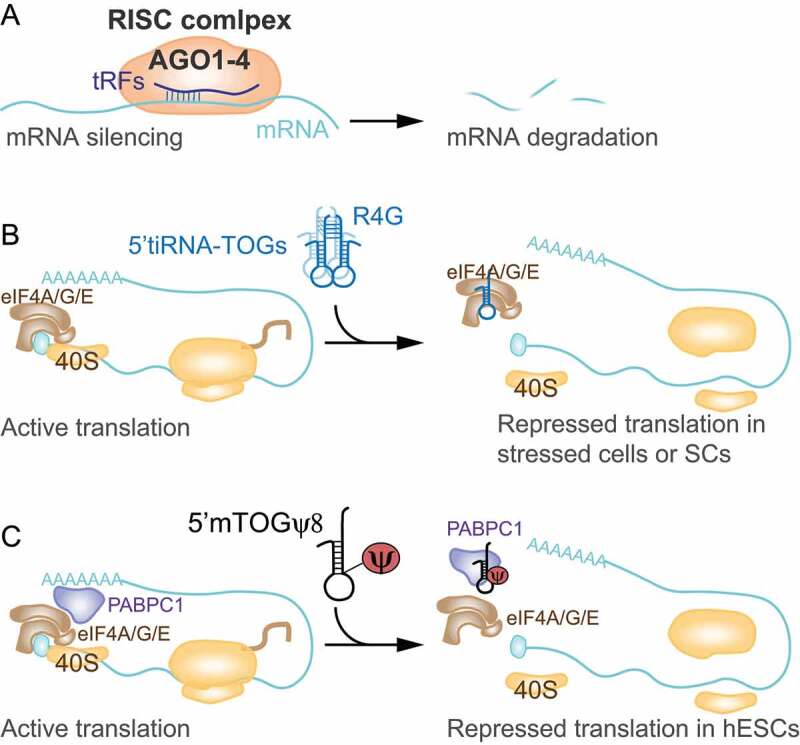
Mechanisms of tRFs-mediated sequence-specific gene silencing or repression of translation initiation. A) tRF-5s and tRF-3s associate with AGO proteins and sequence-specifically silence mRNAs. Target sites are found typically at the 3ʹ UTR, but also distributed all over the respective mRNAs. B) 5′tiRNAs with a 5′ TOG motif form an R4G structure that is required to displace the translation initiation complex eIF4A/G/E from capped mRNAs repressing translation initiation in cells under stress or in stem cells (SCs). C) In human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), 5′tiRNAs with a 5′ TOG and Ψ at position 8 displace PABPC1 from the translation initiation complex repressing translation of capped mRNAs.
Translation regulation by tRNA fragments
The finding that oxidative stress inhibited protein translation in cells expressing a non-phosphorylatable form of eIF2α set Paul Anderson and co-workers to find the alternative translation control pathway [55]. Their discovery introduced stress-induced tRNAs fragments as previously unappreciated components of the mammalian stress response [15]. The finding that transfected 5ʹ but not 3ʹtiRNAs inhibited protein synthesis revealed a functional difference between these tRNA fragments and excluded the possibility that the observed translation repression was not due to depletion of the pool of cytoplasmic tRNA. In addition, Thompson et al. discovered that tRNA cleavage was a conserved and regulated response to several stress signals in eukaryotes and was not a mechanism for quality control of non-functional tRNAs [10], in fact, the proportion of cleaved tRNAs was smaller than 1% of the pool of mature tRNAs [10,15,31]. To date, several mechanisms of translation inhibition have been discovered for these novel class of small ncRNAs.
In 2011, Ivanov et al. characterised one of the most studied translation inhibition mechanisms to date. They found that only the activity of 5ʹtiRNA-Ala and 5ʹtiRNA-Cys was able to trigger stress-induced translation repression [56]. Those 5ʹtiRNAs were characterised for binding to the translational repressor Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1, YBX1), and containing a stretch of five guanosine residues at the 5ʹ-end (TOG motif) [16]. Mechanistically, the authors showed that TOGs would assume G quadruplex (G4) structures and blocked translation initiation by specifically displacing 4eIF4G/eIF4A from capped mRNA preventing the assembly of the canonical translation pre-initiation complex [56]. This was shown to be partially due to the capacity of TOG-containing tiRNAs to bind to YB-1, since knocking down YB-1 only partially reversed translation repression, suggesting that other mechanisms were also involved in 5ʹtiRNA translation repression [16,57] (Fig. 2B). YB-1 interaction was later shown to be critical for packaging of tiRNA-repressed mRNAs into stress granules (SGs) but it was dispensable for tiRNA-mediated translational repression [30,58]. By contrast, in another recent study, it was shown that tiRNAs interaction with YB-1 displaced YB-1 from specific mRNAs resulting in the downregulation of those transcripts in breast cancer and mammary epithelial cells [27]. The different mechanisms showed by both studies was most likely due to the type of tiRNAs involved. While P. Ivanov showed that TOG-containing 5ʹtiRNAs bound to YB-1, in Goodarzi et al. tiRNAs were characterised for mapping to the anticodon region and containing a common linear sequence motif (SCUBYC) that could bind to YB-1. Whether YB-1-tiRNAs interaction can mediate eIF4G displacement from capped mRNAs remains to be elucidated.
More recently, Guzzi et al. have shown that in hESCs a specific class of 18-nt TOG-containing 5ʹtRFs (mTOGs) was able to displace eIF4A/G from m7G-coated beads. Remarkably they found that the presence ofαψ at position 8 was required for efficient mTOG-dependent displacement of eIF4A/G from capped-mRNAs. More importantly, they discovered that mTOGs containing ψ8 (mTOG-ψ8) preferentially bound to polyadenylate-binding protein 1 (PABPC1), another factor which interacts with eIF4G to enhance eIF4F formation and stimulate translation, resulting in the displacement of PABPC1 from capped mRNA and repressing translation [17] (Fig. 2C). They also showed that YB-1 was instead mostly bound by ψ-unmodified mTOGs. These data demonstrate that tiRNAs can impair translation initiation complex formation and in addition, RNA modifications govern mTOG function by regulating their binding to specific proteins tuning the function of 5ʹtRFs in translation.
Other tRFs have been shown to inhibit protein synthesis by alternative mechanisms. Gebetsberger et al. found that 26-nt long 5ʹtiRNAs derived from tRNA-Val and produced upon stress (Val-tRF) in Haloferax volcanii were able to repress translation by directly binding to the small ribosome subunit [9]. More recently, the authors found that Val-tRF binds to the mRNA channel and competes with mRNA binding to the small ribosomal subunit and thus interfering with the formation of the translation initiation complex [59]. Other works demonstrated that both stress-dependent 5ʹand 3ʹtiRNAs in S. cerevisiae are able to block protein synthesis under stress conditions by binding to ribosomes [60]. Hutvagner’s group presented similar data showing that 19-nt long 5ʹtRF derived from tRNA-Gln characterised for containing 3′ terminal ‘GG’ dinucleotide motifs that were able to repress translation in human cells by interacting with the Multisynthetase complex (MSC), a complex involved in translation [61,62].
While most reports have shown that stress-induced tRFs interfere with initiation complex formation or the interaction of mRNA and the ribosomal subunits, other reports have described alternative mechanisms that either stimulate or inhibit global protein translation. ANG, besides the ability to cleave in the anticodon region of tRNAs, it cleaves 3ʹ CCA end of tRNAs [63]. While this report indicated an alternative role of ANG-induced tRNA cleavage in translation inhibition through a global depletion of translationally competent tRNAs, ANG endonuclease activity on the 3ʹ CCA ends has only been shown in vitro and in vivo data remains unclear. In contrast, other reports have indicated that tRF can affect translation of specific transcripts without affecting global translation. In Kim et al., the authors discovered how a 22-nt long 3′tRF derived from tRNA-Leu-CAG (LeuCAG3′ tsRNA) enhances specific transcript translation in hepatocellular cancer cells [64]. The authors established that there is a direct physical interaction between LeuCAG3′ tsRNA and mRNAs of at least two ribosomal proteins, RPS28 and RPS15. They found that the inhibition of LeuCAG3′ led to a decrease in RPS28 protein levels, which in turn blocked pre-18S rRNA processing, resulting in a reduction of 40S ribosomal subunits. More recently they have shown the functional target sites present in many vertebrates suggesting that LeuCAG3ʹ-regulated translation is a conserved gene regulatory mechanism [65]. Further investigation will be required to establish whether other tsRNAs may regulate translational of specific transcripts in a similar fashion. tRFs can enhance global translation too. In a recent study published by Polacek’s group, the authors have identified 3ʹtRNA halves that when associated with ribosomes and polysomes unexpectedly stimulated global translation during the stress recovery phase particularly after prolonged starvation Trypanosoma brucei [66]. They further described that 3ʹtRNA halves derived from tRNA-Thr lacking the 3′ CCA end produced during nutritional stress and during the stationary phase in the procyclic form of T.brucei. They concluded that mechanistically tRNA-Thr halves lacking the 3′ CCA counteracted and inhibited the activity of inhibitory small RNAs in the same size range, including tRNA-derived RNAs, present in stressed cells.
It is well established that stress-induced tRFs and ANG have been reported to mediate a stress response, which results in SG assembly and inhibition of protein synthesis [30]. However, the exact mechanism underlying the regulation of stress response processes remains still unclear. SGs formation upon tRNAs cleavage induction promotes cell survival by sequestering proapoptotic signalling proteins, translationally stalled ribonucleoprotein complexes and promoting selective recruitment of ribosomes to mRNAs whose protein products are required for responding to stress (reviewed in [67]). For instance, ribosome profiling data from Nsun2 deficient mice or human cells derived from patients carrying inactivating mutations in NSUN2 showed an increased production of 5ʹtiRNAs and increased translation of genes associated to stress response pathways [19]. While the exact mechanism and whether 5ʹtiRNAs directly favoured translation of the specific set of transcripts are still unknown, mechanistically the data showed an increased ribosomal density on 5ʹ UTRs. Importantly the data also showed decreased ribosomal densities on genes associated with development, differentiation, and migration, indicating that 5ʹtiRNAs could regulate too cell motility and differentiation processes. Indeed, accumulation of 5ʹtiRNAs in Nsun2-deficient cells was associated with decreased development, defective differentiation and reduced cell migration in mouse embryos and adult tissues [18,19,46,47]. In a similar study, lack of Dnmt2 in mice led too to 5ʹtRNA halves accumulation and deficient haematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [44]. Similarly in Krishna et al., the authors observed that a specific set of 5′tRFs was enriched during differentiation of mouse ESCs, which sequestered the ribosomal binding protein IGF2BP1 from cMyc mRNA, a potent regulator of pluripotency, which in turn is no longer stabilized and gets degraded perpetuating differentiation processes [20]. Similar results were found in Guzzi et al. [17]. They observed that PUS7 was preferentially enriched in hESCs and its loss led to decreased pseudouridylated mTOGs production, increased protein translation rates, defective mesoderm specification, and haematopoietic stem cell commitment. While the authors could show that translation initiation was regulated by pseudouridylated mTOGs, it is still undetermined the exact mechanism by which those tiRNAs regulate differentiation processes. In addition, given that extensive base modifications in tRNAs are crucial for their function, future studies should address the potential role of these modifications in tRNA fragments as well as whether they can cooperate to redirect the translation machinery to specific sets of mRNAs.
In sum, all these mechanisms indicate an adaptive translation control by which cells quickly modulate their biological processes in response to environmental changes. This processes may lead to the generation of proteins with distinct functions that may help the cells to adapt to a new environment or stress condition.
tRNA fragments and Immunity
The connection between small ncRNAs and immune system has already been well documented, given the role that miRNA and siRNA play in suppressing gene expression. miRNA and siRNA affect all facets of immune system development, from haematopoiesis to activation in response to infection and host–virus interaction [68]. For instance upon viral infections, host cells alter their small ncRNA expression profiles as a defence mechanism. On the other hand, viruses can circumvent host defence and promote their propagation by altering cellular small ncRNA expression or by expressing their own small ncRNAs [69]. Most of the information about this mechanism is related to RNAi pathways while other kind of small ncRNAs remain largely unexplored. For this reason, and for the previous analysed association with AGO proteins, there are strong indications that also tRNA fragments could influence the immune system responses.
In 2013 in Wang et al. the authors analysed the effect that the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) had on the immune system response. They showed that in human airway epithelial cells, RSV was able to induce tRNA cleavage in the anticodon site, resulting in the induction of tRNA halves formation [70]. They found that RSV-induced tRFs derived mainly from 5ʹ ends and resulted to be important molecules for viral replication. In addition, one of the identified tRFs, tRF-5-GluCTC, exhibited trans-silencing capability against target genes and therefore had gene-silencing activity that was, in any case, different from that of miRNAs/siRNAs. They concluded that the positive effects of tRFs on viral replication were most likely due to the suppression of host defence gene expression.
In order to identify the molecular mechanism by which RSV–induced tRNA fragments can inhibit host immune system, in Deng et al., the authors used an unbiased approach combining biochemical screenings, gene expression data analysis and in silico sequence complementary prediction to identify tRF targets [54]. In particular, they studied the tRF5-GluCTC previously described in Wang et al. [70] because of its trans-silencing capability and found different tRF5-GluCTC sequence-complementary targets. One of the targets under study was the apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (APOER2), a cell surface receptor involved in many processes, such as neuronal development and immunity. They found that tRF5-GluCTC was able to suppress APOER2 mRNA expression using its 3′-portion to recognize a target site in the APOER2 3′ UTR (Fig. 3A). Among all the different functions of the receptor, APOER2 can inhibit RSV replication. The inhibition promoted by tRF5-GluCTC on the receptor had, therefore, a positive effect on virus replication [54].
Figure 3.
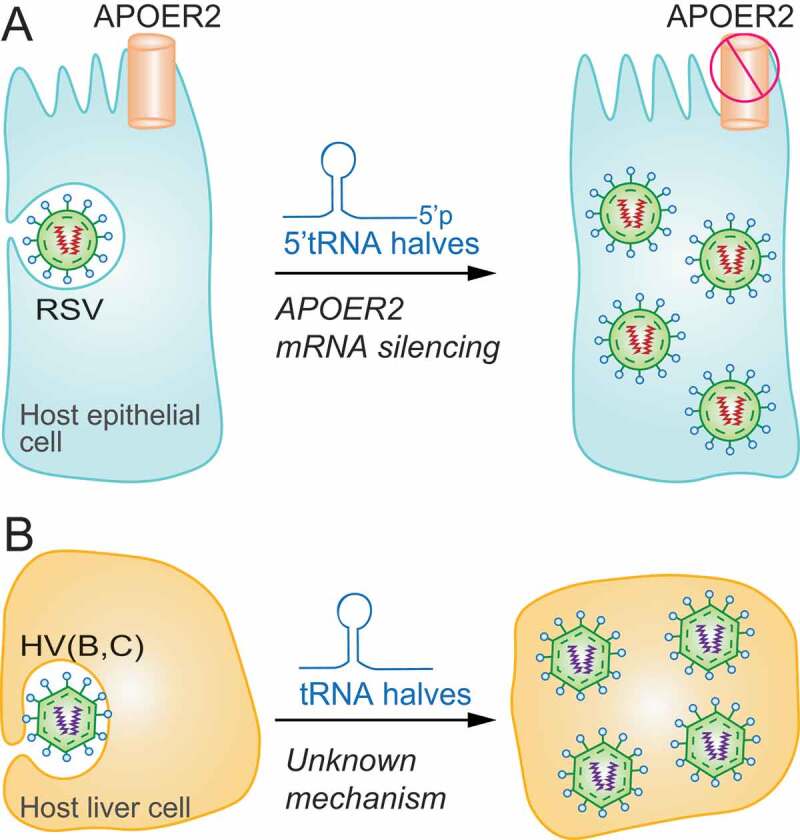
tRFs facilitate viral infections. A) 5ʹtRNA half biogenesis increases upon respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection to silence the expression of host genes (APOER2) and facilitate viral replication in epithelial cells. B) Hepatitis B and C virus (HV (B, C)) trigger tRNA half biogenesis which in turn facilitate viral replication via an unknown molecular mechanism in hepatocytes.
Considering the connection between tRFs and RSV infection, other studies have aimed to analyse the process and prove whether tRNA cleavage is one of the mechanisms carried out by viruses to escape from host immune system. In contrast with RSV, increased accumulation of tRFs was not observed in cells infected with human metapneumovirus (hMPV), despite considerable alterations in the miRNA pool [71]. Nevertheless, in hepatocytes of patients affected by B and C hepatitis, a considerable accumulation of tRNA fragments was found. Specifically, the levels of tRNA halves resulted significantly increased in non-malignant liver tissue of patients with chronic viral infections, while ANG mRNA levels were reduced in both B and C associated cancer compared to non-malignant tissue [72]. Even if the reason for such accumulation of tRFs and the biological function are still undescribed, evidences support that infection-induced tRF biogenesis is a mechanism that enhances viral replication, as observed for RSV, as well as a response mechanism to specific types of cellular stress (Fig. 3B). Another function assigned to tRFs is priming activity for reverse transcriptase. A tRF-3 derived from tRNA-Pro was shown to be capable of priming HTLV-1 (Human T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma virus type 1) reverse transcriptase, thus suggesting an important role of these tRFs in HTLV-1 viral infection [22].
In addition, there are strong evidences supporting the idea that tRNA fragments could regulate immune cells. For instance deep sequencing studies revealed that tRFs derived from the 5ʹ and 3ʹ ends of mature tRNAs were abundant in the cytoplasm of immune cells and small RNAs derived mostly from the 5ʹ ends were selectively enriched in vesicles derived from these immune cells [73]. In Maute et al., a significative down-regulation of CU1276, a DICER1-dependent tRF-3, was observed in lymphoma cell lines and biopsies [14]. CU1276 was shown to repress endogenous RPA1, a specific gene involved in genome replication. The reduced expression of CU1276 in mature B cells and the lack of RPA1 repression could confer a growth advantage to B cells. Regarding the role of tRFs in T cell activation during an immune response, in Chiou et al., they documented an enrichment of tRFs in T cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) in comparation to all the other cellular small RNA species during host defence activation [74]. Furthermore, the authors found that the number of tRFs was higher in EVs derived from activated T cells compared to non-activated lymphocytes, and the inhibition of EV biogenesis specifically led to the accumulation of these activation-induced EV-enriched tRFs within multivesicular bodies and the consequent inhibition of T cell activation. In contrast, the use of antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit these tRFs enhanced T cell activation [74]. Furthermore, if used as adjuvant of hepatitis B antigens in mice, tRNA fragments induced Th1 response, characterized by the production of Interferons (IFNs) through recognition of TLR3 [75]. Considering that the Protein Kinase Receptor (PKR) is IFN-effector protein and its action in the presence of double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) modulates translational inhibition [76], the activation of the PKR pathway could be another alternative way for tRNA fragments of blocking protein translation. Even if no data referring to this hypothesis are present in the literature, recently, Ivanov et al., showed as tRNA fragments can inhibit translation, independently from the eIF-2 pathway, by displacing the elongation factor eIF-4 from the initiation translational complex [16].
All this information indicates a strong connection between tRNA fragments and immune system. This observation is also supported by the discovery of a higher presence of tRNA fragments both in human and mice haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues compared to other tissues [77]. Furthermore, these fragments have been found in high presence in circulating mouse and human bloodstream [78]. The presence of tRNA fragments in the extracellular environment and their role in the modulation of different biological functions including the immune response, suggests a possible role of cell-cell communication immune signalling molecules. To support this hypothesis, another interesting observation is that the largest human tRNA gene cluster is located in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) [79], the set of genes that encode for cell surface proteins that are essential both in the innate and adaptatively immune response indicating a closed transcriptional association between immunity and tRNA fragments.
In summary, these observations provide support that circulating 5ʹtRFs are highly expressed in haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, which strongly suggest that tRFs may act as immune signalling molecules. Future studies addressing their biogenesis regulation, secretion and uptake, and functional role in immune cells and associated tissues will provide insights into the proposed role of tRFs in the immune and haematopoietic systems or other as yet undetermined functions as well as in haematopoietic disorders.
tRNA fragments associated to cancer progression
Early studies detected tRFs in the urine of cancer patients raising the possibility that tRFs could be used as biomarkers for early cancer detection and that they may have potential oncogenic activity [5]. Nonetheless, the investigation of tRFs as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in cancer did not begin till recently. In 2009, tRF-1001 was the first tRF to be found highly expressed in several cancer cell lines [11]. Because tRF-1001 was produced by tRNase Z (ELAC2) activity and since ELAC2 is a known prostate cancer susceptibility gene, tRF-1001 was thought to be oncogenic, and indeed its biogenesis inhibition impaired cell proliferation [11] (Fig. 4A). Later, other studies have identified other rare tRF-1s in cancer samples confirming an association between cancer and these potential regulatory tRFs [37,80,81].
Figure 4.
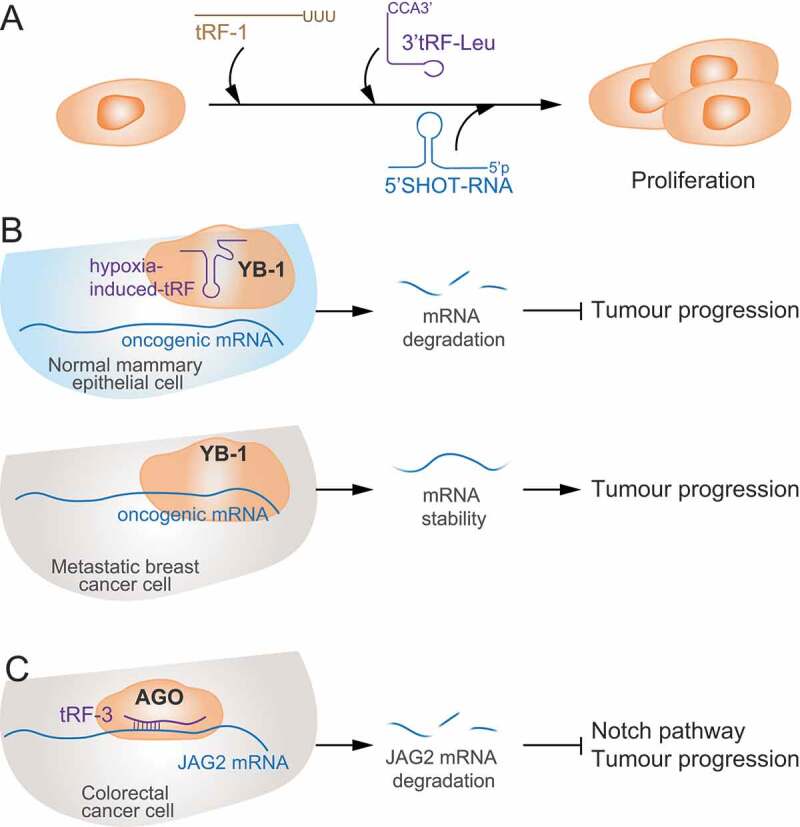
Association of tRFs with cancer initiation and progression. A) tRFs and tRNA halves can foster cancer cell proliferation. B) tRNA fragments mapping to the anticodon loop of tRNAs are induced upon hypoxic stress in normal mammary epithelial and breast cancer cells to sequester YB-1 from oncogenic transcripts and induce their degradation suppressing cancer progression. As metastatic breast cancer cells inhibit generation of these tRNA fragments, YB-1 binds and stabilizes tumour-promoting mRNAs (lower panel). C) In colon cancer cells, tRF-3s promote JAG2 mRNA degradation inactivating the cancer-promoting Notch signalling pathway.
Since then the expression of other tRFs has been found to be associated with cancer are being explored as alternative biomarkers of disease [37,80,81]. Sex hormone-dependent tRNA-derived RNAs (also known as SHOT-RNAs) were identified to be highly and constitutively expressed in breast and prostate cancer cell lines but were absent in other cancer tissues [21]. Other type of 5ʹ stress-derived tRFs were identified to be specifically altered in serum of breast cancer and in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients [82,83]. In clear cell renal cell carcinoma, the expression of a 5ʹ tRNA half derived from tRNA-Val was found downregulated and its expression was correlated with the stage and grade of the disease [84]. In myelodysplastic syndrome patients, the differential expression of six tRFs were correlated with treatment response [85]. In other studies, downregulation of specific tRNA-derived ncRNAs was associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia [86]. In Balatti Vet al., by analysing the data from chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, lung, colon, breast, and ovarian cancer samples, the authors found a cancer-specific signature of 31 differently expressed tRFs that was able to discriminate the cancer type as well as the cancer development and staging [87].
In a recent attempt to explore the whole transcriptome of tRFs in cancer, Pliatsika et al. processed all data of The Cancer Genome Atlas datasets (TCGA) and identified the expression of 23 413 tRFs associated to cancer [88,89]. While differential expression of tRFs have been associated with several cancer types, prostate cancer shows the highest repertoire of tRFs. In Olvedy M et al., the expression of tRFs transcripts was analysed in patient cohorts of different stages of prostate cancer [80]. The analysis identified 598 differentially expressed tRFs whose deregulation was correlated with cancer stage, highlighting their potential as candidate biomarkers for the detection of prostate cancer. Most of the upregulated tRFs belong to the tRF-5 series and the majority of the downregulated tRFs belong to the tRF-3 series.
Generation of tRNA fragments has been shown to be involved in regulating tumorigenesis too. Similar to stress-dependent tiRNAs, SHOT-RNAs were found to be produced by endonucleolytic cleavage at the anticodon loop, however, their biogenesis was not triggered by stress [21]. Instead, their expression was hormone-dependent and knockdown of ER and AR resulted in their decreased abundance. The authors also found that tRFs expression induced proliferation in cancer cells, and concluded that tRFs could represent a mechanism of tumour progression in response to oncogenic stress (Fig. 4A). Regardless of their expression not been triggered under stress, the authors suggested that SHOT-RNAs were too produced by ANG [21]. ANG was discovered and characterized by its ability to promote angiogenesis in tumours, and is widely established to be consistently up-regulated in different cancers making it a potential anti-cancer therapeutic target [90]. While the mechanisms by which ANG promotes angiogenesis are still not fully established, it is dependent upon its catalytic activity, suggesting that ANG-induced tRFs may be involved in carcinogenesis.
Other tRFs have been reported to have oncogenic activity. For instance, a tRNA-Leu-CAG-derived tRF-3 was recently reported to increase cell viability and its inhibition induced apoptosis in rapidly dividing cells in vitro as well as in a hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the formation of 80S ribosomal complexes [64,65] (Fig. 4A). These studies showed that inhibition of tRFs could reduce proliferation or induce apoptosis of tumorigenic cells thus indicating that blocking or repressing tRFs expression could be a novel therapeutic strategy.
While some studies have revealed tRNA fragments to have pro-oncogenic effects on cancer cells, in contrast, recent studies have reported that tRNA-derived fragments can too supress proliferation and metastasis [27]. So far, the best mechanistic explanation for the role of tRFs in cancer progression was found for a specific set of hypoxia-induced tRFs [27]. As hypoxia is a major stress encountered during at cancer onset and early progression, Goodarzi et al. analysed the pool of tRFs induced under low-oxygen conditions and found a group of tRFs that were specifically induced in breast cancer cell lines as well as in normal mammary epithelial. Mechanistically, endogenous tRFs were found associated with the oncoprotein YB-1 [27]. YB-1 is an oncogene up-regulated in a wide variety of cancers which binds to and stabilizes mRNA targets encoding for genes that promotes tumorigenesis [91]. Mechanistically, tRFs complexed to YB-1 were able to destabilize oncogenic transcripts inhibiting tumour progression [27] (Fig. 4B). Consistently, they found that highly metastatic breast cancer cells evaded this mechanism by blocking the induction of these tumour suppressive tRFs and thus fostering metastatic properties. The authors concluded that tRF expression may represent a mechanism of tumour suppression in response to oncogenic stress. However, such tumour suppression mechanism is likely inactivated during metastatic progression by decreased expression of tRFs and YB-1 up-regulation.
Similar results were found in other cancer types. In prostate cancer, while samples from primary tumours showed upregulation of a set of tRFs, samples from metastatic tumours expressed other set of tRFs, indicating that specific tRF populations may play different roles during tumour onset and progression [92]. In colorectal cancer, the tRNA-Leu-derived miR-1280 suppressed cancer stem cell functions and metastasis [93]. Mechanistically miR-1280 inhibited Notch signalling pathway by directly binding to the 3ʹ UTR of Jagged Canonical Notch Ligand 2 (JAG2) and inducing its degradation (Fig. 4C). Thus, its downregulated expression in colon cancer correlated with its tumour suppressive role. Likewise, in B cell lymphoma cell lines, several tRNA-derived fragments were shown to suppress cell proliferation and modulate DNA damage respond by regulating the expression of DNA damage response genes [14,94]. In lung cancer cell lines, tRFs ts-46 and ts-47 were shown to inhibit cell growth and colony formation suggesting that their deficiency could favour cell proliferation and cancer onset and progression [87]. ts-53 (previously designated as ‘miR-3676’) was found to be down-regulated in CLL and mechanistically was shown to target the 3′ UTR of TCL1 mRNA, a key oncogene in the development of aggressive CLL, and thus its down-regulation inversely correlated with TCL1 expression in leukaemic cells [95].
While further work is needed to better understand the role of tRNA fragments in cancer, it can be concluded that tRNA fragments are broadly associated with cancer and have oncogenic or tumour suppressor functions, depending on the tRNA and tumour type. These studies further suggest the use of tRFs as novel therapeutic targets to repress tumour progression.
Small ribosomal RNA-related fragments
Compared to mRNA and tRNA, rRNA is the most common form of RNA in cells, and similar to tRNAs, rRNA can be cleaved into small ribosomal RNA-related fragments (rRFs). Eukaryotic ribosomes are constituted by four different rRNAs: 5S, 5.8S, 18S, and 28S (higher eukaryotes)/25S (yeast) [96]. Ribosome production is initiated in the nucleolus, where a single rRNA precursor (47S rRNA) containing 5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNAs and spacer regions known as external and internal transcribed spacers (EST, ITS1, and ITS2), is transcribed by RNA polymerase I, while 5S rRNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III [97] (Fig. 5A). Traditionally, reads corresponding to rRNA were removed in RNA sequencing analysis and rRFs casually identified during the analysis were considered as by-products of rRNA degradation [98,99]. In addition, rDNA is not usually included in reference genome assemblies and, even when included, information can be missed since reference transcriptomes do not include all rDNA possible variations [97]. Despite these limitations, interest for studying these rRNA-related fragments is steadily growing and there is increasingly evidence that short reads mapping rRNA are stable and may play a functional role in the cell.
Figure 5.
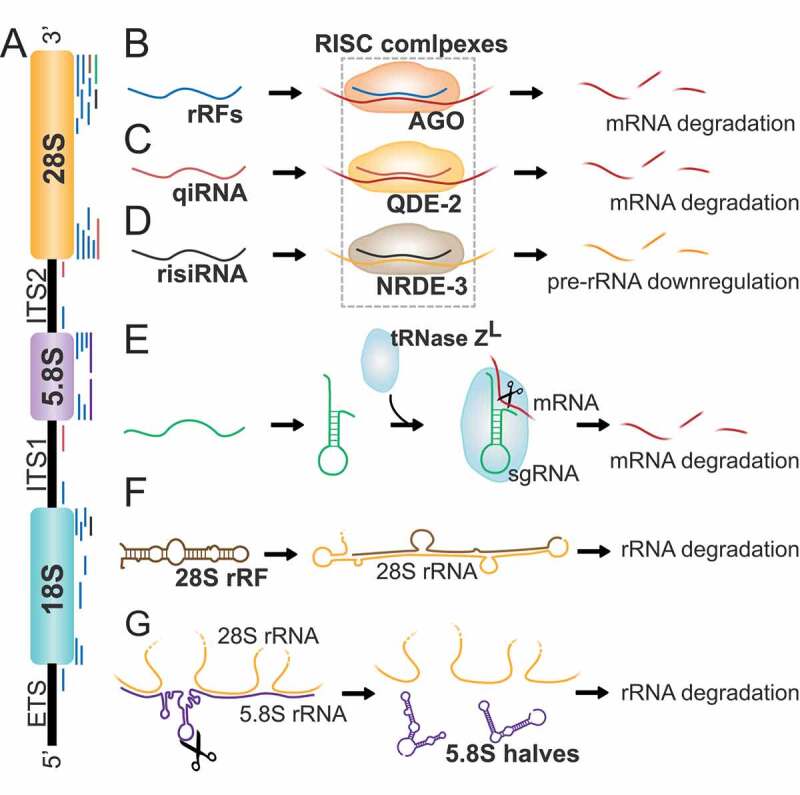
Ribosomal RNA-derived fragments. A) Eukaryotic ribosomes are constituted by four different rRNAs: 5S, 5.8S, 18S, and 28S (higher eukaryotes). Ribosome production is initiated in the nucleolus, where a single rRNA precursor (47S rRNA) containing 5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNAs and spacer regions known as external and internal transcribed spacers (EST, ITS1, and ITS2), is transcribed. B) rRFs derived from rRNAs and transcribed spacers in humans, flies, and mice interact with AGO proteins and downregulate several mRNAs by sequence complementary. C) qiRNAs derived from 3ʹ ends of 28S rRNA and spacers ITS1 and ITS2 interact with AGO protein QDE-2 to contribute to mRNA degradation in N. Crassa. D) risiRNAs derive from 28S and 18S rRNA and act through the RNAi pathway by association with the AGO protein NRDE-3 to downregulate pre-rRNA in C. elegans. E) Some 28S rRNA-related fragments may function as small guide RNAs (sgRNA) to guide the endonuclease tRNase ZL in human cells to downregulate the levels of specific mRNAs. F) rRFs derived from the 3ʹ end of 28S rRNA can reverse complement a mature 28S rRNA molecule and induce its degradation. G) Mature 5.8S and 28S rRNAs interact in 3 regions by sequence complementarity. The cleavage of 5.8S rRNA in halves leads to the formation of strong stem loop structures between 28S rRNA and 5.8S rRNA halves preventing the interaction with 5.8S mature rRNA and thus participating in rRNA separation during ribosome degradation.
Types and biogenesis of rRFs
Similar to tRFs, rRFs have been identified in several species and are classified depending on the domain of rRNA where they derive from (Table 2). The first report documenting the existence of rRFs was Lee H et al. in 2009 [100]. The authors found that DNA damage in Neurospora crassa induced the accumulation of a novel class of small ncRNAs, named QDE-2-interacting small RNAs (qiRNAs), which were mainly originated from 28S rRNA and the external and internal transcribed spacers of 47S rRNA ETS, ITS1, and ITS2 (Fig. 5A). It was proposed that rRFs were subsequently matured by consecutive actions of an RNA polymerase (RdRP or QDE-1), a helicase (QDE-3) and DICER [100]. Since then, many studies have reported the existence of rRFs in other species.
Table 2.
Definition of several features of the most common rRNA-related fragments.
| Name and type | Origin | Length (nt) | Strand | Function | Biogenesis | Organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qiRNA | 28S, ETS and ITS | 20-21 | Both strands | RNA-mediated gene silencing (quelling) by interaction with the AGO protein QDE-2 in fungus | QDE-1, QDE-3 and DICER-dependent in fungus. OsRecQ1, OsRDR1 and DICER-dependent in plants |
Filamentous fungus and plants | [100,115] |
| risiRNA | 18S and 26S | 22 | Antisense | pre-rRNA downregulation by interaction with que AGO protein NRDE-3 | RdRP-dependent, DICER-independent | C. elegans | [108] |
| risiRNA | rDNA, ETS and ITS | 21-22 | Both strands | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO1 complexes | XRN2, XRN3, RDR1/6, DCL2/4 -dependent | Plants | [109] |
| phasiRNA | 28S and 5.8S rRNA | 21 or 24 | Sense | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO proteins | AGO, RDR6, SGS3 and DCL4-dependent | Plants | [110] |
| Endo-siRNAs | 5.8S | 18-24 | Both strands | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO2 complexes | DICER-dependent | Mouse | [101,102,111] |
| 28S rRFs | 28S | Multiple lengths. Peak at 21 nt in humans and 80 nt in zebrafish | Mainly sense orientation | Co-immunoprecipitated with AGO complexes in human, plants and Drosophila. co-immunoprecipitated with tRNase ZL in human Predicted to participate in 28S rRNA degradation in zebrafish |
Not reported | Human, mouse, Drosophila, yeast, thick, zebrafish and plants | [10,39,104–107,116] |
| 18S rRFs | 18S | Multiple lengths 21 nt peak (maternal-type rRNA) and 130 nt (Somatic-type rRNA) in zebrafish |
Mainly sense orientation | Predicted to participate in gene silencing by interaction with AGO complex in zebrafish Function not reported in other organisms |
Not reported | Human, mouse, Drosophila, yeast, thick and plants | [104,106,107] |
| 5.8S rRFs | 5.8S | Multiple lengths | Mainly sense orientation | Co-immunoprecipitated with AGO complexes in plants Function not reported in other organisms |
Not reported | Human, mouse, Drosophila, yeast, thick, zebrafish and plants | [104,106,107] |
| 5.8S halves | 5.8S | 75-76 and 83 nt (maternal-type rRNA). 74 and 81 nt (Somatic-type rRNA) | Sense | Predicted to participate in 28S and 5.8S separation | Endonuclease not known | Zebrafish | [106] |
| 25S rRFs | 25S | Multiple lengths | Not reported | Not reported | Rny1p- and other endonucleases- dependent | Yeast | [10,33] |
| mmu-miR-5102 | 28S | 24 | Both strands | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO proteins | DICER-independent | Mouse | [101] |
| mmu-miR-5105 | 28S | 20 | Antisense | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO proteins | DICER-independent | Mouse | [101] |
| mmu-miR-5109 | 28S | 23 | Antisense | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO proteins | DICER-independent | Mouse | [101] |
| mmu-miR 5115 | 28S | 19 | Sense | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO proteins | DICER-independent | Mouse | [101] |
| mmu-miR-712 | ITS2 | 21 nt | Not reported | Gene silencing by a mechanism not reported. Plays a role in inflammation and atherosclerosis | XRN1 and DICER-dependent | Mouse | [113] |
| mir-10,404/mir-ITS1 | ITS1 | 22 nt | Sense | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO1 complexes | DICER-dependent, DROSHA-independent | Drosophila | [112] |
| has-miR-663 | ITS1 | 22 nt | Antisense | Gene silencing by interaction with AGO proteins | Not reported | Human | [103] |
In humans and mice, analysis of small RNA high-throughput sequencing datasets has revealed a significant percentage of reads that mapped to rDNA. Among those rRFs, about 9.6–15.1%, 8.1–15.8%, and 67.6–80.4% were distributed in regions coding 18S, 5.8S, and 28S rRNA, respectively [104] (Fig. 5A). rRFs have been found to be produced from either end (3ʹ or 5ʹ) of the three rRNAs, with preference for the 3ʹ end in human cell lines, yeast, and the tick Amblyomma testudinarium [10,39,105]. This differs from Danio rerio and plants in which 5ʹ end rRFs are more abundant [106,107]. In zebrafish, both maternal- and somatic-type 5.8S, 18S and 28S rRNAs produce several fragments, with a strong bias for 3ʹ and 5ʹ ends [106]. Interestingly, 5.8S also yields 2 fragments roughly corresponding to 3ʹ and 5ʹ halves, which are most likely generated by a single cut of the molecule, similarly to what happens with tRNAs [31], although the endonuclease responsible for this cleavage is still unknown.
Several reports have documented the existence of rRFs produced under distinct conditions and in some cases the responsible endonuclease has been identified. In Saccharomyces, similar to tRFs, Rny1p produces rRFs mainly derived from 25S rRNA and under oxidative stress conditions [33]. Yet, Rny1p knock-out strains still present rRFs, suggesting that other endonucleases might participate in rRFs formation. Caenorhabditis elegans possesses a type of DICER-independent rRNA fragments called antisense ribosomal RNAs (risiRNAs) with sequence complementarity to 18S and 26S rRNA [108]. risiRNAs have been recently identified in Arabidopsis thaliana too [109]. In this recent study, Cui and Mo’s group found that risiRNAs are generated from both rDNA strands and from ETS/ITS regions of the rDNA loci in the absence of the dephosphorylating enzyme FIERY1 involved in several biological processes such as stress signalling or plant immunity, suggesting a role of risiRNAs in stress and infections regulation [109]. In addition, the authors identified that rRNA production was dependent on both nuclear exoribonucleases including EXORIBONUCLEASE2 (XRN2) and XRN3, and cytoplasmic exonucleases including RNA-dependent direct polymerase 1 (RDR1) and RDR16 and DICER-like 2 (DCL2) and DCL4, complicating predictions about the subcellular localization of risiRNA biogenesis. In a similar study in plants, other family of rRFs called phased small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs) were found to be generated from 28S and 5.8S rRNAs by the cytoplasmic exonuclease DCL [110]. In mice, endogenous small interference RNAs (endo-siRNAs) are generated from loci that mapped to rDNA loci and are capable of forming dsRNA in a DICER-dependent manner, and are specially abundant in spermatozoa [111]. Interestingly, several miRNAs and piRNAs have been found to map to rDNA loci too, demonstrating that they are actually rRFs. For instance, mmu-miR-5102, mmu-miR-5105, mmu-miR-5109, and mmu-miR 5115 are produced from 28S rRNA in mice, while mmu-miR-712 in mice, mir-10,404/mir-ITS1 in Drosophila and has-miR-663 in humans derive from spacer regions [112,113].
Similar to tRFs, rRFs production seems to be linked to post-transcriptional modifications. Indeed, defects of post-transcriptional N1-methyladenosine (m1A), N7-methylguanosine (m7G) and N6-dimethyladenosine (m62Am62A) modifications in C. elegans 18S rRNA have been shown to induce the accumulation of risiRNAs [114].
In summary, the different rRNA domains of origin of rRFs, together with the differential size distribution, and their expression under distinct cell conditions support the hypothesis that the formation of rRFs is not a random degradation process, instead it shows that rRFs biogenesis is highly specific and regulated endonucleolytic process, and thus suggesting that similar to tRFs, they are regulatory molecules with capacity to fine tune cell processes.
Functional role of rRFs
Similar to tRFs, several rRFs have shown to interact with AGO proteins suggesting a role in gene silencing. In human fibroblasts, around 7% of the rRFs were found to co-immunoprecipitate with AGO proteins (Fig. 5B). Interestingly, those rRFs differed in distribution and size patterns compared to the pool of total rRFs, suggesting a specific role for some rRFs in silencing [104]. Indeed, overexpression or inhibition of several rRFs in mouse hepatoma cells showed to alter the expression of several key metabolic enzymes, suggesting that rRFs can regulate metabolic processes in a similar manner to miRNAs or siRNAs [104]. In Drosophila, rRFs were also shown to co-immunoprecipitate with AGO1 and AGO2 complexes, in a distinct distribution patterns, further confirming to have a defined role [104]. In Neurospora, qiRNAs are associated with QDE-2, an AGO protein required for quelling, an RNA-mediated gene silencing phenomenon [100] (Fig. 5C). qiRNAs were found to be involved in the protein synthesis inhibition process occurred after DNA damage in Neurospora [100] and required for the DNA damage response and repair pathways in plants [115], thus qiRNAs production was suggested to be a conserved mechanism that contributes to DNA damage checkpoints. In C. elegans, risiRNAs have been found to act, at least in part, through the nucleolar RNAi pathway by associating with the AGO protein NRDE-3 to downregulate pre-rRNA [108,114] (Fig. 5D). Apart from AGO proteins, other complexes can bind rRFs. For instance, some 28S rRNA-related rRFs co-immunoprecipitate with tRNase ZL in human kidney 293 cells and may function as a small guide RNAs to downregulate the levels of specific mRNAs [116] (Fig. 5E).
rRFs have been shown to be precursors for the production of miRNAs. In zebrafish, rRFs derived from the 5ʹ end of 18S rRNA form a secondary structure containing a stem which is thought to act as a non-canonical precursor for the biogenesis of miRNAs [106]. In addition, analysis of published AGO-complexed small-RNA pool datasets in humans and mice confirmed that both guide and passenger strand of the homologous stem are detected in the small RNA pool that co-immunoprecipitates with AGO proteins, further confirming their role as miRNAs precursors [106]. Those findings, together with several piRNA sequences matching with rRFs [104,111,112], further support an important functional role of rRFs in gene expression regulation.
The function of rRFs is not limited to gene silencing, in fact, their structure is also thought to play a crucial functional distinct role in rRNA stability. For instance, structural analysis of zebrafish 28S rRNA-related fragments revealed that their 3ʹ ends can bind 3ʹ ends of complete 28S rRNAs and may play a role in their degradation [106] (Fig. 5F). Similarly, 5.8S halves maintain a strong secondary structure with long stable stems, which could prevent 28S to interact to 5.8S rRNA [106]. Thus, 5.8S halves are thought to participate in 28S and 5.8S rRNAs separation during ribosome degradation (Fig. 5G). However, their specific role remains to be elucidated.
Physiological relevance of rRFs
Similar to tRFs, rRFs production is highly linked to stress responses. For instance, in C. elegans risiRNAs are upregulated after UV radiation and cold shock to silence pre-rRNA expression to avoid the accumulation of erroneous rRNA [108]. In yeast, levels of some rRFs also increase during oxidative stress and entry into stationary phase [10].
rRFs function has been linked to other physiological processes. Overexpression or inhibition of several rRFs in mouse hepatoma cells showed to alter the expression of several key metabolic enzymes, suggesting that rRFs can regulate metabolic processes in a similar manner to miRNAs or siRNAs [104]. In addition, miRNAs mapping to rDNA such as mmu-mir-712 in mice and hsa-miR-663 in humans have been reported to play a role in inflammatory responses [113,117]. In human kidney 293 cells, tRNase ZL guided by rRFs downregulate the levels of DYNC1H1 (Dynein Cytoplasmic 1 Heavy Chain 1), suggesting a role in mitosis regulation [116]. All these evidences suggest that rRFs play significant roles in stress responses, proliferation, metabolic, and inflammatory processes and thus suggesting implications in disease development or progression as it has been described for tRNA-derived fragments.
Altogether, the data reveal that several fragments can be generated from rRNA precursors and from mature molecules. rRNA degradation products are nearly undetectable in normal conditions, since they are rapidly degraded [118]. This suggest that detected rRFs are likely stable products generated by highly regulated processes rather than random degradation, as it has been previously considered [98,99,106]. Among these fragments, a large subgroup has been found to interact with ribonucleoprotein complexes, and might play a role in rRNA processing and gene expression regulation [100,104,106,108,114,116]. In addition, while defective accumulation or loss of rRFs have not been associated with disease yet, their physiological implications in stress responses, mitosis, inflammation or metabolic regulation strongly indicate an association to diseased processes. Further studies will shed light on the functional role and pathological relevance of these abundant rRNA-related fragments.
Concluding remarks
With advances in technology and experimental approaches, we are beginning to appreciate the variety of small ncRNAs derived from tRNA and other long ncRNAs that can tune gene expression and protein biogenesis in a cell- and tissue-specific manner, and the precision by which stress and other signals are coordinated to induce their biogenesis. With the development of next-generation sequencing technologies, the repertoire of regulatory small ncRNAs derived from other RNAs is growing [119,120] and it will be fully uncovered in the near future. Improved understanding of their functions will provide valuable insights into human physiology and pathology.
The biogenesis and biological functions of most tRFs and other RNA-derived fragments are still unclear. Nonetheless, to date research into RNA fragments biology has shed light on the existence of another layer of gene expression regulation. tRNA and rRNA fragments are pieces of a big puzzle that adjust and tune posttranscriptional gene expression regulation coordinating the silencing and translation machinery. For instance, novel research has shown that 5ʹtRFs can suppress the expression of transcripts that are driven by the long terminal repeat (LTR)-retrotransposon MERVL in the developing mouse embryo [23]. Similar observations were made for other LTR-retrotransposons, where 3′tRNA fragments were shown to block their reverse transcription by binding to the primer binding site (PBS) of LTR-retrotransposon transcripts or reduce their transcript levels in an RNAi-mediated manner [121]. In addition, recent findings have established tRNA fragments as ‘non-genetic’ inheritance factors of metabolic traits that drive epigenetic remodelling of gametes [122]. This is a key area of research that will enable us to understand more clearly the complexity behind the transcriptome regulation.
The availability of genome sequencing data from patients with diverse conditions has already resulted in the identification of tRNA-derived fragments signatures and to some extend they have been shown to have oncogenic or tumour suppressive activity. The mechanisms that give rise to those fragments that can either suppress or promote tumorigenesis need to be uncovered. tRFs are also induced by viral infections establishing a posttranscriptional mechanism that can fine-tune gene expression during other pathological states and provides a potential new target for treating infection diseases or immune-related disorders including cancer. The real challenge now is to ascertain whether these tRNA fragments are the core of the molecular pathology of the disease and whether they are best diagnostic tools of druggable targets to develop potent and efficient therapeutic strategies. In the past year, several preclinical formulations of RNA-based therapies have shown clinical benefits for treating cancer and other diseases [123,124]. The data shown in this review indicates a promising therapeutic potential of targeting these small ncRNAs derived from RNA fragments disrupting their functions to treat cancer, immune-associated diseases and other disorders. In the near future, tRFs- or rRFs-based therapies may become valuable to provide treatment for previously untreatable diseases.
Secondary products originating from mature RNAs that were considered to be metabolically stable might be functionally relevant in cancer. For instance, several recent studies have demonstrated a link between tRNA modifications and tumour cell survival in response to chemotherapy. While, the modification status of these RNAs fragments and whether or not RNA modifications contribute to tRF functions remain still unknown, however, some are already known to contribute to their biogenesis. The coordinated depositions of m5C by NSUN2 and m7G by METTL1 to tRNAs were implicated in mediating sensitivity of yeasts and HeLa cells towards the cytotoxic agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) [125,126]. Deletion of Nsun2 in mouse skin tumours increased the number of ANG-induced 5ʹtRFs and Nsun2-lacking tumour initiating cells were highly sensitive towards treatment with 5-FU and cisplatin [19]. Removal of similar RNA modifications in yeast also induced sensitivity to cytotoxic stress [126]. These findings highlight the importance of the dynamic deposition of modifications into tRNAs and the possible use as therapeutic targets to increase cancer cells sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents. Thus, it will be important to decipher the tRFs epigenetic RNA ‘code’ directing tRFs biogenesis and activity.
The challenge will be separating the functional impact of RNA-derived fragments from their molecules of origin. Recent advances in targeted gene disruption in mammalian cells offer a useful tool to assess the contribution of single genes, including tRNA genes, to pathology. In addition, knowledge of the tRNA and rRNA fragments biology in different tissues will allow us to gain a more accurate understanding of the tissue-specific aspects that modulate disease severity and progression.
Acknowledgments
D.R. is supported by Programa de Apoyo a Planes Estratégicos de Investigación de Estructuras de Investigación de Excelencia co-funded by the Castilla–León autonomous government and the European Regional Development Fund (CLC–2017–01). J.L. is a PhD student supported by The Scientific Foundation AECC (Spanish Association Against Cancer) PhD fellowship (PRDSA19002LÓPE). S.B. is a Research Scientist of the Spanish Research Council. We acknowledge funding from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Innovation (MINECO) and Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI) and co-financed by the European Development Regional Fund (FEDER) under grant no. SAF2016-78667-R (AEI/FEDER, UE). In addition, we acknowledge funding from The Scientific Foundation AECC under grant no. LABAE19040BLAN, and the University of Salamanca and Fundación Memoria de Samuel Solorzano Barruso under grant no. FS/21-2018. AUTHOR’s institution is supported by the Programa de Apoyo a Planes Estratégicos de Investigación de Estructuras de Investigación de Excelencia cofunded by the Castilla–León autonomous government and the European Regional Development Fund (CLC–2017–01).
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Agencia Estatal de Investigación [SAF2016-78667-R];Fundación Científica Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer (ES) [PRDSA19002LÓPE];Programa de Apoyo a Planes Estratégicos de Investigación de Estructuras de Investigación de Excelencia cofunded by the Castilla–León autonomous government and the European Regional Development Fund (ES) [CLC–2017–01];Fundación Científica Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer (ES) [LABAE19040BLAN];Fundación Memoria de Samuel Solorzano Barruso (ES) [FS/21-2018].
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- [1].Mattick JS, Makunin IV.. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(Spec No 1):R17–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Phizicky EM, Hopper AK. tRNA biology charges to the front. Genes Dev. 2010;24:1832–1860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Cech TR, Steitz JA. The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157:77–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Borek E, Baliga BS, Gehrke CW, et al. High turnover rate of transfer RNA in tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 1977;37:3362–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Kumar P, Anaya J, Mudunuri SB, et al. Meta-analysis of tRNA derived RNA fragments reveals that they are evolutionarily conserved and associate with AGO proteins to recognize specific RNA targets. BMC Biol. 2014;12:78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Andersen KL, Collins K. Several RNase T2 enzymes function in induced tRNA and rRNA turnover in the ciliate Tetrahymena. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:36–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Schaefer M, Pollex T, Hanna K, et al. RNA methylation by Dnmt2 protects transfer RNAs against stress-induced cleavage. Genes Dev. 2010;24:1590–1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Gebetsberger J, Zywicki M, Kunzi A, et al. tRNA-derived fragments target the ribosome and function as regulatory non-coding RNA in Haloferax volcanii. Archaea. 2012;2012:260909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Thompson DM, Lu C, Green PJ, et al. tRNA cleavage is a conserved response to oxidative stress in eukaryotes. RNA. 2008;14:2095–2103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Lee YS, Shibata Y, Malhotra A, et al. A novel class of small RNAs: tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs). Genes Dev. 2009;23:2639–2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Tuck AC, Tollervey D. RNA in pieces. Trends Genet. 2011;27:422–432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Tomecki R, Dziembowski A. Novel endoribonucleases as central players in various pathways of eukaryotic RNA metabolism. RNA. 2010;16:1692–1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Maute RL, Schneider C, Sumazin P, et al. tRNA-derived microRNA modulates proliferation and the DNA damage response and is down-regulated in B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:1404–1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Yamasaki S, Ivanov P, Hu GF, et al. Angiogenin cleaves tRNA and promotes stress-induced translational repression. J Cell Biol. 2009;185:35–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Ivanov P, Emara MM, Villen J, et al. Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation initiation. Mol Cell. 2011;43:613–623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Guzzi N, Ciesla M, Ngoc PCT, et al. Pseudouridylation of tRNA-Derived Fragments Steers Translational Control in Stem Cells. Cell. 2018;173:1204–16 e26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Blanco S, Dietmann S, Flores JV, et al. Aberrant methylation of tRNAs links cellular stress to neuro-developmental disorders. Embo J. 2014;33:2020–2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Blanco S, Bandiera R, Popis M, et al. Stem cell function and stress response are controlled by protein synthesis. Nature. 2016;534:335–340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Krishna S, Yim DG, Lakshmanan V, et al. Dynamic expression of tRNA-derived small RNAs define cellular states. EMBO Rep. 2019;20:e47789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Honda S, Loher P, Shigematsu M, et al. Sex hormone-dependent tRNA halves enhance cell proliferation in breast and prostate cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:E3816–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Ruggero K, Guffanti A, Corradin A, et al. Small noncoding RNAs in cells transformed by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: a role for a tRNA fragment as a primer for reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 2014;88:3612–3622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Sharma U, Conine CC, Shea JM, et al. Biogenesis and function of tRNA fragments during sperm maturation and fertilization in mammals. Science. 2016;351:391–396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].van Hoof A, Wagner EJ. A brief survey of mRNA surveillance. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:585–592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Kuscu C, Kumar P, Kiran M, et al. tRNA fragments (tRFs) guide Ago to regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally in a Dicer-independent manner. RNA. 2018;24:1093–1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Taft RJ, Glazov EA, Lassmann T, et al. Small RNAs derived from snoRNAs. RNA. 2009;15:1233–1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Goodarzi H, Liu X, Nguyen HC, et al. Endogenous tRNA-Derived Fragments Suppress Breast Cancer Progression via YBX1 Displacement. Cell. 2015;161:790–802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Telonis AG, Loher P, Honda S, et al. Dissecting tRNA-derived fragment complexities using personalized transcriptomes reveals novel fragment classes and unexpected dependencies. Oncotarget. 2015;6:24797–24822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Saikia M, Krokowski D, Guan BJ, et al. Genome-wide identification and quantitative analysis of cleaved tRNA fragments induced by cellular stress. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:42708–42725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Emara MM, Ivanov P, Hickman T, et al. Angiogenin-induced tRNA-derived stress-induced RNAs promote stress-induced stress granule assembly. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:10959–10968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Fu H, Feng J, Liu Q, et al. Stress induces tRNA cleavage by angiogenin in mammalian cells. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:437–442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Lee SR, Collins K. Starvation-induced cleavage of the tRNA anticodon loop in Tetrahymena thermophila. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:42744–42749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Thompson DM, Parker R. The RNase Rny1p cleaves tRNAs and promotes cell death during oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 2009;185:43–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Su Z, Kuscu C, Malik A, et al. Angiogenin generates specific stress-induced tRNA halves and is not involved in tRF-3-mediated gene silencing. J Biol Chem. 2019;294:16930–16941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Donovan J, Rath S, Kolet-Mandrikov D, et al. Rapid RNase L-driven arrest of protein synthesis in the dsRNA response without degradation of translation machinery. RNA. 2017;23:1660–1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Cole C, Sobala A, Lu C, et al. Filtering of deep sequencing data reveals the existence of abundant Dicer-dependent small RNAs derived from tRNAs. RNA. 2009;15:2147–2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Haussecker D, Huang Y, Lau A, et al. Human tRNA-derived small RNAs in the global regulation of RNA silencing. RNA. 2010;16:673–695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Babiarz JE, Ruby JG, Wang Y, et al. Mouse ES cells express endogenous shRNAs, siRNAs, and other Microprocessor-independent, Dicer-dependent small RNAs. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2773–2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Li Z, Ender C, Meister G, et al. Extensive terminal and asymmetric processing of small RNAs from rRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, and tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:6787–6799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Chan CT, Dyavaiah M, DeMott MS, et al. A quantitative systems approach reveals dynamic control of tRNA modifications during cellular stress. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Basanta-Sanchez M, Temple S, Ansari SA, et al. Attomole quantification and global profile of RNA modifications: epitranscriptome of human neural stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:e26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Wang X, Matuszek Z, Huang Y, et al. Queuosine modification protects cognate tRNAs against ribonuclease cleavage. RNA. 2018;24:1305–1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Vitali P, Kiss T. Cooperative 2ʹ-O-methylation of the wobble cytidine of human elongator tRNA(Met)(CAT) by a nucleolar and a Cajal body-specific box C/D RNP. Genes Dev. 2019;33:741–746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Tuorto F, Herbst F, Alerasool N, et al. The tRNA methyltransferase Dnmt2 is required for accurate polypeptide synthesis during haematopoiesis. Embo J. 2015;34(18):2350–2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Gkatza NA, Castro C, Harvey RF, et al. Cytosine-5 RNA methylation links protein synthesis to cell metabolism. PLoS Biol. 2019;17:e3000297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Flores JV, Cordero-Espinoza L, Oeztuerk-Winder F, et al. Cytosine-5 RNA methylation regulates neural stem cell differentiation and motility. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8:112–124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Blanco S, Kurowski A, Nichols J, et al. The RNA-methyltransferase Misu (NSun2) poises epidermal stem cells to differentiate. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Martinez FJ, Lee JH, Lee JE, et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies a splicing mutation in NSUN2 as a cause of a Dubowitz-like syndrome. J Med Genet. 2012;49:380–385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Cosentino C, Toivonen S, Diaz Villamil E, et al. Pancreatic beta-cell tRNA hypomethylation and fragmentation link TRMT10A deficiency with diabetes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:10302–10318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [50].Igoillo-Esteve M, Genin A, Lambert N, et al. tRNA methyltransferase homolog gene TRMT10A mutation in young onset diabetes and primary microcephaly in humans. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Studte P, Zink S, Jablonowski D, et al. tRNA and protein methylase complexes mediate zymocin toxicity in yeast. Mol Microbiol. 2008;69:1266–1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Lu J, Esberg A, Huang B, et al. Kluyveromyces lactis gamma-toxin, a ribonuclease that recognizes the anticodon stem loop of tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:1072–1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [53].Luo S, He F, Luo J, et al. Drosophila tsRNAs preferentially suppress general translation machinery via antisense pairing and participate in cellular starvation response. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:5250–5268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Deng J, Ptashkin RN, Chen Y, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus utilizes a tRNA fragment to suppress antiviral responses through a novel targeting mechanism. Mol Ther. 2015;23:1622–1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [55].McEwen E, Kedersha N, Song B, et al. Heme-regulated inhibitor kinase-mediated phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 inhibits translation, induces stress granule formation, and mediates survival upon arsenite exposure. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:16925–16933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [56].Lyons SM, Gudanis D, Coyne SM, et al. Identification of functional tetramolecular RNA G-quadruplexes derived from transfer RNAs. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [57].Ivanov P, O’Day E, Emara MM, et al. G-quadruplex structures contribute to the neuroprotective effects of angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:18201–18206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [58].Lyons SM, Achorn C, Kedersha NL, et al. YB-1 regulates tiRNA-induced Stress Granule formation but not translational repression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:6949–6960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [59].Gebetsberger J, Wyss L, Mleczko AM, et al. A tRNA-derived fragment competes with mRNA for ribosome binding and regulates translation during stress. RNA Biol. 2017;14:1364–1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [60].Bakowska-Zywicka K, Kasprzyk M, Twardowski T. tRNA-derived short RNAs bind to Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomes in a stress-dependent manner and inhibit protein synthesis in vitro. FEMS Yeast Res. 2016;16(6):fow077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [61].Sobala A, Hutvagner G. Small RNAs derived from the 5ʹ end of tRNA can inhibit protein translation in human cells. RNA Biol. 2013;10:553–563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [62].Keam SP, Sobala A, Ten Have S, et al. tRNA-Derived RNA fragments associate with human Multisynthetase Complex (MSC) and modulate ribosomal protein translation. J Proteome Res. 2017;16:413–420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [63].Czech A, Wende S, Morl M, et al. Reversible and rapid transfer-RNA deactivation as a mechanism of translational repression in stress. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [64].Kim HK, Fuchs G, Wang S, et al. A transfer-RNA-derived small RNA regulates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 2017;552:57–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [65].Kim HK, Xu J, Chu K, et al. A tRNA-derived small RNA regulates ribosomal protein S28 protein levels after translation initiation in humans and mice. Cell Rep. 2019;29:3816–24 e4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [66].Fricker R, Brogli R, Luidalepp H, et al. A tRNA half modulates translation as stress response in Trypanosoma brucei. Nat Commun. 2019;10:118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [67].Panas MD, Ivanov P, Anderson P. Mechanistic insights into mammalian stress granule dynamics. J Cell Biol. 2016;215:313–323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [68].Davidson-Moncada J, Papavasiliou FN, Tam W. MicroRNAs of the immune system: roles in inflammation and cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1183:183–194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [69].Boss IW, Renne R. Viral miRNAs: tools for immune evasion. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010;13:540–545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [70].Wang Q, Lee I, Ren J, et al. Identification and functional characterization of tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs) in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mol Ther. 2013;21:368–379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [71].Deng J, Ptashkin RN, Wang Q, et al. Human metapneumovirus infection induces significant changes in small noncoding RNA expression in airway epithelial cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014;3:e163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [72].Jackowiak P, Hojka-Osinska A, Philips A, et al. Small RNA fragments derived from multiple RNA classes - the missing element of multi-omics characteristics of the hepatitis C virus cell culture model. BMC Genomics. 2017;18:1–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [73].Nolte-’t Hoen EN, Buermans HP, Waasdorp M, et al. Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:9272–9285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [74].Chiou NT, Kageyama R, Ansel KM. Selective export into extracellular vesicles and function of tRNA fragments during T cell activation. Cell Rep. 2018;25:3356–70 e4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [75].Wang Z, Xiang L, Shao J, et al. The 3ʹ CCACCA sequence of tRNAAla(UGC) is the motif that is important in inducing Th1-like immune response, and this motif can be recognized by Toll-like receptor 3. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006;13:733–739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [76].Pindel A, Sadler A. The role of protein kinase R in the interferon response. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31:59–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [77].Dhahbi JM, Spindler SR, Atamna H, et al. tRNA halves are present as abundant complexes in serum, concentrated in blood cells, and modulated by aging and calorie restriction. BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [78].Meiri E, Levy A, Benjamin H, et al. Discovery of microRNAs and other small RNAs in solid tumors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:6234–6246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [79].Horton R, Wilming L, Rand V, et al. Gene map of the extended human MHC. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:889–899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [80].Olvedy M, Scaravilli M, Hoogstrate Y, et al. A comprehensive repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:24766–24777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [81].Kumar P, Mudunuri SB, Anaya J, et al. tRFdb: a database for transfer RNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D141–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [82].Victoria Martinez B, Dhahbi JM, Nunez Lopez YO, et al. Circulating small non-coding RNA signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:19246–19263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [83].Dhahbi JM, Spindler SR, Atamna H, et al. Deep sequencing of serum small RNAs identifies patterns of 5ʹ tRNA Half and YRNA fragment expression associated with breast cancer. Biomark Cancer. 2014;6:37–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [84].Nientiedt M, Deng M, Schmidt D, et al. Identification of aberrant tRNA-halves expression patterns in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [85].Guo Y, Bosompem A, Mohan S, et al. Transfer RNA detection by small RNA deep sequencing and disease association with myelodysplastic syndromes. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [86].Pekarsky Y, Balatti V, Palamarchuk A, et al. Dysregulation of a family of short noncoding RNAs, tsRNAs, in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:5071–5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [87].Balatti V, Nigita G, Veneziano D, et al. tsRNA signatures in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114:8071–8076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [88].Pliatsika V, Loher P, Magee R, et al. MINTbase v2.0: a comprehensive database for tRNA-derived fragments that includes nuclear and mitochondrial fragments from all the cancer genome atlas projects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:D152–D9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [89].Pliatsika V, Loher P, Telonis AG, et al. MINTbase: a framework for the interactive exploration of mitochondrial and nuclear tRNA fragments. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:2481–2489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [90].Yu D, Cai Y, Zhou W, et al. The potential of angiogenin as a serum biomarker for diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis Markers. 2018;2018:1984718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [91].Maurya PK, Mishra A, Yadav BS, et al. Role of Y Box Protein-1 in cancer: as potential biomarker and novel therapeutic target. J Cancer. 2017;8:1900–1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [92].Martens-Uzunova ES, Jalava SE, Dits NF, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic signatures from the small non-coding RNA transcriptome in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:978–991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [93].Huang B, Yang H, Cheng X, et al. tRF/miR-1280 suppresses stem cell-like cells and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3194–3206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [94].Martens-Uzunova ES, Olvedy M, Jenster G. Beyond microRNA–novel RNAs derived from small non-coding RNA and their implication in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;340:201–211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [95].Balatti V, Rizzotto L, Miller C, et al. TCL1 targeting miR-3676 is codeleted with tumor protein p53 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:2169–2174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [96].Ben-Shem A, de Loubresse NG, Melnikov S, et al. The structure of the eukaryotic ribosome at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 2011;334:1524–1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [97].Zentner GE, Saiakhova A, Manaenkov P, et al. Integrative genomic analysis of human ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:4949–4960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [98].Choy JY, Boon PL, Bertin N, et al. A resource of ribosomal RNA-depleted RNA-Seq data from different normal adult and fetal human tissues. Sci Data. 2015;2:150063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [99].Fowler EK, Mohorianu I, Smith DT, et al. Small RNA populations revealed by blocking rRNA fragments in Drosophila melanogaster reproductive tissues. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0191966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [100].Lee HC, Chang SS, Choudhary S, et al. qiRNA is a new type of small interfering RNA induced by DNA damage. Nature. 2009;459:274–277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [101].Castellano L, Stebbing J. Deep sequencing of small RNAs identifies canonical and non-canonical miRNA and endogenous siRNAs in mammalian somatic tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:3339–3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [102].Zhu C, Yan Q, Weng C, et al. Erroneous ribosomal RNAs promote the generation of antisense ribosomal siRNA. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2018;115:10082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [103].Ni C-W, Qiu H, Jo H. MicroRNA-663 upregulated by oscillatory shear stress plays a role in inflammatory response of endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H1762–H9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [104].Wei H, Zhou B, Zhang F, et al. Profiling and identification of Small rDNA-derived RNAs and their potential biological functions. Plos One. 2013;8:e56842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [105].Chen Z, Sun Y, Yang X, et al. Two featured series of rRNA-derived RNA fragments (rRFs) constitute a novel class of small RNAs. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0176458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [106].Locati MD, Pagano JFB, Abdullah F, et al. Identifying small RNAs derived from maternal- and somatic-type rRNAs in zebrafish development. Genome. 2018;61:371–378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [107].Asha S, Soniya EV. The sRNAome mining revealed existence of unique signature small RNAs derived from 5.8SrRNA from Piper nigrum and other plant lineages. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [108].Zhou X, Feng X, Mao H, et al. RdRP-synthesized antisense ribosomal siRNAs silence pre-rRNA via the nuclear RNAi pathway. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2017;24:258–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [109].You C, He W, Hang R, et al. FIERY1 promotes microRNA accumulation by suppressing rRNA-derived small interfering RNAs in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [110].Zheng Y, Wang S, Sunkar R. Genome-wide discovery and analysis of phased small interfering RNAs in Chinese sacred lotus. Plos One. 2014;9:e113790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [111].García-López J, Hourcade J, Alonso L, et al. Global characterization and target identification of piRNAs and endo-siRNAs in mouse gametes and zygotes. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2014;1839:463–475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [112].Chak LL, Mohammed J, Lai EC, et al. A deeply conserved, noncanonical miRNA hosted by ribosomal DNA. RNA. 2015;21:375–384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [113].Son DJ, Kumar S, Takabe W, et al. The atypical mechanosensitive microRNA-712 derived from pre-ribosomal RNA induces endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. 2013;4:3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [114].Zhu C, Yan Q, Weng C, et al. Erroneous ribosomal RNAs promote the generation of antisense ribosomal siRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115:10082–10087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [115].Chen H, Kobayashi K, Miyao A, et al. Both OsRecQ1 and OsRDR1 are required for the production of small RNA in response to DNA-damage in rice. Plos One. 2013;8:e55252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [116].Elbarbary RA, Takaku H, Uchiumi N, et al. Modulation of gene expression by human cytosolic tRNase Z(L) through 5ʹ-half-tRNA. PLoS One. 2009;4:e5908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [117].Ni CW, Qiu H, Jo H. MicroRNA-663 upregulated by oscillatory shear stress plays a role in inflammatory response of endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:H1762–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [118].Houseley J, Tollervey D. The Many Pathways of RNA Degradation. Cell. 2009;136:763–776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [119].Pircher A, Bakowska-Zywicka K, Schneider L, et al. An mRNA-derived noncoding RNA targets and regulates the ribosome. Mol Cell. 2014;54:147–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [120].Fish L, Zhang S, Yu JX, et al. Cancer cells exploit an orphan RNA to drive metastatic progression. Nat Med. 2018;24:1743–1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [121].Schorn AJ, Gutbrod MJ, LeBlanc C, et al. LTR-Retrotransposon Control by tRNA-Derived Small RNAs. Cell. 2017;170:61–71 e11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [122].Chen Q, Yan M, Cao Z, et al. Sperm tsRNAs contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired metabolic disorder. Science. 2016;351:397–400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [123].Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16:203–222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [124].Lieberman J. Tapping the RNA world for therapeutics. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018;25:357–364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [125].Okamoto M, Fujiwara M, Hori M, et al. tRNA modifying enzymes, NSUN2 and METTL1, determine sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in HeLa cells. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [126].Gustavsson M, Ronne H. Evidence that tRNA modifying enzymes are important in vivo targets for 5-fluorouracil in yeast. RNA. 2008;14:666–674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


