Abstract
Background
Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most common spine diseases and represents the most frequent cause of absence from work in developed countries. Approximately 40% of chronic LBP is related to discogenic origin. The goal of the study is producing a review of literature to describe analytically the techniques of intradiscal injections.
Methods
PubMed database was searched for clinical studies with the different key terms: “intradiscal”, “injection”, “steroid” “procedures”, “techniques”, “CT”, “MRI”, “fluoroscopy”, “fluoroscopic”, “guidance”, “ozone”, “ultrasound”, “images”. Only studies written in English, French, or Italian in which the intradiscal injection represents the main procedure for the low back discopathy treatment on humans were considered. We excluded the articles that do not mention this procedure; those which indicated that the intradiscal injection had happened accidentally during other treatments; those reporting the patient’s pain was determined by other causes than the discopathy (facet joint syndrome, tumor, spondylodiscitis).
Results
Thirty-one articles dated from 1969 to 2018 met the criteria. The examined population was 6843 subjects, 52.3% male and 47.7% female, with a mean age of 45.9±10.1 years. The techniques are highly variable in terms of procedure: different operators, needle guidance, injection sites, drugs, tilt angle of the needle).
Conclusion
The efficacy and the safety of the intradiscal procedures are not easily comparable due to different types of studies and their limited number. Further studies are needed to standardize the intradiscal injection technique/procedure to improve safety, repeatability and effectiveness, and last but not least to reduce peri- and postoperative care and health-care costs.
Keywords: discopathy, guidance, injection, intradiscal injections, low back pain, safety
Background
Low Back Pain (LBP) is one of the most common spine diseases and represents the most frequent reason of absence from work in developed countries. Around 80% of adults suffer from LBP during their lifetime, and 55% suffer from back pain associated with radicular syndrome.1 Chronic LBP is often responsible for a low quality of life due to pain, for disability and loss of work productivity and, in addition, for high health-care costs for society.2–4 Regarding its etiology, in literature it has been reported that approximately 40% of chronic LBP has a discogenic origin.5,6 Currently in the advanced phases of discopathy and in high symptomatic subjects, the elective treatment still remains spinal surgery. In the other less complicated cases, the therapeutical steps could vary from a simple pharmacological therapy to a physical therapy, as the low back traction, over to spinal injection (epidural, periradicular, intradiscal and intra-articular procedures). Moreover, intervertebral disk decompression techniques are minimally invasive outpatient procedures for the treatment of disk herniation. Under imaging guidance and via a percutaneous approach, a needle is inserted in the nucleus pulposus of the herniated disk. A variety of decompressive device of thermic, chemical or mechanical nature are introduced inside the nucleus pulpous with minimal disruption of the surrounding tissues, assuring its partial removal and a significant decrease of intradiscal pressure. Thermal decompression is achieved using laser fiber, plasma, energy electrode, and radiofrequency coil/electrode. Chemical decompression is achieved by alcohol gel or ozone intradiscal injection, which causes dehydration and breakdown of the nucleus pulposus. Lately, there has been a trend for biomaterial implantation (hydrogel, platelet-rich plasma and stem cell therapy) aiming for intervertebral disk regeneration. Symptomatic intervertebral disk herniation (refractory to 4–6 weeks of a conservative therapy course), occupying less than one third of the spinal canal, as confirmed by MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), is an indication for percutaneous decompressive disk therapies. The mean success rate for all techniques is approximately 85%. The mean complication rate (infections like spondylodiscitis, allergic reaction, hemorrhage, neurologic injury) is <0.5%.7 The goal of the study is producing a review of literature to describe analytically the actual techniques of intradiscal injections, the type of intervention performed, the used imaging guidance, the inoculated drug, the approach to the intervertebral disc, the patient’s position, the specialty of the operator performing the procedure, the type of anesthesia and the use of antibiotic prophylaxis.
Methods
Search Strategy
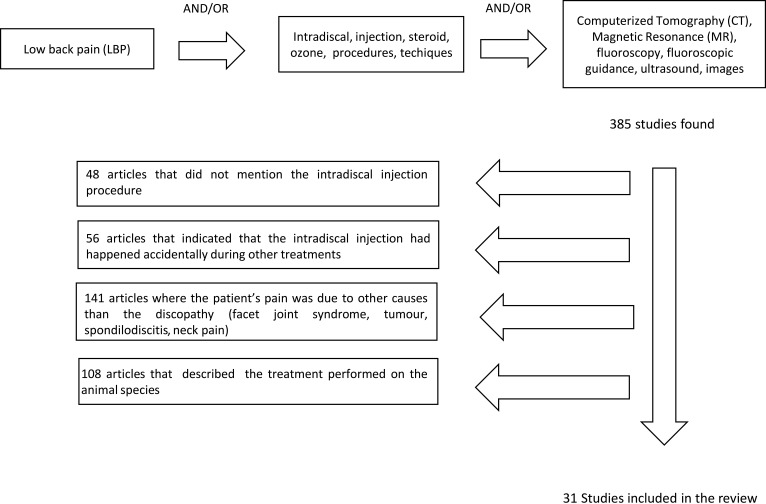
The PubMed database was searched for clinical studies with the following key terms: “intradiscal”, “injection”, “steroid” “procedures”, “techniques”, “CT” (computerized tomography), “MRI”, “fluoroscopy”, “fluoroscopic”, “guidance”, “ozone”, “ultrasound”, “images”. We made our research throw the combination of this terms, inserted between the Boolean operators “AND”/“OR”. We limited the research to studies on humans and types of articles were: case reports, clinical trials, controlled clinical trials, reviews, comparative studies, multicenter studies, and randomized controlled trials. The search was expanded through the bibliography within recruited texts (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flow diagram illustrating published literature on intradiscal injection.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
For our review, we only considered studies written in English, French, or Italian in which the intradiscal injection represents the main procedure for the low back discopathy treatment, both isolated and in combination. We excluded the articles that did not mention that procedure or those which indicated that the intradiscal injection had happened accidentally during other treatments (ie during transforaminal injection). We excluded the articles where the patient’s pain was due to other causes than the discopathy (facet joint syndrome, tumor, spondylodiscitis), and also those articles that described the treatment performed on an animal species. We checked the bibliography to make sure that the articles were compatible with our research.
Results
Initially using the term “intradiscal injection” as a search key on PubMed, we found 385 articles; the results were reduced when we added other search keys or other selection criteria, as we showed in the description of our strategy of research. Depending on the abstracts or full texts we excluded the studies that did not satisfy the inclusion criteria. Moreover, in this review we included other articles shown as bibliography in previous research. The final result consisted of 31 articles4,8-26,35–44 dated from 1969 to 2018, and the examined population was 6843 subjects (Table 1). We did not consider the number of patients treated in the Giurazza et al study38,40 because being a review, it considered not only intradiscal, but also paravertebral injections. We also decided to cite other authors that described the varied and numerous procedures that are available to the image-guided interventions who may provide these therapies for the spine.27–31
Table 1.
Clinical Characteristics of Trials Employment of Intradiscal Injection
| Authors, Date | Study Design | Population | End Points | Disease Treated | Intervention | Medicament | Guidance | Approach | Outcomes | Results | Follow-up | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kallewaard et al4 2015 | Multicenter pilot study | 174 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | Blue methylene | Fluor | ND | VAS, ODI, SF-36, PGIC | Pain relief in 40% of patients | 24 weeks | No |
| Mineta et al8 2014 | Case report | 1 | Association Modic type I-inflammation | LBP | ID | Cs | ND | ND | VAS and Modic change | Modic type switch depends on inflammation | ND | ND |
| Zhang et al10 2013 | Case–control | 172 | Comparison between 2 groups of the treatments | LBP | ID/IF | Ozone | Fluor | PL | VAS, JOA score | Significant pain relief in both groups | 3, 24, 48 weeks | No |
| ID/IF | Ozone Cs | Differences between treatments | No statistically significant differences | |||||||||
| Beaudreuil et al11 2012 | Observational Retrospective study | 97 | Efficacy in (EG) compared to (C) | LBP±Modic | ID | Cs | Fluor | ND | VAS and self-assessed of pain | Significant pain decrease in EG compared to CG | 24 h, 48–56 weeks | No |
| Lehnert et al12 2012 | Observational prospective study | 283 | Efficacy of the treatment | LBP | ID | Ozone | CT | EL | Disk volume reduction evaluated with CT | Decrease in 91.1% of patients and increased in 3.9% of patients | 24 weeks | Impaired sensitivity lower limb 24 cases |
| PG | ||||||||||||
| de Seze et al13 2012 | Observational prospective study | 79 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | Discogel | Fluor | PL | Verbally numeric scale (from 0 to 10) | Free pain in 60.7% of patients | 8, 24 weeks | No |
| Fukui et al14 2012 | Observational prospective study | 45 | Comparison of effectiveness between 2 treatment | ID | Saline sol LA | Fluor | PO | VAS, JOA score | Pain improvement for IDHP compared to MED | 2, 12 weeks | No | |
| MED | / | |||||||||||
| Yu et al15 2012 | Case–control study | 45 | Comparison of effectiveness between 2 treatment | LBP | ID | Cs | CT | ND | VAS, ODI | Improvement of pain in the EC compared to CG | 1, 4, 12, 24 weeks | ND |
| Saline sol | ||||||||||||
| Cao et al16 2011 | RCT | 120 | Comparison of effectiveness between 2 treatment | LBP | ID | Cs ± Songmeile | CT | PL | VAS, ODI | Significant pain improvement in the EC compared to CG | 12, 24 weeks | ND |
| Saline sol | ||||||||||||
| Muto et al17 2008 | Observational Retrospective study |
2900 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | Lumbar disk herniation | ID/PG/PR | Ozone | CT | PvO | VAS, ODI | Significant pain decrease in 85% of cases | 24, 48 weeeks | No |
| Oder et al18 2007 | Observational Prospective study | 621 | Efficacy of treatment in different groups | LBP | ID/PG/Ep | Ozone, Cs, LA | CT+ Fluor | Post | VAS | Significant pain improvement in 59.4% of all patients | 24 weeks | No |
| Fayad et al19 2007 | Pilot study | 74 | Comparison of effectiveness between Modic type Groups | LBP + Modic | ID | Cs | Fluor | PL | VAS, PGA | Significant pain improvement ModicI >Modic I-2 > ModicII-1 | 4, 12, 24 weeks | No |
| Gallucci et al20 2007 | RCT | 159 | Comparison of effectiveness between 2 groups | LBP disk herniation | ID/IF | Cs + LA | CT | Pv | Oswestry Low Back Pain Disability Questionnaire | Significant pain decrease for 47% in group A, 74% in group B | 24 weeks | No |
| ID/IF | Cs, LA, ozone | IL | ||||||||||
| Miller et al21 2006 | Prospective study | 76 | Efficacy of the treatment | LBP + leg pain | ID | HyD LA | Fluor | ND | Numeric pain score scale | Pain improvement in 43.4% of patients | 6, 164 weeks | ND |
| Benyahya et al22 2004 | Observational retrospective study | 85 | Efficacy/safety of the treatment | LBP Modic | ID | Cs | CT | PL | Global appreciation “good or excellent” of the patient in % | 71.8% at 1 month 55.3% at 3 months 43.5% at 6 months | 4, 12.24 weeks | Collapse 2 discs |
| Khot et al23 2004 | RCT | 120 | Comparison of effectiveness between 2 groups | LBP | ID | Cs | Fluor | PL | VAS, ODI | No improvement in experimental group compared with placebo | 48 eeks | No |
| Saline sol | ||||||||||||
| Andreula et al24 2002 | Multicenter study | 600 | Comparison of effectiveness between 2 groups | LBP | ID/PG | Ozone + O3 | Fluor | EL | Modified MacNab method | Successful of the treatment in 70.3% group A 78.3% group B | 24 eeks | Impaired sensitivity lower limb 2 cases |
| ID/PG | Ozone, Cs, LA | CT | ||||||||||
| Feffer et al25 1969 | Observational prospective study | 244 | Efficacy of the treatment | LBP | ID | Cs | Fluor | PL | Back pain (yes/no), radicular pain (yes/no) | Complete remission in 46.7% of patients; “no initial response” in 53.3% of patients. | 4–10 years | Discitis 1 case |
| Pettine et al35 2017 | Observational prospective study | 26 | Efficacy of the treatment | LPB | ID | AT-BMC | Flour | PL | VAS, ODI | VAS: 82.1 (±2.6) at baseline and 21.9±4.4 at 3 Y. ODI: 56.7 (±3.6) at baseline and 17.5±3.2 at 3 years. | 3 years | No. Only 6 patients had progression to surgery |
| Yin et al9 2014 | Multicenter study | 15 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | FS | Flour | PL | VAS, RMDQ, Rx/MRI | VAS 72.4, 31.7, 35.4, 33 at baseline, 26, 52, 104 weeks. (significant improvement) RMDQ 15.2, 8.9, 6.2; 5.6 at baseline, 26, 52, 104 weeks. Rx/MRI similar to baseline | 104 weeks | Low back muscle spasm 2 cases. Discitis 1 case |
| Sainoh et al36 2016 | Prospective randomized study | 60 | Efficacy of the treatment | LBP | ID | TNF-α I | Flour | PL | VAS, ODI | Significant pain improvement in 57% of all patients at 8 weeks in patient treated with TNF-α I. No significant difference about ODI | 8 weeks | Not |
| Noriega et al44 2017 | Randomized, controlled trial | 24 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | Nd | Nd | Nd | ND | VAS, ODI, SF-12 | Average 28% improvement in pain and disability 1 year after the intervention | 1 year | ND |
| Giurazza et al38 2017 | Review | ND | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | Oz | Flour; CT | PL, Pv/IL, TF | VAS, ODI | Improvement in pain and disability | Up to 10 years | 0.1% Paraesthesias; temporary impaired bilateral sensitivity; vitreoretinal hemorrhages; thunderclap headache 1 case of vertebrobasilar stroke 1 case of septicemia |
| Pettine et al42 2015 | Observational prospective study | 26 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | AT- BMC | Flour | PL | VAS, ODI | (71% VAS reduction) and ODI improvements (>64%) through 2 years. | 2 years | No. only 5 patients had progression to surgery |
| Nguyen et al34 2017 | Prospective, parallel-group, double-blind, randomized, controlled, multicenter study. | 135 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | Cs | Flour | PL | VAS, MRI at 12 months | The percentage of responders (LBP intensity <40) at 1 month was higher in the GC IDI group in than the control group; At 12 months, the groups did not differ in pain intensity or most other secondary outcomes. No difference at MRI | 1 year | 1 event increase in sciatica pain in the 24 h after the intervention |
| Perri et al41 2016 | Observational prospective study | 517 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | Oz+Cs+LAVs Cs+LA | CT | P | VAS | The study group had a successful outcome in 80% of patients after 6 months, while the control group had a successful outcome in 31.5% | 6 months | Not |
| Zhang et al37 2016 | Observational study | 33 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | BM | Flour | PL | NRS, ODI, MRI (apparent diffusion coefficient in T2) | Significant improvement at short-term minimum of 2 points reduction of rating scale scores at 1, 3, and 6 months after treatment, but less than 2 points reduction at 12 months; 50% improvement on the ODI at 1, 3, and 6 months after treatment, but not at 12 months. Apparent diffusion coefficient and T2 value were significantly higher at 6 and12 months after treatment, but no difference at 3 months. | 12 months | Not |
| Levi et al46 2016 | Prospective study | 22 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | Discogenic LBP | ID | PRP | Flour | PL | VAS, ODI | Significant improvement | 6 months | Not |
| Tuakli-Wosornu et al39 2016 | Prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled study. | 47 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | Discogenic LBP | ID | PRP | Flour | PL | NRS, FRI, SF-36, NASS | Significant improvement | 1 year | Not |
| Kumar41 2017 | Single-arm phase I clinical trial | 10 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | AT-MSC | Flour | PL | VAS, ODI, SF-36, MR-ADC | Significant improvement; 3 patients increased water content based on the ADC map at the 12-month follow-up | 1 year | Not |
| Centeno et al43 2017 | Pilot study | 33 | Efficacy and safety of the treatment | LBP | ID | AT-MSC, LA | Flour | PL | NRS, SANE, FRI, MIDPD | Significant improvement; the patients treated underwent post treatment MRI and 85% had a reduction in disc bulge size, with an average reduction size of 23% post -treatment |
6 years | Not |
Abbreviations: ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; AL-MSC, allogenic mesenchymal stem cells; AL, anterolateral; AT-BMC, autologous bone marrow concentrate; AT-MSC, adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells; BM, blue methylene; C, control group; Cs, corticosteroid; EG, experimental group; EL, extraspinal lateral; Ep, epidural; EQ-5, EuroQol; Fluo, fluoroscopy; FRI, Functional Rating Index; FS, fibrin sealant; HA, hyaluronic acid; HyD, hypertonic dextrose; ID, intradiscal injection; LA, local anesthetic; LBP, low back pain; MGPQ, McGill Pain Questionnaire; MIDPD, measurement of the intervertebral disc posterior dimension; MSC, mesenchymal stem cells; NASS, the modified North American Spine Society; ND, not described; NRS, Numeric Rating Scale; ODI, Oswestry Disability Index; P, pain; PG, periganglionic injection; PL, posterolateral; PO, posterior-oblique; Post, posterior; PR, periradicular injection; PRP, platelet-rich plasma; Pv/IL, paravertebral/interlaminar; PvO, paravertebral-oblique; RCT, randomized controlled trial; RMDQ, Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire; SANE, modified single assessment numeric evaluation; SF-36, short form-36; SNRB, selective nerve block; TF, transforaminal; TNF-α I, tumor nerosis factoralpha inhibitor; VAS, visual analog scale;.
Characteristics of Included Articles (Table 1)
The review includes three observational retrospective studies,12,18,23 12 observational prospective studies,13–15,19,22,26,36-38,41,43,44 two multicenter pilot studies,4,10 two case–control studies,11,16 six randomized controlled trials,4,8,17,21,24,35,42 one multicenter study25 two pilot studies,20,43 one case report,9 one single arm phase I clinical trial44 and one review.40
Population
Our population is composed of 6843 subjects, 52.3% male and 47.7% female, with a mean age of 45.9±10.1 years.
End Points
The aim of the study was to review literature for scientific evidence of intradiscal injections, to describe analytically the actual techniques, the type of intervention performed, the used imaging guidance, the inoculated drug, the approach to the intervertebral disc, the patient’s position, the operator who performed the treatment, the type of anesthesia used, antibiotic prophylaxis, if used.
Treated Disease
In all selected articles,4,9-26,35–38,39–44 the patients suffered from lumbar discopathy.
Type of Procedure
Different types of treatments are reported in the studies: intradiscal injection,4,8-26,35–44 epidural19 intraforaminal11,21 and facet joint injection, selective nerve block (SNRB),8 intradiscal high pressure injection (IDHP),15 microendoscopic discectomy (MED).16
Intradiscal Injection
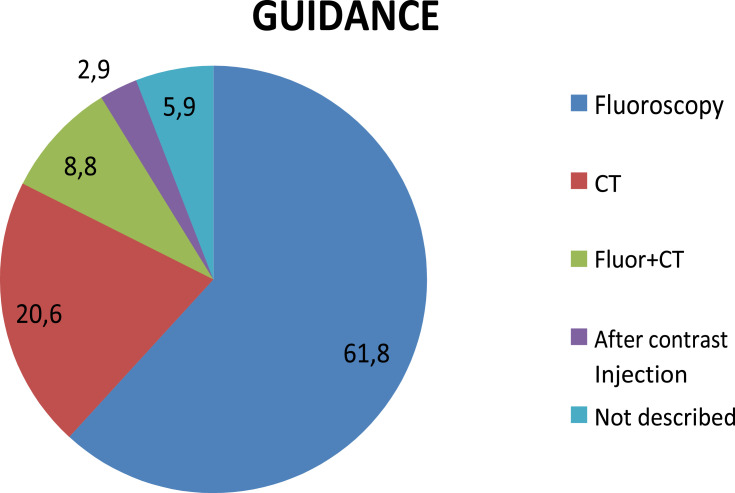
The technique of intradiscal injection is reported in 31 articles. In 24 studies,4,9,10,12,14,16,17,20,22-24,26,35–44 it is the only treatment while, in the remaining seven studies11,13,15,18,19,21,25 it is compared to, or in association with, other minimally invasive procedures. (Table 2). In 19 articles the procedure was realized under fluoroscopy,4,10-12,14,15,20,22,24,26,35–39,41,42,44 in seven articles under CT guide,13,16–18,21,23,43 and in three studies both by fluoroscopy and CT guided, in comparison25 or in association;19,40 in two articles was not specified9,44 (Figure 2).
Table 2.
Characteristics of Intradiscal Injection Techniques
| Authors | Intervention | Drugs | Guidance | C-Arm | Approach | Needle | Injection Site | Injection Check | Operator | Patients Position | Sedation | Local Anesthesia | Antib Prophilax | Rest After Injection | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kallewaard et al4 | ID | BM, LA | Fluor | No | ND | ND | ND | AP/L | ND | ND | ND | ND | Yes | 2 h | |
| Mineta et al8 | ID | Cs | ND | No | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Yin et al9 | ID | FS | Fluor | No | PL | 18G | CTh | RTMF | ND | ND | No | Yes | Yes | 1, 1/2 h | |
| Zhang et al10,11 | ID/IF | Oz | Fluor | Yes | PL | 21G | C | AP/L | ND | * | No | Yes | ND | 10 min | |
| ID/IF | Oz Cs | ||||||||||||||
| Beaudreuil et al11 | ID | Cs | Fluor | No | ND | ND | C | ND | ND | ND | No | Yes | ND | 12/24 h | |
| Lehnert et al12 | ID | Oz | CT | No | EL | 22G | ND | ND | ND | ND | Nt | Yes | ND | 6 h | |
| PG | |||||||||||||||
| De Seze et al13 | ID | Discogel | Fluor | No | PL | 22G | C | AP/L | ND | ND | DS | No | ND | 3 h | |
| Fukui et al14 | ID | Saline sol, LA | Fluor | No | PO | 22G | MPHD | AP/O/L | ND | P | ND | ND | ND | 1 h | |
| Yu et al15 | ID | Cs | CT | No | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Saline sol | |||||||||||||||
| Cao et al16 | ID | Cs, Songmeile | CT | No | PL | 22G | C | ND | Authors | ND | ND | ND | ND | 3 h | |
| Saline sol | |||||||||||||||
| Muto et al17 | ID/PG/PR | Oz | CT | No | PvO | 18/20G | C | ND | ND | P | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Oder et al18 | ID/PG/Ep | Cs, LA, Oz | CT/Fluor | No | Post | 22G | C | CT scan | ND | P | Yes | Yes | Yes | 12 h | |
| Fayad et al19 | ID | Cs | Fluor | No | PL | 22G | C | AP/L | Radiol | ND | No | No | ND | ND | |
| Gallucci et al20 | ID/IF | Cs, LA | CT | No | Pv/IL | 22G | C | CT scan | NeuroR | P | No | Yes | Yes | 2 h | |
| ID/IF | Cs, LA, Oz | ||||||||||||||
| Miller et al21 | ID | HyD, LA | Fluor | No | ND | 22G | C | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Benyahya et al22 | ID | Cs | CT | No | PL | ND | C | ND | Radiol | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Khot et al23 | ID | Cs | Fluor | No | PL | ND | ND | ND | Authors | ND | AwS | No | ND | ND | |
| Andreula et al24 | ID/PG | Oz, O3 | Fluor | No | EL | 22G | ND | ND | ND | ND | No | No | ND | 2 h | |
| ID/PG | Oz, Cs, LA | CT | |||||||||||||
| Feffer et al25 | ID | Cs | Fluor | No | PL | 22G | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Centeno et al43 | Ep/ID | AT-MSC, LA | Fluor | No | PL | ND | ND | ND | ND | P | No | Yes | ND | ND | |
| Zhang et al37 | ID | BM | Fluor | Yes | PL | ND | C | Dis | ND | P | ND | ND | ND | 24 h | |
| Tuakli-Wosornu et al39 | ID | Prp | Fluor | ND | PL | 20G/25 G | C | Dis | Physiatrist | P | No | Yes | Yes | ND | |
| Kumar et al41 | ID | AT-MSC, HA | Fluor | Yes | PL | 22 G | C | CT scan | Spine surgeon | P | ND | Yes | Yes | 4 h | |
| Levi et al46 | ID | Prp | Fluor | ND | PL | 22G/25 G | C | ND | Physiatrist | P | Yes | Yes | Yes | ND | |
| Pettine et al35 | ID | AT-BMC | Fluor | ND | PL | 22G | C | ND | ND | P | No | Yes | ND | ND | |
| Sainoh et al36 | ID | TNF-α I | Fluor | ND | PL | 22 G | C | RTMF | ND | LD | No | Yes | ND | ND | |
| Noriega et al44 | ND | AL-MSC | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | Radiologists | ND | ND | Yes | ND | ND | |
| Giurazza et al38 | ID | O2-O3 | Fluor, CT | ND | PL, Pv/IL, TF | 18–22 G | C | ND | Radiologists | P | Yes | ND | ND | ND | |
| Pettine et al42 | ID | AT-BMC | Fluor | NDd | PL | 22 G | C | ND | ND | P | No | Yes | No | ND | |
| Nguyen et al34 | ID | Cs | Fluor | ND | PL | 18/22 G | C | ND | Radiologists | LD | No | No | No | ND | |
| Perri et al40 | ID | O2-O3 | CT | ND | Pv/IL | 22 G | C | CT | Neuroradiologists | P | No | Yes | Yes | ND | |
Note: *A pillow was placed under the waist of patients.
Abbreviations: AL- MSC, allogenic mesenchymal stem cells; AL, anterolateral; AT-BMC, autologous bone marrow concentrate; AT-MSC, adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells; Aw S, awake sedation; BM, blue methylene; C, center of the disc; Cs, corticosteroid; CTh, central third of the disc; Dis, discography; DP, deep sedation; EL, extraspinal lateral; Ep, epidural; Fluor, fluoroscopy; FS, fibrin sealant; G, gauge; h, hours; HA, hyaluronic acid; HyD, hypertonic dextrose; ID, intradiscal injection; IDHP, intradiscal high pressure injection; L, lateral; LA, local anesthesia; LD, lateral decubitus; MED, microendoscopic discectomy; min, minutes; MPHD, mid portion of herniated disc; MSC, mesenchymal stem cells; ND, not described; NeuroR, neuroradiologists; Oz, ozone; P, prone; PG, periganglionic injection; PL, posterolateral; PO, posterior-oblique; PR, periradicular injection; Prp, platelet-rich plasma; Pv/IL, paravertebral/interlaminar; PvO, paravertebral-oblique; Radiol, radiologists; RTMF, real-time multiplanar fluoroscopic imaging; SNRB, selective nerve block; Songm, Songmelie; TF, transforaminal; TNF-α I, tumor nerosis factor-α.
Figure 2.
Different type of image guidance for intradiscal injection.
The patients of the de Seze et al trial,13 Levi et al46 and Giurazza et al38 works were subjected to neurosedation, in the trials by Khot et al23 and Oder et al18 they were subjected to conscious sedation. In the studies by Fayad et al19 and Andreula et al24 and another five works34,37–39 the patients were neither sedated nor subjected to local anesthesia. In eleven trials,10,11,13,19,21,36,37,41–44 all patients were subjected to local anesthesia. The antibiotic prophylaxis was used in eight trials.4,10,19,21,41–44 The interventions were performed by highly experienced operators in the Lehnert’s trial12 two clinicians (two authors) in the Cao et al’s study;16 Fayad et al,19 Benyahya et al,22 Noriega et al,44 Giurazza et al,38 and Nguyen et al34 report the experienced radiologists, Gallucci et al20 and Perri et al40 neuroradiologists, Tuakli-Wosornu et al39 and Levi40,46 physiatrist and Khot et al23 two senior authors.
In 17 articles the required patients position was described according to the procedure: in 11 studies a prone position was used,15,18,19,21,36,38,40–44 Nguyen et al34 and Sainoh et al36 propose a lateral decubitus and Zhang et al10 advised use of a pillow under the waist to get the widest intervertebral spaces.
For the procedure spinal needles of 18- (n=4), 20- (n=2), 21- (n=1), 22- (n=17) and 23- (n=1) gauge were used, with variable length to 7 from 17.8 cm. For example the Muto et al’s study17 mentioned a 22-gauge spinal needle with paravertebral oblique access, Lehnert et al’s study12 mentioned an extraspinal lateral approach with a 22-gauge 17.8-cm spinal needle and Gallucci et al20 a paravertebral/interlaminar approach with a 9- or 15-cm 22-gauge spinal needle Five articles13,14,21,22,25 have specified that the side of the injection was chosen on the basis of the main location of symptoms.
The percutaneous approach is always posterior for the lumbar access: in 15.10,11,14,17,20,23,24,26,35,36,38,40–44 out of 31 articles it was specified as a posterolateral access, in other studies it was extralaminar12 or paravertebral access,20 posterior-oblique14 paravertebral-oblique,17 or anterolateral access. In the Gallucci et al’s study20 the intradiscal and intraforaminal injections were administered with a paravertebral approach in 92.4% of the patients and an interlaminar approach in 7.6% of the patients. The needle was advanced through the intraforaminal space, with an angle usually between 45° and 60°. In seven articles the point of access is not described.4,9,12,16,22,39,44 Oder et al’s study18 specified that the percutaneous approach was about 45° along the lateral margin of the inferior articular process of the vertebra and through the neuroforamen for preserving the nerve root. Muto et al17 used a needle inclination in a craniocaudal direction in the case of a lower herniation.
The site of injection is the center of the disc in 22 studies,7,10,11,13,16-22,35–44 the central third of the disc in the Yin et al’s study9 and in the mid portion of the herniated disc in the Fukui et al’s study.14 The position of the needle was confirmed by fluoroscopy using anteroposterior and lateral views in 20 studies;4,8,10–12,14,15,20,22,24,25,35–39,41,42,44 in Yin et al’s trial9 the procedures were performed with real time multiplanar fluoroscopy, with CT scan in seven other articles,13,16–18,21,23,43 in three articles with both fluoroscopy and CT,19,25,40 in two articles the position of the needle is not described.9,40
Some authors recommend the time remaining in supine position after injection: respectively 10 minutes;10 one hour,14 one, half an hour,9 two hours,4,21,25,39 three hours,13,16 four hours,41 six hours;12 12 h,18 12/24 h.11,37
Medicaments Injected
Several drugs have been injected, and were used individually or in association with each other: an oxygen-ozone mixture (O2O3) in eight studies,10,12,17,18,20,24,38,40 a saline solution in four studies;14–16,23 in 13 articles the steroids have been administered (methylprednisolone, acetate of prednisolone, hydrocortisone, betamethasone),8,10,11,15,16,18–20,22–25,34 and in six trials the local anesthetic (bupivacaine, lidocaine) were injected.4,14,20,21,24 For the remaining studies hypertonic dextrose,21 fibrin sealant,9 blue methylene,4,37 discogel,13 autologous bone marrow concentrate,35,42 allogenic mesenchymal stem cell and hyaluronic acid,41 tumour necrosis factor α1 inhibitor36 and songmeile16 (a kind of synthetic liquid of polypeptidic biological factors extracted from Chinese herbal medical ingredient) were used.
Outcomes Measures
Pain was the most frequently tested variable. It was expressed as percentage of patients with pain relief or as mean improvement on a continuous scale. The outcome measures shown in the studies were: VAS (visual analog score), NRS (numeric rating scale), McGill Pain Questionnaire. Outcome assessment of patient satisfaction are reported by “modified MacNab scale” or using Odom criteria (“Excellent”, “Good”, “Satisfactory” and “Poor”). Back-specific disability is expressed on a back-specific index, such as the Roland Disability Questionnaire or the Oswestry Disability Index and JOA score (widely used in Japan to evaluate disabilities associated with low-back pain and includes the following items: subjective symptoms; clinical signs; restriction of activities of daily living. JOA score ranges from 29 as the most positive score to minus six for the worst a global measure of improvement). Quality of life is measured by the SF-12, SF-36, and EuroQol.
Patients Global Impression of Change (PGIC) measured by a seven-point Likert scale. The evaluations of general health status or well being, disability for work, and patient satisfaction have all so been reported.
The disc volume was evaluated by MRI and CT images.
Clinical and/or radiologic short term follow-up were mainly performed at four or six weeks; the long-term follow-up were performed from 12, 24, 48, weeks up to 4–10 years.
Efficacy
The efficacy of the treatment is the target in 30 articles,4,9–25,34–44 The results are reported as clearly satisfactory in 27 out of the 30 articles,4,9–20,22,24,34–44 In the Muto et al’s study, for example, the results on 2900 patients, treated for LBP with intradiscal injection of O2–O3, were evaluated with the modified MacNab classification, the VAS and the Oswestry Disability Index at six and 12 months. Success rates were 75–80% for soft disc herniation, 70% for multiple-disc herniations and 55% for failed back surgery syndrome. None of the patients suffered early or late neurological or infectious complications.17 Benyahya et al22 made a retrospective study of medical records of 85 patients (55 women, mean age 49±9 years) to assess the effectiveness of intradiscal injection of acetate of prednisolone for the treatment of LBP. They used the global appreciation of the patient (excellent, good, mild, none, worse) concerning the result of the intradiscal injection, at one, three and six months. For effectiveness of intradiscal injection, the results showed that 71.8% of the patients considered the result good or excellent at one month, 55.3% at three months and 43.5% at six months.
Adverse Events
Six trials have reported the side effects,9,12,22,24,26,34 overall 32 cases for 6843 patients (0.47% of patients): three cases of discitis, two after injection of corticosteroid,25 one after injection of fibrin sealant;9 26 patients present impairment of sensitivity in the lower limb ipsilateral to the treatment with injection oxygen-ozone;12,24 two discs showed a collapse after injection of corticosteroid,22 1 case of increase in sciatica pain in the 24 hafter the intervention.34
Two trials were performed under CT guidance;12,22 two studies were performed by fluoroscopy,9,25 and only one case by both fluoroscopy and CT guide.24 Adverse events occurred in about 0.7% of the patients with CT guided injection and in 0.2% of the patients with fluoroscopic guided injection. In Yin et al’s trials,9 the patients have even been subjected to antibiotic prophylaxis, in others articles this was not described.
Yin et al, Lehnert et al, Benyahya et al, Andreula et al and Feffer et al9,12,22,24,25 report a posterolateral/extraspinal-lateral approach. Giurazza et al report that
The overall procedural complications rate is estimated around 0.1%. Have been reported in the literature: paresthesia on the anterolateral portion of the left leg and foot, suggesting nerve injury; few temporary episodes of impaired bilateral sensitivity; vitreoretinal hemorrhages; thunderclap headache related to pneumoencephalus as a consequence of inadvertent intrathecal puncture; and 1 case of vertebrobasilar stroke.38
Discussion
For the low back pain management, patients with a small or contained herniated disc with no response to medical treatments, can be candidates for one of the minimally invasive percutaneous techniques. Generally, the minimally invasive techniques offer good results with patient compliance and low cost, showing a very low side effects percentage.20 Only 0.47% of patients have manifested adverse events after intradiscal injection. The procedure is carried out on an outpatient basis by highly experienced operators such as radiologists,19,22 neuroradiologists,20 physiatrists46,39 and orthopedics.23 The procedure is of interest for many medical areas, for this reason standardizing this method allows it to be extended to various practitioners.
For preoperative management there is no consensus regarding sedation, local anesthesia, or antibiotic prophylaxis. Only seven authors mention antibiotic use,4,9,20,46–41 only two articles describe conscious sedation18,23 and three describe a deep sedation.13,38,46 Some unreviewed medical articles28,29 do not recommend local or general anesthesia because they could mask the nerve root puncture symptoms; the needle passes very close to the nerve root and may often touch it, causing a strong electric shock sensation which is quite harmless; if the patient is conscious they will feel the pain. About 0.19% of the patients subjected to antibiotic prophylaxis have had adverse events; while without antibiotics about 0.09% of the population have had side effects; current data do not allow a statistical analysis; for this reason prospective clinical trials are needed. Some authors advise setting up an aseptic room for anesthesiology care, ensuring peripheral access to the patient.29
A concordance has emerged about the patient position, the injection site and the needle type. The most included articles14,17,20,26,28–30,35,37-44 report a prone position as the best to increase the intervertebral space, also using a support under the abdomen to reduce lumbar lordosis. The lateral decubitus was reported in two works34,36 and in an unreviewed journal on chemiodiscolysis with ozone.28 According to five of the articles,12,13,20,21,24 de Santis et al29 recommend an access side at the same side as the symptoms.
The chosen injection site is the center of the disc, and the injection point was checked by fluoroscopic projections,4,9–11,13,14,19,21,23,25,34–39,41,43 CT scans;12,15–18,20,23,24,38,40 we highlight the need for trials to evaluate the more effective, safe, and less expensive methods, especially if using a toxic or very expensive drugs. For the safety, the data do not clarify which is the least injurious method, even though we have recorded a greater percentage of adverse events with the CT guided injection (Table 1). Clinical trials with same medication comparing the fluoroscopy and CT guided injections are needed.
During the procedure, the needle can be readily shifted a few millimeters to pass through without damaging the nerve. The approach and the needle inclination are essential criteria for a successful and safe procedure. In some articles it appears that the lumbar approach has a lateral inclination of 45° to 60° with respect to the axial line18,20 and that for the lower discs an additional cranial-caudal inclination is needed.20 We did not find accurate descriptions on the needle insertion procedure because the needle course was always evaluated radiographically and the access site was chosen accordingly. The authors recommend and/or use a fluoroscopy performed with the C-arm, that allows identification the trajectory of optimal access for needle placement into each disc.10,29,30 An image-guided procedure handbook30 describes a window of anatomical access to the intradiscal injection delineated by the superior articular process medially, the superior endplate below, and the traversing nerve root laterally and above. Staying close to the superior articular process could keep the needle as far as possible from the traversing nerve root.
The postintervention management was different between treatments, the authors have advised several rest times depending on the procedure (Table 2).
The efficacy and the safety of the intradiscal procedures are not easily comparable because the techniques are highly variable in terms of procedure (different operators, needle guidance, injection sites, drugs, tilt angle of the needle) (Table 2).
Conclusions
The efficacy and the safety of the intradiscal procedures are not easily comparable because of differences in the design of studies and their limited number.
The intradiscal injection is a technique widely used in the LBP management of patients with no response to rehabilitative and medical treatments. Differences of agreement between researchers are present on the technical aspects of the procedure in terms of imaging guidance, of injected substances, and efficacy of evaluation tools.
Further studies are needed in order to standardize the intradiscal injection technique/procedure as well as to improve efficacy, safety, repeatability, and to assess cost-effectiveness.
Funding Statement
This work is not supported by funds.
Abbreviations
ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; AL-MSC, allogenic mesenchymal stem cells; AT-BMC, autologous bone marrow concentrate; AT-MSC, adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells; BM, blue methilene; C, control group; Cs, corticosteroid; CT, computerized tomography; EG, experimental group; EL, extraspinal lateral; Ep, epidural; EQ-5D, EuroQol; Fluor, fluoscopy; AL, anterolateral; FRI, Functional Rating Index; FS, fibrin sealant; HA, hyaluronic acid; HyD, hypertonic dextrose; ID, intradiscal injection; LA, local anesthetic; LBP, low back pain; MGPQ, McGill Pain Questionnaire; MIDPD, measurement of the intervertebral disc posterior dimension; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MSC, mesecnchymal stem cells; NASS, the modified North American Spine Society; NRS, Numeric Rating Scale; ODI, Oswestry Disability Index; P, periganglionic injection; PL, posterolateral; PO, posterior-oblique; Post, posterior; PR, periradicular injection; PRP, platelet-rich plasma; Pv/IL, paravertebral/interlaminar; PvO, paravertebral-Oblique; RCT, randomized controlled trial; RMDQ, Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire; SANE, modified single assessment numeric evaluation; SF-36, short form-36; SNRB, selective nerve block; TF, transforaminal; TNF-α I, tumor nerosis factor α inhibitor; Treatm, treatment; VAS, visual analog scale.
Data Sharing Statement
All data analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
References
- 1.Guarnieri G, Vassallo P, Pezzullo MG, et al. A comparison of minimally invasive techniques in percutaneous treatment of lumbar herniated discs. Neuroradiol J. 2009;22(1):108–121. doi: 10.1177/197140090902200116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Becker A, Held H, Redaelli M, et al. Implementation of a guideline for lowback pain management in primary care: a cost effectiveness analysis. Spine. 2012;37:701–710. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31822b01bd [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Leadley RM, Armstrong N, Lee YC, Allen A, Kleijnen J. Chronic diseases in the European Union: the prevalence and health cost implications of chronic pain. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2012;26:310–325. doi: 10.3109/15360288.2012.736933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kallewaard JW, Geurts JW, Kessels A, Willems P, van Santbrink H, van Kleef M. Efficacy, safety, and predictors of intradiscal methylene blue injection for discogenic low back pain: results of a multicenter prospective clinical series. Pain Pract. 2015. doi: 10.1111/papr.12283 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL, Michael CJ. The tissue origin of low back pain and sciatica: a report of pain response to tissue stimulation during operations on the lumbar spine using local anesthesia. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991;22:181–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. The relative contributions of the disc and zygapophyseal joint in chronic lowback pain. Spine. 1994;19:801–806. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199404000-00013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Santiago FR, Kelekis A, Alvarez LG, Filippiadis DK. Interventional procedures of the spine. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2014;18(3):309–317. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1375572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mineta K, Higashino K, Sakai T, Fukui Y, Sairyo K. Recurrence of type I modic inflammatory changes in the lumbar spine: effectiveness of intradiscal therapy. Skeletal Radiol. 2014;43(11):1645–1649. doi: 10.1007/s00256-014-1947-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yin W, Pauza K, Olan WJ, Doerzbacher JF, Thorne KJ. Intradiscal injection of fibrin sealant for the treatment of symptomatic lumbar internal disc disruption: results of a prospective multicenter pilot study with 24-month follow-up. Pain Med. 2014;15:16–31. Wiley Periodicals, Inc. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang Y, Ma Y, Jiang J, Ding T, Wang J. Treatment of the lumbar disc herniation with intradiscal and intraforaminal injection of oxygen-ozone. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2013;26(3):317–322. doi: 10.3233/BMR-130386 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Beaudreuil J, Dieude P, Poiraudeau S, Revel M. Disabling chronic low back pain with modic type 1 MRI signal: acutereduction in pain with intradiscal corticotherapy. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;55:139–147. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2012.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lehnert T, Naguib NN, Wutzler S, et al. Analysis of disk volume before and after CT-guided intradiscal and periganglionic ozone-oxygen injection for the treatment of lumbar disk herniation. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(11):1430–1436. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2012.07.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.De Seze M, Saliba L, Mazaux J-M. Percutaneous treatment of sciatica caused by a herniated disc: an exploratory study on the use of gaseous discography and discogel1 in 79 patients. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2013;56:143–154. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2013.01.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fukui S MD PhD, Iwashita N MD, Nitta K MD, Tomie H MD, Nosaka S MD PhD. The results of percutaneous intradiscal high-pressure injection of saline in patients with extruded lumbar herniated disc: comparison with microendoscopic discectomy. Pain Med.2012;13:762–768. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2012.01400.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yu Y, Liu W, Song D, Guo Q, Jia L. Diagnosis of discogenic low back pain in patients with probable symptoms but negative discography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(5):627–632. doi: 10.1007/s00402-011-1448-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cao P, Jiang L, Zhuang C, et al. Intradiscal injection therapy for degenerative chronic discogenic low back pain with endplate modic changes. Spine J. 2011;11(2):100–106. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2010.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Muto M, Ambrosanio G, Guarnieri G, et al. Low back pain and sciatica: treatment with intradiscal-intraforaminal O(2)-O(3) injection. Our experience. Radiol Med. 2008;113(5):695–706. doi: 10.1007/s11547-008-0302-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oder B, Loewe M, Reisegger M, Lang W, Ilias W, Thurnher SA. CT-guided/steroid therapy for the treatment of degenerative spinal disease–effect of age, gender, disc pathology and multi-segmental changes. Neuroradiology. 2008;50(9):777–785. doi: 10.1007/s00234-008-0398-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fayad F, Lefevre-Colau MM, Rannou F, et al. Relation of inflammatory modic changes to intradiscal steroid injection outcome in chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(7):925–931. doi: 10.1007/s00586-006-0301-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gallucci M, Limbucci N, Zugaro L, et al. Sciatica: treatment with intradiscal and intraforaminal injections of steroid and oxygen-ozone versus steroid only. Radiology. 2007;242(3):907–913. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2423051934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miller Matthew R DSc, PA-C, Mathews RS MD, PhD, Dean RK MD. Treatment of painful advanced internal lumbar disc derangement with intradiscal injection of hypertonic dextrose. Pain Physician. 2006;9:115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Benyahya R, Lefevre-Colau MM, Fayad F, et al. Intradiscal injection of acetate of prednisolone in severe low back pain: complications and patients assessment of effectiveness. Ann Readapt Med Phys. 2004;47:621–626. doi: 10.1016/S0168-6054(04)00193-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Khot A, Bowditch M, Powell J, Sharp D. The use of intradiscal steroid therapy for lumbar spinal discogenic pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2004;29:833–836. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200404150-00002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Andreula CF, Simonetti L, De Santis F, et al. Minimally invasive oxygenozone therapy for lumbar disk herniation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:996–1000. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Feffer HL. Therapeutic intradiscal hydrocortisone. A long-term study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1969;67:100–104. doi: 10.1097/00003086-196911000-00015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Andreula C, Muto M, Leonardi M. Interventional spinal procedures. Eur J Radiol. 2004;50:112–119. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2003.10.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muto M, Andreula C, Leonardi M. Treatment of herniated lumbar disc by intradiscal and intraforaminal oxygen-ozone (O2-O3) injection. J Neuroradiol. 2004;31(3):183–189. doi: 10.1016/S0150-9861(04)96989-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Leonardi M. La puntura discale sotto fluoroscopia. Riv Ital Ossigeno Ozonoterapia. 2002;1:73–78. [Google Scholar]
- 29.De Santis F, Leonardi M, Simonetti L, Dall’Olio M, Princiotta C, Menetti F. Ossigeno-Ozonoterapia: la tecnica intradiscale. Int J Ozone Ther. 2009;8:138–146. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mathis. Image-Guided spine Interventions. New York: Springer; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Migliore T, Laganà P, Granata B, et al. Safety of intra-articular hip injection of hyaluronic acid products by ultrasound guidance: an open study from ANTIAGE register. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(13):1752–1759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Migliore A, Bizzi E, Massafra U, et al. A new technical contribution for ultrasound-guided injections of sacro-iliac joints. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14(5):465–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jee H, Lee JH, Park K 3, Ahn J, Park Y. Ultrasound-guided versus fluoroscopy-guided sacroiliac joint intra-articular injections in the noninflammatory sacroiliac joint dysfunction: a prospective, randomized, single-blinded study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(2):330–337. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.09.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nguyen C, Boutron I, Baron G, et al. Intradiscal glucocorticoid injection for patients with chronic low back pain associated with active dicopathy. Ann Intern Med. 2017. doi: 10.7326/M16.1700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pettine A, Suzuki RK, Sand TT, Murphy MB. Autologous bone marrow concentrate intradiscal injection for the treatment of degenerative disc disease with three-year follow up. Int Orthop. 2017;41:2097. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3560-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sainoh T, Orita S, Miyagi M, et al. Single intradiscal administration of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor, etanercept, for patients with discogenic low back pain. Pain Med. 2016;17:40–45. doi: 10.1111/pme.12892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang XJ, Hao J, Hu ZM, Yang HT. Clinical evaluation and magnetic resonance imaging assessment of intradiscal methylene blue injection for the treatment of discogenic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2016;19:E1189–E1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Giurazza F, Guarnieri G, Murphy KJ, Muto M. Intradiscal O2O3: rationale, injection technique, short- and long-term outcomes for the treatment of low back pain due to disc herniation. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2017;68:171–177. doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2016.12.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tuakli-Wosornu YA, Terry A, Boachie-Adjei K, et al. Lumbar intradiskal Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injections: a prospective, double-blind, Randomized Controlled Study. Pmrjournal. 2016;8:1–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perri M, Marsecano C, Varrassi M, et al. Indications and efficacy of O2–O3 intradiscal versus steroid intraforaminal injection in different types of disco vertebral pathologies: a prospective randomized double‑blind trial with 517 patients. Radiol Med. 2016;121:463–471. doi: 10.1007/s11547-015-0598-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kumar H, Ha DH, Lee EJ, et al. Safety and tolerability of intradiscal implantation of combined autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic acid in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain: 1-year follow-up of a phase I study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:262. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0710-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pettine K, Suzuki R, Sand T, Murphy M. Treatment of discogenic back pain with autologous bone marrow concentrate injection with minimum two year follow-up. Int Orthop. 2015. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2886-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Centeno C, Markle J, Dodson E, et al. Treatment of lumbar degenerative disc disease‑associated radicular pain with culture‑expanded autologous mesenchymal stem cells: a pilot study on safety and efficacy. J Transl Med. 2017;15:197. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1300-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Noriega DC, Ardura F, Hernández-Ramajo R, et al. Intervertebral disc repair by allogeneic mesenchymal bone marrow cells: a randomized controlled trial. Transplantation. 2017;101(8):1945–1951. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001484 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hartung W, Ross CJ, Straub R, et al. Ultrasound-guided sacroiliac joint injection in patients with established sacroiliitis: precise IA injection verified by MRI scanning does not predict clinical outcome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(8):1479–1482. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Levi D, Horn S, Tyszko S, Levin J, Hecht-Leavitt C, Walko E. Intradiscal platelet-rich plasma injection for chronic discogenic low back pain: preliminary results from a prospective trial. Pain Med. 2016;17:1010–1022. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnv053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]