Figure 7.
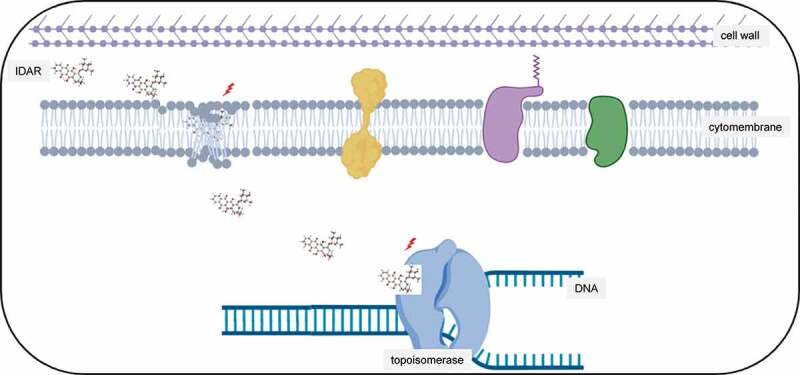
Antimicrobial model of the mechanism of IDAR. Red lighting indicates the target of IDAR. IDAR penetrates the cell wall into the cell membrane, disrupts the normal structure of the phospholipid bilayer, and in addition, some IDAR penetrates the cytoplasm and interacts with the topoisomerase IIA subunits GyrA and GyrB, inhibiting DNA replication and cell growth and showing bactericidal effects.
