Abstract
Simple Summary
Nucleosomes composed of DNA and histone proteins enter the extracellular space and end eventually in the circulation when cells die. In blood plasma, they could represent a nonspecific marker of cell death, potentially useful for noninvasive monitoring of cancer. The aim of this study was to analyze circulating nucleosomes in relation to patient/tumor characteristics and prognosis in nonmetastatic breast cancer. This study included 92 patients with breast cancer treated with surgery. Plasma nucleosomes were detected in samples taken in the morning on the day of surgery. Circulating nucleosomes were positively associated with the systemic inflammation but not with other patient/tumor characteristics. Patients with lower nucleosomes had lower risk of disease recurrence compared to patients with higher nucleosomes. Our data suggest that plasma nucleosomes in nonmetastatic breast cancer are associated with systemic inflammation and might have a prognostic value. The underlying mechanisms require further studies.
Abstract
When cells die, nucleosomes composed of DNA and histone proteins enter the extracellular space and end eventually in the circulation. In plasma, they might serve as a nonspecific marker of cell death, potentially useful for noninvasive monitoring of tumor dynamics. The aim of this study was to analyze circulating nucleosomes in relation to patient/tumor characteristics and prognosis in primary breast cancer. This study included 92 patients with breast cancer treated with surgery for whom plasma isolated was available in the biobank. Plasma nucleosomes were detected in samples taken in the morning on the day of surgery using Cell Death Detection ELISA kit with anti-histone and anti-DNA antibodies. Circulating nucleosomes were positively associated with the systemic inflammatory index (SII), but not with other patient/tumor characteristics. Patients with high SII in comparison to low SII had higher circulating nucleosomes (by 59%, p = 0.02). Nucleosomes correlated with plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, IL-15, IL-16, IL-18, and hepatocyte growth factor. Patients with lower nucleosomes had significantly better disease-free survival (HR = 0.46, p = 0.05). In a multivariate analysis, nucleosomes, hormone receptor status, HER2 status, lymph node involvement, and tumor grade were independent predictors of disease-free survival. Our data suggest that plasma nucleosomes in primary breast cancer are associated with systemic inflammation and might have a prognostic value. The underlying mechanisms require further studies.
Keywords: primary breast cancer, circulating nucleosomes, circulating tumor cells, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, cytokines
1. Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death among women in developed countries [1]. Despite advances in cancer prevention, diagnoses, and treatment, still approximately 5% of patients are diagnosed with metastatic disease, and 20–30% of initially primary breast cancer develops metastasis subsequently, during the course of the disease.
Extracellular DNA (ecDNA), also called cell-free DNA, is present in blood plasma in various forms [2]. EcDNA in the circulation of cancer patients contains tumor DNA from the primary tumor, metastasis, or circulating tumor cells, as well as healthy host cells mostly of hematopoietic origin [3,4,5]. Plasma ecDNA is partially free unbound DNA and, so, sensitive to rapid cleavage, but it also can be protected as ecDNA hidden in apoptotic bodies and/or bound to proteins such as histones in the form of nucleosomes [5].
Nucleosomes are composed of DNA wound around histone proteins and represent the basic structural unit of chromatin in the nucleus [6]. After cell death, membranes and nuclei disintegrate and cell-free nucleosomes can get into the circulation. Plasma nucleosomes might serve as a nonspecific biomarker of cell death [7]. This might be of interest in patients not only with autoimmune diseases, but also with sepsis or cancer [8,9,10]. The prognostic value of the concentration of circulating nucleosomes was shown in several types of cancer including lung, pancreatic, or colorectal cancer [11,12,13,14,15]. For example, in pancreatic cancer, high nucleosome levels during treatment, but not pretherapeutic levels, correlate with time to progression [16]. Similarly, in non-small cell lung cancer, high baseline nucleosome level and/or during chemotherapy was associated with poor response to treatment and these data suggested that circulating nucleosomes are a valuable tool for early prediction of chemotherapy efficacy in cancer patients [17]. However, when it comes to primary breast cancer, data in the published literature are limited.
In this study, we aimed to analyze circulating nucleosomes in relation to patients/tumor characteristics and prognosis in primary breast cancer.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Patients
This study included 92 primary breast cancer patients (stage I–III) treated with surgery from March to November 2012, for whom plasma isolated in the morning on the day of surgery was available in the biobank. This study represents a substudy of a translational trial that aimed to evaluate prognostic value of circulating tumor cells in primary breast cancer [18]. Study eligibility criteria and study details were described previously [18]. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the National Cancer Institute of Slovakia (TRUSK002, 20.6.2011). Each participant provided signed informed consent before study enrollment.
2.2. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in Peripheral Blood
CTCs were detected in peripheral blood by a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)-based assay of peripheral blood as described previously [18,19,20].
2.3. Plasma Isolation
Venous peripheral blood samples were collected in EDTA-treated tubes in the morning on the day of surgery and centrifuged at 1000× g for 10 min at room temperature within 2 h of venipuncture and processed as described previously [21].
2.4. Quantification of Circulating Nucleosomes
The commercially available Cell Death Detection kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) was used for the measurement of nucleosomes. Briefly, 20 mL of plasma was mixed with biotin-labeled anti-histone and peroxidase-conjugated anti-DNA antibodies. After incubation and washing, the substrate for the peroxidase enzyme was added. Absorbance was measured at 405 nm in arbitrary units after stopping the reaction. Interassay and intra-assay coefficients of variation were below 10% and 5%, respectively.
2.5. Measurement of DD, TF, uPA, and PAI-1 in Plasma
Plasma tissue factor (TF), d-dimer (DD), urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) were analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) as described previously [21].
2.6. Plasma Cytokines and Angiogenic Factors Analysis
Plasma samples were analyzed for 51 plasma cytokines and angiogenic factors: TGF-β1, TGF-β2, TGF-β3, IFN-α2, IL-1α, IL-2Rα, IL-3, IL-12p40, IL-16, IL-18, CTACK, Gro-α, HGF, LIF, MCP-3, M-CSF, MIF, MIG, β-NGF, SCF, SCGF-β, SDF-1α, TNF-β, TRAIL, IL-1β, Il-1RA, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13, IL-15, IL-17, Eotaxin, FGF basic, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IP-10, MCP-1, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, PDGF bb, RANTES, TNF-α, VEGF using predesigned panels as described previously and were available for subset of patients (Bio-Plex Pro TGF-β assay, Bio-Plex Pro Human Cytokine 21- and 27-plex immunoassays; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) [22]. The large panel of cytokines was analyzed as data were available from the previous study [22].
2.7. Complete Blood Count and Inflammation-Based Scores
Complete blood count (CBC) and CBC-derived inflammation-based scores were calculated as described previously [23,24]. For CBC-derived inflammation-based scores, identical cut-off values as published previously for metastatic breast cancer patients were used [23,24]. Data for calculation of NLR, PLR, MLR, SII were available for 54, 52, 48, and 52 patients, respectively.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The characteristics of patients is summarized using mean (range) for continuous variables and frequency (percentage) for categorical variables. The median follow-up period was calculated as the median observation time among all patients and among those who were still alive at the time of their last follow-up. Disease-free survival (DFS) was calculated from the date of blood sampling to the date of disease recurrence (locoregional or distant), secondary cancer, death, or last follow-up. DFS was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier product limit method and compared between groups by log-rank test. For survival analysis, circulating nucleosomes were dichotomized to “low” or “high” (nucleosome level below vs. above mean, respectively). Univariate analyses with Chi squared or Fisher’s exact test were performed to find associations between prognostic factors.
A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model for DFS was used to assess differences in outcome on the basis of the nucleosomes status (above mean vs. below mean), hormone receptor status (positive for either vs. negative for both), HER-2 status (positive or negative), axillary lymph node involvement (N0 vs. N+), grade (grade 3 vs. grade 1 and 2). Stepwise regression techniques were used to build multivariate models using a significance level of 0.10 to remain in the model. All p values presented are two-sided, and associations were considered significant if the p value was less than or equal to 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using NCSS 11 Statistical Software (2016, NCSS, LLC., Kaysville, UT, USA, ncss.com/software/ncss).
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
The study population consisted of 92 primary breast cancer patients with a median age of 60 years (range: 25–83 years). The patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. There were 79 (85.9%) patients with estrogen receptor-positive (ER) and/or progesterone receptor-positive (PR) tumors, and 16 (17.4%) patients with HER2/neu-positive tumors.
Table 1.
Patients’ characteristics.
| Variable | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| All Patients | 92 | 100.0 |
| T-stage | ||
| T1 | 58 | 63.0 |
| >T1 | 34 | 37.0 |
| Histology | ||
| IDC | 76 | 82.6 |
| other | 16 | 17.4 |
| Grade | ||
| low and intermediate | 49 | 53.3 |
| high grade | 41 | 44.6 |
| unknown | 2 | 2.2 |
| Lymph nodes | ||
| N0 | 57 | 62.0 |
| N+ | 34 | 37.0 |
| unknown | 1 | 1.1 |
| LVI | ||
| present | 69 | 75.0 |
| absent | 23 | 25.0 |
| Hormone receptor status (cut-off 1%) | ||
| negative for both | 13 | 14.1 |
| positive for either | 79 | 85.9 |
| Estrogen receptor-positive (cut-off 1%) | ||
| negative | 16 | 17.4 |
| positive | 76 | 82.6 |
| Progesterone receptor-positive (cut-off 1%) | ||
| negative | 25 | 27.2 |
| positive | 67 | 72.8 |
| HER2 status | ||
| positive | 16 | 17.4 |
| negative | 76 | 82.6 |
| P53 status | ||
| negative | 59 | 64.1 |
| positive | 32 | 34.8 |
| unknown | 1 | 1.1 |
| BCL-2 | ||
| negative | 27 | 29.3 |
| positive | 65 | 70.7 |
| unknown | ||
| Ki67 status (cut-off 14%) | ||
| <14% | 48 | 52.2 |
| >14% | 44 | 47.8 |
| Molecular subtype | ||
| Luminal A | 43 | 46.7 |
| Luminal B | 36 | 39.1 |
| HER2+ | 1 | 1.1 |
| Triple-negative (TN) | 12 | 13.0 |
| CTC EP | ||
| negative | 75 | 81.5 |
| positive | 17 | 18.5 |
| CTC EMT | ||
| negative | 76 | 82.6 |
| positive | 16 | 17.4 |
| CTC ANY | ||
| negative | 62 | 67.4 |
| positive | 30 | 32.6 |
Abbreviations: CTC EP, circulating tumor cells with epithelial phenotype; CTC EMT, circulating tumor cells with epithelial–mesenchymal transition phenotype; CTC ANY, circulating tumor cells irrespective of phenotype; LVI, lymphovascular invasion.
3.2. Association between Nucleosomes and Patient/Tumor Characteristics
The characteristics of patients and the associations with circulating nucleosomes are shown in Table 2. The concentration of circulating nucleosomes was not associated with any patient/tumor characteristics except the systemic inflammatory index (SII), where patients with high SII had significantly higher levels of circulating nucleosomes compared to patients with low SII (0.17 vs. 0.27, p = 0.02). There was also a trend for higher level of circulating nucleosomes in patients with high neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (p = 0.07). There was no association between molecular subtype and plasma nucleosomes, even if molecular subtypes of breast cancer were further segregated by tumor grade. We also analyzed association of chronic medication/comorbidities (Appendix A, Table A1) and circulating nucleosomes, but we found no association.
Table 2.
Association between nucleosomes and patient/tumor characteristics.
| Variable | N | Mean | SEM | Median | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 92 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.13 | NA |
| T-stage | |||||
| T1 | 58 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.30 |
| >T1 | 34 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.13 | |
| Histology | |||||
| invasive ductal carcinoma | 76 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.61 |
| other | 16 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.13 | |
| Grade | |||||
| low and intermediate | 49 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.91 |
| high grade | 41 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.13 | |
| unknown | 2 | ||||
| Lymph nodes | |||||
| N0 | 57 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.10 |
| N+ | 34 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.17 | |
| unknown | 1 | ||||
| Lymphovascular invasion | |||||
| absent | 69 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| present | 23 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.16 | |
| Hormone receptor status (cut-off 1%) | |||||
| negative for both | 13 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.17 |
| positive for either | 79 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.14 | |
| HER2 status | |||||
| negative | 76 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.91 |
| positive | 16 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.15 | |
| P53 status | |||||
| negative | 59 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.51 |
| positive | 32 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.13 | |
| unknown | 1 | ||||
| BCL-2 | |||||
| negative | 27 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.52 |
| positive | 65 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.13 | |
| Ki67 status (cut-off 14%) | |||||
| <14% | 48 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.38 |
| >14% | 44 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.13 | |
| unknown | |||||
| Molecular subtype | |||||
| Luminal A | 43 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.22 |
| Luminal B | 36 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.14 | |
| HER2+ | 1 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.25 | |
| Triple-negative (TN) | 12 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.09 | |
| CTC EP | |||||
| negative | 75 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.44 |
| positive | 17 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.14 | |
| CTC EMT | |||||
| negative | 76 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.78 |
| positive | 16 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.13 | |
| CTC ANY | |||||
| negative | 62 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.19 |
| positive | 30 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.15 | |
| NLR (neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio) * | |||||
| <3 | 43 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.07 |
| >3 | 11 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.17 | |
| PLR (platelet/lymphocyte ratio) * | |||||
| <210 | 43 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.71 |
| >210 | 9 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.15 | |
| MLR (monocyte/lymphocyte ratio) * | |||||
| <0.34 | 40 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.60 |
| >0.34 | 8 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.14 | |
| SII (systemic inflammatory index) * | |||||
| <836 | 40 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 |
| >836 | 12 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.17 |
Abbreviations: CTC EP, circulating tumor cells with epithelial phenotype; CTC EMT, circulating tumor cells with epithelial–mesenchymal transition phenotype; CTC ANY, circulating tumor cells irrespective of phenotype. * Data for calculation of NLR, PLR, MLR, SII were available for 54, 52, 48, and 52 patients, respectively; NA, not applicable. p-Values < 0.05 are written in Bold.
3.3. Association between Nucleosomes and Plasma Cytokines
Patients with nucleosomes above mean in peripheral blood had significantly elevated plasma IL-16 (p = 0.005), IL-18 (p = 0.0004), and hepatocyte growth factor (p = 0.043), as compared to patients with nucleosomes below mean, while there was an inverse correlation between nucleosomes and IL-15 (p = 0.036). There was also a trend for higher IFN-α2 (p = 0.055) and RANTES (p = 0.053) in patients with higher nucleosome level (Table 3).
Table 3.
Association between nucleosomes and plasma cytokines.
| Variable | N | Mean | SEM | Median | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN_a2 (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 57 | 101.6 | 3.2 | 102.2 | 0.055 |
| nucleosomes high | 26 | 114.5 | 4.7 | 114.7 | |
| IL_16 (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 58 | 349.2 | 19.8 | 330.9 | 0.005 |
| nucleosomes high | 27 | 446.7 | 29.0 | 419.5 | |
| IL_18 (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 57 | 60.4 | 12.9 | 33.8 | 0.0004 |
| nucleosomes high | 26 | 120.0 | 19.1 | 69.7 | |
| HGF (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 58 | 760.8 | 184.7 | 222.7 | 0.043 |
| nucleosomes high | 27 | 1312.2 | 270.8 | 438.6 | |
| M_CSF (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 58 | 10.7 | 1.5 | 6.9 | 0.066 |
| nucleosomes high | 27 | 14.8 | 2.2 | 12.4 | |
| IL_15 (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 39 | 22.0 | 2.1 | 16.7 | 0.036 |
| nucleosomes high | 22 | 13.6 | 2.9 | 12.8 | |
| RANTES (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 58 | 8890.2 | 816.2 | 7644.8 | 0.053 |
| nucleosomes high | 27 | 7185.2 | 1196.2 | 4352.3 |
Abbreviations: SEM, standard error of the mean. p-Values < 0.05 are written in Bold.
3.4. Nucleosomes and Coagulation
There was no association between circulating nucleosomes and DD, TF, and/or uPA, while patients with nucleosomes above mean had significantly elevated levels of plasma PAI-1 (Table 4).
Table 4.
Association between nucleosomes and coagulation.
| Variable | N | Mean | SEM | Median | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue factor (pg/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 61 | 66.2 | 2.2 | 60.4 | 0.464 |
| nucleosomes high | 31 | 62.1 | 3.0 | 60.0 | |
| D-dimer (ng/mL) | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 61 | 412.3 | 53.6 | 312.2 | 0.394 |
| nucleosomes high | 31 | 552.3 | 75.2 | 401.7 | |
| uPA (ng/mL) * | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 59 | 4.8 | 0.5 | 3.8 | 0.925 |
| nucleosomes high | 31 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 3.7 | |
| PAI_1 (pg/mL) * | |||||
| nucleosomes low | 59 | 285.5 | 21.6 | 269.2 | 0.042 |
| nucleosomes high | 31 | 387.4 | 29.8 | 305.2 |
Abbreviations: SEM, standard error of the mean; uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. * uPA and PAI-1 were not determined in two patients. p-Values < 0.05 are written in Bold.
3.5. Prognostic Value of Nucleosomes on Disease-Free Survival in Primary Breast Cancer
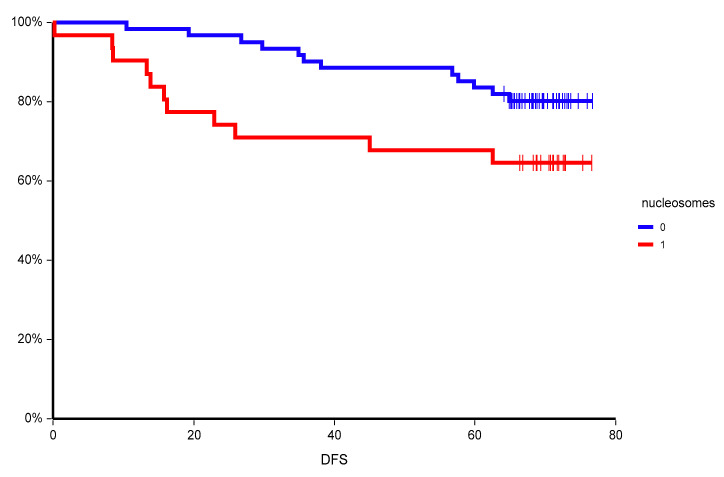
At a median follow-up time of 55.0 months (range = 4.9–76.7 months), 23 patients (25.0%) had experienced a DFS event, and 15 patients (16.3%) had died. Herein, we present DFS analysis due to the immaturity of overall survival data. Patients with lower than mean nucleosomes had significantly better disease-free survival (HR = 0.46, 95% CI 0.19–1.12, p = 0.05) (Figure 1). The prognostic value of circulating nucleosomes was most pronounced in lymph node-positive disease with high proliferation rate and in patients with detectable circulating tumor cells with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, but negative for epithelial circulating tumor cells (Table 5). In a multivariate analysis, nucleosomes, hormone receptor status, HER2 status, lymph node involvement, and tumor grade were independent predictors of disease-free survival (Table 6).
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier estimates of probabilities of disease-free survival according to plasma nucleosome status in primary breast cancer patients (n = 92). HR = 0.46. 95% CI 0.19–1.12, p = 0.05, 0—nucleosomes below mean, 1—nucleosomes above mean.
Table 5.
Prognostic value of nucleosomes on disease-free survival in primary breast cancer (nucleosomes dichotomized below vs. above mean).
| Variable | HR | 95% CI Low | 95% CI High | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0.46 | 0.19 | 1.12 | 0.05 |
| T-stage | ||||
| T1 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 1.02 | 0.04 |
| >T1 | 0.56 | 0.14 | 2.19 | 0.33 |
| Histology | ||||
| IDC | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.91 | 0.01 |
| other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 |
| Grade | ||||
| low and intermediate | 0.31 | 0.07 | 1.34 | 0.09 |
| high grade | 0.48 | 0.15 | 1.55 | 0.15 |
| Lymph nodes | ||||
| N0 | 0.86 | 0.15 | 4.92 | 0.86 |
| N+ | 0.36 | 0.13 | 1.04 | 0.03 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | ||||
| absent | 0.46 | 0.14 | 1.53 | 0.15 |
| present | 0.54 | 0.15 | 1.97 | 0.31 |
| Hormone receptor status (cut-off 1%) | ||||
| negative for both | 0.36 | 0.04 | 3.33 | 0.21 |
| positive for either | 0.41 | 0.15 | 1.15 | 0.06 |
| HER2 status | ||||
| negative | 0.55 | 0.19 | 1.6 | 0.23 |
| positive | 0.3 | 0.06 | 1.55 | 0.09 |
| P53 status | ||||
| negative | 0.48 | 0.16 | 1.44 | 0.13 |
| positive | 0.39 | 0.08 | 1.86 | 0.20 |
| BCL-2 | ||||
| negative | 0.25 | 0.05 | 1.17 | 0.02 |
| positive | 0.59 | 0.19 | 1.85 | 0.33 |
| Ki67 status (cut-off 14%) | ||||
| <14% | 0.73 | 0.11 | 4.71 | 0.72 |
| >14% | 0.35 | 0.12 | 1 | 0.02 |
| CTC EP | ||||
| negative | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.83 | 0.01 |
| positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 |
| CTC EMT | ||||
| negative | 0.68 | 0.23 | 2.03 | 0.46 |
| positive | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.9 | 0.01 |
| CTC ANY | ||||
| negative | 0.45 | 0.13 | 1.52 | 0.14 |
| positive | 0.5 | 0.14 | 1.87 | 0.27 |
p-Values < 0.05 are written in Bold.
Table 6.
Multivariate analysis of factors associated with disease-free survival.
| Variable | HR | 95% CI Low | 95% CI High | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleosomes | ||||
| above mean vs. below mean | 2.67 | 1.12 | 6.36 | 0.0268 |
| Hormone receptor status (cut-off 1%) | ||||
| positive for either vs. negative for both | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.80 | 0.0164 |
| HER2 status | ||||
| amplified vs. nonamplified | 3.06 | 1.21 | 7.79 | 0.0187 |
| Lymph nodes | ||||
| positive vs. negative | 6.56 | 2.50 | 17.21 | 0.0001 |
| Grade | ||||
| grade 3 vs. grade 1 and 2 | 2.85 | 1.14 | 7.08 | 0.0246 |
p-Values < 0.05 are written in Bold.
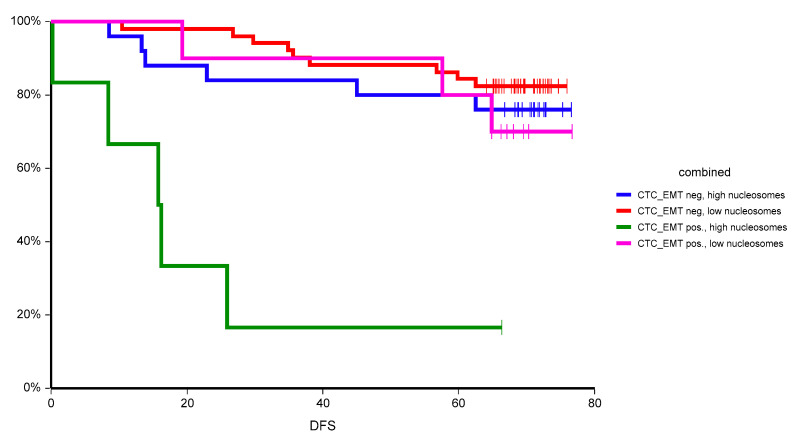
Circulating nucleosomes added prognostic value also to prognostic value of CTC_EMT, where double-positive patients (positive for both CTC_EMT and high-circulating nucleosomes) had worse prognosis compared to all other groups of patients (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier estimates of probabilities of disease-free survival according to plasma nucleosome status and CTC_EMT in primary breast cancer patients (n = 92). Patients positive for CTC_EMT and high level of circulating nucleosomes had significantly worse survival compared to all other groups (p = 0.0000003).
4. Discussion
In this translational study, circulating nucleosomes showed neither an association with basic patient/tumor characteristics nor a correlation to CTCs. The origin of circulating nucleosomes is unclear and likely complex [25]. While there is no correlation between CTCs and SII and/or neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio [23,24], this study showed for the first time an association between plasma nucleosomes and SII. Patients with high SII had significantly higher level of nucleosomes. Similarly, there was a trend of higher nucleosomes in patients with high neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, however, the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is part of the SII.
Tumor-induced systemic changes in immune cells contribute to cancer progression and metastasis. Various forms of ecDNA including extracellular nucleosomes and naked ecDNA differ in their cytotoxic and proinflammatory effects [26]. For example, histones in the nucleosomes induce proinflammatory signaling via toll-like receptors (TLR2/4), with subsequent production of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and myeloperoxidase, but they exhibit TLR-independent cytotoxicity as well [26,27,28]. On the other hand, the ecDNA as part of the nucleosomes is recognized by the TLR9 [29]. In our study, nucleosomes were associated with several proinflammatory cytokines, suggesting the association of circulating nucleosomes with systemic inflammation. Histones in the nucleosomes could induce formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which contain nucleosomes and stimulate further NETs production in a positive feedback loop [27]. On the other hand, nucleosomes could induce different inflammatory pathways, as they, in contrast to histones, seem not to be cytotoxic to the endothelium [28]. The analyzed nucleosomes could be from tumor cells, but also from the released NETs. This would explain the observed association between circulating nucleosomes and systemic inflammation in primary breast cancer patients. NETs contain nuclear DNA and proteins that possess antibacterial characteristics crucial for fighting pathogens [30,31]. The same NETs, however, also induce intravascular coagulation [32] and their overproduction can lead to autoimmune diseases [33]. While circulating ecDNA correlates with activation of coagulation [34], we for the first time describe this association for circulating nucleosomes. Further research is needed to uncover if nucleosomes directly activate PAI-1, or if high PAI-1 is a marker of coagulation activation in more aggressive disease that leads to release of more nucleosomes.
Data on the prognostic value of plasma nucleosomes in breast cancer is limited. In a small study, nucleosomes were elevated in locally confined and metastatic breast cancer in comparison to healthy individuals. During neoadjuvant chemotherapy, patients with no change of a local disease had significantly higher pretherapeutic concentrations of nucleosomes than patients in remission [14]. In another study, plasma nucleosomes were higher in primary breast cancer patients when compared to healthy controls, and similarly to our study, there was no association between nucleosomes and patient/tumor characteristics [15]. Circulating nucleosomes were, however, not able to discriminate between benign and malignant breast lesions [35]. Their concentration was found to be associated with lymph node-positive breast cancer and the presence of distant metastases [35].
In our study, we observed an inferior outcome of primary breast cancer patients with high plasma nucleosomes. This is in contrast to a previous study, where elevated plasma nucleosomes were associated with a better prognosis in both node-negative and node-positive early breast cancer [15]. However, the nucleosome detection method as well as the cut-off value to discriminate “low” and “high” plasma nucleosomes was different compared to our trial and therefore, these differences in results could be due to these factors. In our trial, the prognostic value of nucleosomes was consistent in various subgroups, however, it was most pronounced in poor prognostic subgroups such as lymph node-positive disease with high proliferation rate and in patients with detectable circulating tumor cells with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. The prognostic value of circulating nucleosomes was independent from established prognostic markers and was confirmed in a multivariate analysis. Moreover, when we combined two circulating biomarkers, circulating tumor cells, and circulating nucleosomes, we were able to uncover a subgroup of patients with extremely poor prognosis with two-year DFS of only 33.3%.
Our study has some limitations. The major one is small sample size, especially for associations between inflammatory indexes and nucleosomes. This is associated with decreased statistical power of analyses and increased confidence intervals of results. Other limitations represent the data availability for analysis of association between circulating nucleosomes and various clinic–pathological parameters, which further decreases statistical robustness and could have an impact on study results. Circulating plasma nucleosomes increase in non-neoplastic disease processes including inflammation, autoimmune diseases, sepsis, and stroke. When we analyzed association between chronic medication/comorbidities and circulating nucleosomes, no association was found, however, none of our patients received anti-inflammatory drugs and/or had inflammatory disease that could affect study results. Another limitation is lack of follow-up analysis on patient samples collected postsurgery to examine whether the presurgery baseline levels of circulating plasma nucleosomes were altered postsurgery and whether this alteration in circulating nucleosome levels is correlated with decrease in systemic inflammatory index.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in this translational study, we have shown for the first time that circulating nucleosomes are associated with systemic inflammation and activation of coagulation in primary breast cancer. More importantly, we proved their prognostic value. While it is clear that the underlying mechanisms of nucleosome release, their origin, and their fate require further studies, we suggest that the quantification of plasma nucleosomes could be added to the established prognostic markers in breast cancer. Future trials should focus on validation of these results to establish prognostic utility of plasma circulation nucleosomes in addition to established prognostic factors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Denisa Manasova for her excellent technical help. We are grateful to all patients for their participation in the study.
Appendix A
Table A1.
Drug history in the last 6 months.
| Chronic Medication | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| NSAID | 0 | 0.0 |
| Corticosteroids | 0 | 0.0 |
| L-thyroxin | 8 | 8.7 |
| ACEi | 11 | 12.0 |
| Sartans | 14 | 15.2 |
| Betablockers | 27 | 29.3 |
| Statins | 15 | 16.3 |
| Metformin | 4 | 4.3 |
| Insulin | 2 | 2.2 |
| LMWH | 7 | 7.6 |
| Warfarin | 0 | 0.0 |
Abbreviations: ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; LMWH, low-molecular-weight heparin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C., and M.M.; Data curation, G.M., T.S., and K.K.; Formal analysis, G.M., T.S., P.G., D.C., and P.C.; Funding acquisition, P.C., G.M., and M.M.; Investigation, M.K., G.M., J.B., and M.M.; Methodology, G.M., T.S., and P.C.; Project administration, P.C. and M.M.; Resources, J.M., K.K., M.K., J.B., and M.M.; Validation, P.C. and M.M.; Visualization, K.K., D.P., and J.M.; Writing—Original draft, P.C., and M.M.; Writing—Review & editing, all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Slovak Research and Development Agency (APVV), grant number APVV-16-0010, APVV-16-0178, by ERA-NET EuroNanoMed II INNOCENT and by Scientific Grant Agency (VEGA), contracts No. 1/0724/11, 1/0044/15, 1/0271/17, and 2/0052/18.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R.L., Torre L.A., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McAnena P., Brown J.A., Kerin M.J. Circulating Nucleosomes and Nucleosome Modifications as Biomarkers in Cancer. Cancers. 2017;9:5. doi: 10.3390/cancers9010005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lui Y.Y., Chik K.W., Chiu R.W., Ho C.Y., Lam C.W., Lo Y.M. Predominant hematopoietic origin of cell-free DNA in plasma and serum after sex-mismatched bone marrow transplantation. Clin. Chem. 2002;48:421–427. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/48.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sun K., Jiang P., Chan K.C., Wong J., Cheng Y.K., Liang R.H., Chan W.K., Ma E.S., Chan S.L., Cheng S.H., et al. Plasma DNA tissue mapping by genome-wide methylation sequencing for noninvasive prenatal, cancer, and transplantation assessments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:E5503–E5512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508736112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kustanovich A., Schwartz R., Peretz T., Grinshpun A. Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer Biol. 2019;20:1057–1067. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1598759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Khorasanizadeh S. The nucleosome: From genomic organization to genomic regulation. Cell. 2004;116:259–272. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jiang N., Reich C.F., 3rd, Monestier M., Pisetsky D.S. The expression of plasma nucleosomes in mice undergoing in vivo apoptosis. Clin. Immunol. 2003;106:139–147. doi: 10.1016/S1521-6616(02)00027-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Holdenrieder S., Nagel D., Schalhorn A., Heinemann V., Wilkowski R., von Pawel J., Raith H., Feldmann K., Kremer A.E., Muller S., et al. Clinical relevance of circulating nucleosomes in cancer. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2008;1137:180–189. doi: 10.1196/annals.1448.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zeerleder S., Zwart B., Wuillemin W.A., Aarden L.A., Groeneveld A.B., Caliezi C., van Nieuwenhuijze A.E., van Mierlo G.J., Eerenberg A.J., Lammle B., et al. Elevated nucleosome levels in systemic inflammation and sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2003;31:1947–1951. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000074719.40109.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pisetsky D.S. The complex role of DNA, histones and HMGB1 in the pathogenesis of SLE. Autoimmunity. 2014;47:487–493. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2014.921811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bauden M., Pamart D., Ansari D., Herzog M., Eccleston M., Micallef J., Andersson B., Andersson R. Circulating nucleosomes as epigenetic biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2015;7:106. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0139-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rahier J.F., Druez A., Faugeras L., Martinet J.P., Gehenot M., Josseaux E., Herzog M., Micallef J., George F., Delos M., et al. Circulating nucleosomes as new blood-based biomarkers for detection of colorectal cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2017;9:53. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0351-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang K., Shan S., Wang S., Gu X., Zhou X., Ren T. HMGB1-containing nucleosome mediates chemotherapy-induced metastasis of human lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018;500:758–764. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stoetzer O.J., Fersching D.M., Salat C., Steinkohl O., Gabka C.J., Hamann U., Braun M., Feller A.M., Heinemann V., Siegele B., et al. Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients by circulating apoptotic biomarkers nucleosomes, DNAse, cytokeratin-18 fragments and survivin. Cancer Lett. 2013;336:140–148. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuroi K., Tanaka C., Toi M. Plasma Nucleosome Levels in Node-Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Breast Cancer. 1999;6:361–364. doi: 10.1007/BF02966454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wittwer C., Boeck S., Heinemann V., Haas M., Stieber P., Nagel D., Holdenrieder S. Circulating nucleosomes and immunogenic cell death markers HMGB1, sRAGE and DNAse in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer. 2013;133:2619–2630. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Holdenrieder S., Stieber P., von Pawel J., Raith H., Nagel D., Feldmann K., Seidel D. Circulating nucleosomes predict the response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004;10:5981–5987. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mego M., Karaba M., Minarik G., Benca J., Silvia J., Sedlackova T., Manasova D., Kalavska K., Pindak D., Cristofanilli M., et al. Circulating Tumor Cells With Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition Phenotypes Associated With Inferior Outcomes in Primary Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019;39:1829–1837. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mego M., Cierna Z., Janega P., Karaba M., Minarik G., Benca J., Sedlackova T., Sieberova G., Gronesova P., Manasova D., et al. Relationship between circulating tumor cells and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in early breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:533. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1548-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mego M., Mani S.A., Lee B.N., Li C., Evans K.W., Cohen E.N., Gao H., Jackson S.A., Giordano A., Hortobagyi G.N., et al. Expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors in primary breast cancer: The effect of neoadjuvant therapy. Int. J. Cancer. 2012;130:808–816. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mego M., Karaba M., Minarik G., Benca J., Sedlackova T., Tothova L., Vlkova B., Cierna Z., Janega P., Luha J., et al. Relationship between circulating tumor cells, blood coagulation, and urokinase-plasminogen-activator system in early breast cancer patients. Breast J. 2015;21:155–160. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mego M., Cholujova D., Minarik G., Sedlackova T., Gronesova P., Karaba M., Benca J., Cingelova S., Cierna Z., Manasova D., et al. CXCR4-SDF-1 interaction potentially mediates trafficking of circulating tumor cells in primary breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:127. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2143-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.De Giorgi U., Mego M., Scarpi E., Giordano A., Giuliano M., Valero V., Alvarez R.H., Ueno N.T., Cristofanilli M., Reuben J.M. Association between circulating tumor cells and peripheral blood monocytes in metastatic breast cancer. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019;11:1758835919866065. doi: 10.1177/1758835919866065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Miklikova S., Minarik G., Sedlackova T., Plava J., Cihova M., Jurisova S., Kalavska K., Karaba M., Benca J., Smolkova B., et al. Inflammation-Based Scores Increase the Prognostic Value of Circulating Tumor Cells in Primary Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2020;12:1134. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thierry A.R., El Messaoudi S., Gahan P.B., Anker P., Stroun M. Origins, structures, and functions of circulating DNA in oncology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016;35:347–376. doi: 10.1007/s10555-016-9629-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chaudhary S., Mittra I. Cell-free chromatin: A newly described mediator of systemic inflammation. J. Biosci. 2019;44:32. doi: 10.1007/s12038-019-9849-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abrams S.T., Zhang N., Manson J., Liu T., Dart C., Baluwa F., Wang S.S., Brohi K., Kipar A., Yu W., et al. Circulating histones are mediators of trauma-associated lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013;187:160–169. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201206-1037OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xu J., Zhang X., Pelayo R., Monestier M., Ammollo C.T., Semeraro F., Taylor F.B., Esmon N.L., Lupu F., Esmon C.T. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat. Med. 2009;15:1318–1321. doi: 10.1038/nm.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kang T.H., Mao C.P., Kim Y.S., Kim T.W., Yang A., Lam B., Tseng S.H., Farmer E., Park Y.M., Hung C.F. TLR9 acts as a sensor for tumor-released DNA to modulate anti-tumor immunity after chemotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2019;7:260. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0738-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang H., Biermann M.H., Brauner J.M., Liu Y., Zhao Y., Herrmann M. New Insights into Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Mechanisms of Formation and Role in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016;7:302. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brinkmann V., Reichard U., Goosmann C., Fauler B., Uhlemann Y., Weiss D.S., Weinrauch Y., Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1532–1535. doi: 10.1126/science.1092385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McDonald B., Davis R.P., Kim S.J., Tse M., Esmon C.T., Kolaczkowska E., Jenne C.N. Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice. Blood. 2017;129:1357–1367. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-741298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kaplan M.J., Radic M. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Double-edged swords of innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2012;189:2689–2695. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Von Meijenfeldt F.A., Burlage L.C., Bos S., Adelmeijer J., Porte R.J., Lisman T. Elevated Plasma Levels of Cell-Free DNA During Liver Transplantation Are Associated With Activation of Coagulation. Liver Transpl. 2018;24:1716–1725. doi: 10.1002/lt.25329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Roth C., Pantel K., Muller V., Rack B., Kasimir-Bauer S., Janni W., Schwarzenbach H. Apoptosis-related deregulation of proteolytic activities and high serum levels of circulating nucleosomes and DNA in blood correlate with breast cancer progression. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]