Figure 4.
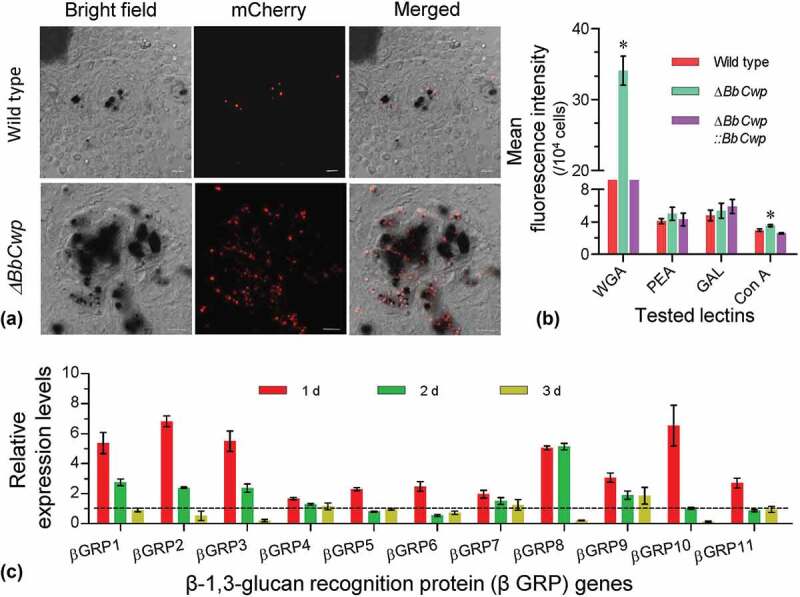
BbCwp protects fungus from host recognition. (a) Disruption of BbCwp resulted in an enhanced hemocyte encapsulation. Fungal strain was labeled by expressing the mCherry gene. Conidial suspension (5 µl, 105 conidia/ml) was injected into host. After an incubation of 3 h at 25°C, hemocyte encapsulation was examined under a fluorescence microscope. (b) Conidial lectin-binding pattern. Lectins included concanavalin A (ConA), Galanthus nivalis lectin (GNL), peanut agglutinin (PNA), and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). ΔBbCwp mutant strain displayed a significant increase in fluorescence intensity of WGA. (c) Relative expression levels of β-1, 3-glucan recognition protein genes (βGRP). In G. mellonella, there are 11 βGRP genes. Comparative analyses between the wild type/ΔBbCwp were performed at different time points during infection process. Gene disruption led to a significant up-regulation of all tested genes at 1 d post infection. Tukey’s HSD was used to determine the statistical significance using a threshold of P < 0.05. Error bars: standard deviation.
