Key Points
Question
How are temporal changes in the level of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at which long-term dialysis is initiated among at-risk patients associated with the number of patients with end-stage kidney disease in the population?
Findings
This cohort study of 983 122 individuals in the initial 3-year interval (2001-2003) to 1 844 317 individuals in the final interval (2016-2018) used data from a large, integrated health care delivery system in Northern California and found that an increase in the number of individuals starting dialysis with an eGFR of 10 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2 was associated with changes over time in the likelihood of receiving dialysis at this eGFR independent of the number of people in the underlying population who had this same eGFR. Estimated incidence of new end-stage kidney disease cases would have been 16% lower with no changes in system-level practice patterns or other factors besides timing of long-term dialysis initiation.
Meaning
The timing of long-term dialysis initiation is associated with the number of individuals with end-stage kidney disease.
Abstract
Importance
In the last 2 decades, there have been notable changes in the level of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at which patients initiate long-term dialysis in the US and around the world. How changes over time in the likelihood of dialysis initiation at any given eGFR level in at-risk patients are associated with the population burden of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) has not been not well defined.
Objective
To examine temporal trends in long-term dialysis initiation by level of eGFR and to quantify how these patterns are associated with the number of patients with ESKD.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Retrospective cohort study analyzing data obtained from a large, integrated health care delivery system in Northern California from 2001 to 2018 in successive 3-year intervals. Included individuals, ranging in number from as few as 983 122 (2001-2003) to as many as 1 844 317 (2016-2018), were adult members with 1 or more outpatient serum creatinine levels determined in the prior year.
Main Outcomes and Measures
One-year risk of initiating long-term dialysis stratified by eGFR levels. Multivariable logistic regression was performed to assess temporal trends in each 3-year cohort with adjustment for age, sex, race, and diabetes status. The potential change in dialysis initiation in the final cohort (2016-2018) was estimated using the relative difference between the standardized risks in the initial cohort (2001-2003) and the final cohort.
Results
In the initial 3-year cohort, the mean (SD) age was 55.4 (16.3) years, 55.0% were women, and the prevalence of diabetes was 14.9%. These characteristics, as well as the distribution of index eGFR, were stable across the study period. The likelihood of receiving dialysis at eGFR levels of 10 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2 generally increased over time. For example, the 1-year odds of initiating dialysis increased for every 3-year interval by 5.2% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.052; 95% CI, 1.004-1.102) among adults with an index eGFR of 20 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2, by 6.6% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.066; 95% CI, 1.007-1.130) among adults with an eGFR of 16 to 17 mL/min/1.73 m2, and by 5.3% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.053; 95% CI, 1.008-1.100) among adults with an eGFR of 10 to 13 mL/min/1.73 m2, adjusting for age, sex, race, and diabetes. The incidence of new cases of ESKD was estimated to have potentially been 16% (95% CI, 13%-18%) lower if there were no changes in system-level practice patterns or other factors besides timing of initiating long-term dialysis from the initial 3-year interval (2001-2003) to the final interval (2016-2018) assessed in this study.
Conclusions and Relevance
The present results underscore the importance the timing of initiating long-term dialysis has on the size of the population of individuals with ESKD.
This large cohort study assesses temporal trends in initiating long-term kidney dialysis by level of estimated glomerular filtration rate to evaluate whether an association exists between these trends and the number of patients with end-stage kidney disease.
Introduction
In the last 2 decades, there have been notable changes in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at which long-term dialysis is initiated in the US and around the world.1 For example, according to the nationally comprehensive US Renal Data System registry, the proportion of new patients with end-stage renal disease in the US with an eGFR of 10 to 15 mL/min/1.73 m2 at the start of dialysis increased from 10% in 1996 to a peak of 28% in 2010.2 Although several previous publications have examined dialysis initiation over time, a key remaining knowledge gap is the distribution of eGFR in the underlying at-risk population from which the end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) cases are derived. Thus, secular trends in the likelihood of dialysis initiation at any given eGFR level could not be defined in previous studies, and the implications of potential trends in changes in the size of the at-risk population on the number of patients with ESKD in the population could not be estimated.
Nationally, the societal and patient burden of ESKD is high, with Medicare fee-for-service spending for beneficiaries with ESKD rising from $33.8 billion to $35.4 billion between 2015 and 2016.2 Furthermore, national rates of morbidity and death are very high surrounding initiation of long-term dialysis.3,4,5 Initiation of long-term dialysis can also be associated with declines in cognitive function and functional status6,7 and worsening cardiac structure.8 The July 2019 Advancing American Kidney Health initiative issued by the White House targeted as a major national priority reducing the number of new ESKD cases by 25% by 2030.9
Because ESKD is operationally defined as receiving long-term dialysis or a kidney transplant, we hypothesized that the number of patients with incident ESKD can vary considerably depending on decisions between patients and physicians about the choice and timing of kidney replacement therapy, and particularly of initiating dialysis. Consistent with this, after publication of the Initiating Dialysis Early and Late (IDEAL) trial—a randomized clinical trial showing no significant difference in death or other outcomes with earlier (eGFR of 9.0 mL/min/1.73 m2) vs later (eGFR of 7.2 mL/min/1.73 m2) initiation of dialysis10—a rapid drop in early dialysis initiation was observed in Canada.11 Although early dialysis initiation was defined in that study as dialysis initiation at eGFR higher than 10.5 mL/min/1.73 m2, there was no information regarding how the number of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) in the underlying population with eGFR higher than 10.5 mL/min/1.73 m2 may have changed during the relevant period.
To date, no study has quantified how secular patterns in the likelihood of dialysis initiation at any given eGFR level can impact the number of patients with incident ESKD in a population over time. We addressed this important knowledge gap by examining temporal trends in dialysis initiation by level of kidney function within a large, community-based population to provide information relevant for policies supporting the national advancement of kidney health.
Methods
Source Population
Kaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) is a large, integrated health care delivery system currently providing comprehensive care for more than 4.5 million members. Its membership is sociodemographically diverse and highly representative of the local and statewide population.12 Nearly all aspects of care are captured through KPNC’s integrated electronic health record system, with access to clinical data elements from all practice settings (eg, laboratory test results and vital signs) as well as previously validated algorithms that incorporate relevant diagnostic or procedure codes and pharmacy dispenses. This study was approved by the KPNC institutional review board, which also waived the requirement for obtaining informed consent because this study was a retrospective data-only analysis of linked data that were deidentified before analysis.
Study Sample, Outcome, and Covariates
We assembled cohorts of all adult members (18 years or older) with at least 1 valid outpatient serum creatinine measurement from 2001 through 2018 grouped into 3-year intervals (ie, 2001-2003, 2004-2006, 2007-2009, 2010-2012, 2013-2015, and 2016-2018), which provided more stable and precise estimates of ESKD rates. Individuals with 12 or more months of continuous health plan membership were included in 3-year cohorts on the first eligible January 1st within each 3-year interval. Approximately 15% of eligible patients were excluded in each cohort owing to insufficient prior continuous membership. Patients with a prior kidney transplant or who were already undergoing long-term dialysis were also excluded (approximately 5% of each cohort).
Our primary outcome was initiation of long-term dialysis within the first eligible year in each 3-year interval, ascertained through a comprehensive, manually validated health plan ESKD treatment registry.13 Patients are entered into the registry after manual review to confirm that receipt of dialysis was not temporary or only for acute kidney injury. We removed cases of preemptive kidney transplant (3% of ESKD cases). Initial dialysis modality (hemodialysis vs peritoneal dialysis) was ascertained from registry files. We defined urgent dialysis starts as being preceded by an episode of dialysis-requiring acute kidney injury13 within 28 days before long-term dialysis initiation. All cases not meeting this definition were considered elective starts.
Age, sex, and self-reported race were obtained from electronic health records to calculate eGFR and to account for potential changes in the source population. Targeted comorbidities in the study population were defined using validated International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision and Tenth Revision diagnostic codes, laboratory results, and receipt of medications using electronic health record–based data that were cleaned and linked at the individual-patient level into the KPNC Virtual Data Warehouse as previously described and validated.14,15,16,17 We ascertained outpatient laboratory test results, including the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration equation–based eGFR and proteinuria.18
Statistical Analysis
For each 3-year cohort, we calculated the 1-year risk of initiating long-term dialysis, overall and by urgent vs elective starts, directly standardized to the 2001 to 2003 KPNC population by age, sex, and index eGFR (ie, most recent outpatient measurement before cohort entry). We estimated a potential change in dialysis initiation in the final cohort (2016-2018) using the relative difference between the standardized risks and associated 95% CIs in the initial cohort (2001-2003) and the final cohort.
We next stratified the study population into a priori selected index eGFR levels of 60 to 150, 30 to 59, 25 to 29, 20 to 24, 18 to 19, 16 to 17, 14 to 15, 10 to 13, 6 to 9, and 0 to 5 mL/min/1.73 m2. Within each eGFR stratum, we calculated the 1-year risk of receiving long-term dialysis across each 3-year interval. All crude temporal trends were evaluated using Cochrane-Armitage tests for trend. To assess multivariable-adjusted temporal trends, we evaluated the significance and odds ratios (95% CIs) of an ordinal 3-year cohort term in a logistic regression model adjusting for age, sex, race, and diabetes status and used a generalized estimating equations approach to account for correlations between repeated individuals across calendar cohorts.
To enhance comparability with previous studies, we also report the mean (SD) eGFR at dialysis initiation in each time interval, using the most recent outpatient eGFR measurement before dialysis initiation.2 This eGFR value is separate from the index eGFR value used for assembly of calendar year cohorts.
All data were analyzed using SAS, version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc). A 2-sided P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Characteristics
Between 2001 and 2018, the size of the eligible population increased consistent with growth in overall KPNC enrollment and more frequent outpatient serum creatinine testing per patient (Table 1). In the first 3-year interval (2001-2003) the mean (SD) age in the eligible population was 55.4 (16.3) years, 55.0% were women, and the prevalence of diabetes was 14.9%. These characteristics as well as the distribution of index eGFR were stable across the study period. The prevalence of documented hypertension and dyslipidemia increased since 2001, although this was largely due to increased detection and changing systemwide practice guidelines. In later years, we also observed a higher prevalence of Asian/Pacific Islander and Hispanic patients.
Table 1. Characteristics of Adults With Valid Serum Creatinine Measurements Receiving Care at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 2001-2018.
| Characteristic | Adults, No. (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001-2003 (n = 983 122) | 2004-2006 (n = 1 241 537) | 2007-2009 (n = 1 411 690) | 2010-2012 (n = 1 482 883) | 2013-2015 (n = 1 607 737) | 2016-2018 (n = 1 844 317) | |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 55.4 (16.3) | 54.7 (16.3) | 54.2 (16.3) | 54.6 (16.4) | 54.9 (16.7) | 54.7 (16.9) |
| Age categories, y | ||||||
| 18-40 | 179 731 (18.3) | 240 543 (19.4) | 286 716 (20.3) | 295 446 (19.9) | 328 504 (20.4) | 399 867 (21.7) |
| 41-60 | 416 351 (42.3) | 539 286 (43.4) | 615 565 (43.6) | 622 535 (42.0) | 638 647 (39.7) | 705 825 (38.3) |
| 61-75 | 259 110 (26.4) | 310 287 (25.0) | 346 504 (24.5) | 390 589 (26.3) | 447 649 (27.8) | 524 846 (28.5) |
| >75 | 127 930 (13.0) | 151 421 (12.2) | 162 905 (11.5) | 174 313 (11.8) | 192 937 (12.0) | 213 779 (11.6) |
| Women | 540 490 (55.0) | 682 077 (54.9) | 773 307 (54.8) | 817 276 (55.1) | 883 892 (55.0) | 1 007 674 (54.6) |
| Self-reported race | ||||||
| White | 573 225 (58.3) | 697 084 (56.1) | 769 082 (54.5) | 797 395 (53.8) | 850 849 (52.9) | 927 541 (50.3) |
| Black/African American | 79 894 (8.1) | 94 415 (7.6) | 103 164 (7.3) | 108 548 (7.3) | 115 687 (7.2) | 129 088 (7.0) |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 121 761 (12.4) | 173 116 (13.9) | 221 400 (15.7) | 257 561 (17.4) | 299 665 (18.6) | 370 711 (20.1) |
| Other/unknown | 208 242 (21.2) | 276 922 (22.3) | 318 044 (22.5) | 319 379 (21.5) | 341 536 (21.2) | 416 977 (22.6) |
| Hispanic ethnicity | 129 213 (13.1) | 178 716 (14.4) | 222 922 (15.8) | 238 701 (16.1) | 269 953 (16.8) | 334 194 (18.1) |
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Current | 103 728 (10.6) | 169 502 (13.7) | 156 589 (11.1) | 134 965 (9.1) | 134 051 (8.3) | 140 041 (7.6) |
| Former | 13 477 (1.4) | 48 476 (3.9) | 243 301 (17.2) | 352 580 (23.8) | 403 922 (25.1) | 457 932 (24.8) |
| CKD-EPI eGFR, mean (SD), mL/min/1.73 m2 | 85.3 (21.5) | 86.0 (21.4) | 85.1 (21.3) | 88.2 (21.2) | 87.5 (21.0) | 88.6 (21.2) |
| CKD-EPI eGFR category, mL/min/1.73 m2 | ||||||
| 60-150 | 863 987 (87.88) | 1 098 418 (88.5) | 1 240 252 (87.9) | 1 336 995 (90.2) | 1 447 191 (90.0) | 1 672 049 (90.7) |
| 30-59 | 110 721 (11.3) | 133 503 (10.8) | 160 126 (11.3) | 135 829 (9.2) | 150 083 (9.3) | 161 204 (8.7) |
| 25-29 | 3865 (0.39) | 4507 (0.36) | 5654 (0.40) | 4927 (0.33) | 5055 (0.31) | 5255 (0.28) |
| 20-24 | 2260 (0.23) | 2684 (0.22) | 3035 (0.21) | 2755 (0.19) | 2855 (0.18) | 2990 (0.16) |
| 18-19 | 604 (0.06) | 709 (0.06) | 782 (0.06) | 720 (0.05) | 713 (0.04) | 809 (0.04) |
| 16-17 | 468 (0.05) | 536 (0.04) | 610 (0.04) | 536 (0.04) | 607 (0.04) | 649 (0.04) |
| 14-15 | 369 (0.04) | 408 (0.03) | 444 (0.03) | 427 (0.03) | 438 (0.03) | 496 (0.03) |
| 10-13 | 553 (0.06) | 515 (0.04) | 563 (0.04) | 490 (0.03) | 542 (0.03) | 611 (0.03) |
| 6-9 | 264 (0.03) | 220 (0.02) | 201 (0.01) | 178 (0.01) | 220 (0.01) | 222 (0.01) |
| 0-5 | 31 (0.00) | 37 (0.00) | 23 (0.00) | 26 (0.00) | 33 (0.00) | 32 (0.00) |
| Medical history | ||||||
| Acute myocardial infarction | 14 415 (1.5) | 16 256 (1.3) | 16 703 (1.2) | 14 693 (1.0) | 12 878 (0.8) | 11 974 (0.6) |
| Atrial fibrillation/flutter | 24 511 (2.5) | 33 494 (2.7) | 40 430 (2.9) | 47 405 (3.2) | 56 902 (3.5) | 66 575 (3.6) |
| Ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack | 14 146 (1.4) | 16 883 (1.4) | 16 211 (1.1) | 14 892 (1.0) | 16 176 (1.0) | 23 080 (1.3) |
| Heart failure | 19 853 (2.0) | 24 918 (2.0) | 30 433 (2.2) | 31 475 (2.1) | 31 440 (2.0) | 34 018 (1.8) |
| Mitral or aortic valvular disease | 15 789 (1.6) | 25 266 (2.0) | 31 274 (2.2) | 30 817 (2.1) | 31 171 (1.9) | 36 021 (2.0) |
| Venous thromboembolism | 4656 (0.5) | 5377 (0.4) | 6118 (0.4) | 6822 (0.5) | 8927 (0.6) | 13 127 (0.7) |
| Diabetes | 146 298 (14.9) | 185 806 (15.0) | 219 498 (15.5) | 237 431 (16.0) | 262 638 (16.3) | 312 960 (17.0) |
| Hypertension | 307 243 (31.3) | 446 279 (35.9) | 544 853 (38.6) | 588 694 (39.7) | 614 317 (38.2) | 660 973 (35.8) |
| Dyslipidemia | 321 948 (32.7) | 516 220 (41.6) | 644 239 (45.6) | 706 601 (47.7) | 774 987 (48.2) | 857 073 (46.5) |
| Hyperthyroidism | 26 761 (2.7) | 36 463 (2.9) | 40 837 (2.9) | 42 933 (2.9) | 47 680 (3.0) | 56 325 (3.1) |
| Hypothyroidism | 101 838 (10.4) | 127 484 (10.3) | 144 472 (10.2) | 156 335 (10.5) | 172 232 (10.7) | 195 849 (10.6) |
| Chronic liver disease | 17 136 (1.7) | 29 510 (2.4) | 39 983 (2.8) | 47 458 (3.2) | 55 878 (3.5) | 76 039 (4.1) |
| Chronic lung disease | 273 959 (27.9) | 238 618 (19.2) | 268 455 (19.0) | 320 192 (21.6) | 334 295 (20.8) | 359 858 (19.5) |
| Diagnosed dementia | 11 718 (1.2) | 16 908 (1.4) | 23 404 (1.7) | 25 442 (1.7) | 28 665 (1.8) | 31 160 (1.7) |
| Diagnosed depression | 108 859 (11.1) | 159 655 (12.9) | 190 748 (13.5) | 201 285 (13.6) | 200 943 (12.5) | 218 521 (11.8) |
Abbreviations: CKD-EPI, Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Temporal Trends in eGFR at Dialysis Initiation
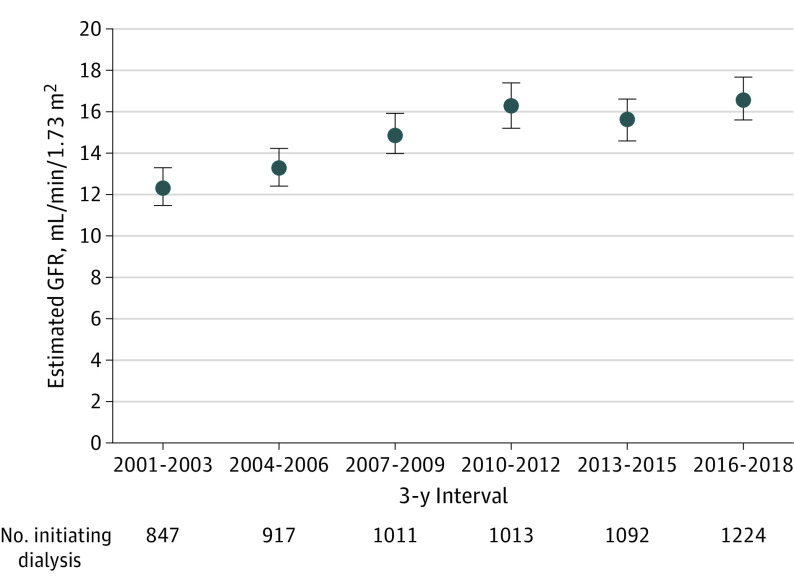
Overall, the temporal trend in mean eGFR at dialysis initiation mirrored that seen in the general US population,19 with a progressively higher mean eGFR through the first decade of the 21st century, followed by a plateau (Figure 1). Mean (SD) eGFR at dialysis initiation for patients starting long-term dialysis was 12.4 (13.1) mL/min/1.73 m2 in 2001 to 2003, rose to 16.3 (17.7) mL/min/1.73 m2 in 2010 to 2012, and did not further increase through 2016 to 2018. These temporal trends were similar for elective starts and for all patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis (eFigure 1 in the Supplement).
Figure 1. Mean Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) at Dialysis Initiation Among Patients Initiating Dialysis Between 2001 and 2018, by 3-Year Intervals.
Data are based on outpatient, nonemergency department serum creatinine level closest to dialysis initiation date. Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
Temporal Trends in Dialysis Initiation
In our study population, the number of eligible patients who started dialysis was 847 (0.086% of 983 122 at risk) in 2001 to 2003, 917 (0.074% of 1 241 537) in 2004 to 2006, 1011 (0.072% of 1 411 690) in 2007 to 2009, 1013 (0.068% of 1 482 883) in 2010 to 2012, 1092 (0.068% of 1 607 737) in 2013 to 2015, and 1224 (0.066% of 1 844 317) in 2016 to 2018. The proportion of elective ESKD cases was 85.6% in 2001 to 2003, 89.2% in 2004 to 2006, 94.1% 2007 to 2009, 74.9% in 2010 to 2012, 87.2% in 2013 to 2015, and 84.0% in 2016 to 2018. In addition, the proportion of new ESKD cases initiating peritoneal dialysis was 13.7% in 2001 to 2003, 14.2% in 2004 to 2006, 11.0% in 2007 to 2009, 13.4% in 2010 to 2012, 21.7% in 2013 to 2015, and 20.8% in 2016 to 2018. As recently reported,20 KPNC has made a concerted systemwide effort to increase peritoneal dialysis as the preferred initial modality since approximately 2008.
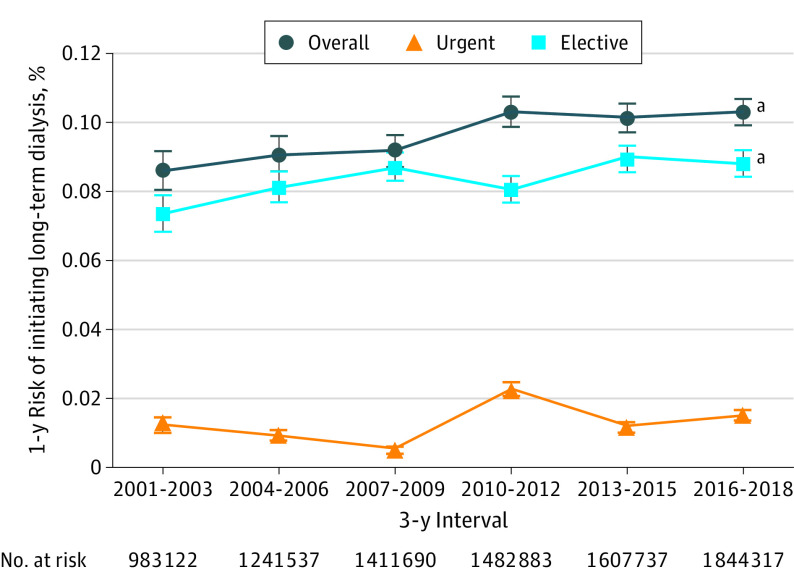
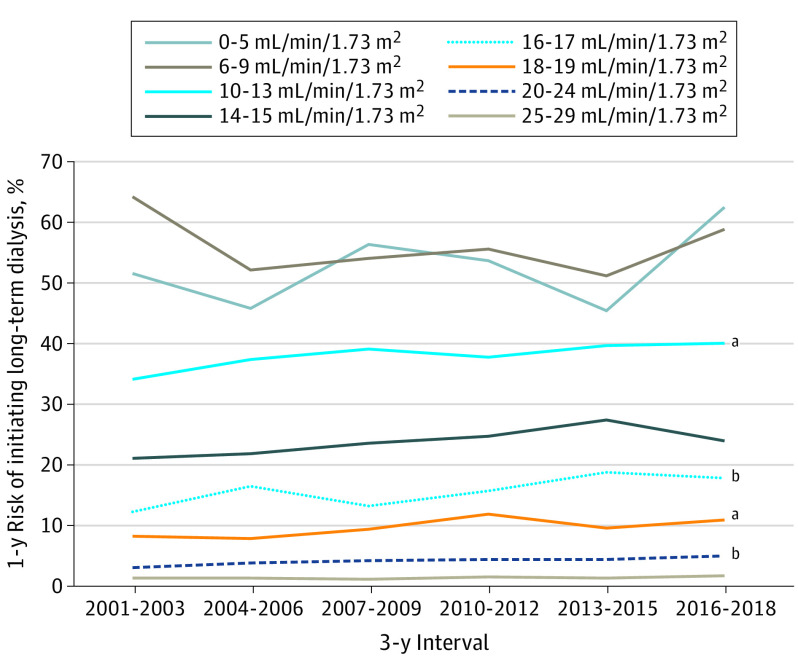
The likelihood of long-term dialysis initiation within 1 year increased from 0.086% (95% CI, 0.080%-0.092%) in 2001 to 2003, to 0.103% (95% CI, 0.099%-0.107%) in 2016 to 2018 (P < .001 for trend) (Figure 2). When examining the annual risk of initiating long-term dialysis by index eGFR between 2001 and 2018, the most prominent secular trends were noted in those with an index eGFR of 20 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2 (from 3.2% to 5.1%; P = .001), those with an index eGFR of 18 to 19 mL/min/1.73 m2 (from 8.3% to 11.0%; P = .03), those with an index eGFR of 16 to 17 mL/min/1.73 m2 (from 12.4% to 17.9%; P = .005), and those with an index eGFR of 10 to 13 mL/min/1.73 m2 (from 34.2% to 40.3%; P = .03) (Figure 3; eFigure 2 in the Supplement). After adjustment for age, sex, race, and diabetes, statistically significant temporal increases in 1-year odds of initiating dialysis persisted among eGFR categories of 20 to 24, 16 to 17, and 10 to 13 mL/min/1.73 m2 (Table 2). Among patients with an index eGFR of 20 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2, the 1-year odds of initiating dialysis increased for every 3-year interval by 5.2% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.052; 95% CI, 1.004-1.102); among patients with an eGFR 16 to 17 mL/min/1.73 m2, the 1-year odds of initiating dialysis increased by 6.6% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.066; 95% CI, 1.007-1.130); and among patients with an eGFR of 10 to 13 mL/min/1.73 m2, the 1-year odds of initiating dialysis increased by 5.3% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.053; 95% CI, 1.008-1.100) (Table 2). By contrast, among patients with very low index eGFR (≤9 mL/min/1.73 m2), we observed stable or decreased unadjusted and adjusted odds of initiating dialysis over time. These patterns were similar among the subset of patients with elective dialysis starts (eTable in the Supplement).
Figure 2. Age-, Sex-, and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate–Standardized Annual Risk of Initiating Long-term Dialysis Among Adults With Serum Creatinine Measurements at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 2001-2018, Overall and by Elective vs Urgent Dialysis Start.
Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
aP < .001 for trend.
Figure 3. Annual Risk of Initiating Long-term Dialysis by Calendar Year and Index Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate, 2001-2018.
See Table 2 for unadjusted P values.
aP < .05 for trend.
bP < .01 for trend.
Table 2. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations for Calendar Year Trend in the Annual Risk of Initiating Dialysis by Index eGFR Category at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 2001-2018, by 3-Year Interval.
| eGFR category, mL/min/1.73 m2 | No. | P value | AOR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusteda | Adjustedb | |||
| 60-150 | 7 658 892 | .89 | .70 | 0.989 (0.934-1.047) |
| 30-59 | 851 466 | .14 | .74 | 1.007 (0.966-1.049) |
| 25-29 | 29 263 | .17 | .68 | 1.012 (0.955-1.073) |
| 20-24 | 16 579 | .001 | .03 | 1.052 (1.004-1.102) |
| 18-19 | 4337 | .03 | .07 | 1.060 (0.996-1.129) |
| 16-17 | 3406 | .005 | .03 | 1.066 (1.007-1.130) |
| 14-15 | 2582 | .08 | .13 | 1.044 (0.987-1.105) |
| 10-13 | 3274 | .03 | .02 | 1.053 (1.008-1.100) |
| 6-9 | 1305 | .21 | .06 | 0.938 (0.878-1.002) |
| 0-5 | 182 | .47 | .97 | 0.996 (0.825-1.201) |
Abbreviations: AOR, adjusted odds ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Cochrane-Armitage test for trend.
Reflects the significance of an ordinal 3-year cohort term in a logistic regression model for end-stage kidney disease adjusting for age, sex, race, and diabetes.
Overall, we estimated that incidence of ESKD could have potentially been 16% (95% CI, 13%-18%) lower if there were no changes in system-level practice patterns or other factors besides timing of initiation of long-term dialysis from the initial 3-year interval (2001-2003) to the final 3-year interval (2016-2018) assessed in this study.
Discussion
In this study using a large, integrated health care delivery system that facilitated accurate determination of the size and eGFR distribution of the underlying source population, we estimated that incidence of ESKD could have potentially been 16% (95% CI, 13%-18%) lower if there were no changes in system-level practice patterns or other factors besides timing of initiation of long-term dialysis from the initial 3-year interval (2001-2003) to the final 3-year interval (2016-2018) assessed in this study.
The optimal time to initiate long-term dialysis in patients with kidney disease remains unclear,10,21,22,23,24,25,26,27 with a high degree of variability in practice patterns over time and across health systems.1 Among 11 215 older US veterans with sustained eGFR lower than 15 mL/min/1.73 m2, Tamura et al28 observed that patients exclusively using fee-for-service Medicare for nephrology care had 28% higher frequency of dialysis initiation compared with those exclusively using Department of Veterans Affairs nephrology care. Based on US Renal Data System data, the percentage of patients with incident kidney failure who initiated dialysis at an eGFR of 10 mL/min/1.73 m2 or higher increased steadily from the mid-1990s (13%) until 2010 (43%), when it remained stable or slightly declined.2 Similar temporal trends have been observed in the Veterans Affairs health system29 and in other countries, such as the United Kingdom.30
We hypothesize that the level of eGFR at which long-term dialysis was started during the 2 decades internationally has been influenced by a variety of system-, physician-, and patient-level factors.1 On a national level, perspectives from opinion leaders31 combined with high-profile, consensus-based clinical practice guidelines32,33 contributed to an emphasis on recommending a “healthy/timely” dialysis,1 which included efforts to promote the placement of arteriovenous fistulas at higher eGFR levels.34 This may have contributed to patients accepting dialysis at relatively higher eGFR levels during the present study period, especially if they had a mature arteriovenous fistula and symptoms that are challenging to manage medically. In addition, because KPNC promoted the use of peritoneal dialysis as the initial modality during the study period, the need for a significant amount of time to train patients and caregivers may have also contributed, in part, to our observed patterns of dialysis starts at a higher eGFR. The concurrent expansion of educational efforts to raise awareness of kidney disease and empower patients with CKD regarding their options may have affected patterns in timing of initiation of dialysis. Of note, as a fully integrated health care delivery system, KPNC had no financial incentives to initiate dialysis earlier vs later.
An alternative possibility that would also lead to the identical observation of an increase in the number (and percentage) of individuals starting dialysis with an eGFR of 10 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2 is that there are relatively more people in the underlying source population who had an eGFR of 10 to 24 mL/min/1.73 m2 in more recent years, with no change over time in the likelihood of receiving dialysis at this eGFR.29 A recent interrupted time series analysis provided circumstantial evidence that the progressive increase in mean eGFR level at the start of dialysis may likely be driven more by secular trends in practice patterns or other factors and not by secular trends in the distribution of eGFR in the underlying at-risk population. Ferguson et al11 showed that after publication of the IDEAL trial in 2010, which found no systematic clinical benefit for initiation of earlier vs later dialysis, there was an immediate decrease in the proportion of early dialysis starts (ie, at eGFR >10.5 mL/min/1.73 m2) in Canada. However, Ferguson et al did not have data on the underlying at-risk Canadian population. By contrast, a major strength of our study is that we captured the underlying at-risk population whose distribution of eGFR was known.
Few prior studies have attempted to quantify the public health and cost implications of changes in timing of dialysis initiation. Using US Renal Data System data and observed rates of eGFR loss from a CKD cohort, O’Hare et al35 estimated that long-term dialysis was initiated nationally a mean of approximately 5 months earlier (and approximately 8 months earlier for those aged ≥75 years) in 2007 vs 1997, leading to more than $1.5 billion of cost annually. However, that study did not consider the association of changes in timing of dialysis initiation with the number of incident ESKD cases, which our present analysis showed is notable. To put the observed relative 16% change between 2001 and 2018 in context, this is approximately two-thirds of the target relative 25% reduction in new ESKD cases by 2030 called for in the 2019 White House Advancing American Kidney Health initiative.9 In addition, if there was a 16% smaller ESKD population, the estimated cost difference could be up to $2.2 billion because Medicare Part B spending for total outpatient dialysis–related services was $13.7 billion in 2016 to 2017.36 This cost is likely an underestimate because it does not include indirect costs of care (eg, patient and caregiver travel time; costs associated with creating and maintaining functioning dialysis access; potential loss of employment; and costs associated with caregiver and patient burnout).
Our study has several important implications. Given the lack of strong evidence that earlier initiation of long-term dialysis has net clinical benefit,10,21,22,23,24,25,26,27 careful evaluation of contemporary dialysis initiation practices is needed,35 along with ongoing improved shared decision-making efforts to personalize the approach with patients.34 Dialysis is currently recommended when kidney function is “low” and a patient has symptoms or signs consistent with kidney failure. However, some symptoms and signs (eg, fatigue or pruritus) may be nonspecific and caused by comorbid conditions, whereas others (eg, anorexia or hypoalbuminemia) can change over time and may improve spontaneously without dialysis therapy. In most cases, long-term dialysis is initiated not to treat an immediately life-threatening condition (eg, uremic pericarditis or refractory hyperkalemia). As noted previously, the aggressive promotion of earlier arteriovenous fistula placement in patients with CKD may also affect patient and physician expectations about the timing of initiating dialysis. Thus, decisions about when to start dialysis are not always fully objective, and policy decisions that have encouraged systematic earlier dialysis initiation can be adjusted. For example, O’Hare et al29 suggested reimposing scrutiny by the Health Care Financing Administration and renal networks of an upper eGFR limit at which elective dialysis initiation would trigger a review. Following publication of the IDEAL trial, there have also been calls for starting dialysis later.37 The United Kingdom National Institute for Health and Care Excellence now recommends waiting until an eGFR of 5 to 7 mL/min/1.73 m2 or the presence of symptoms affecting daily life before starting dialysis.38 Furthermore, the Japanese Society of Nephrology guidelines recommend patients “endure under conservative treatment until the GFR is <8 mL/min/1.73 m2 even when the symptoms of renal failure are observed.”39(p97)
Our results also support the perspective that practice patterns or other factors beyond just population CKD burden may impact the number of new ESKD cases. Thus, incidence of ESKD (as currently defined) in a population may not be an entirely optimal quality metric to reflect the success or failure of renoprotective efforts, and policy makers and public health officials should consider other metrics as well.40
Limitations
Our study was limited in that we only assessed the association between the timing of dialysis initiation and incident ESKD rates within an integrated health care delivery system in California. However, the KPNC membership is sociodemographically diverse and highly representative of the local and statewide population.12 Supporting the external validity of our findings is the observation that the temporal trend in mean eGFR at the start of dialysis among KPNC members—progressively increasing through the first decade of this century (Figure 1)—matches that reported by the US Renal Data System,2 US Department of Veterans Affairs,29 Canadian Organ Replacement Register,11 and United Kingdom Renal Registry.30 We did not have information on the specific system-, physician-, and patient-level reasons that may have contributed to the observed trends, nor did we analyze how changing the timing and threshold for dialysis initiation may have affected clinical outcomes (including in frail25 or older41 persons). However, previous studies do not provide convincing evidence that systematically starting dialysis earlier confers net benefits,10,26,27,42 including the only large randomized trial performed to date.10
Conclusions
In conclusion, choices regarding the timing of dialysis initiation should be made on a patient-by-patient basis to maximize the net benefit for individual patients with kidney disease, including taking into account the results of large randomized clinical trials, such as the IDEAL trial.10 Our results underscore the importance the timing of initiating long-term dialysis has on the size of the population of patients with ESKD.
eTable. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations for Calendar Year Trend in the Annual Risk of Initiating Elective Dialysis, by Index eGFR Category at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 2001-2018, by 3-Year Interval
eFigure 1. Mean (95% Confidence Interval) Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate at Dialysis Initiation Among 4,865 Patients Initiating Dialysis Within 1 Year Between 2001-2018, by 3-Year Interval: Elective vs Urgent Dialysis and Peritoneal vs Hemodialysis
eFigure 2. One-Year Risk of Initiating Dialysis (Overall) by Calendar Period, by Index Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate, 2001-2018
References
- 1.Johansen KL. Time to rethink the timing of dialysis initiation. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(5):382-383. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;73(3)(suppl 1):A7-A8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.01.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ivory SE, Polkinghorne KR, Khandakar Y, et al. Predicting 6-month mortality risk of patients commencing dialysis treatment for end-stage kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32(9):1558-1565. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chan KE, Maddux FW, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R, Hakim RM. Early outcomes among those initiating chronic dialysis in the United States. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(11):2642-2649. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03680411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Foley RN, Chen SC, Solid CA, Gilbertson DT, Collins AJ. Early mortality in patients starting dialysis appears to go unregistered. Kidney Int. 2014;86(2):392-398. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kurella Tamura M, Vittinghoff E, Hsu CY, et al. ; CRIC Study Investigators . Loss of executive function after dialysis initiation in adults with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017;91(4):948-953. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.11.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kurella Tamura M, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe K, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE. Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1539-1547. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0904655 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bansal N, Keane M, Delafontaine P, et al. ; CRIC Study Investigators . A longitudinal study of left ventricular function and structure from CKD to ESRD: the CRIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8(3):355-362. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06020612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Patel S, Boehler A, Uehlecke N. A vision for advancing American kidney health: view from the US Department of Health and Human Services. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;14(12):1789-1791. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10460919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cooper BA, Branley P, Bulfone L, et al. ; IDEAL Study . A randomized, controlled trial of early versus late initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(7):609-619. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1000552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ferguson TW, Garg AX, Sood MM, et al. Association between the publication of the Initiating Dialysis Early and Late Trial and the timing of dialysis initiation in Canada. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(7):934-941. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.0489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kaiser Permanente. Sociodemographic and health-related characteristics of members in Kaiser Permanente’s Northern California region, 2014/2015: internal report, division of research, Kaiser Permanente medical care program, Oakland, CA. Published October 2017. Accessed August 28, 2020. https://divisionofresearch.kaiserpermanente.org/projects/memberhealthsurvey/SiteCollectionDocuments/mhs11reg.pdf
- 13.Lo LJ, Go AS, Chertow GM, et al. Dialysis-requiring acute renal failure increases the risk of progressive chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2009;76(8):893-899. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ross TR, Ng D, Brown JS, et al. The HMO Research Network Virtual Data Warehouse: a public data model to support collaboration. EGEMS (Wash DC). 2014;2(1):1049. doi: 10.13063/2327-9214.1049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Go AS, Hsu CY, Yang J, et al. Acute kidney injury and risk of heart failure and atherosclerotic events. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(6):833-841. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12591117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gurwitz JH, Magid DJ, Smith DH, et al. Treatment effectiveness in heart failure with comorbidity: lung disease and kidney disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(12):2610-2618. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Go AS, Magid DJ, Wells B, et al. The Cardiovascular Research Network: a new paradigm for cardiovascular quality and outcomes research. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2008;1(2):138-147. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.108.801654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, et al. ; CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) . A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(9):604-612. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-9-200905050-00006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rivara MB, Mehrotra R. Timing of dialysis initiation: what has changed since IDEAL? Semin Nephrol. 2017;37(2):181-193. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.12.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pravoverov LV, Zheng S, Parikh R, et al. Trends associated with large-scale expansion of peritoneal dialysis within an integrated care delivery model. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(11):1537-1542. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.3155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Korevaar JC, Jansen MA, Dekker FW, et al. ; Netherlands Cooperative Study on the Adequacy of Dialysis Study Group . When to initiate dialysis: effect of proposed US guidelines on survival. Lancet. 2001;358(9287):1046-1050. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06180-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Traynor JP, Simpson K, Geddes CC, Deighan CJ, Fox JG. Early initiation of dialysis fails to prolong survival in patients with end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13(8):2125-2132. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000025294.40179.E8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rosansky SJ, Clark WF, Eggers P, Glassock RJ. Initiation of dialysis at higher GFRs: is the apparent rising tide of early dialysis harmful or helpful? Kidney Int. 2009;76(3):257-261. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rosansky SJ, Eggers P, Jackson K, Glassock R, Clark WF. Early start of hemodialysis may be harmful. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(5):396-403. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bao Y, Dalrymple L, Chertow GM, Kaysen GA, Johansen KL. Frailty, dialysis initiation, and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(14):1071-1077. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Crews DC, Scialla JJ, Boulware LE, et al. ; DEcIDE Network Patient Outcomes in End Stage Renal Disease Study Investigators . Comparative effectiveness of early versus conventional timing of dialysis initiation in advanced CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(5):806-815. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.12.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Crews DC, Scialla JJ, Liu J, et al. ; Developing Evidence to Inform Decisions about Effectiveness (DEcIDE) Patient Outcomes in End Stage Renal Disease Study Investigators . Predialysis health, dialysis timing, and outcomes among older United States adults. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25(2):370-379. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013050567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kurella Tamura M, Thomas IC, Montez-Rath ME, et al. Dialysis initiation and mortality among older veterans with kidney failure treated in Medicare vs the Department of Veterans Affairs. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(5):657-664. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.0411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.O’Hare AM, Wong SP, Yu MK, et al. Trends in the timing and clinical context of maintenance dialysis initiation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(8):1975-1981. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013050531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Renal Association: UK Renal Registry. 2017—The twentieth annual report. Accessed March 10, 2020. https://www.renalreg.org/reports/2017-twentieth-annual-report/
- 31.Hakim RM, Lazarus JM. Initiation of dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995;6(5):1319-1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.National Kidney Foundation . NKF-DOQI clinical practice guidelines for peritoneal dialysis adequacy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;30(3)(suppl 2):S67-S136. doi: 10.1016/S0272-6386(97)70028-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.National Kidney Foundation . 2006 Updates: clinical practice guidelines and recommendations: peritoneal dialysis adequacy. Published 2006. Accessed March 10, 2020. https://www.kidney.org/sites/default/files/docs/12-50-0210_jag_dcp_guidelines-pd_oct06_sectionb_ofc.pdf
- 34.Kalloo S, Blake PG, Wish J. A patient-centered approach to hemodialysis vascular access in the era of fistula first. Semin Dial. 2016;29(2):148-157. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.O’Hare AM, Choi AI, Boscardin WJ, et al. Trends in timing of initiation of chronic dialysis in the United States. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(18):1663-1669. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2011.436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Medicare Medical Payment Advisory Commission March 2019 report. Accessed March 10, 2020. http://medpac.gov/docs/default-source/reports/mar19_medpac_ch6_sec.pdf?sfvrsn=0
- 37.Di Micco L, Torraca S, Pota A, et al. Setting dialysis start at 6.0 ml/min/1.73 m2 eGFR—a study on safety, quality of life and economic impact. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(11):3434-3440. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gilbert J, Lovibond K, Mooney A, Dudley J; Guideline Committee . Renal replacement therapy: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2018;363:k4303. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k4303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Watanabe Y, Yamagata K, Nishi S, et al. ; “Hemodialysis Initiation for Maintenance Hemodialysis” Guideline Working Group, Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy . Japanese society for dialysis therapy clinical guideline for “hemodialysis initiation for maintenance hemodialysis”. Ther Apher Dial. 2015;19(S1)(suppl 1):93-107. doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12293 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion: Healthy People 2020. Chronic kidney disease. Accessed June 4, 2019. https://www.healthypeople.gov/2020/topics-objectives/topic/chronic-kidney-disease/objectives
- 41.Kurella Tamura M, Desai M, Kapphahn KI, Thomas IC, Asch SM, Chertow GM. Dialysis versus medical management at different ages and levels of kidney function in veterans with advanced CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(8):2169-2177. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017121273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Scialla JJ, Liu J, Crews DC, et al. ; DEcIDE Network Patient Outcomes in End Stage Renal Disease Study Investigators . An instrumental variable approach finds no associated harm or benefit with early dialysis initiation in the United States. Kidney Int. 2014;86(4):798-809. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eTable. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations for Calendar Year Trend in the Annual Risk of Initiating Elective Dialysis, by Index eGFR Category at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 2001-2018, by 3-Year Interval
eFigure 1. Mean (95% Confidence Interval) Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate at Dialysis Initiation Among 4,865 Patients Initiating Dialysis Within 1 Year Between 2001-2018, by 3-Year Interval: Elective vs Urgent Dialysis and Peritoneal vs Hemodialysis
eFigure 2. One-Year Risk of Initiating Dialysis (Overall) by Calendar Period, by Index Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate, 2001-2018