Dear Editor,
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) due to severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to an unprecedented medical crisis across the world, with medical services diverted to and overwhelmed by an urgent need of caring for sick patients with COVID-19. Tertiary care centres were the first responders for patients with COVID-19 with major resource reallocation to COVID-19, and even though strategies were planned to minimize suffering of patients with non-COVID emergencies, major hardship and possible neglect of patients with acute non-COVID medical emergencies ensued.
Acute Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, the most common GI emergency, is associated with a mortality of around 10% [1], which may be higher especially in patients with variceal bleeding depending on the severity of the underlying liver disease. The cornerstone for achieving hemostasis and subsequent reduction in mortality in patients with GI bleeding is endoscopic therapy within 12–24 h of presentation which is effective in >90% of cases [2,3]. Upper GI endoscopy however, is an aerosol-generating procedure with possibility of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 to healthcare workers (HCWs) during the procedure [4]. Therefore, concerns have been raised about endoscopic procedures in patients with GI diseases who are potentially infected with COVID-19, with a few societies issuing consensus guidelines regarding the indications, precautions such as the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and procedure-related technical issues for effective and safe endoscopy procedures [5].
In view of the concerns about spread of infection, reallocation of resources, use of PPE, and restricted access to medical care, we conducted an ambispective observational study in five tertiary care academic institutions in India to examine the efficacy and safety of therapeutic GI endoscopic procedures in patients with acute GI bleeding during the COVID-19 pandemic that led to the aforementioned changed scenario. The participating centres were All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi; Govind Ballabh Pant Hospital (GBPH), New Delhi; Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore; Postgraduate Institute of Medical Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh; and Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute (SGPGI), Lucknow. Data were collected from a prospectively maintained database for the month of April 2020 and prospectively for the month of May 2020.
We included all patients >12 years of age undergoing GI endoscopic procedures for overt or occult GI bleeding from 1st April to 31st May 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic and nationwide lockdown.
There was no universal policy of testing for SARS-COV2 prior to the endoscopy in view of urgency of the procedure except in one of the five centres. Patients and HCWs were tested by RT-PCR for SARS-CoV2 infection only if they were symptomatic or had history suggestive of exposure to a COVID-19 positive patient. Details of measures for prevention of cross infection and protocol for the management of GI bleeding are summarized in supplementary document 1. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Institute Ethics Committee. Informed consent was waived by the ethics committee and only anonymized data are being reported.
Efficacy and safety of endoscopic therapy for GI bleeding was the primary outcome. Efficacy was defined as successful endoscopic therapy for the underlying cause of bleeding. Safety was defined in terms of complication of the endoscopic procedure and transmission of COVID-19 infection to HCWs and/or patients during endoscopic procedures. Secondary outcomes were rebleeding rate and mortality during hospital stay and within 28 days of index bleed.
All the centers reported 85%−95% reduction in number of endoscopic procedures performed during the nationwide lockdown because only urgent endoscopies were being undertaken. A total of 1294 endoscopic procedures [Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)−1064, colonoscopy-230] were performed across 5 centers from April 1 to May 31, 2020 (Table 1 ). Of these, 638 (49.3%) procedures (EGD-500 and colonoscopy-138) were done for GI bleeding, which was the most common indication for performing an endoscopic procedure. Of the 500 patients who underwent an EGD, 177 (35.4%) patients had non-variceal bleeding (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 1) and 323 (64.6%) patients had variceal bleeding (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 2). The most common cause of non-variceal bleeding was an ulcer related bleed in 87 (49.1%) patients: 47 (26.5%) having duodenal ulcer and 40 (22.6%) having gastric ulcer. Among the 323 patients with portal hypertension related bleeding, the following findings were detected: esophageal varices in 248 (76.8%) patients, fundal varices in 52 (16.1%) patients, portal hypertensive gastropathy in 56 (17.3%) patients, post endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) ulcer in 12 (3.7%) patients and gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE) in 9 (2.8%) patients. Therapeutic intervention was required in 256 (51.2%) patients and was successful in 250 patients but not in 6 (1.2%) patients; Twenty (4.0%) patients with variceal bleeding had rebleeding during the hospital stay. In-hospital mortality was 4.4% (22/497) and the 28-day mortality was 6.7%.
Table 1.
Nature of endoscopic procedures, therapeutic modality and outcomes for gi bleeding across five tertiary academic centres during nationwide lockdown.
| Characteristics | AIIMS | GBPH | PGIMER | CMC | SGPGI | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of Procedures Performed | 243 | 274 | 228 | 474 | 75 | 1294 |
| Total number of procedures performed for GI bleeding, N (Percentage) | 169 (69.5%) | 158 (57.7%) | 130 (57%) | 131 (27.6%) | 50 (66.7%) | 638 (49.3%) |
| Mean age (Years) | 46 ± 13.7 | 48.3 ± 16.2 | 46.4 ± 16.7 | 53 ± 16.6 | 46 ± 5 | 49.1 ± 15.3 |
| Sex (Male, female) | Males: 71.6% Females: 28.4% |
Males: 73.4% Females: 30.8% |
Males: 69.2% Females: 30.8% |
Males: 67.9% Female: 32.1% |
Males: 84.4% Females: 15.6% |
Males: 70.5% Females: 29.5% |
| A. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy | ||||||
| Total number of EGD performed | 220 | 234 | 183 | 367 | 60 | 1064 |
| EGD performed for UGI bleeding | 148 (67.3%) | 129 (55.1%) | 87 (47.5%) | 96 (26.1%) | 40 (66.6%) | 500(47%) |
| Therapeutic intervention done | 99 (66.9%) | 60 (46.5%) | 50 (61.7%) | 33 (34.3%) | 14 (48.3%) | 256 (51.2%) |
| Outcomes of EGD | ||||||
| Primary hemostasis achieved | 145 (97.8%) | 129 (100%) | 86 (98.8%) | 94 (97.9%) | 40 (100%) | 494 (98.8%) |
| Failure of endotherapy | 3 (2%) | 0 | 1 (1.1%) | 2 (2.1%) | 0 | 6 (1.2%) |
| Rebleeding | 6 (4.1%) | 8 (6.2%) | 4 (4.9%) | 2 (2.1%) | 0 | 20 (4.0%) |
| In-hospital mortality | 11(7.4%) | 7 (5.4%) | 2 (2.5%) | 2 (2.1%) | 0 | 22 (4.4%) |
| 28-day mortality | 16 (10.8%) | 9 (7.0%) | 2 (2.5%) | NA* | 0 | 27 (6.7%) |
| B. Colonoscopy | ||||||
| Total number of procedures performed | 23 | 40 | 45 | 107 | 15 | 230 |
| Colonoscopy performed for lower GI bleeding | 21 (91.3%) | 29 (72.5%) | 43 (95.6%) | 35 (32.7%) | 10 (66.7%) | 138 (60%) |
| Therapeutic intervention done | 3(14.3%) | 3 (10.4%) | 1 (2.4%) | 2 (5.7%) | 2 (20%) | 11 (7.9%) |
| Outcomes of therapy performed | ||||||
| Primary hemostasis Achieved | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Failure of endotherapy | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Rebleeding requiring repeat colonoscopy | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| In- hospital mortality | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| 28-day mortality | None | None | None | NA* | None | None |
| C. Complications directly related to endoscopic procedure | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1# | 0 | 1 |
Institutes: AIIMS: All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India; CMC: Christian Medical college, Vellore, India; GBPH: Govind Ballabh Pant Hospital, New Delhi, India; PGIMER: Post Graduation Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India; SGPGI: Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute, Lucknow, India.
Abbreviations: EGD: esophagogastroduodenoscopy; n.a: not available; UGI: Upper gastrointestinal.
28 day mortality data not available for the center.
(CMC): Post-biopsy bleeding- managed conservatively.
Table 2.
Demographic characteristics, endoscopic findings and outcome of endotherapy in patients with gastrointestinal bleed.
| A. EGD performed for Non variceal UGI bleeding | N = 177 |
| Findings on EGD, N (percentage) | |
| Duodenal Ulcer | 47 (26.5) |
| Gastric ulcer | 40 (22.6) |
| Gastric malignancy | 5 (2.8) |
| Gastritis | 25 (14.1) |
| Esophagitis | 3 (1.7) |
| Mallory Weiss Tear | 8 (4.5) |
| Normal study | 39 (22.0) |
| Others | 10 (5.6) |
| Therapy Performed during EGD | |
| Hemoclip application | 22 (12.4) |
| Hemospray | 1 (0.6) |
| APC Application | 7 (3.9) |
| Others | 6 (3.4) |
| Outcomes of EGD | |
| Primary hemostasis achieved | 176 (99.4) |
| Failure of endotherapy | 1 (0.6)£ |
| Rebleeding | 0 |
| In-hospital mortality | 1 (0.6) |
| 28-day mortality | 1(0.8%)* |
| B. EGD performed for variceal upper GI bleeding | N = 323 |
| Findings on EGD, N (percentage) | |
| Esophageal varices | 248 (76.8) |
| Fundal Varices | 52 (16.1) |
| PHG | 56 (17.3) |
| Gastric Antral Vascular ectasia | 9 (2.8) |
| Post EVL ulcer | 12 (3.7) |
| Ectopic variceal bleed | 1 (0.3) |
| Therapy Performed during EGD | |
| Esophageal variceal band ligation | 169 (52.3) |
| Sclerotherapy | 8 (2.4) |
| Glue injection | 42 (12.6) |
| APC application | 4 (1.2) |
| Outcomes of EGD | |
| Primary hemostasis achieved | 318 (98.4) |
| Failure of endotherapy | 5 (1.5) |
| Rebleeding | 20 (6.1) |
| In-hospital mortality | 21 (6.5) |
| 28-day mortality | 26 (9.2)* |
| C. Colonoscopy performed for lower GI bleeding | 138 |
| Findings on colonoscopy, N (Percentage) | |
| No source of bleed | 40 (29.0) |
| Colonic ulcers (IBD related) | 30 (21.7) |
| Colonic ulcers (infective) | 12 (8.7) |
| Colonic malignancy | 12 (8.7) |
| Internal Hemorrhoids | 24 (17.4) |
| Radiation Proctitis | 3 (2.2) |
| SRUS | 1 (0.7) |
| Diverticular bleed | 3 (2.2) |
| Others | 15 (10.9) |
| Therapy Performed during colonoscopy | |
| APC Application | 4 (2.9) |
| Hemoclip Application | 2 (1.5) |
| Others | 5 (3.6) |
£ One patient has acute pancreatitis with walled-off necrosis and had pseudoaneurysmal massive bleed.
Abbreviations: APC: Argon plasma coagulation; EGD: esophagogastroduodenoscopy; EVL: Endoscopic Variceal Ligation; GI: gastrointestinal; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; PHG: Portal Hypertensive Gastropathy.
Patients from CMC excluded to calculate 28 day mortality as follow up data not available.
A total of 138 colonoscopies were performed for lower GI bleeding (Table 2 and Supplementary Table 3). Thirty (21.7%) patients had inflammatory bowel disease, 12 (8.7%) patients had infective colitis, 12 (8.7%) patients had colonic malignancy, 3 (2.2%) patients had radiation proctitis, 3 (2.2%) patients had diverticular bleed, 24 (17.4%) patients had hemorrhoidal bleed, and 16 patients had other causes. Therapeutic intervention was needed only in 11 (8%) patients. Hemostasis was achieved in all patients with lower GI bleeding and there was no rebleeding. There was no mortality in patients with lower GI bleeding. As compared to upper GI bleeding, the need for therapeutic intervention was significantly less in lower GI bleeding (51.2% vs. 7.9%; p <0.001).
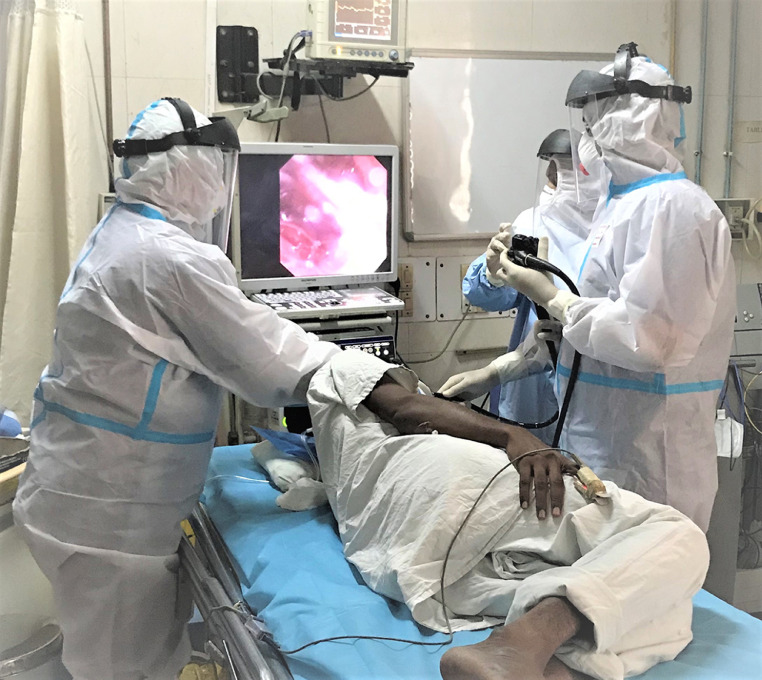
Of the 638 procedures performed for GI bleeding, four patients turned out to be COVID-19 positive within 72 h after the endoscopic procedure was performed. Of 94 HCWs associated with endoscopy procedures which included doctors, nurses and technicians, only 3 (3.1%) developed COVID-19. The overall risk of an HCW getting COVID-19 positive with the use of adequate PPE (Fig. 1 ) was 0.49% per 100 endoscopic procedures performed (Supplementary Table 4). At one center (SGPGI) that was performing mandatory COVID-19 testing prior to endoscopy, none of the HCWs developed COVID-19 infection. The mean level of difficulty faced by the endoscopists was 2 (range 2–3) on a 4-point Likert scale primarily due to ergonomics challenges imposed by wearing level 2 PPE kit.
Fig. 1.
Figure demonstrating endoscopy for gastrointestinal bleeding with personal protective equipments.
Thus, our study has shown a marked reduction in the number of endoscopy procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the number of endoscopy procedures performed for GI bleeding was similar to those reported previously from one center (130 over 2 months for UGI bleeding - 43% non-variceal and 57% variceal) [6]. Primary hemostasis was achieved in 98.8% of patients with a 4.0% rebleeding rate and 6.7% 28-days mortality in patients with upper GI bleeding. In patients with lower GI bleeding, it was controlled in all patients with no mortality. The results of the present study are comparable to our published results in terms of hemostasis and mortality in both variceal and non-variceal bleeding before COVID crisis.
Previously published reports showed that most patients with GI bleeding during COVID-19 pandemic were managed with pharmacotherapy and the strategy was to avoid endoscopic procedures [7,8]. This may be due to fear of increased risk of transmission of infection to endoscopy personnel as there is high aerosol generation during EGD and risk of contact with virus present in feces during colonoscopy [9]. However, our study has demonstrated that endoscopy could be performed for urgent indications such as GI bleeding with a very low risk of transmission of COVID-19 (0.49% per 100 endoscopies per HCW) with the use of adequate PPE, even without a policy of universal pre-procedure COVID-19 testing. The low rate of infection among endoscopy personnel during this period which suggests that proper PPE use, adherence to infection control practices and proper protocol in place are effective measures to contain this infection. Our findings thus validate the recommendations of various endoscopic societies guidelines in this regard [10].
There are several limitations of our study. Our was an ambispective study with data collected retrospectively for the first month but there was no significant difference between the 2 months. There was some difference in the incidence of COVID-19 across centres which could have affected the proportion of positive patients, the policy of testing for COVID-19 prior to endoscopic procedure varied between different centers, there were subtle differences between choice of treatment protocol e.g. somatostatin versus terlipressin and the selection of endoscopic procedures was usually decided by the institutional policy and at the discretion of the endoscopist.
In summary, endoscopic therapy with adequate precautions is safe and effective for gastrointestinal bleeding with relatively low risk of cross-infection during COVID-19 pandemic. These observations call for and support resumption of optimum level of endoscopic services during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic even without a policy of universal pre-procedure testing for SARS-CoV2 particularly in resource limited settings.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Writing assistance
None.
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved by the Institute Ethics committee.
Patient consent
Patient consent was waived-off by ethics committee and only anonymized data are being reported.
Permission to reproduce material from other sources
Not Required.
Guarantor of article
Dr Anoop Saraya.
Members of GAIN study group (in alphabetical order)
Ashish Agarwal, MD1; Samagra Agarwal, MD1; Vineet Ahuja, MD1; Abhinav Anand, MD1; Rajat Bansal, MD1; Vikas Banyal, MD1; Ptaviva Chandra, Bsc (Nursing)4; Kaushik Chatterjee, MD3; Sudipta Dhar Chowdhury, MD3; Anugrah Dhooria, MD1; Amit Kumar Dutta, MD3; Usha Dutta, MD2; Anshuman Elhence, MD1; Pramod Garg, MD1; John Titus George, MD3; Roshan George, MD5; Srikanth Gopi, MD1; Deepak Gunjan, MD1; Arpan Jain, MD5; Rajeeb Jaleel, MD3; Yegurla Jatin, MD1; Vikas Jindal, MD1; Anjilivelil Joseph, MD3; Bhaskar Kante, MD1; Kanav Kaushal, MD1; Saurabh Kedia, MD1; Rakesh Kochhar, MD2; Soumya Jagannath Mahapatra, MD1; Govind Makharia, MD1; Harshal S Mandavdhare, MD2; Anurag Mishra, MD5; Samir Mohindra, MD4; Srikant Mohta, MD1; Gaurav Muktesh, MD2; Sandeep Kumar Mundhra, MD1; Piyush Pathak, MD1; Shubham Prasad, MD1; Mahendra Singh Rajput1; Praveer Rai, MD2; Atul Rana, MD1; Sanjeev Sachdeva, MD5; Anoop Saraya, MD1; Pabitra Sahu, MD1; Jayanta Samanta, MD2; Vivek Saraswat, MD4; Rahul Sethia, MD1; Jimil Shah, MD2; Shalimar, MD1; Sanchit Sharma, MD1; Vishal Sharma, MD2; Jayendra Shukla, MD2; Ebby George Simon, MD3; Alok Kumar Singh, MD5; Amit Anurag Singh, MD1; Manas Vaishnav, MD1; Sudheer Kumar Vuyurru, MD1.
Declaration of Competing Interest
We declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.10.009.
Appendix. Supplementary materials
References
- 1.Stanley A.J., Laine L. Management of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. BMJ. 2019;364:l536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garcia-Tsao G., Abraldes J.G., Berzigotti A. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatol Baltim Md. 2017;65:310–335. doi: 10.1002/hep.28906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barkun A.N., Almadi M., Kuipers E.J. Management of nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding: guideline recommendations from the international consensus group. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171:805–822. doi: 10.7326/M19-1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Soetikno R., Teoh A.Y.B., Kaltenbach T. Considerations in performing endoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic. Gastrointest Endosc. March 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.03.3758. Epub ahead of print 27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Castro Filho E.C., Castro R., Fernandes F.F. Gastrointestinal endoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic: an updated review of guidelines and statements from international and national societies. Gastrointest Endosc. April 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.03.3854. Epub ahead of print 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rout G., Sharma S., Gunjan D. Comparison of various prognostic scores in variceal and non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding: a prospective cohort study. Indian J Gastroenterol Off J Indian Soc Gastroenterol. 2019;38:158–166. doi: 10.1007/s12664-018-0928-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kim J., Doyle J.B., Blackett J.W. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on outcomes for patients admitted with gastrointestinal bleeding in New York city. Gastroenterology. May 2020 doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.031. Epub ahead of print 13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cavaliere K., Levine C., Wander P. Management of upper GI bleeding in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Gastrointest Endosc. April 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.04.028. Epub ahead of print 20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen Y., Chen L., Deng Q. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the feces of COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92:833–840. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chiu P.W.Y., Ng S.C., Inoue H. Practice of endoscopy during COVID-19 pandemic: position statements of the asian pacific society for digestive endoscopy (APSDE-COVID statements) Gut. 2020;69:991–996. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.