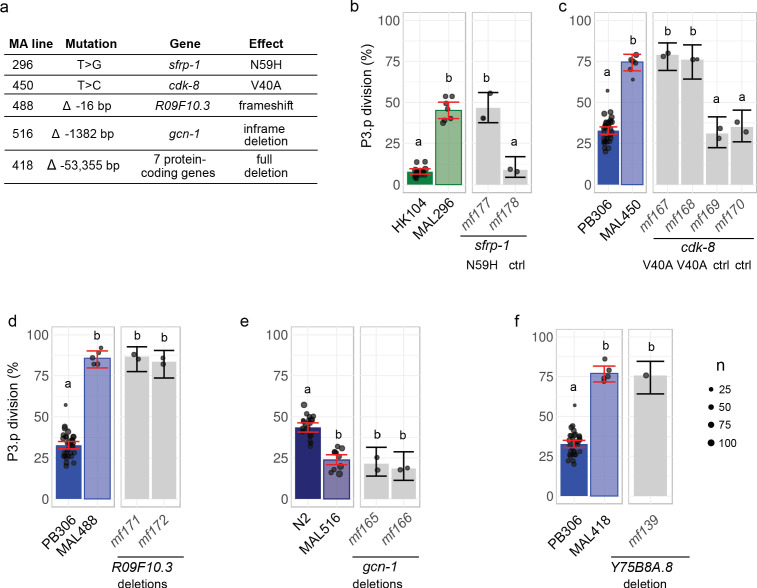
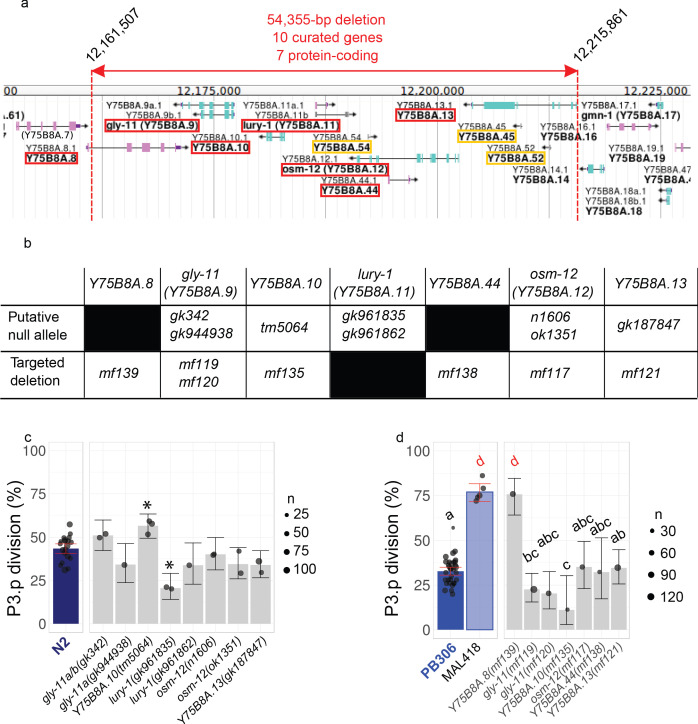
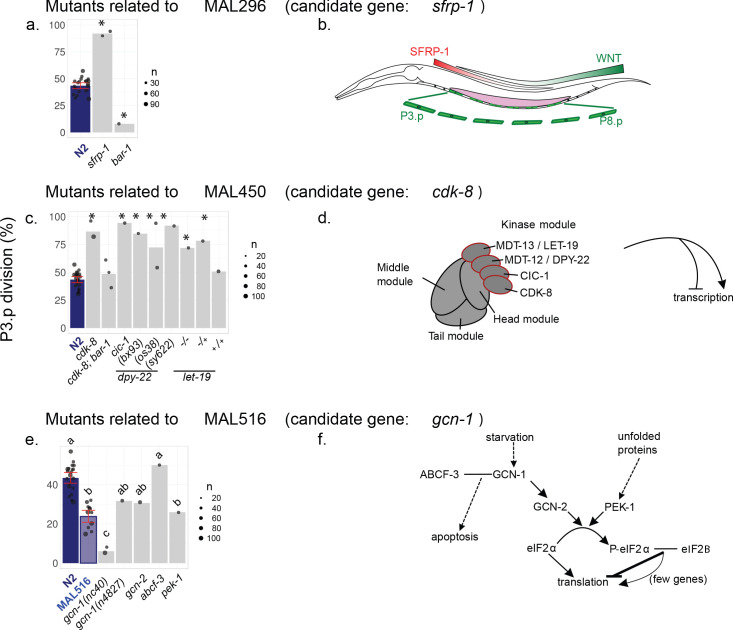
Figure 4. Validation by precise genome editing of candidate causal mutations responsible for P3.p cell fate evolution in MA lines.
(a) Summary table of the molecular nature, underlying gene and molecular effect of the candidate mutations. (b) P3.p division frequency after editing the sfrp-1 locus in ancestor HK104 with a repair template coding only for synonymous substitutions (mf178) or introducing the N59H substitution as well (mf177). (c) P3.p division frequency after editing the cdk-8 locus in ancestor PB306 with a repair template coding for synonymous substitutions only (independent edits mf169 and mf170) or introducing the V40A substitution as well (independent edits mf167 and mf168). (d) P3.p division frequency after editing the R09F10.3 locus in ancestor PB306 to reproduce the exact same 16 bp deletion as in MA line 488 (independent edits mf171 and mf172). (e) P3.p division frequency after editing the gcn-1 locus in ancestor N2 to reproduce the exact same 1344 bp deletion as in MA line 516 (independent edits mf165 and mf166). (f) P3.p division frequency after deleting the entire Y75B8A.8 locus in ancestor PB306. Each dot is an independent experiment, with dot size scaled to the number of scored individuals(n). The bar is the mean frequency obtained by pooling all replicates; error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. For each graph, leftmost panels provide the scores of ancestor and MA lines as reference (identical data to Figure 2b). Different letters indicate a significant difference (Fisher's exact test, fdr level: 0.05).