Figure 5.
DNA Methylation Profiles in ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim Spermatogonia
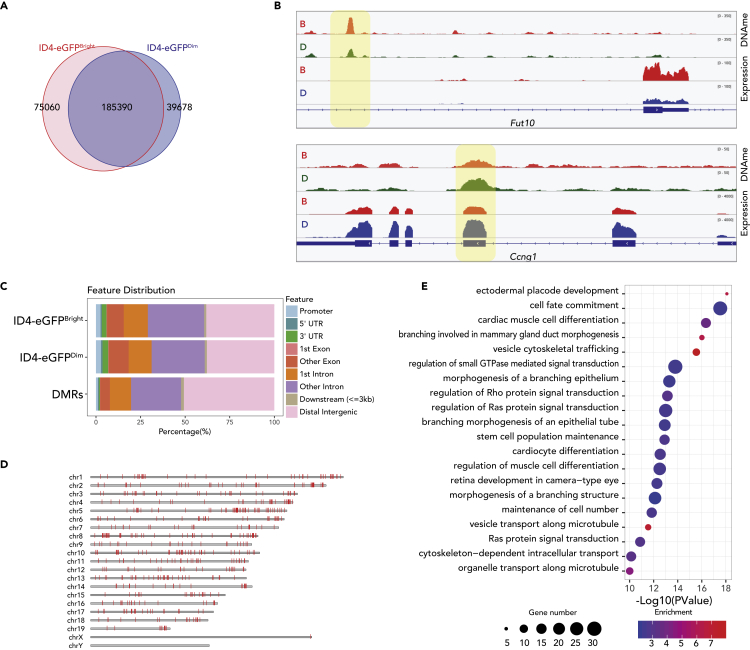
(A) Venn diagrams show proportions of DNA methylation peaks unique to ID4-eGFPBright spermatogonia, common to both ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia, or unique to ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia.
(B) Genome browser snapshots showing correlations or lack thereof between DNA methylation and transcript peaks in ID4-eGFPBright (B, orange tracks) and ID4-eGFPDim (D, green or blue tracks) spermatogonia in regions encompassing a gene that is up-regulated in ID4-eGFPBright spermatogonia (Fut10) and a gene that is up-regulated in ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia (Ccng1). Differentially methylated regions within gene bodies, but not at promoters, appear to be positively correlated with gene expression levels.
(C) The distribution of DNA methylation peaks in each spermatogonial subtype and DMRs between the two subtypes is shown. DMRs were rare at promoters but abundant in intra- and intergenic regions.
(D) DMRs were found throughout the autosomes, but, with one exception, not on the sex chromosomes. Genomic coordinates of DMRs are shown in Table S4.
(E) GREAT-GO analysis of genes associated with DMRs. The color code indicates the enrichment levels of DMR-associated genes (blue–red = low–high). Dot diameters indicate the number of DMR-associated genes within each GO term.