Figure 4. The roles of Mst1, Yap and Taz in cytosolic nucleic acid sensing.
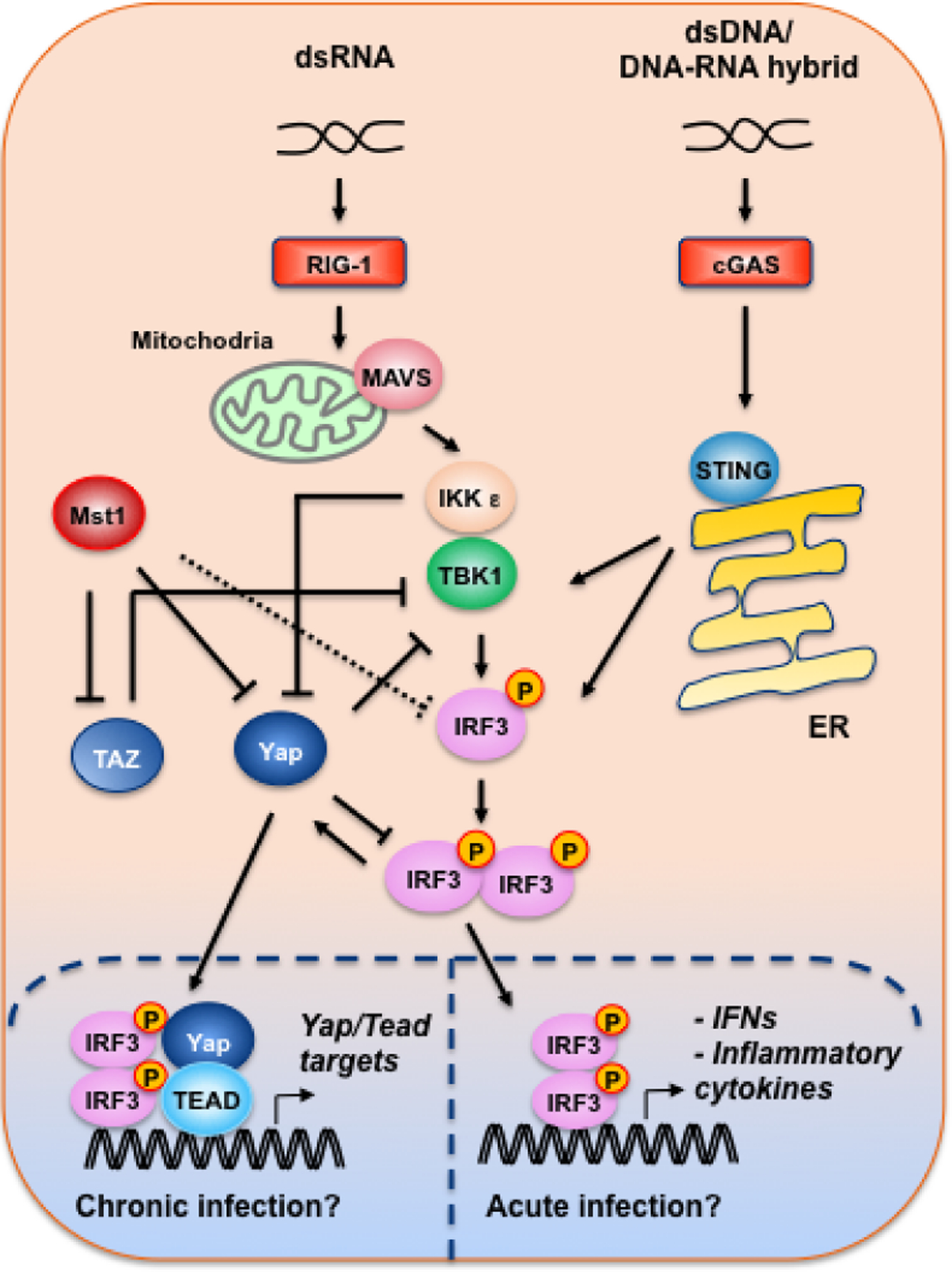
dsRNA and dsDNA or DNA-RNA hybrid activate the RIG-1-MAVS and cGAS-STING cytosolic sensors, respectively, leading to the activation of the TBK1-IKKε complex. In contrast to its reported roles in promoting bacteria-induced TLR-IRF3 signaling70,72, Mst1 was found to directly phosphorylate IRF3, inhibiting IRF3 activity in response to viral infections76. Yap and Taz were shown to directly bind TBK1 and block its interaction with other adaptors/substrates78. Moreover, Yap was reported to directly interfere with IRF3 dimerization, and IKKε relieves Yap inhibition of IRF3 by directly phosphorylating and targeting Yap for lysosomal degradation77. Finally, it was reported that during chronic (>48 hours) viral infection, dimerized IRF3 promotes Yap nuclear translocation and complexes with Yap and Tead in inducing the expression Yap/Tead target genes85.
