In the coming fall, graduate medical education will be adapting to the disruptions in resident recruitment caused by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Out of concern for the safety of medical students, the upcoming recruitment season will be conducted remotely.
The benefits of remote interviews are obvious: an elimination of the risk for contagion during travel and face-to-face interviews. Additionally, remote interviews are inexpensive and convenient—and therein lies the problem. Remote interviews will almost certainly exacerbate the problem of overapplication that has plagued the match since the introduction of the Electronic Residency Application Service (ERAS).
Overapplication in ERAS
Before the advent of ERAS, the cumbersome process of applying to residency programs limited the number of applications medical students were willing to send. However, with ERAS, medical students had the ability to apply to all programs of their choice with a click of the mouse. Because modest increases in numbers of applications tended to increase applicants’ chances of matching, it made sense to apply widely.
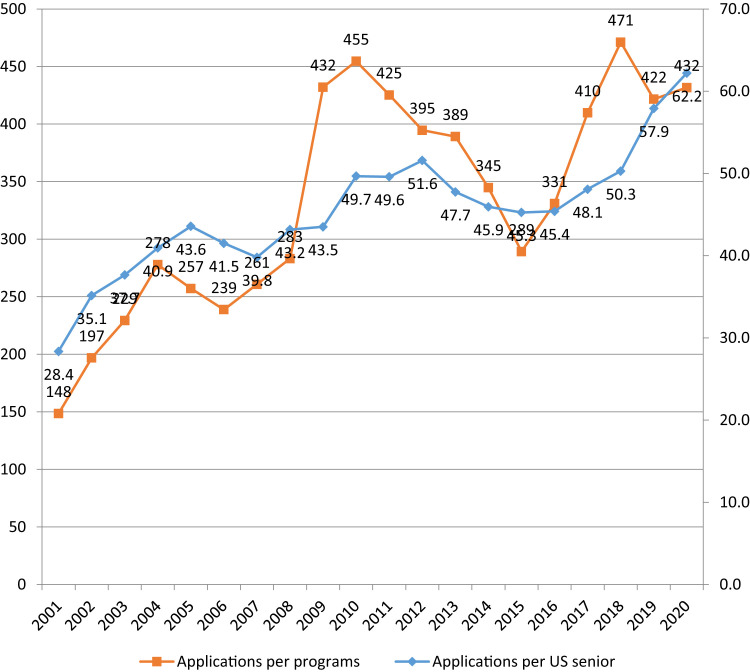
As a result, since 2001 the average number of applications per applicant through ERAS has increased every year in every participating specialty [1]. In radiology, the number of applications per US medical school senior has more than doubled, and the number of applications per training program has more than tripled (Fig. 1 ). Faced with a deluge of applications, residency programs increasingly relied on the US Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 score filter, leading to its own set of problems. To remedy the situation, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) initiated the Apply Smart web page, which allowed medical students to determine the point of diminishing returns for each subsequent application depending on their USLME scores. Still, the number of applications per person continued to rise. Weissbart et al [2] explained the phenomenon using the concept of the prisoner’s dilemma (Table 1 ), predicting that as long as their peers are not limited in number of applications, medical students will try to stay ahead of the competition by applying to more and more programs.
Fig 1.
Mean number of applications per US medical student and per program applying to radiology residencies in the Electronic Residency Application Service [6].
Table 1.
The prisoner’s dilemma applied to the ERAS application strategy
| Group 1: Students apply to and accept interviews from only their top-choice programs | Group 1: Students apply to as many programs as possible | |
| Group 2: Students apply to and accept interviews from only their top-choice programs | Training programs grant more interviews to truly interested and qualified students with less emphasis on ERAS filters such as USMLE scores and in-state location resulting in a more diverse resident body. Students are less constrained by in-state location. Both groups of students benefit. | Group 2 students who applied only to their top-choice programs are more likely to fail in the match. Group 1 students benefit by overapplication. |
| Group 2: Students apply to as many programs as possible | Group 1 students who applied only to their top-choice programs are more likely to fail in the match. Group 2 students benefit by overapplication. | Training programs are overwhelmed with applications and filter them by the USMLE score and in-state location. Qualified students with lower USLME scores cannot get interviews, resulting in a less diverse resident body. Students are more constrained by in-state location. Both groups of students are harmed by overapplication. |
Note: ERAS = Electronic Residency Application Service; USMLE = US Medical Licensing Examination.
COVID-19 and the Upcoming Interview Season
It is likely that remote interviews will further exacerbate the problem by taking the cost of time and travel off the table. Fogel et al [3] reported that 41% of medical students declined some residency interviews for financial reasons. According to the most recent National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) 2017 applicant survey [4], on average, applicants received 16 invitations and attended 12 interviews. Thus, in an average interview season, up to a quarter of interview offers are declined at least in part because of costs of time and travel.
We predict that transition to remote interviews will result in increased numbers of interview requests (ERAS applications) and a higher interview acceptance rate. In the nearly costless scenario, medical students lose nothing from every additional encounter while improving their interviewing skills. Because the most desirable students are usually invited first, we foresee that the competitive cohort is likely to displace other qualified applicants who would have been granted interviews in prior years. If this comes to pass, programs will interview the same applicants, resulting in a smaller rank pool and an increase in the number of unfilled positions and unmatched applicants.
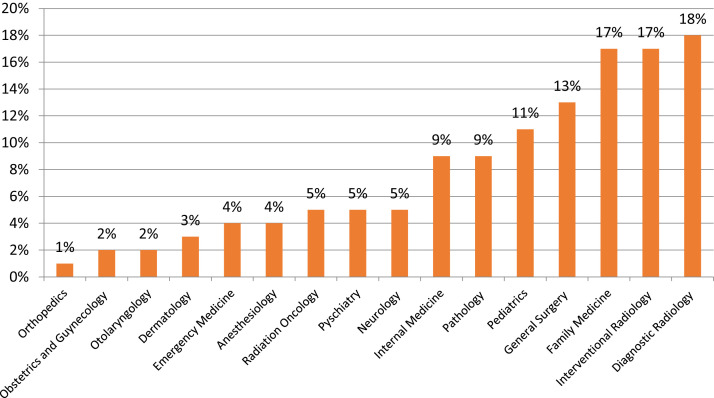
Radiology would be particularly affected because of its frequent use by applicants as a “backup” specialty (Fig. 2 ). The higher the percentage of such applicants in a given specialty, the more it must compete with other specialties for qualified candidates. If the cost constraints of in-person interviews are removed, top-tier applicants using a specialty for “backup” may further displace qualified candidates for whom that specialty is the first or only choice.
Fig 2.
Percentage of US medical students who matched to the specialty while ranking it as not their first choice [7].
Immediate Solutions
The calls by programs for hard application caps [2] are unacceptable to medical students, and the calls by medical student groups for program-specific data on characteristics of matched applicants are unacceptable to programs. Attempts at making the application process less generic, such as the 2015 requirement of a program-specific paragraph introduced in the otolaryngology match, may have contributed to a decline in applications and increase in unmatched programs [5]. Regardless, none of these steps correct the fundamental problem because they do not allow applicants to determine their competitiveness and signal their preferences to training programs.
All program directors receive numerous expressions of interest from applicants, but such declarations are of little value because programs cannot judge the sincerity of such an expression. We recently surveyed radiology program directors as to whether they would consider an “early action” period, whereby for a short time (eg, 2 weeks) at the beginning of the interview season, ERAS could allow medical students to apply to a small number (eg, 10) of programs of their choice, thus allowing a clear indication of special interest in a program. More than three-quarters of respondents were willing to participate in such a program.
Unfortunately, our repeated attempts at persuading ERAS to pilot the solutions did not gain traction. It is possible that the AAMC, the parent of ERAS, did not see this to be a problem for medical students. However, medical students clearly saw it as a problem and, recently, appear to have taken matters into their own hands with the creation of Signal, the Residency Application Preference Signaling Platform (https://signaltokens.org). This platform allows medical students, for a fee of $25, to signal their interest to 12 training programs of their choice. Participating programs may sign up at no cost. The website is up and running at this time. It is uncertain whether the platform can enroll enough match participants to decrease applicant congestion in the match this season. However, if it succeeds it is likely to do much good. As remote residency interviews, like remote work, telemedicine, and online instruction, are likely to remain in some form, at the very least Signal and other novel solutions would send a message to the AAMC, ERAS, and NRMP that “business as usual” cannot continue and urgent reform must take place.
In conclusion, while the NRMP algorithm continues to fulfill its promise of a strategy-free residency match, the current application and interview process is increasingly flawed. We worry that the COVID-19 pandemic, with its transition to remote interviews, will exacerbate the problem. In the coming match season, residency administrators should keep in mind that a rise in the number of applications and a higher interview acceptance rate from highly qualified applicants do not mean greater interest in either their programs or radiology as a specialty. Rather, many desirable candidates may use the additional screen time to hone their interview skills. Some novel solutions, such as the Signal platform, are already available. Training programs that decide against using the new methods would do well to interview more applicants this fall in order to fill all positions on match day. This year in particular we cannot be complacent.
Caveat emptor.
Footnotes
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest related to the material discussed in this article. Dr Rozenshtein is a nonpartner employee, and is the Director of Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging in the Department of Radiology at the Westchester Medical Center, Valhalla, New York. Dr Griffith is a nonpartner employee and is the Director of the Diagnostic Radiology Residency Program at Henry Ford Hospital. Dr Ruchman is a nonpartner employee and is the Chief of Radiology at the Advent Health Medical Group.
References
- 1.Weissbart S.J., Kim S.J., Feinn R.S. Relationship between the number of residency applications and the yearly match rate: time to start thinking about an application limit? J Grad Med Educ. 2015;7:81–85. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-14-00270.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Weissbart S.J., Hall S.J., Fultz B.R., Stock J.A. The urology match as a prisoner’s dilemma: a game theory perspective. Urology. 2013;82:791–798. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.04.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fogel H.A., Liskutin T.E., We K. The economic burden of residency interviews on applicants. Iowa Orthop J. 2018;38:9–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.National Resident Matching Program Results of the 2017 NRMP applicant survey by preferred specialty and applicant type. https://mk0nrmp3oyqui6wqfm.kinstacdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Applicant-Survey-Report-2017.pdf Available at:
- 5.Kramer S. Is the program-specific paragraph responsible for declining application numbers? A commentary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;158:215–216. doi: 10.1177/0194599817751053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Association of American Medical Colleges ERAS statistics. https://www.aamc.org/eras-statistics-2019 Available at:
- 7.National Resident Matching Program Results and data: 2020 main residency match. https://mk0nrmp3oyqui6wqfm.kinstacdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/MM_Results_and-Data_2020-1.pdf Available at: