Figure 3.
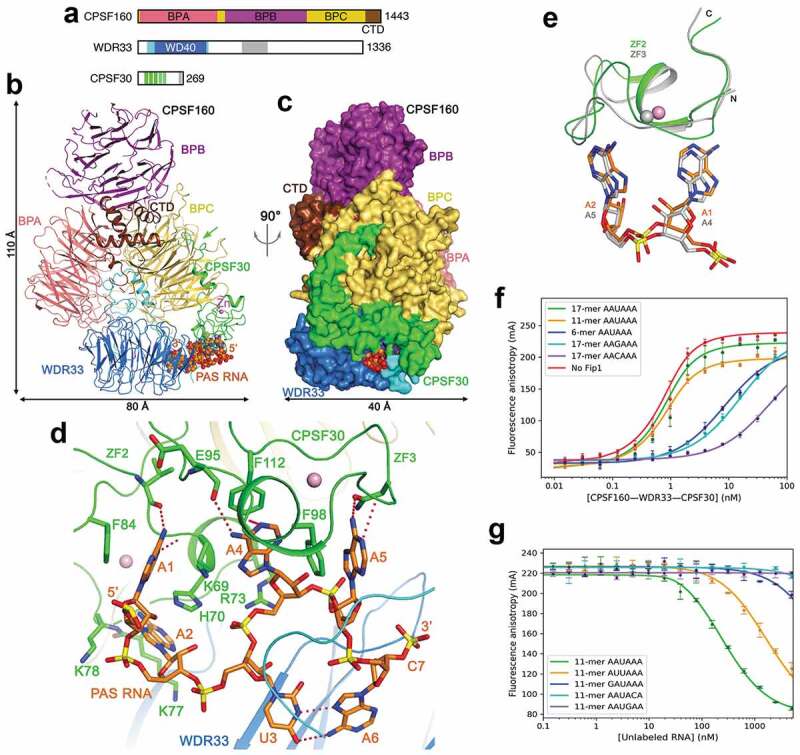
Recognition of the AAUAAA PAS by mPSF. (a). Domain organization of human CPSF160, WDR33 and CPSF30. The segments just before and after the WD40 domain of WDR33 are in cyan, and the collagen repeat region in gray. The ZFs of CPSF30 are in green, and the zinc knuckle in gray. (b). Schematic drawing of the structure of the human CPSF160-WDR33-CPSF30-PAS RNA quaternary complex [23]. The proteins are colored as in panel a, and the PAS RNA in orange. The green arrow points to the interaction between the N-terminal segment of CPSF30 and BPC of CPSF160. (c). The structure of the complex, viewed after a 90° rotation around the vertical axis. The proteins are shown as molecular surface. (d). Interactions between the AAUAAA hexamer and CPSF30 and WDR33. Hydrogen-bonding interactions are shown as dashed lines in red. (e). Overlay of the binding mode of A1-A2 to ZF2 (in color) with that of A4-A5 to ZF3 of CPSF30 (in gray). (f). Fluorescence anisotropy binding curves of various RNAs to CPSF160-WDR33-CPSF30-hFip1 [47]. (g). Fluorescence anisotropy competition binding curves of various PAS hexamers to CPSF160-WDR33-CPSF30-hFip1. Structure figures were produced with PyMOL (www.pymol.org) unless otherwise noted.
