Figure 1.
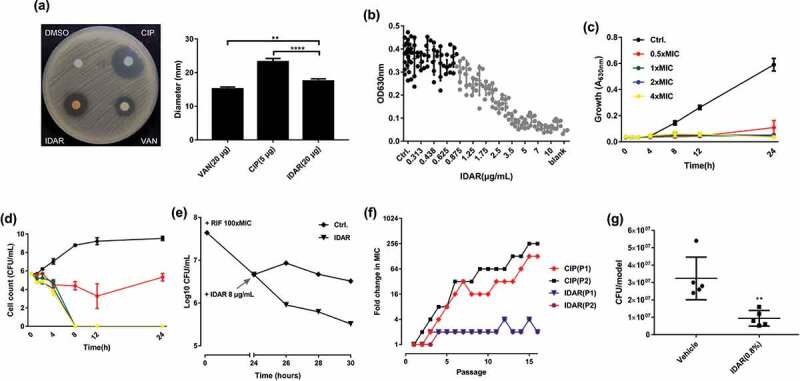
IDAR exhibits bactericidal activity against MRSA and persister cells. (a) Disk diffusion assay of IDAR showing activity against S. aureus ATCC 43300. The amounts of VAN, CIP, and IDAR were 20 μg, 5 μg, and 20 μg per disk, respectively. (b) Dose-dependent efficacy of IDAR against ATCC 43300 determined by the broth microdilution assay. (c) Cell growth inhibitory effects of IDAR at 0.5–4 × MIC against ATCC 43300 at different timepoints. (d) Time-dependent bactericidal effects of IDAR against ATCC 43300 at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 4 × MIC. (e) Persister cells induced by RIF at 100 × MIC, followed by treatment with 8 μg/ml IDAR for a total of 6 h. Viable cell counts were recorded by the serial dilution method. (f) Appearance of ATCC 43300 spontaneous resistance in the presence of IDAR and CIP over 16 d of serial passage in duplicate (P1 and P2). (g) MRSA antimicrobial effects of 8 h of treatment with an ointment containing IDAR (0.8%, wt/wt) in an acute wound model infected by ATCC 43300.
