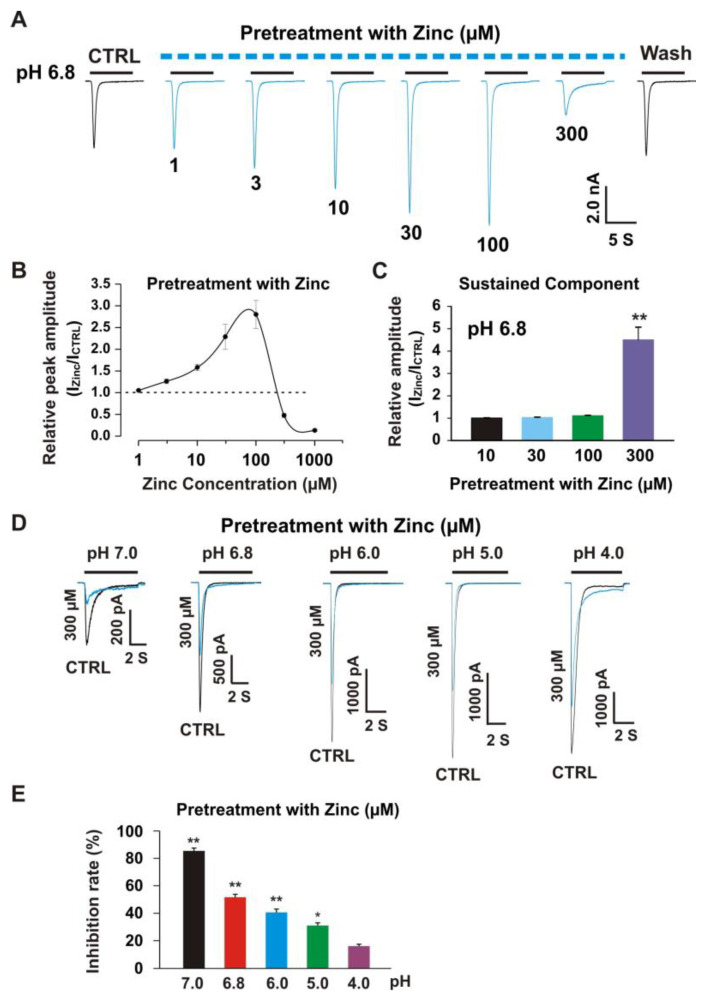
Figure 5.
Pretreatment with zinc revealed dual effects on heteromeric ASIC1a/3 currents with pH dependence. (A) Representative traces show that pretreatment with zinc (from 3 to 100 µm) was dose-dependently enhanced, whereas pretreatment with zinc at a concentration of 300 µM inhibited the currents of heteromeric ASIC1a/3 channels recorded on a CHO cell expressing both ASIC1a and ASIC3. The dashed blue line represents pretreatment with zinc in pH 7.4 extracellular solution and the solid black line represents co-application of zinc with pH 6.8 (each recoding with 7 s of zinc application); (B) Dose-dependent curve of pretreatment with zinc on heteromeric ASIC1a/3 currents. The curve displays a bell-like shape. The EC50 for zinc concentrations between 1 and 100 µM was 23.7.0 ± 3.2 µM (n = 8) and the EC50 for zinc pretreatment between 100 and 250 µM was 127.6 ± 15.6 µM (n = 8). The IC50 for pretreatment with zinc was 306.0 ± 43.7 µM (n = 8); (C) Statistical bar graphs show that pretreatment with zinc at a concentration of 300 µM, but not 10, 30, and 100 µM, enhance the sustained component of the heteromeric ASIC1a/3 currents triggered by a pH drop from 7.4 to 6.8; (D) Representative traces show that pretreatment with zinc at a concentration of 300 µM inhibit the heteromeric ASIC1a/3 currents triggered by pH drops from 7.4 to 7.0, 6.8, 6.0, and 5.0, but not 4.0, respectively; (E) Statistical data show that pretreatment with zinc at a concentration of 300 µM inhibit the peak amplitude of heteromeric ASIC1a/3 currents with pH dependence (n = 6 to 10). Whole-cell patch-clamp recording was performed. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. CTRL, control; ICTRL, ASIC current without any treatment; IZinc, ASIC current by zinc treatment. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.